
دانلود رایگان مقاله یک سیستم مدیریت انرژی مبتنی بر MAS برای یک ریزشبکه مستقل در ارتفاع بالا
چکیده
در این مقاله, یک سیستم مدیریت انرژی مبتنی بر سیستم چند عامله (EMS) برای پیاده سازی یک ریزشبکه هیبرید PV-کوچک آبی (MG) در ارتفاع بالا ارائه می شود. بر اساس اطلاعات محلی، منابع تولید توزیع شده (DG) در MG از طریق EMS برای رسیدن به عملکرد کارآمد و پایدار سیستم کنترل می شوند. مناقصه مجازی برای ایجاد سریع برنامه ریزی عملیات سیستم و ذخیره ظرفیت استفاده می شود. علاوه بر این، اعزام های توان در زمان واقعی از طریق کنترل پیش بینی مدل برای تعادل در تقاضای بار و تولید توان در MG انجام می شود. مدل دینامیکی و استراتژی مدیریت انرژی MG در یک پلت فرم شبیه سازی مشترک در زمان واقعی RTDS-PXI شبیه سازی می شود. نتایج شبیه سازی نشان می دهد که مدیریت انرژی پیشنهادی و استراتژی کنترل بهینه را می توانند به طور بهینه منابع DG را در MG برای رسیدن به عملیات های اقتصادی و امن کل سیستم اعزام نمایند.
1. مقدمه
ریزشبکه (MG) به طور گسترده به عنوان پلت فرمی موثر برای یکپارچه سازی و مدیریت منابع تولید توزیع شده (DG) و برای پیاده سازی مدیریت طرف تقاضا (DSM) مطالعه شده است. از یک طرف، MGS متصل به شبکه می تواند به افزایش قابلیت اطمینان سیستم، کاهش انتشار آلاینده ها و بهبود کارایی سیستم کمک نماید [1]. از سوی دیگر، MGS مستقل به عنوان یک راه جذاب برای تامین برق برای مناطق دور افتاده با حذف نیاز ساخت و ساز خطوط انتقال توان جدید و استفاده از منابع انرژی تجدیدپذیر بهتر محلی [2-5] در نظر گرفته شده اند.
پژوهش حاضر در سیستم های مدیریت انرژی برای MGS عمدتاً بر طرح های کنترل تمرکزیافته متمرکز می شود. تحت یک چارچوب متمرکز، یک کنترل کننده مرکزی ریزشبکه (MGCC) را می توان برای انجام اعزام های توان اقتصادی برای DG ها و سیستم های ذخیره انرژی (ESS) در مقیاس های زمانی متعدد طراحی نمود [6-11]. با این حال، با افزایش مقیاس زمان، طراحی کنترل کننده تمرکزیافته با چالش هایی از خطاهای پیش بینی بزرگتر در تولید های تجدید پذیر و پیچیدگی بیشتر در حل مسائل بهینه سازی مبارزه می کند. هنگامی که اندازه سیستم و تعداد قطعات بیشتر شود، تحقق بخشیدن به مدیریت زمان واقعی, نیز بیشتر به چالش کشیده می شود. علاوه بر این، قابلیت اطمینان یکی دیگر از نگرانی ها برای طرح های متمرکز است زیرا یک خطا در MGCC می تواند از کار کل سیستم جلوگیری نماید [11]. حتی اگر الگوریتم های اکتشافی و سیستم های خبره را بتوان برای طراحی یک سیستم مدیریت مرکزی عملی یک ریزشبکه مورد استفاده، چنین طراحی فاقد انعطاف پذیری و مقیاس پذیری [12-16] است.
