دانلود مقاله تولید هارمونیک های دوم و سوم برای یک تعلیق غیرآبکی از ذرات پوشش دار با ناهمسانگردی دی الکتریک شعاعی
چکیده
ما عبارت هایی را برای تانسورهای پذیرفتاری غیرخطی موثر برای تولید هارمونیک دوم (SHG) و تولید هارمونیک سوم القایی (THG) ذرات کامپوزیت غیرخطی را استخراج می کنیم، که در آن ذرات پوشش دار غیرآبکی با ناهمسانگردی دی الکتریک شعاعی بطور تصادفی در میزبان خطی قرار داده شده اند. دو نوع از ذرات پوشش دار در نظر گرفته شده اند. اولین نوع نوعی است که هسته دارای یک پذیرفتاری غیرخطی مرتبه دوم است و پوسته خطی و بطور شعاعی ناهمسانگرد است، درحالیکه دومین نوع نوعی است که هسته با ناهمسانگردی شعاعی خطی است و پوسته یک پذیرفتاری غیرخطی مرتبه دوم دارد. ما تاحدزیادی پذیرفتاری SHG و THG بهبود یافته ای را در چندین فرکانس تشدید پلاسمون خطی مشاهده می کنیم. برای مدل دوم، با توجه به فلزی بودن ماده پوششی، دو فرکانس تشدید بنیادی ωc1 و ωc2 وجود دارند، که اختلاف آن ωc2−ωc1 قویا وابسته به پارامتر بین سطحی و ناهمسانگردی دی الکتریک شعاعی می باشد. به علاوه، در هر دو سیستم، تنظیم ناهمسانگردی دی-الکتریک منجر به بهبود پذیرفتاری های SHG و THG القایی در فرکانس های تشدید پلاسمون سطحی نسبت به سیستم های همسانگرد متناظر می شود. بنابراین، هردو ساختار هسته-پوسته و ناهمسانگردی دی الکتریک نقش مهمی در تعیین بهبود غیرخطی و فرکانس های تشدید سطحی ایفا می کنند.
1- مقدمه
بررسی های تجربی و نظری در مواد تابعی با خصوصیات اپتیکی غیرخطی بزرگ و زمان واکنش سریع در سال های اخیر به خاطر کاربردهای بالقوه آن ها در سوییچینگ فوق سریع، پردازنده های سیگنال اپتیکی و دستگاه های حافظه با دو حالت پایا اهمیت زیادی پیدا کرده اند [1-3]. مواد کامپوزیت ممکن است دارای خصوصیات اپتیکی غیرخطی بزرگتری مانند پذیرفتاری غیرخطی مرتبه سوم [4]، پذیرفتاری تولید هارمونیک دوم (SHG) و پذیرفتاری تولید هارمونیک سوم (THG) [5] نسبت به همتایان خودشان داشته باشند و حتی ویژگی های دو حالت پایا و چند حالت پایای جدیدی را تولید کنند [6،7] که هیچ یک از ترکیبات دیگر ندارند. این خصوصیات فیزیکی جالب محیط های کامپوزیت انتظار می رود که از مکانیزم نفوذ [8] و ناهمگنی میدان های محلی در کامپوزیت ها [9] نتیجه می شوند.
5- بحث و نتیجه گیری
در این مقاله، ما پذیرفتاری های غیرخطی موثر برای تولید هارمونیک دوم (SHG) و تولید هارمونیک سوم القایی (THG) مواد کامپوزیت غیرخطی را بررسی کرده ایم، که در آن ذرات پوشش دار غیرآبکی با ناهمسانگردی دی-الکتریک شعاعی در میزبان خطی قرار دارند. دو ماده پوشش دار نوعی مطالعه می شوند. در ماده اول هسته غیرخطی مرتبه دوم است و پوسته بطور شعاعی ناهمسانگرد دی الکتریک است، در ماده دوم هسته ناهمسانگرد است و پوسته غیرخطی است. در هر دو مورد، ما بهبود بزرگ پذیرفتاری های SHG و THG القایی را در چندین فرکانس تشدید پلاسمون سطحی مشاهده می کنیم.
Abstract
We derive expressions for the effective nonlinear susceptibility tensors for both the second harmonic generation (SHG) and induced third harmonic generation (THG) of nonlinear composite materials, in which nondilute coated particles with radial dielectric anisotropy are randomly embedded in the linear host. Two types of coated particles are considered. The first is that the core possesses a second order nonlinear susceptibility and the shell is linear and radially anisotropic, while the second is that the core is linear with radial anisotropy and the shell has a second order nonlinear susceptibility. We observe greatly enhanced SHG and THG susceptibilities at several surface plasmon resonant frequencies. For the second model, due to the coating material being metallic, there exists two fundamental resonant frequencies ωc1 and ωc2, whose difference ωc2−ωc1 is strongly dependent on the interfacial parameter and the radial dielectric anisotropy. Furthermore, in both systems, the adjustment of the dielectric anisotropy results in larger enhancement of both SHG and induced THG susceptibilities at surface plasmon resonant frequencies than the corresponding isotropic systems. Therefore, both the core-shell structure and the dielectric anisotropy play important roles in determining the nonlinear enhancement and the surface resonant frequencies.
1 Introduction
Theoretical and experimental investigations on functional materials with large nonlinear optical properties and fast response time are of great interest in recent years for their potential applications in ultra-fast switching, optical signal processors, and bistable memory devices [1–3]. Composite materials may possess larger nonlinear optical properties such as third-order nonlinear susceptibility [4], second harmonic generation (SHG) susceptibility and third harmonic generation (THG) susceptibility [5] than those of their components, and even produce novel optical bistable and multi-stable properties [6,7] that none of the components have. These interesting physical properties of composite media are believed to result from the percolation mechanism [8] and the inhomogeneity of the local fields within the composites [9].
5 Discussion and conclusion
In this paper, we have investigated the effective nonlinear susceptibilities for second harmonic generation (SHG) and induced third harmonic generation (THG) of nonlinear composite materials, in which nondilute coated particles with radial dielectric anisotropy are embedded in the linear host. Two typical coated particles are studied. The first is that the core being second order nonlinear and the shell being radially dielectric anisotropic, while the second is the core being anisotropic and the shell being nonlinear. In both cases, we observe large enhancement of SHG and induced THG susceptibilities at several surface plasmon resonant frequencies.
1- مقدمه
2- پذیرفتاری های غیرخطی موثر برای SHG و THG
3- پذیرفتاری های SHG و THG برای مدل A
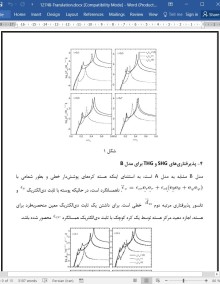
4- پذیرفتاری های SHG و THG برای مدل B
5- بحث و نتیجه گیری
منابع
Abstract
1 Introduction
2 effective nonlinear susceptibilities for SHG and THG
3 SHG and THG susceptibilities for model A
4 SHG and THG susceptibilities for Model B
5 Discussion and conclusion
References
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه