
دانلود رایگان مقاله مدیریت دانش و مدیریت ارتباط با مشتری در کسب و کار
چکیده
هدف - هدف این مقاله ارائه تجزیه و تحلیل کاملی از مفاهیم هوش کسب و کار (BI)، مدیریت دانش (KM) و CRM تحلیلی (aCRM) و ایجاد چارچوبی برای تلفیق هر سه با یکدیگر است. این مقاله همچنین به دنبال ایجاد یک مدیریت دانش و چارچوب مبتنی بر aCRM با استفاده از تکنیک های داده کاوی (DM) است که به تصمیم گیری سرمایه گذاری کمک می کند. هدف به اشتراک گذاشتن این مورد است که چگونگه مدیریت دانش و aCRM می تواند در چارچوب تجزیه و تحلیل بدون مشکل برای حفظ برتری در تصمیم گیری با استفاده از تکنیک های موثر داده کاوی یکپارچه سازی شود و چگونه کار بر روی چنین سیستم aCRM برای فعالسازی سازمان در ارائه راه حل های کامل می تواند موثر باشد.
طرح / روش / رویکرد - این مقاله بر اساس مطالعه متمرکز شده و اختصاص داده شده به نوشته های حاضر در مورد aCRM، مدیریت دانش و تکنیک های داده کاوی است. این مقاله در نظر گرفته که چگونه توسعه یک استراتژی و چارچوب عملیاتی که aCRM را بر پایه تکنیک هایDM موجود و روش مدیریت دانش برای مقابله با چالش های کسب و کار، صورت می گیرد. بر اساس این پژوهش، یک چارچوب سفارشی و یکپارچه برای مطابقت با نیازهای کسب و کار طراحی شده است.
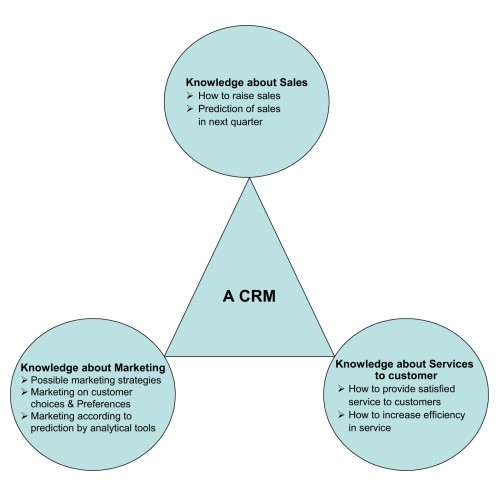
یافته ها - مدیریت دانش روی مدیریت دانش KM و aCRM روی به دست آوردن اطلاعات تحلیلی از داده های مشتری تمرکز می کند. KM و aCRM به فرایند و درک تصمیم گیری کمک می کنند. کشف این دانش سخت. از این رو، این مقاله اهمیت ابزارها و تکنیک های داده کاوی برای کشف دانش توسط ادغام بین KMوaCRM. را توضیح می دهد. این مقاله مدیریت دانش یکپارچه و چارچوب مبتنی بر aCRM را با استفاده از تکنیک های DM.ارائه می دهد.
محدودیتها/مفاهیم تحقیق - همه شرکت ها نمی توانند مدیریت دانش در حالی که aCRM. را اجرا می کنند، را اتخاذ نمایند. مدیریت دانش نیاز به گذراندن دوره نقاهت از فرهنگ سازمانی، نوآوری های فن آوری، نیروی کار موثر در به رساندن اوج انتشار دانش در حوزه های کسب و کار دارد.
مفاهیم عملی: - سازمان های پیاده سازی کننده این چارچوب aCRM فعال شده دانش به راحتی قادر به تبدیل دانش کسب و کار خود از طریق CRM تحلیلی برای حل بسیاری از مسائل کسب و کار، مانند افزایش نرخ پاسخ به پست الکترونیکی مستقیم، تلفن، پست الکترونیکی، و کمپین های بازاریابی تحویل داده شده اینترنت ، افزایش فروش و خدمات افزایش یافته خواهند بود. با aCRM، کارخانه ها می توانند سودآور ترین مشتریان خود را شناسایی و از این دانش برای طرح های تبلیغاتی برای مشتریان و همچنین مشتریان آینده با پیش بینی در ROI استفاده نمایند.
