
دانلود رایگان مقاله رویکرد داده کاوی مکانی مبتنی بر GIS برای مکان یابی و برنامه ریزی ظرفیت بهینه تاسیسات تولید انرژی
چکیده
این مقاله در درجه اول در نظر دارد یک GIS (سیستم اطلاعات جغرافیایی) مبتنی بر روش داده کاوی را برای انتخاب بهینه مکان و تعیین ظرفیت تجهیزات نصب شده به منظور راه اندازی سیستم های تولید برق زیست توده پراکنده در زمینه برنامه ریزی انرژی غیرمتمرکز را برای مناطق روستایی توسعه دهد. مکان های بهینه در یک گروه از روستاها توسط تطبیق ظرفیت ثابت موردنیاز با تقاضای برق برای به حداقل رساندن هزینه های انتقال انرژی زیست توده ای از منابع پراکنده به سیستم تولید برق و هزینه های توزیع برق از سیستم تولید برق به مراکز تقاضا یا روستاها بدست می آیند. این روش که استفاده از آن مورد تایید قرار گرفته است، برای توسعه یک طرح بهینه به منظور اجرای سیستم های قدرت مبتنی بر زیست توده پراکنده برای رفع نیازهای برق روستایی منطقه تومکور در هند که متشکل از 2700 روستا اجرا شده است. روش الگوریتم خوشه بندی K-medoid کل ناحیه را به خوشه هایی از روستاها تقسیم می کند و سیستم های تولید برق زیست توده ای را در medoid ها قرار می دهد . مقدار بهینه k با تکرار اجرای الگوریتم در کل فضای جستجو برای مقادیر مختلف k همراه با تطبیق محدودیت های عرضه درخواستی تعیین می شود. مقدار بهینه k بطوری انتخاب شده است که کل هزینه نصب سیستم، هزینه های انتقال زیست توده ای و انتقال و توزیع را به حداقل برساند. یک منطقه کوچکتر، شامل 293 روستا برای مطالعه حساسیت نتایج به پارامترهای عرضه و تقاضای متفاوت انتخاب شده بود. نتایج حاصل از خوشه بندی بر روی یک نقشه GIS برای این منطقه ارائه شده اند.
1. مقدمه
این یک واقعیت شناخته شده است که برق انگیزه ای برای توسعه اقتصادی و همچنین انسان فراهم می کند. با این حال در اکثر کشورهای درحال توسعه، بخش عمده ای از جمعیت، بویژه در نواحی روستایی، از مزایای دسترسی به برق و همچنین توسعه اقتصادی محروم هستند. کشور هند مستثنا از این نیست چرا که 364 میلیون نفر فقیر در این کشور فاقد دسترسی به برق هستند [1]. از طرف دیگر، سوخت های فسیلی مرسوم براساس، سیستم های تولید برق متمرکز شده عمدتا نیازهای صنعتی و شهری را برای پاسخگو می باشند اما برای رسیدگی به نیازهای انرژی مردم فقیر روستاها با شکست مواجه شده اند [2]. از سوی دیگر، استخراج بی رویه باعث محدود شدن منایع موجود سوخت های فسیلی برای تولید برق شده است. این مستلزم نیاز فوری به بررسی گزینه های انرژی تجدیدپذیر است که می توانند در حالت غیرمتمرکز در ظرفیت کوچکتر که در مقدار زیادی موجود هستند عمل کنند. در میان تمام گزینه های انرژی های تجدیدپذیر برای تولید برق، خط سیر انرژی زیست توده ای در نظرگرفته شده برای به صرفه بودن آن، زیرا : (i) می توانند آنها را در هر محل که پوشش گیاهی و پرورش حیوانات وجود دارد راه اندازی کرد، (ii) آنها در تمام طول سال دردسترس هستند و هیچ تغییرات فصلی وجود ندارد، حصول اطمینان از عرضه غیرمتناوب و (iii) این انرژی ارزان است، براحتی قابل حمل و خطرات زیست محیطی آن حداقل می باشد[2]. زیست توده چوبی موردنیاز برای تولید برق را می توان بدون از بین بردن جنگل های طبیعی با رشد مزارع اختصاص داده شده که بر روی زمین رها و تخریب شده اند و استفاده رقابتی زیادی ندارد تولید کرد. همچنین می توان زیست توده را از پسماندهای های محصولات کشاورزی و مزارع بدست آورد. برق تولید شده از زیست توده دیگر مزایای نامحسوسی مانند توسعه زمین های بایر، احیای زمین های تخریب شده، کاهش خطرات زیست محیطی و ایجاد اشتغال محلی دارد. [3].
کشور هند دارای پتانسیل منابع زیست توده ای بزرگی از نظر پسماندهای کشاورزی و جنگلی می باشد وسعت زیادی در حدود 40 میلیون هکتار از زمین های بایر برای رشد زیست توده وجود دارد. پتانسیل موجود برای تولید برق از پسماندهای کشاورزی و جنگلی به تنهایی 16000 مگاوات تخمین زده می شود[4]. بنابراین، برای کشور هند، گسترش استفاده از منابع زیست توده ای منطقه ای موجود برای تولید برق یک استراتژی منطقی به منظور رسیدگی به چالش برق روستایی می باشد. توزیع زیست توده ای در یک منطقه جغرافیایی به شدت یکنواخت نیست و زمانی که منابع زیست توده ای موجود محلی کافی نباشند برای تامین نیازهای برق محلی در یک منطقه، زیست توده باید وارد عمل شده باشد. زمانی که پسماندهای زیست توده ی بسیاری از روستاها جمع آوری و به تجهیزات تولید برق انتقال داده شد، سیستم های انتقال باید بطور موثرتری طراحی شوند و آنها باید به مسئله ی محل بهینه تجهیزات قدرتی زیست توده ای رسیدگی کنند.
تصمیمات مکان یابی با توجه به تجهیزات تولید برق زیست توده ای بطورعمده به دو بخش از هزینه های متغییر وابسته است. بخش اول مربوط به هزینه های متحمل شده در تهیه زیست توده و انتقال زیست توده از منابع پراکنده به تجهیزات تولید برق (یا سیستم های تولید برق زیست توده ای)است. بخش دوم از هزینه مربوط به انتقال برق تولیدی و تامین آن برای مراکز تقاضای مختلف (خانواده ها، کشاورزی، میکرو صنعت و غیره) است. در این زمینه، هزینه های مریوطه را به سیستم انتقال محلی و سیستم توزیع مرتبط می کنند. از آنجا که سیستم های برق زیست توده ای ظرفیت های کوچکی دارند وغیر متمرکز هستند، هزینه غالب برای سیستم توزیع نسبت به انتقال بیشتر خواهد بود. بنابراین، سیستم های انرژی زیست توده ای می توانند به هزینه های عملیاتی موثری توسط استراتژی مکان یابی سیستم انرژی با کاهش هزینه انتقال زیست توده ای از منبع و هزینه انتقال و توزیع از سیستم تولید انرژی برای مراکز تقاضا شوند. به عنوان یک توانمندساز برای حمایت از چنین تصمیمی، در این مقاله، ما به بحث و گفتگو درمورد توسعه و اعتبار یک مدل ریاضی برای تعیین محل بهینه سیستم های برق زیست توده ای به منظور کاهش هزینه های انتقال پرداخته ایم. علاوه براین، این مدل تصمیم هایی با توجه به ظرفیت ثابت بهینه سیستم های زیست توده ای توسط تطبیق تقاضای داده شده برای برق و مقدار موجود زیست توده را تسهیل می بخشد. عنصر کلیدی در مطالعات حاضر برای روستاهای خوشه بندی شده در ناحیه مورد مطالعه، مراکز تولید برق زیست توده ای در داخل خوشه ها هستند، جمع آوری زیست توده از روستاهای مختلف (واحدهای تغذیه) و مقادیر کافی انتقال زیست توده به مراکز تولید برق در خوشه ها، به منظور تحقق نیازهای نیروگاه با هزینه کمتر است بطوری که برای توان درخواست شده دینامیکی پاسخگو باشد. منطقه تومکور در هند شامل 2700 روستا می باشد که برای اعتبار دهی مدل انتخاب شده است. دو سناریو، میان مدت (2015) و دیگری بلند مدت (2030) برای اعتباردهی مدل با تقاضای طرح ریزی شده برای تولید انرژی، پتانسیل زیست توده ای و بارهای دینامیکی توسعه داده شده است.
