دانلود مقاله مدیریت ریسک کیفیت در زنجیره تامین برای تحریک عملکرد شرکت
چکیده
رسوایی زیان و آسیب محصول به عنوان کابوس یک شرکت در نظر گرفته می شود. در بسیاری از موارد، منبع مولفه های معیوب یا ناامن ممکن است از خود شرکت تولیدی نباشد، ممکن است مسائل ذاتی در شبکه ی تامین وجود داشته باشد. هدف این پژوهش، بررسی تاثیرات دو اقدام مدیریت ریسک متمرکز تحت عنوان توسعه ی تامین کننده و فراخوان محصول پیشگیرانه بر عملکرد شرکت است. برای بررسی دقیق تاثیر دو نوع مکانیزم کنترل، کنترل اجتماعی و کنترل رسمی را به عنوان سوابق اقدامات مدیریت ریسک مورد بررسی قرار می دهیم و نقش تعدیل کننده ی آن ها بر رابطه ی بین اقدامات مدیریت ریسک و عملکرد شرکت را کشف می کنیم. بر مبنای داده های به دست آمده از 209 تولیدکننده ی چینی، مدل سازی معادلات ساختاری و رگرسیون سلسله مراتبی برای آزمون فرضیات پیشنهادی مورد استفاده قرار گرفتند. نتایج نشان می دهند که توسعه ی تامین کننده فراخوان محصول به طور قابل توجهی بر عملکرد شرکت و عملکرد کیفیت نقش دارند. علاوه براین، کنترل اجتماعی و رسمی، سوابق قابل توجه دو اقدام مدیریت ریسک هستند. از همه مهم تر، نقش تعدیل کننده ی مکانیزم های کنترل بر رابطه ی بین اقدامات مدیریت ریسک و عملکرد شرکت را بررسی می کنیم. شاغلین حرفه ای باید آگاه باشند که مکانیزم های کنترل دارای تاثیرات تعدیل کننده ی مختلفی هستند، نوع مختلفی از مکانیزم کنترل باید برای تسهیل اقدامات مدیریت ریسک به کار گرفته شود تا عملکرد بهتر شرکت محقق شود.
1. مقدمه
بزرگترین مقیاس فراخوان محصول در صنعت تلفن همراه، برای مثال بحران سامسونگ گلکسی NOTE7، توجه ویژه ای را در مورد کنترل کیفیت تولید تجهیزات الکترونیک به خود جلب کرده است. بحران فراخوان موجب ایجاد سوالاتی در این خصوص شده است که امروزه یک شرکت تولیدی چگونه می تواند مانع از ایجاد مساله ی کیفیت در زنجیره ی تامین خود گردد، از همه مهم تر این که، چگونه می تواند خود را برای کیفیت محصول آماده سازد. مساله ی کیفیت محصول یک مساله ی کنونی اما قدیمی است. از سال 2006 تا پایان سال 2015، تعداد موارد فراخوان محصول در اتحادیه ی اروپا به سرعت افزایش یافت (23 درصد). دانشمندان و شاغلین حرفه ای ادعا می کنند که دلایل اصلی برای این افزایش سریع عبارتنداز: میزان منبع یابی جهانی مواد و میزان برون سپاری تولید محصولات مارک دار برای تولیدکنندگان قراردادی (روس و تسای و پالمان و گری 2008). طولانی شدن زنجیره ی تامین جهانی، عدم اطمینان را افزایش داده و ملاحظات کیفیت بیشتری را به محصولات نهایی می افزاید. از آن جایی که بسیاری از شرکت ها تولید خود را به خارج از شرکت انتقال داده اند، تضمین کیفیت و ایمنی محصولات آن ها بسیار دشوار است (تسای و تان و چانگ و لیم 2011).
6. نتیجه گیری
این پژوهش دو فعالیت مدیریت ریسک (SD,PPR) را بیان کرده و روابط آن ها با کیفیت محصول و عملکرد مالی را مورد آزمون قرار داد. این دو اقدام بر FP,QP تاثیر می گذارند. نظریه ی نمایندگی را می توان به عنوان نظریه ی اولیه برای تامین دیدگاه پویا از همکاری بین شرکتی در مدیریت ریسک انتخاب کرد. دو شکل از مکانیزم کنترل،FC,SC، دارای تاثیر مثبت بر دو نوع فعالیت مدیریت ریسک هستند. با این حال، نقش های تعدیل کننده ی مکانیزم های کنترل تاحدی شگفت آور است. این پژوهش در می یابد که فقط FC دارای تاثیر تعدیل کننده بر رابطه ی بین PPR و هر دو نوع عملکرد است، در حالی که تنها SC تاثیر SC بر FP را تقویت می کند. ما بیان می کنیم که فراخوان محصول در چین می تواند فوق العاده پیچیده و بسیار نامطمئن باشد، شرکت ها باید برای مشخص نمودن مسئولیت ها و کنترل عدم اطمینان، بر FC تکیه نمایند. هم چنین بیان می کنیم که با SC بیشتر، شرکت ها می توانند تضمین نمایند که آن ها فعالیت های SD تامین کنندگان را بازپس خواهند داد. بنابراین، SC تاثیر SD بر عملکرد کسب و کار خریدار را تقویت می کند.
