
دانلود رایگان مقاله ثبت تصویر SAR با استفاده از تجانس فاز و SIFT غیرخطی
چکیده
الگوریتم تبدیل ویژگی های نامتغیر با-مقیاس (SIFT) به طور گسترده برای ثبت اپتیکال تصویر اعمال می شود. با این حال، عمدتا به دلیل نویز نقطه ای ضربی، زمانی که SIFT به طور مستقیم برای تصویر روزنه ساختگی رادار (SAR) اعمال شود، دارای یک عملکرد محدود است. در این مقاله، یک روش ثبت جدید SAR ارائه شده است، که بر اساس ترکیبی از SIFT، انتشار غیرخطی، و تجانس فاز است. در الگوریتم پیشنهادی ما، ارائه یک تصویر SAR در چند مقیاس توسط انتشار غیرخطی تولید می شود، زیرا لبه های تصویر را بهتر حفظ می کند، برخلاف صاف نمودن گاوسی که در SIFT اصلی استفاده می شود. برای کاهش تاثیر نویز نقطه ای ضربی، نسبت اپراتور متوسط وزنی نمایی برای محاسبه اطلاعات گرادیان در ساخت فضای مقیاس انتشار غیرخطی استفاده می شود. علاوه بر این، اطلاعات تجانس فاز برای حذف نقاط کلیدی اشتباه در نقاط کلیدی اولیه استفاده می شود. نتایج تجربی در مورد تصاویر SAR چند قطبی بودن، چند بانده و چند زمانی نشان می دهند که الگوریتم ما می تواند عملکرد تطبیق را نسبت به روش مبتنی بر SIFT بهبود دهد که برای تمام جفت تصویر مورد آزمایش، منجر به دقت زیر پیکسل می شود.
1. مقدمه
روزنه ساختگی رادار (SAR)، یک سیستم تصویربرداری منسجم است که می تواند تصاویری با رزولوشن بالا تولید نماید و تحت همه زمانها و همه شرایط آب و هوایی کار کند. از این رو، برای کاربردهای متنوع، از جمله ترکیب تصویر، نظارت زیست محیطی، آشکارسازی تغییر [1]، و غیره مفید است. به عنوان یک گام اساسی مورد نیاز در این کاربردها، ثبت تصویر به همراستایی تصاویر همان صحنه به دست آمده تحت شرایط تصویربرداری مختلف، مثلاً زمان های مختلف، از دیدگاه های مختلف، و یا توسط سنسورهای مختلف اشاره می نماید.
به تازگی، با توجه به عدم تغییرات آن به مقیاس، چرخش ها، انتقال ها و تابش جزئی و تغییرات نقطه نظر، تبدیل ویژگی نامتغیر با-مقیاس (SIFT) به طور گسترده ای در بسیاری از وظایف پردازش تصویر استفاده شده است. بر اساس ارائه چند-مقیاسی یک تصویر (یعنی، یک سری از تصاویر تفاوت-گاوسی (DoG))، SIFT، نقاط کلیدی ر با جستجوی مقادیر حدی در هرم DoG تشخیص می دهد و سپس توصیف کننده نقطه کلیدی را در تکه های تصویر محلی در اطراف هر نقطه کلیدی محاسبه می نماید. این توصیف کننده، توزیع گرادیان مکانی را در اطراف یک نقطه کلیدی توسط یک بردار 128 بعدی کدگذاری می کند که برای تطبیق زیر استفاده می شود. جزئیات بیشتر در مورد SIFT را می توان در [2] پیدا نمود.
اگر چه SIFT با موفقیت برای ثبت اپتیکال تصویر اعمال شده است، با توجه به تمایز آن در شرح و توصیف ویژگی، نمی تواند نتایج رضایت بخش را در هنگام اعمال مستقیم برای تصاویر SAR تولید نماید [3]. دلایل ممکن شامل دو جنبه می شود. اول، تصاویر SAR معمولا توسط نویزهای نقطه ای قوی ضربی خراب می شوند که SIFT را برای استخراج نقطه کلیدی بدتر می نماید. بنابراین، بسیاری از نقاط کلیدی نادرست ممکن است با استفاده از روش SIFT ظاهر شوند [4]، [5]. ثانیاً، در نتیجه عمل صاف کردن گاوسی، فضای مقیاس گاوسی (GSS) مورد استفاده در SIFT اغلب اطلاعات لبه و جزئیات ریز را در تصویر تنزل می دهد [6]. با توجه به نقایص از دست دادن جزئیات، مات شدن لبه ها، و مصونیت در برابر نویز نقطه ای ضعیف آن، SIFT بسیاری از نقاط کلیدی اولیه نادرست از سگ DoG را در هنگام سرو کار داشتن با ثبت تصویر SAR به دست می آورد. پس از حذف این نقاط دورافتاده، تطبیقات صحیح در دسترس به منظور محاسبه پارامترهای انتقال بیش از حد ناکافی هستند. در این مورد، SIFT ناموفق خواهد بود.