در چند دهه گذشته، باتوجه به ظهور انبوهی از برنامه های ابتکاری در شرکت های بخش خصوصی و عمومی، یک روش استراتژیک برای قرار دادن امکاناتی مانند انبارها، بیمارستان ها، مدارس و ایستگاه های آتش نشانی به تصویب رسید. تعداد زیادی از مدل های توزیع برای قرار دادن یک مرکز و تخصیص تقاضا و ظرفیت برای این تجهیزات این مرکز مدل شده است. هدف از این مدل ها به حداقل رساندن کل هزینه های نصب و بهره برداری از تجهیزات بود. هر یک از این مدل ها در ساختار ریاضی، زمان محاسبات و پیچیدگی از مدل دیگری متفاوت هستند.
خلاصه ای از مدل های پیوسته مکان، مدل های مکان شبکه، مشکلات برنامه ریزی عددصحیح و دیگر مشکلات مروری توسط مقالات کلوزه و درکسل (2005) [5] ارائه شده است. در مقاله فرانسیس و همکاران (1983) [6]، مروری از تجزیه و تحلیل مکان یابی ارائه شده است. همکاران کنونی (1990) [7] جنبه های چند هدفه را در حوزه مشکلات تجزیه و تحلیل محل تجهیزات بررسی کردند. آنها یافتند که بسیاری از مقالات شامل فرمول کمینه سازی هزینه بودند، برخی از آنها با اهدافی در جهت تقاضا سروکار داشتند و فقط چند مقاله از نوع بیشینه سازی سود بردند.
در مقاله ملکوته و دوسکین (2001)[8] مدلی که بطورهمزمان بهینه سازی محل و توپولوژی شبکه را تغییر می دهد بررسی شده است. آنها در مورد مشکلات مختلف مکان شبکه مانند مجموعه ای از مشکل مکان یابی پوششی، مشکل مکان یابی پوششی حداکثر، مشکلات میانه-P و مرکز-P که در توپولوژی شبکه زمینه ای می تواند تاثیر قابل توجه ای در تصمیم مکان بهینه داشته باشد اشاره کرند. آنها همچنین ثابت کردند که مدلشان می تواند با موفقیت در تعدادی از برنامه های کاربردی مانند برنامه ریزی منطقه ایف توزیع برق، مدیریت انرژی و سایر نواحی اجرا شود. مقاله سایم (2008) [9] یک مدل جایابی مکان با سرور چندگانه بواسطه در نظر گرفتن بسیاری از هزینه های مربوطه و پارامترهای دیگر، از جمله، هزینه انتقال، هزینه تجهیزات، هزینه زمان انتظار، زمان صف بندی، تجهیزات سرور و محدویت های مسافتی فرموله شده است.
در مقاله نما و گوپتا (1999) [10] همسان سازی تکنولوژی پسماند برای مکان یابی کردن تصفیه پسماند و تجهیزات دفع مورد بررسی قرار گرفته است. آنها مشکل چند هدفه پارامترهای ریسک پذیر و هزینه را یکپارچه سازی و فرمول بندی کردند. در مقاله مانیزو و همکاران (1998) [11]، یک سیستم پشتیبانی تصمیم گیری برای قرار دادن دستگاه های مدیریت پسماند صنعتی به منظور به حداقل رساندن کل هزینه ها و تاثیرات زیست محیطی توسعه داده شده است. نتایج فرمول NP -کامل بود که تنها می تواند با اتخاذ روش ابتکاری حل شود. انتخاب بهینه مکان یابی، فن آوری، مسیریابی پسماندهای خطرناک توسط آلومر و کارا (2007) [12] مورد بررسی قرار گرفته است.