برای جلوگیری از اشکالاتی از طرح کنترل تمرکزیافته، سیستم چند عامله (MAS) برای مدیریت انرژی MG پیشنهاد شده است. MAS، یک رویکرد کنترل توزیع شده بر اساس اطلاعات و اقدامات محلی، مناسب برای کنترل زمان واقعی است و دارای ویژگی های زیر است [17-19]:
(1) انعطاف پذیری: ساختار MAS می تواند ادغام منابع DG روشن و خاموش مختلف و تنظیم انطباقی کنترل MG را با توجه به شرایط و اهداف واقعی را انجام دهد.
(2) مقیاس پذیری: برایگسترش توابع از یک MAS بر اساس نیازهای مشتریان مناسب است. و
(3) تحمل خطا: کنترل موضعی DG های فردی, نسبت به به اختلالات و خطاها در MG قوی است.
مطالعات MG EMS مبتنی بر MAS بر روی چارچوب سیستم، الگوریتم های اعزام و استراتژی های هماهنگی DG ها انجام شده است. بررسی دقیق در مورد MAS برای برنامه های مهندسی قدرت در [20،21] داده شده است. در [22]، یک سیستم MAS برای پشتیبانی از ولتاژ با اعزام DG ها در یک فیدر توزیع ارائه شده، در حالی که ویژگی های DG مختلف در نظر گرفته نمی شوند. مدل های مبتنی بر عامل برای تجارت DG ها در بازارهای برق روز در [23،24] ارائه شده است. کنترل ولتاژ DC ریزشبکه در [25] از طریق یک نمودار حالت جریان بر اساس MAS اجرا شد، اما هیچ روش مدیریت انرژی خاصی مورد بحث قرار نگرفت. در [26،27]، روند مناقصه MAS به صورت کوتاه معرفی شد. یک استراتژی MAS بر اساس تغییر سیستم ESS در میان 4 وضعیت [28] توسعه داده شد. در حالی که هیچ مدل و قوانین تصمیم گیری مورد بحث برای DG ها / عوامل خاص وجود ندارد. یک سیستم کنترل چند عامل برای ساختمان ها در [29] ارائه شد که در آن عوامل بر اساس یک شاخص آسایش کار کردند. یکی دیگر از سیستم های کنترل ساختمان در [30] با تمرکز بر مدیریت مصرف انرژی ارائه شد. روش های مدیریت جانب تقاضای مبتنی بر MAS برای متعادل نمودن توان با کمک DG ها مانند الکترولایزر ، سلول کاهنده و آب شیرین کن [31] و یا سیستم های ذخیره انرژی با توجه به ویژگی های شارژ / تخلیه [32] مورد استفاده قرار گرفت. یک چارچوب از روش مدل سازی و مدیریت انرژی مبتنی بر عامل بر اساس الگوریتم ژنتیک بهبود یافته در [33] برای ریزشبکه متصل به شبکه ارائه شد. در [34،35]، مکانیزم های مناقصه قیمت مبتنی بر MAS مختلف برای فرستادن توان با هدف های مختلف ارائه شده است. در [34]، هدف, به حداکثر رساندن درآمد اقتصادی بود، در حالی که هدف در [35] به حداکثر رساندن استفاده از منابع تجدید پذیر بود. نویسندگان [36] یک الگوریتم مبتنی بر MAS را برای متعادل نمودن تولید و تقاضا با تنظیم تولید DG ها در زمان واقعی ارائه نمودند. با این حال، این الگوریتم تنها اعزام DG ها با توجه به توانایی های آنها را هدف قرار می داد و تفاوت ها در واکنش های دینامیکی را در نظر نمی گرفت. علاوه بر این، تمام مطالعات فوق تنها با شبیه سازی های نرم افزاری غیر زمان واقعی مورد آزمایش قرار گرفتند و باید بر روی سیستم عامل سخت افزاری تایید شوند تا بهتر بتوان شرایط عملی را تقلید نمود و پاسخگوی نیازها و استانداردهای صنعتی تأیید شده بود.