اصالت / ارزش - نیاز به یکپارچه سازی مدیریت دانش و aCRM روشن است. این مورد برای اقدام کنندگانی نوشته شده است که به دنبال روشی به منظور بهبود عملکرد کسب و کار و حفظ سود بالا برای کسب و کار خود توسط ترکیب aCRM فعال شده دانش در تنظیمات خود هستند.
1. مقدمه
مدیران کسب و کار تحقق بخشیدن به اهمیت تحلیلی مدیریت ارتباط با مشتریرا (aCRM) در رویکرد خود برای ارتباط با مشتریان شروع کرده اند.
استفاده از این روش تحلیلی به سازمانهای کسب و کار کمک می کند تا مزایایی که از طریق تجزیه و تحلیل مستمر داده های مشتری به دست می آید را درک نمایند. چارچوب عملیاتی سنتی اطلاعات مربوط به مشتری به حداکثر منافع خود رسیده است و در حال حاضر تماس تحلیلی با داده های عملیاتی اطلاعات اضافی مربوط به مشتریان را فراهم می کند. این اطلاعات از اطلاعات پنهان و ناشناخته مربوط به مشتریان برای کمک به بازار در تجزیه و تحلیل سبد خرید متفاوت است.
ACRM پیدا کردن اطلاعات پنهان و ناشناخته از داده های مشتری کمک می کند. موتور تحلیلی دانش مورد نیاز در مورد مشتریان برای مدیر کسب و کار را فراهم می کند. Doyle (2005) یک نقشه نمونه راه را برای aCRM نشان داد. Shogini (2003) دریافت که چگونه تجزیه و تحلیل CRM برای پرداخت به کاربران آن شروع می شود. این به درک مشتریان با روشی بهتر کمک می کند و به مدیران کمک می کند تا تعامل نزدیک با مشتریان داشته باشند.
Macsweeney (2001) اهمیت تحلیلی CRM را با توجه به آن به صورت گام بعدی در دنیای کسب و کار دریافت و متحقق ساخت. تجزیه و تحلیل داده های مشتری منجر به مدیریت موثر در درون سازمان می شود. این امر به مدیران کمک کرده تا استراتژی خود را بالاتر از نقطه تماس به مرکز طرح ریزی نمایند که تنها برای ارائه اطلاعات موجود مربوط به مشتری مورد استفاده قرار می گیرد. تجزیه و تحلیل سبد بازار، فروش متقابل را با اتخاذ aCRM در سازمان افزایش می دهد. Thomas (2003) اهمیت رو به رشد تجزیه و تحلیل CRM در کسب و کار را دریافت.. Xu و Walton (2005) اهمیتaCRM را برای به دست آوردن دانش مشتری نشان داد.Qiaohong و همکاران. (2007) چارچوبرا aCRM برای داده های توزیع شده طراحی نمودند. Kadayam (2002) اهمیت مدیریت علم و دانش (KM) را برای به دست آوردن ROI از هوش تجاری نشان داد (BI). همانطور که aCRM در حال حاضر در حال جلب کردن و روش های مدیریت دانش در حال پیشرفت است، جوهره aCRM و ارزش آن را می توان در یک سازمان تنها با اصول KM و داده کاوی (DM) احساس نمود. Nemati و همکاران (2002) انبار دانش را به عنوان یکپارچه سازی مدیریت دانش، پشتیبانی تصمیم گیری، هوش مصنوعی و انبارش داده ها مصطلح نمودند. Nemati موفقیت سازمانی را، یک ظرفیت تصمیم گیری KM استدلال می کند، DM ضروری است. این مشتق شده یک واقعیت است که برای مدیریت دانش موفق CRM مبتنی بر تحلیلی همراه با DM ضروری است. این مورد یک حقیقت را نتیجه داد که برای CRM موفقیت آمیز مبتنی بر تحلیل، KM جفت شده با DM ضروری است. Cody و همکاران. (2002) اثربخشی اجرای مدیریت دانش و هوش را نشان دادند. این مورد از این واقعیت گرفته شده که DM و KM روش های ضروری برای تجزیه و تحلیل کسب و کار است. Hameed (2004) برای آوردن تفاوت بین مدیریت دانش و BI تلاش نمودند.
Abstract
Purpose – The purpose of the paper is to provide a thorough analysis of the concepts of business intelligence (BI), knowledge management (KM) and analytical CRM (aCRM) and to establish a framework for integrating all the three to each other. The paper also seeks to establish a KM and aCRM based framework using data mining (DM) techniques, which helps in the enterprise decision-making. The objective is to share how KM and aCRM can be integrated into this seamless analytics framework to sustain excellence in decision making using effective data mining techniques and to explore how working on such aCRM system can be effective for enabling organizations delivering complete solutions.