برای غلبه بر مشکلات فوق، انتشار غیرخطی در این مقاله برای تولید فضای مقیاس استفاده شده است [به عنوان مثال، فضای مقیاس انتشار غیرخطی (NDSS)]، که دارای مزیت حفظ لبه ها و جزئیات نسبت به GSS خطی است [7]، [8]. در همین حال، نسبت اپراتور متوسط وزنی (ROEWA) نمایی برای محاسبه اطلاعات گرادیان در طول ساخت NDSS استفاده می شود. علاوه بر این، نقاط کلیدی اولیه به دست آمده توسط کاوش اطلاعات تجانس فاز اصلاح می شوند. در مقایسه با روش مبتنی بر SIFT، روش پیشنهادی برای مشکل ثبت SAR مناسب است، همانطور که توسط آزمایش های ما نشان داده شده است.
بقیه این مقاله به شرح زیر است: روش پیشنهادی ثبت تصویر SAR در بخش دوم با تاکید بر تولید NDSS و روش حذف نقاط دورافتاده معرفی می شود و نتایج تجربی الگوریتم پیشنهادی و روش های دیگر ثبت ارائه می شوند و در بخش سوم مقایسه می شوند. نتایج در بخش 4 داده می شود.
2. ثبت SAR با استفاده از تجانس فاز و SIFT بر اساس انتشار غیرخطی
در اینجا، SIFT بهبود یافته برای ثبت SAR با جزئیات معرفی شده است. در مقایسه با الگوریتم SIFT اصلی، روش پیشنهادی روی بهبودهای زیر متمرکز است: 1) استفاده از انتشار غیرخطی برای تولید فضای مقیاس در SIFT بهبود یافته. 2) معرفی یک روش قوی برای محاسبه اطلاعات گرادیان مرتبط در NDSS برای تصویر SAR. و 3) ارائه یک مرحله حذف نقطه دورافتاده که بر اساس اطلاعات تجانس فاز است. جزئیات در زیر تشریح خواهد شد.
A. ایجاد فضای مقیاس با انتشار غیرخطی
GSS مورد استفاده در روش SIFT از کانوولوشن تصویر اصلی با فیلترهای گاوسی در مقیاس های مختلف تولید می شود [2]. هموارسازی گاوسی دارای اثر حذف نویز است؛ با این حال، برخی از جزئیات ریز مهم در تصویر ممکن است از دست برود که ممکن است دارای یک اثر بد در تشخیص ویژگی باشد.
پارامتر K، ضریب کنتراست است که سطح انتشار را کنترل می کند، و تعیین می کند که لبه باید نگه داشته شود و یا لغو شود. هرقدر مقدار K بالا باشد، اطلاعات لبه کمتر حفظ خواهد شد. مقدار K می تواند از نظر تجربی تثبیت شود و یا از هیستوگرام گرادیان تصویر برآورد شود [6].
Abstract
The scale-invariant feature transform (SIFT) algorithm has been widely applied to optical image registration. However, mostly because of multiplicative speckle noise, SIFT has a limited performance when directly applied to synthetic aperture radar (SAR) image. In this letter, a novel SAR image registration method is proposed, which is based on the combination of SIFT, nonlinear diffusion, and phase congruency. In our proposed algorithm, the multiscale representation of a SAR image is generated by nonlinear diffusion, since it better preserves edges in the image as opposed to Gaussian smoothing, which is used in the original SIFT. To reduce the influence of multiplicative speckle noise, the ratio of exponential weighted average operator is used to compute the gradient information in the construction of nonlinear diffusion scale space. Moreover, phase congruency information is utilized to remove the erroneous keypoints within the initial keypoints. Experimental results on multipolarization, multiband, and multitemporal SAR images indicate that our algorithm can improve the match performance compared to the SIFT-based method, which leads to a subpixel accuracy for all the tested image pairs.
I. INTRODUCTION
SYNTHETIC aperture radar (SAR) is a coherent imaging system, which can produce high-resolution images and work under all time and all weather conditions. Hence, it is useful for diverse applications, including image fusion, environmental surveillance, change detection [1], and so on. As a fundamental step required by these applications, image registration refers to the alignment of images of the same scene obtained under different imaging conditions, such as at different times, from different viewpoints, or by different sensors.