در این مقاله، EMS مبتنی بر MAS- جدید برای ریزشبکه PV-کوچک آبی ترکیبی (PVSHH) ارائه می شود. در EMS پیشنهادی، اعزام بهینه DG ها با استفاده از مناقصه مجازی (VBD) به دست آمد. بر اساس VBD، برنامه زمانبندی سیستم عامل و ظرفیت ذخیره تعیین می شود. DG ها برای دنبال نمودن برنامه زمانبندی با توجه به استراتژی کنترل فردی و اطلاعات محلی کنترل می شوند. علاوه بر این، خطای کنترل توان در زمان واقعی توسط DG ها با ذخیره ظرفیت با استفاده از یک روش کنترل پیش بینی مدل (MPC) جبران می شود. EMS پیشنهادی بر روی یک پلت فرم شبیه سازی RTDS-PXI زمان واقعی تست می شود. MAS بر روی یک پلت فرم فیزیکی NI-PXI برای تحقق بخشیدن به استراتژی های کنترل و توابع نماینده محلی مانند تنظیم قیمت پویا اجرا می شود. مدل دینامیکی ریزشبکه ترکیبی بر اساس یک شبیه ساز دیجیتال زمان واقعی (RTDS) توسعه یافته است. ارتباط بین NI-PXI و RTDS بر IEC 61850 بر اساس نتایج شبیه سازی است. نشان می دهد که EMS پیشنهادی, تمام الزامات عملی سخت را برآورده می سازد و می توان آن را برای پیاده سازی یک ریزشبکه ترکیبی آبی واقعی PV-کوچک استفاده نمود.
باقی مانده مقاله به شرح زیر است: بخش 2 پروژه ریزشبکه PVSHH به صورت مختصر و اصول طراحی EMS آن معرفی می شود. EMS پیشنهادی در بخش 3، پس از مطالعه VBD و اعزام های توان پویا مورد بحث قرار می گیرد. بخش 4, ساختار MAS و پیاده سازی آن بر روی پلت فرم شبیه سازی RTDS-PXI زمان واقعی را توضیح می دهد. هر دوی نتیجه فوری و نتایج شبیه سازی طولانی مدت در بخش 5 ارائه می شوند. بخش 6 این مقاله, نتیجه گیری می باشد.
2. پروژه ریزشبکه ترکیبی PV-آبی کوچک
EMS که در این مقاله پیشنهاد شده است, برای یک پروژه ریزشبکه PVSHH است که توسط حالت چین تایید شده است. MG مستقل در یک منطقه دور افتاده در ارتفاع بالای 4000 متر توسعه یافته است. در محیط فلات، درجه حرارت کم و کمبود اکسیژن باعث احتراق ناقص سوخت می شود که منجر به بهره وری سیستم کم و تولید گازهای گلخانه ای آلاینده بالا می شود. با این حال، منابع انرژی خورشیدی در منطقه فراوان و بسیار پایدار هستند، که آن را برای توسعه تولید توان فتوولتائیک (PV) مناسب ساخته است.
MG اصلی یک نیروگاه تولید توان کوچک آبی (SHGP) با چهار ژنراتور کوچک برق آبی 1.6 مگاوات و یک نیروگاه تولید دیزل (DGP) با چهار دیزل ژنراتور 2.5 مگاوات است. SHGP دارای مخزنی به اندازه 6.4 میلیون مترمکعب و مسئول مدولاسیون فرکانس اولیه است. در فصل مرطوب، به عنوان مثال فصل بهار و تابستان، مخزن نزدیک به کامل است. با این حال، آب در مخزن به طور معمول برای پاسخگویی به تقاضای آب و برق در فصل خشک به اندازه کافی است.
Abstract
A multi-agent system based energy management system (EMS) is proposed in this paper for implementing a PV-small hydro hybrid microgrid (MG) at high altitude. Based on local information, the distributed generation (DG) sources in the MG are controlled via the EMS to achieve efficient and stable system operation. Virtual bidding is used to quickly establish the scheduling of system operation and capacity reserve. In addition, real-time power dispatches are carried out through model predictive control to balance load demand and power generation in the MG. The dynamic model and the energy management strategy of the MG have been simulated on a RTDS–PXI joint real-time simulation platform. The simulation results show that the proposed energy management and control strategy can optimally dispatch the DG sources in the MG to achieve economic and secure operations of the whole system.