Abstract
This paper primarily intends to develop a GIS (geographical information system)-based data mining approach for optimally selecting the locations and determining installed capacities for setting up distributed biomass power generation systems in the context of decentralized energy planning for rural regions. The optimal locations within a cluster of villages are obtained by matching the installed capacity needed with the demand for power, minimizing the cost of transportation of biomass from dispersed sources to power generation system, and cost of distribution of electricity from the power generation system to demand centers or villages. The methodology was validated by using it for developing an optimal plan for implementing distributed biomass-based power systems for meeting the rural electricity needs of Tumkur district in India consisting of 2700 villages. The approach uses a k-medoid clustering algorithm to divide the total region into clusters of villages and locate biomass power generation systems at the medoids. The optimal value of k is determined iteratively by running the algorithm for the entire search space for different values of k along with demandesupply matching constraints. The optimal value of the k is chosen such that it minimizes the total cost of system installation, costs of transportation of biomass, and transmission and distribution. A smaller region, consisting of 293 villages was selected to study the sensitivity of the results to varying demand and supply parameters. The results of clustering are represented on a GIS map for the region.
1. Introduction
It is a well known fact that electricity provides impetus to economic as well as human development. However, in majority of the developing countries, the major section of the population, especially in rural areas, is deprived of the benefits of electricity access as well as economic development. India is not an exception to this with 364 million poor people lacking access to electricity [1]. On one hand, the conventional, fossil fuel based, centralized power generation systems have been catering mainly to meet the urban and industrial needs but have failed to address the energy needs of the rural poor [2]. On the other hand, there is an uncontrolled exploitation of the finitely available fossil fuel resources for power generation. This necessitates an urgent need to explore renewable energy options that can be operated on decentralized mode at smaller capacities and are available in plenty. Among all the renewable energy alternatives to generate power, biomass energy route is considered to be advantageous, because: (i) They could be set up at any location where plant vegetation and animal rearing are present, (ii) It is available all round the year and there are no seasonal variations, ensuring non-intermittent supply and (iii) It is cheap, easily portable and environmental hazards are minimal [2]. Woody biomass required for power generation can be generated without destroying the natural forests by growing dedicated plantations on abandoned and degraded land which do not have much competitive uses. Biomass can also be obtained from the crop residues from agricultural lands and plantations. The power generated from biomass offers other intangible benefits such as wasteland development, degraded land reclamation, environmental hazard reduction and local employment generation [3].
India has a large biomass resource potential in terms of agro and forest residues, and large tracts of approximately 40 million ha of wasteland for growing biomass. Current potential for power generation from Agro and forest residues alone is estimated to be 16,000 MW [4]. Therefore, for India, expanding the usage of locally available biomass resources to generate electricity is a logical strategy to address the rural power challenge. The distribution of biomass is not strictly uniform in a geographical region and when locally available biomass resources are insufficient to meet the local electricity needs in the region, biomass has to be imported. When biomass is collected from many villages and transported to a power generation facility, logistic systems have to be designed more efficiently and they should address the issue of optimal location of biomass power facility.
The location decisions with respect to biomass power generation facility mainly depend on two components of variable costs. The first component relates to cost incurred on biomass procurement and biomass transportation from the dispersed sources to the power generation facilities (or biomass power generation systems). Second component of the cost is with respect to evacuating the generated electricity and supplying it to various demand centers (households, agriculture, micro-industry, etc.). In this context, the relevant costs are related to local transmission and distribution systems. Since these biomass power systems are of small capacities and decentralized, the dominant cost will be for the distribution system rather than transmission. Therefore, biomass energy systems can become operationally cost effective by strategizing the location of the energy systems by minimizing transportation cost of biomass from the source, and transmission and distribution cost from energy production system to the demand centers. As an enabler to support such decisions, in this paper, we present a discussion on the development and validation of a mathematical model to determine the optimal location of biomass power systems to minimize the cost of transportation. In addition, the model also facilitates decisions with respect to optimal installed capacity of the biomass systems by matching the given demand for power and available quantity of biomass. The key element in the current study is to cluster villages in the study area, define biomass power generation centers within the clusters, collect biomass from various villages (supply points) and transport sufficient quantities of biomass to the biomass power generation center within the cluster, in order to satisfy the power plant requirement at the least cost so as to meet the dynamic demand for power. Tumkur district in India consisting of 2700 villages is selected for validating the model. Two scenarios, one medium-term (2015) and the other one long-term (2030) were developed for validating model with projected demand for energy, dynamic loads and biomass potential.