Recently, due to its invariances to scale changes, rotations, translations and partially to illumination and viewpoint changes, scale-invariant feature transform (SIFT) has been widely applied to many image processing tasks. Based on the multiscale representation of an image (i.e., a series of difference-of-Gaussian (DoG) images), SIFT detects keypoints,by searching extremal values in the DoG pyramid, and then computes a keypoint descriptor in the local image patches around each keypoint. The descriptor encodes the spatial gradient distribution around a keypoint by a 128-dimensional vector, which is used for the following match. More details about SIFT can be referred to [2].
Although SIFT has been successfully applied to optical image registration, owing to its distinctiveness in feature description, it may not produce satisfying results when directly applied to SAR images [3]. The reasons may consist of two aspects. First, SAR images are usually corrupted by strong multiplicative speckle noises, which deteriorate SIFT for keypoint extraction. Therefore, many incorrect keypoints may appear with the SIFT method [4], [5]. Second, the Gaussian scale space (GSS) used in SIFT often degrades edge information and fine details in the image as a result of the Gaussian smoothing operation [6]. Due to the defects of losing details, blurring edges, and its weak speckle noise immunity, SIFT will obtain many erroneous initial keypoints from DoG, when dealing with SAR image registration. After removal of these outliers, correct matches available are too insufficient for us to calculate transformation parameters. In this case, SIFT fails.
To overcome the problems aforementioned, nonlinear diffusion is utilized in this letter to generate the scale space [i.e., nonlinear diffusion scale space (NDSS)], which has an advantage of preserving edges and details over the linear GSS [7], [8]. Meanwhile, the ratio of exponential weighted average (ROEWA) operator is used to compute the gradient information during the construction of NDSS. In addition, the obtained initial keypoints are refined by exploring their phase congruency information. Compared with the SIFT-based method, the proposed approach is competent to the problem of SAR image registration, as shown by our experiments.
The rest of this letter is organized as follows: The proposed SAR image registration approach is introduced in Section II, with emphasis on the generation of NDSS and the procedure of outlier removal, and the experimental results of the proposed algorithm and other registration methods are presented and compared in Section III. Concluding remarks are given in Section IV.
II. SAR IMAGE REGISTRATION USING PHASE CONGRUENCY AND NONLINEAR DIFFUSION-BASED SIFT
Here, the improved SIFT for SAR image registration is introduced in detail. In comparison with the original SIFT algorithm, the proposed method focuses on the following improvements: 1) utilizing nonlinear diffusion to generate the scale space in the improved SIFT; 2) introducing a robust approach to compute the gradient information involved in the NDSS for SAR image; and 3) providing an outlier removal stage that is based on the phase congruency information. Details will be elaborated in the following subsections.
A. Creation of Scale Space With Nonlinear Diffusion
The GSS used in the SIFT method is produced from the convolution of the original image with Gaussian filters at different scales [2]. Gaussian smoothing has the effect of denoising; however, some important fine details in the image may be lost as well, which will have a bad effect on feature detection.
The parameter K is the contrast factor that controls the level of diffusion, and it determines which edges have to be kept or cancelled. The greater the K value is, the less edge information will be preserved. The K value can be either empirically fixed or estimated from the image gradient histogram [6].
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. ثبت SAR با استفاده از تجانس فاز و SIFT بر اساس انتشار غیرخطی
A. ایجاد فضای مقیاس با انتشار غیرخطی
B. حذف نقطه دورافتاده با استفاده از تجانس فاز
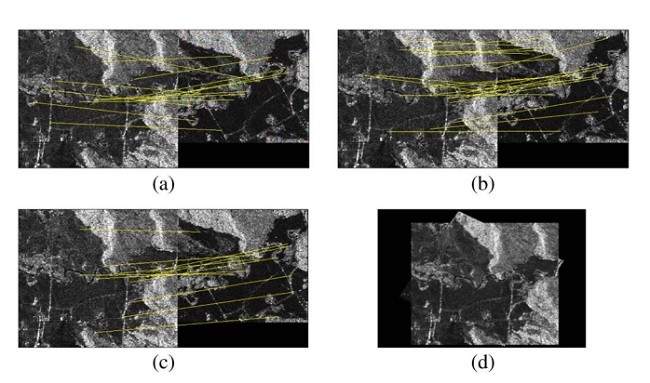
3. نتایج و تجزیه و تحلیل تجربی
A. عملکرد NDSS
B. مقایسه با سایر روش های ثبت تصویر
4. نتیجه گیری
Abstract
I.Introduction
II.SAR Image Registration Using Phase Congruency and Nonlinear Diffusion-Based SIFT
A. Creation of Scale Space With Nonlinear Diffusion
B. Outlier Removal Using Phase Congruency
III.Experimental Results and Analysis
A. Performance of NDSS
B. Comparison With Other Image Registration Methods
IV.Conclusion