1. Introduction
Microgrid (MG) has been extensively studied as an effective platform for integrating and managing distributed generation (DG) sources and for implementing demand side management (DSM). On the one hand, grid-connected MGs can help enhance system reliability, reduce pollutant emissions, and improve system efficiency [1]. On the other hand, stand-alone MGs have been considered as an attractive way to provide electricity for remote areas by eliminating the need of construction of new power lines and by better utilizing the local renewable energy resources [2–5].
Current research on energy management systems for MGs is mainly focused on centralized control schemes. Under a centralized framework, a microgrid central controller (MGCC) can be designed to carry out economic power dispatch for DGs and energy storage systems (ESS) at multiple time scales [6–11]. However, as the time scale increases, the design of a centralized controller struggles with challenges from larger prediction errors in renewable generation and more complexity in solving optimization problems. When the system size and the number of components are getting larger, it also becomes more challenging to realize real-time management. Moreover, reliability is another concern for centralized schemes since a single fault at the MGCC can cause the whole system stop working [11]. Even though heuristic algorithms and expert systems can be used to design a practical central management system of a microgrid, such design is lack of flexibility and scalability [12–16].
To avoid the drawbacks of centralized control scheme, multi-agent system (MAS) has been proposed for MG energy management. MAS, a distributed control approach based on local information and actions, is suitable for real-time control and has the following features [17–19]:
(1) Flexibility: The MAS structure can integrate various plugand-play DG sources and adaptively adjust the control of MG according to actual conditions and targets.
(2) Scalability: It is convenient to extend the functions of an MAS based on the needs of customers; and
(3) Fault-tolerance: The localized control of individual DGs is robust to disturbances and faults in the MG.
The studies of MAS-based MG EMS have been carried out on the system framework, dispatch algorithms and coordination strategies of DGs. Detailed reviews on MAS for power engineering applications were given in [20,21]. In [22], it proposed an MAS system for voltage support by dispatching DGs on a distribution feeder, while the different characteristics of DGs were not considered. The agent-based models for trading DGs in the day-ahead electricity markets were presented in [23,24]. DC voltage control of microgrid was implemented in [25] through an MAS based state-flow diagram, but no specific energy management method was discussed. In [26,27], the MAS based bidding process was introduced in brief. An MAS based strategy was developed to switch an ESS system among 4 statuses [28]. While there are no detailed models and decision making rules discussed for specific DGs/agents. A multi-agent control system for buildings was presented in [29], where the agents run based on a proposed comfort index. Another control system of building was presented in [30] with the focus on energy consumption management. MAS based demand side management methods were used to balance power with assistance of DGs such as electrolyzer, fell cell and desalination [31] or energy storage systems considering the charging/discharging characteristics [32]. A framework of agent-based modeling and energy management method based on improved genetic algorithm was presented in [33] for grid-connected microgrid. In [34,35], different MAS-based price bidding mechanisms for power dispatch with different targets were proposed. In [34], the target was to maximize economic revenue, while the objective in was to maximize the utilization of renewable sources. The authors of [36] proposed an MAS-based algorithm to balance the generation and demand by adjusting the generation of DGs in real time. However, the algorithm only targeted the dispatch of DGs according to their capabilities and did not consider the differences in their dynamic responses. In addition, all the above studies were only tested by non-real-time software simulations and need to be verified on hardware platforms that can better emulate practical conditions and meet industrial requirements and standards.