Abstract
Product harm scandal can be viewed as a company's nightmare. In many cases, the source of defective or unsafe components may not be the manufacturing firm itself; rather, there may be problems inherent in the supply network. This research aims to investigate the effects of two focused risk management practices, namely supplier development and proactive product recall, on firms' performance. To scrutinise the impact of two types of control mechanisms, we investigate social control and formal control as antecedents of risk management practices, and explore their moderating roles on the relationship between risk management practices and firm performance. Based on the survey-based data obtained from 209 Chinese manufacturers, structural equation modelling and hierarchical regression are used to test the proposed hypotheses. The results show that both supplier development and proactive product recall significantly contribute to financial performance and quality performance. Furthermore, both formal control and social control are the significant antecedents of the two risk management practices. Most importantly, we examine the moderating roles of the control mechanisms on the relationship between the risk management practices and firm performance. Practitioners should be aware that the control mechanisms have different moderating effects, i.e. different type of control mechanism should be employed to facilitate the risk management practices in order to achieve a better firm performance.
1. Introduction
The largest scale of product recall in mobile phone industry, i.e. Samsung Galaxy Note 7 crisis, has put a spotlight on quality control of electronics production. The recall crisis is also raising questions about how today's manufacturing company could prevent the quality problem raised in their supply chain, and maybe more importantly, how could they prepare if the product quality happened. The product quality problem is a current issue but an old problem. From 2006 until the end of 2015, the number of product recall cases in the EU rose rapidly, by 203%.1 Scholars and practitioners claim that among the major reasons for this rapid increase are the extent of global sourcing of materials and the magnitude of the outsourcing production of branded products to contract manufacturers (Roth, Tsay, Pullman, & Gray, 2008). The lengthening of the global supply chain increases uncertainty and adds extra quality considerations to the final products. Since many firms have moved their production offshore, it becomes more difficult to assure the quality and safety of their products (Tse, Tan, Chung, & Lim, 2011).
6. Conclusions
This research has proposed and tested two risk management practices, SD and PPR, and their relationships with product quality and financial performance. The two practices are found to influence the FP and QP. Agency theory can be selected as the primary theory to provide a dynamic view of inter-firm cooperation in risk management. The two forms of control mechanism, FC and SC, are both found to positively influence the two types of risk management practices. However, the moderating roles of control mechanisms are somewhat surprising. This research finds that only FC has a significant moderating effect on the relationship between PPR and both types of performance, while only SC significantly amplifies the effect of SC on FP. We suggest that given the product recall in China could be extremely complex and highly uncertain, companies should rely on the FC to clarify the responsibilities and control the uncertainty. Also, we suggest that with greater SC, companies could be guaranteed that they will be repaid for SD activities from the suppliers. Therefore, SC amplifies the effect of SD on the buyer's business performance.
Hypothesis 1. SD has a positive effect on QP.
Hypothesis 2. SD has a positive effect on FP.
Hypothesis 3. PPR has a positive effect on QP.
Hypothesis 4. PPR has a positive effect on FP.
Hypothesis 5. FC has a positive effect on SD.
Hypothesis 6. SC has a positive effect on SD.
Hypothesis 7. FC has a positive effect on PPR.
Hypothesis 8. SC has a positive effect on PPR.
Hypothesis 9. FC strengthens the impacts of PPR on (a) QP; (b) FP.
Hypothesis 10. SC strengthens the impacts of PPR on (a) QP; (b) FP.
Hypothesis 11. FC strengthens the impacts of SD on (a) QP; (b) FP.
Hypothesis 12. SC strengthens the impacts of SD on (a) QP; (b) FP.
فرضیه 1. SD دارای تاثیر مثبت بر QP است.
فرضیه 2. SD دارای تاثیر مثبت بر FP است.
فرضیه 3. PPR دارای تاثیر مثبت بر QP است.
فرضیه 4. PPR دارای تاثیر مثبت بر FP است.
فرضیه 5. FC دارای تاثیر مثبت بر SD است.