In the last few decades, owing to emergence of multitudes of innovative applications in both private and public sector enterprises, a strategic approach had to be adopted to locate the facilities such as warehouses, hospitals, schools and fire stations. A vast number of distribution models were formulated to locate a facility and allocate the demand and capacity to these facilities. The objective of these models was to minimize the total installation and operational costs of the facilities. Each one of them differed from the other in mathematical structure, computational time and complexity.
A summary of continuous location models, network location models, integer programming problems and other state-of-the-art problems was presented by Klose and Drexel (2005) [5]. Francis et al. (1983) [6] provided a review of literature of location analysis. Current et al. (1990) [7] reviewed the multi-objective aspects in the problem domain of facility location analysis. They found that most of the literature was comprised of cost minimization formulation, some of them dealt with demand oriented objectives, and only a few papers were of profit maximization type.
Melkote and Duskin (2001) [8] investigated a model that simultaneously optimizes the location and alters the network topology.They mention about different network location problems like set covering location problem, maximum covering location problem, P-median and P-center problems in which underlying network topology can have a significant impact on the optimal location decision. They also proved that their model can be successfully implemented in a number of applications like regional planning, power distribution, energy management and other areas. Syam (2008) [9] formulated a multiple server location-allocation model by considering most of the relevant costs and other parameters, namely, the transportation cost, facility cost, waiting time cost, queuing time, multiple server facilities and distance constraints.
Nema and Gupta (1999) [10] examined the waste-technology compatibility to locate waste treatment and disposal facilities. They formulated a multi-objective problem integrating both cost and risk parameters. Maniezzo et al. (1998) [11], have developed a decision support system for siting industrial waste management plants, minimizing the total costs and environmental impacts. The resulting formulation was NP-complete which could only be solved by adopting heuristic procedures. The optimal choice of location, technology, routing of hazardous waste was investigated by Alumur and Kara (2007) [12].
چکیده
1. مقدمه
1.1. الگوریتم های خوشه بندی—موزائیک کاری فضایی
1.2. مشخصات محل مورد مطالعه
2. ارزیابی زیست توده برای تولید برق
2.1. ارزیابی تقاضای برق در منطقه تومکور
2.2. پارامترهای هزینه
3. الگوریتم پیشنهادی
3.1. پارامترهای الگوریتم
4. پیاده سازی الگوریتم خوشه بندی k-medoid و نتایج آن
4.1. خوشه بندی روستاها در بخش کونیگال- سناریوی فن آوری کارآمد در سال 2015
4.2. خوشه بندی روستاها در بخش کونیگال –سناریوی فن آوری کارآمد در سال 2030
4.3. تجزیه و تحیلیل سطح خوشه منطقه
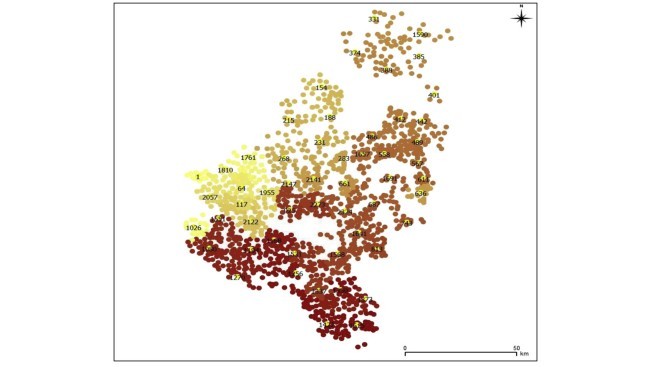
4.4. تجزیه وتحلیل نتایج خوشه بندی
4.5. بحث
5. نتیجه گیری
منابع
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Clustering algorithms e spatial tessellation
1.2. Profile of the study location
2. Biomass assessment for power generation
2.1. Assessment of demand for power in Tumkur district
2.2. Cost parameters
3. Proposed algorithm
3.1. Algorithm parameters
4. Implementation of k-medoid clustering algorithm and results
4.1. Clustering of villages in Kunigal block e efficient technology scenario 2015
4.2. Clustering of villages in Kunigal block e efficient technology scenario 2030
4.3. District level clustering analysis
4.4. Analysis of the clustering results
4.5. Discussion
5. Conclusion
References