In this paper, a new MAS-based EMS is proposed for a PV-small hydro hybrid (PVSHH) microgrid. In the proposed EMS, the optimal dispatch of DGs is achieved by means of virtual bidding (VBD). Based on the VBD, the system operation schedule and capacity reserve are determined. The DGs are controlled to follow the schedules according to their individual control strategies and local information. In addition, the real-time power control error is compensated by the DGs with capacity reserve using a model predictive control (MPC) method. The proposed EMS is tested on a RTDS–PXI real-time simulation platform. The MAS is implemented based on a NI–PXI physical platform to realize local control strategies and agent functions such as dynamic price adjustment. The dynamic model of the hybrid microgrid is developed based on a real time digital simulator (RTDS). The communication between the NI–PXI and the RTDS is based on IEC 61850. The simulation results show that the proposed EMS meets all the strict practical requirements and can be used to implement a real PV-small hydro hybrid microgrid.
The remainder of the paper is organized as follows: Section 2 introduces the PVSHH microgrid project in brief and the design principles of its EMS. The proposed EMS is discussed in Section 3, followed by the study of the VBD and the dynamic power dispatch. Section 4 describes the structure of the MAS and its implementation on the RTDS–PXI real-time simulation platform. Both the snapshot and long-term simulation results are given in Section 5. Section 6 concludes the paper.
2. PV-small hydro hybrid microgrid project
The EMS proposed in this paper is for a PVSHH microgrid project that has been approved by the government of China. The stand-alone MG to be developed is in a remote area at an altitude above 4000 m. In the plateau environment, the low temperature and the shortage of oxygen cause incomplete combustion of fuels, which results in low system efficiency and high pollutant emissions. However, the solar energy resource in the area is abundant and highly stable, which makes it suitable for the development of photovoltaic (PV) power generation.
The original MG was composed of a small-hydro generation plant (SHGP) with four 1.6 MW small-hydro generators and a diesel generation plant (DGP) with four 2.5 MW diesel generators. The SHGP has a 6.4 million m3 reservoir and is responsible for primary frequency regulation. In the wet season, i.e. spring and summer, the reservoir is close to full. However, the water in the reservoir is normally not enough to meet the electric power and water demand in the dry season.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. PV-small hydro hybrid microgrid project
3. Energy management method based on MAS
3.1. Virtual bidding
3.2. Dynamic power dispatch
4. Implementation of microgrid EMS
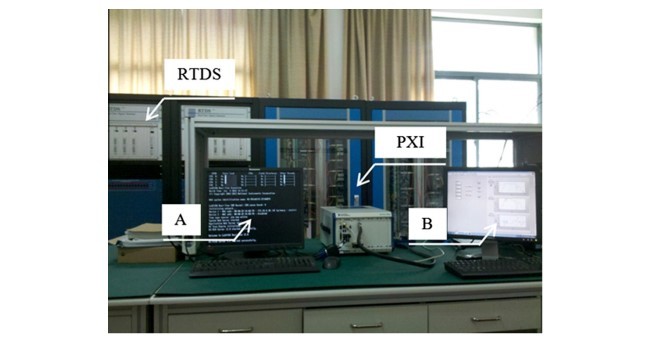
4.1. RTDS–PXI real-time simulation platform
4.2. Structure and implementation of MAS
5. Real-time digital simulation of the microgrid operation
5.1. Snapshot simulation of emergency case
5.2. Continuous simulation of system real-time operation
6. Conclusions
References
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. پروژه ریزشبکه ترکیبی PV-آبی کوچک
3. روش مدیریت انرژی مبتنی بر MAS
3.1. مناقصه مجازی
3.2. اعزام توان پویا
4. پیاده سازی ریزشبکه EMS
4.1. پلت فرم شبیه سازی RTDS-PXI زمان واقعی
4.2. ساختار و پیاده سازی MAS
5. شبیه سازی دیجیتال زمان واقعی عملیات ریزشبکه
5.1. شبیه سازی لحظه ای مورد اورژانس
5.2. شبیه سازی مداوم عملکرد سیستم در زمان واقعی
6. نتیجه گیری ها
منابع