Design/methodology/approach – This paper is based on focused and dedicated study of the literature present on the aCRM, KM and data mining techniques. The paper considered how to develop a strategy and operational framework that would build aCRM on the foundation of existing DM techniques and KM approach to meet the business challenges. Based on this research, a customized, integrated framework, to match the needs of business was designed.
Findings – KM focuses on managing knowledge within the organization and aCRM focuses on gaining analytical information from the customer data. Both KM and aCRM help in the decision making process and understanding. This knowledge is difficult to uncover. Hence, this paper explains the importance of data mining tools and techniques to uncover knowledge by the integration between KM and aCRM. This paper presents an integrated KM and aCRM based framework using DM techniques.
Research limitations/implications – All the firms may not be in favor of adopting KM while implementing aCRM. The KM requires a convalesce of organizational culture, technology innovations, effective work force in culminating knowledge dissemination in all business domains.
Practical implications – The organizations implementing this knowledge enabled aCRM framework would be easily able to convert their business knowledge via the analytical CRM to solve many business issues, such as increase response rates from direct mail, telephone, e-mail, and internet delivered marketing campaigns, increased sales and increased services. With aCRM, firms can identify their most profitable customers and use this knowledge for promotional schemes for those customers as well as identify future customers with prediction on ROI.
Originality/value – The need for the integration of KM and aCRM is clear. It is written for practitioners who are looking for approaches to improve business performance and maintain high profits for their business by incorporating knowledge-enabled aCRM in their setup.
1. Introduction
The business executives have started to realize the importance of the analytical Customer Relationship Management (aCRM) in their approach to deal with customers.
The application of the analytical approach helps the business organizations to understand the benefits that are achieved through continuing analysis of the customer data. The traditional operational framework of the customer information has reached its maximum benefits and now the analytical touch to the operational data provides additional information pertaining to the customers. This information varies from providing the hidden and unknown information related to customers to help in market basket analysis.
ACRM helps to find the hidden and unknown information from the customer data. The analytical engine provides the knowledge required about the customers to the business executive. Doyle (2005) showed a sample road map for aCRM. Shogini (2003) found how CRM analytics started to pay off to the users of it. This helps them to understand the customers in a better way and helps executives to interact closely with the customers.
Macsweeney (2001) found and realized the importance of the CRM analytic by considering it to be the next step in business world. The analysis of the customer data leads to effective management within the organization. This has helped the executives to plan their strategy above the contact center point, which used to provide only the existing information pertaining to the customer. The market basket analysis, cross-selling and up-selling increases with the adoption of aCRM in the organization. Thomas (2003) found the growing importance of the CRM analytics in the business intelligence. Xu and Walton (2005) showed the importance of aCRM to gain the customer knowledge. Qiaohong et al. (2007) designed an aCRM framework for distributed data wares. Kadayam (2002) showed the importance of knowledge management (KM) to gain ROI from business intelligence (BI). As aCRM is currently catching up and KM methodologies are progressing, the essence of aCRM and its value can be felt in an organization only with KM and data mining (DM) principles. Nemati et al. (2002) termed knowledge warehouse as integration of KM, decision support, artificial intelligence and data warehousing. Nemati argued for an organizational success a covalence of KM decision-making, DM is essential. This derived a fact that for a successful analytic based CRM KM coupled with DM is essential. Cody et al. (2002) showed the effectiveness of implementing the KM and BI. This derived the fact that DM and KM are essential methods for any Business analytics. Hameed (2004) tried to bring the difference between the KM and BI.
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. تحقیق و انگیزه های مرتبط
3. طراحی و رویکرد
3.2 تکنیک های جمع آوری داده ها
3.3 تصدیق چارچوب
4. ACRM و DM: مقدمه
5. مدیریت دانش: مقدمه
6. چارچوبی برای aCRM با توجه به عوارض DM و روش از چشم انداز مدیریت دانش
7. نتیجه گیری
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related research and motivation
3. Design and approach
3.1 Research approach and strategy
3.2 Data gathering techniques
3.3 Verification of framework
4. ACRM and DM: an introduction
5. Knowledge management: an introduction
6. Framework for aCRM considering DM tolls and technique from KM perspective
7. Conclusion
References