فرضیه 6.SC دارای تاثیر مثبت بر SD است.
فرضیه 7. FC دارای تاثیر مثبت بر PPR است.
فرضیه 8. SC دارای تاثیر مثبت بر PPR است.
فرضیه 9. FC تاثیر PPR بر QP,FP را تقویت می کند.
فرضیه 10. SC تاثیر PPR بر QP,FP را تقویت می کند.
فرضیه 11. FC تاثیرات SD بر QP.FP را تقویت می کند.
فرضیه 12. SC تاثیرات SD بر QP,FP را تقویت می کند.
Control variable
Company size
Main effect SD
PPR
Moderator Formal
Control (FC)
Social Control (SC)
Moderation effect
FC × SD
FC × RCR
SC × SD
SC × RCR
R2
F
ΔR2
F change
Max VIF
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. ادبات و توسعه ی نظری
2.1 مدیریت ریسک کیفیت و عملکرد شرکت
2.2 نقش های مکانیزم کنترل بین سازمانی
2.2.1 تاثیر مکانیزم های کنترل بر اقدامات SCRM
2.2.2 نقش های تعدیل کننده ی مکانیزم های کنترل
3. متدولوژی
3.1 معیارها
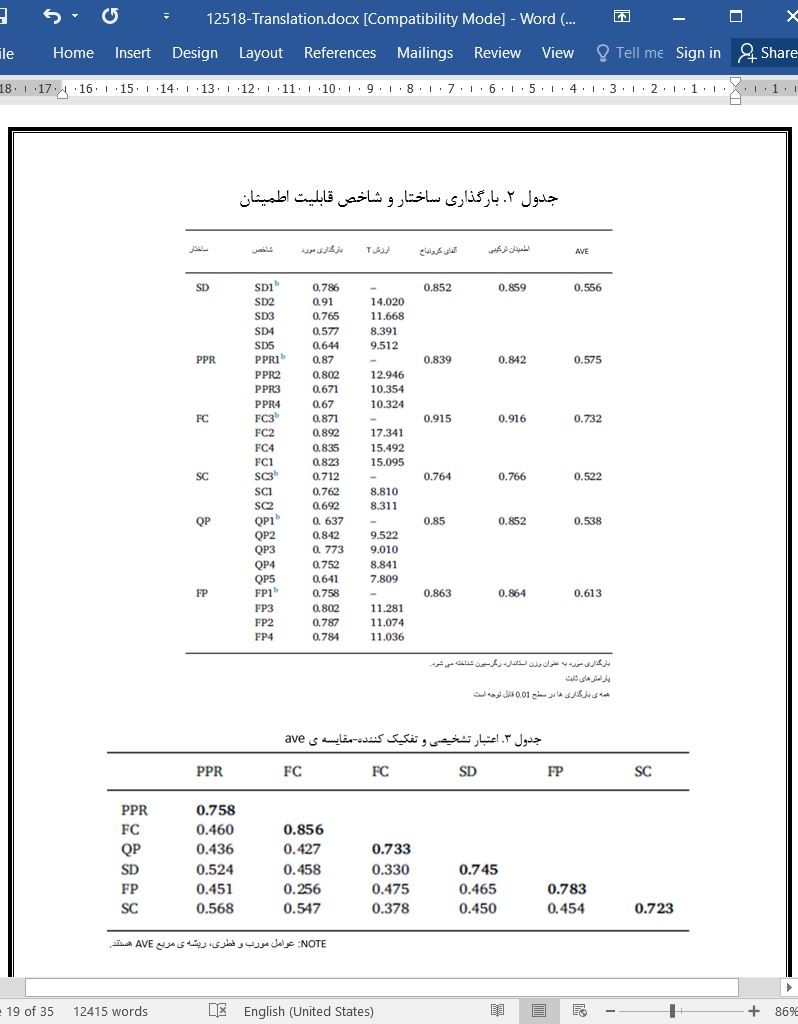
3.2 جمع آوری داده ها
3.3 ارزیابی معیار
4. تجزیه و تحلیل داده ها
4.1 مدل ساختاری
4.2 تحلیل تعدیل و اعتدال
5. بحث
6. نتیجه گیری
منابع
ABSTRACT
1. Introduction
2. Literature and theoretical development
2.1. Quality risk management and firm performance
2.2. Roles of inter-organisational control mechanism
2.2.1. Impact of control mechanisms on SCRM practices
2.2.2. The moderating roles of control mechanisms
3. Methodology
3.1. Measurements
3.2. Data collection
3.3. Measurement assessment
4. Data analysis
4.1. Structural model
4.2. Moderation analysis
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Reference
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه