
دانلود رایگان مقاله ويژگی های ترمولومینسانس حبه های LiF
چکیده
حبه های ترمولومینسانس (TL) LiF:Mg,Cu,Na,Si سوزانده شده برای استفاده در دوزسنجی تابش توسعه یافته اند. حبه های TL LiF: Mg، Cu، Na، Si از حبه های TL با استفاده از یک فرایند سوزاندن (خاکستر شدن) ساخته می شوند، یعنی فشردن و عملیات حرارتی. این حبه ها دارای قطر 4.5 میلیمتر و ضخامت 0.8 میلیمتر و به رنگ آبی هستند و جرم هر یک از آنها 28 میلی گرم است. پس از تولید 400 حبه، آنها تحت تابش اشعه گاما 137Cs قرار گرفتند و نمونه ها با حساسیت در انحراف معیار 5٪± برای استفاده آزمایشی انتخاب شدند. در مطالعه حاضر، خصوصیات فیزیکی و دوزسنجی حبه های TL LiF: Mg، Cu، Na، Si، برای ویژگی های طیف انتشار، پاسخ دوز، پاسخ انرژی و محو شدن مورد بررسی قرار گرفتند. تابش فوتون برای آزمایشات با استفاده از پرتوهای پرتو ایکس و منبع گاما 137Cs در موسسه تحقیقات انرژی اتمی کره (KAERI) انجام شد. متوسط انرژي ها و دوز به ترتیب در محدوده 20-662 کیلو الکترون ولت و Gy 10_6_102 بودند. منحنی های درخشندگی با یک دستگاه قرائت دوزسنجی ترمولومینسانس نوع دستی (سیستم 310، Teledyne) با یک شار نیتروژن ثابت و نرخ گرمایش خطی اندازه گیری شدند. برای یک نرخ گرمایش ثابت 5C.s_1، حداکثر پیک دوزسنجی منحنی درخشندگی در 234 درجه سانتیگراد ظاهر شد، انرژی فعالسازی آن 2.34 الکترون ولت و ضریب فرکانسی 1.00x1023 بود. طیف انتشار TL در ناحیه آبی حول 410 نانومتر ظاهر شد. یک خطی بودن پاسخ دوز فوتون تا 100 Gy حفظ شد. پاسخ های انرژی فوتون نسبت به پاسخ 137Cs در ناحیه انرژی کلی فوتون, درون حدود 20٪ ± بود. هیچ محو شدنی حساسیت TL در حبه های ذخیره شده در دمای اتاق در طی یک سال دیده نشد. بنابراین حبه های TL LiF: Mg، Cu، Na، Si را می توان برای دوزسنجی شخصی استفاده کرد، اما برای بهبود ویژگی ها در استفاده مکرر، تحقیقات بیشتری لازم است.
مقدمه
ICRP توصیه می کند که یک دوز باید به اندازه ای منطقی در حد قابل دستیابی بودن (ALARA) حفظ شود تا در مقابل اثر تصادفی پیش بینی شده توسط مدل خطی غیر-آستانه در گزارش آنها (1) حفظ شود. ارزیابی دوز دقیق در محدوده های دوز-پایین برای حفظ این اصل ALARA مورد نیاز است و با استفاده از مواد TL که حساسیت بیشتری نسبت به مواد موجود دارند، قابل حصول است.
ماده TL LiF: Mg، Ti برای اولین بار بصورت تجاری به صورت (2) TLD-100 فروخته شد و هنوز هم برای نظارت شخصی استفاده می شود حتی اگر دارای حساسیت کم باشد. در سال 1978، Nakajima و همکاران (3), ماده TL LiF: Mg، Cu، P را توسعه دادند که دارای حساسیت 20 تا 40 برابر بیشتر از TLD-100 است که به طور گسترده ای مورد استفاده قرار گرفته است و تحقیقات زیادی در این زمینه در چین -200)، لهستان (MCP-N) و ایالات متحده آمریکا (TLD-100H) (4) انجام شده است..
یک ماده جدید TL، LiF: Mg، Cu، Na، Si فسفرها با حساسیت بالاتر نسبت به LiF: Mg، Cu، P و ویژگی های محو شدن خوب توسط Doh و همکاران (5) در کره ساخته شده است و حبه های LiF: Mg، Cu، Na، Si خاکسترشده اخیراً در موسسه تحقیقات انرژی اتمی کره (KAERI) (6) توسعه یافته اند. از آنجایی که به علت فرآیند پخته شدن با درجه حرارت بالا, حبه های TL دارای ساختار ماده و خصوصیات دوزسنجی کاملاً متفاوت از فسفر TL هستند، تحقیق بر روی خصوصیات فیزیکی و دوزسنجی این حبه ها مورد نیاز است.
در اين مقاله، مشخصات فيزيکي و دوزسنجی حبه هاي LiF: Mg، Cu، Na، Si TL مورد بررسی قرار گرفته است. منحنی های درخشندگی توسط یک برنامه تحلیل پویا جدا شدند و انرژی فعالسازی و ضریب فرکانس برای پیک اصلی محاسبه شدند. طیف انتشار سه بعدی با درجه و فرکانس گرمایش اندازه گیری شد. پاسخ انرژی در دامنه 20-662 کیلو الکترون ولت، پاسخ دوز از تا و نرخ محو شدن برای یک دوره ذخیره سازی 1 سال نیز برای کاربرد در یک سیستم دوزسنجی شخصی مورد بررسی قرار گرفتند.
مواد و روش ها
با فشار دادن در دمای اتاق و سپس یک فرایند خاکستر کردن, حبه های TL LiF: Mg، Cu، Na، Si از فسفرهای TL ساخته شد. این حبه ها دارای قطر 4.5 میلی متر، ضخامت 0.8 میلیمتر با رنگ آبی هستند و جرم آنها 28 میلی گرم است. پس از تولید 400 حبه، آنها تحت تابش اشعه گاما 137Cs قرار گرفتند و نمونه های دارای حساسیت در انحراف معیار 5٪ ± برای استفاده آزمایشی انتخاب شدند.
منحنی های درخشندگی TL و شدت ها حبه های های LiF: Mg، Cu، Na، Si TL با استفاده از یک قرائت کننده TLD تجاری (قرائت کننده 310 TLD سیستم: Teledyne Brown Engineering) کنترل شده توسط یک کامپیوتر شخصی اندازه گیری شدند. اندازه گیری ها با یک نرخ گرمایش خطی در یک جریان نیتروژن تقریباً انجام شدند.
این حبه ها تحت تابش اشعه گاما 137Cs و تابش پرتوی اشعه ایکس روی فانتوم PMMA 10 × 10 × 2 میلی متر در KAERI به منظور بررسی ساختار فیزیکی، پاسخ انرژی، پاسخ دوز، قابلیت استفاده دوباره و ویژگی های محو شدن، مورد بررسی قرار گرفتند. انرژی ها تابشی در گستره 20 تا 662 کیلوالکترون ولت بود.
نتایج و بررسی
منحنی درخشندگی و حساسیت TL
شکل 1، پیک درخشندگی جدا شده از منحنی درخشندگی حبه های TL: Mg، Cu، Na، Si TL را با استفاده از برنامه تحلیل TL نشان می دهد. نرخ گرمایش بود و دمای قرائت, تا 320 درجه سانتیگراد بود. منحنی درخشندگی را می توان به پنج پیک در 104، 145، 189، 234 و 268 درجه سانتیگراد تقسیم کرد. از این پیک ها، پیک اصلی که می توان برای ارزیابی دوز مورد استفاده قرار داد، پیک چهارم (پیک 234 درجه سانتیگراد) است و انرژی فعال سازی و ضریب فرکانسی پیک اصلی تحلیل شده توسط برنامه تحلیل TL, به ترتیب 2.34 الکترون ولت و 1.00 1023 s1 بودند.
Abstract
Sintered LiF:Mg,Cu,Na,Si thermoluminescence (TL) pellets have been developed for application in radiation dosimetry. LiF:Mg,Cu,Na,Si TL pellets were made from TL powders using a sintering process, that is, pressing and heat treatment. These pellets have a diameter of 4.5 mm, and a thickness of 0.8 mm are blue in colour and have a mass of 28 mg each. After 400 pellets had been produced they were irradiated with 137Cs gamma radiation and samples having a sensitivity within a 5% standard deviation were selected for experimental use. In the present study, the physical and dosimetric properties of LiF:Mg,Cu,Na,Si TL pellets were investigated for their emission spectrum, dose response, energy response and fading characteristics. Photon irradiation for the experiments was carried out using X ray beams and a 137Cs gamma source at the Korea Atomic Energy Research Institute (KAERI). The average energies and the dose were in the range of 20–662 keV and 106 102 Gy respectively. The glow curves were measured with a manual type thermoluminescence dosimetry reader (system 310, Teledyne) at a constant nitrogen flux and a linear heating rate. For a constant heating rate of 5°C.s1 , the main dosimetric peak of the glow curve appeared at 234°C, its activation energy was 2.34 eV and the frequency factor was 1.001023. The TL emission spectrum appeared at the blue region centred at 410 nm. A linearity of photon dose response was maintained up to 100 Gy. The photon energy responses relative to the 137Cs response were within 20% in the overall photon energy region. No fading of the TL sensitivity of the pellets stored at room temperature was found over the course of a year. Therefore LiF:Mg,Cu,Na,Si TL pellets can be used for personal dosimetry, but more research is needed to improve the characteristics for repeated use.
INTRODUCTION
ICRP recommend that a personal dose should be maintained as low as reasonably achievable (ALARA) to protect against the stochastic effect predicted by the linear non-threshold model in their report(1). Precise dose evaluation is needed in the low-dose ranges of 104 –101 mGy to maintain this ALARA principle, and it can be achieved by using TL materials which are more sensitive than existing ones.
LiF:Mg,Ti TL material was first sold commercially as TLD-100(2) and it is still used for personal monitoring even though it has a low sensitivity. In 1978, Nakajima et al(3) developed LiF:Mg,Cu,P TL material which has a sensitivity 20 to 40 times greater than the widely used TLD-100, and much research is now being done on this material in China (GR-200), Poland (MCP-N) and the USA (TLD-100H)(4).
A new TL material, LiF:Mg,Cu,Na,Si phosphors, with a higher sensitivity than LiF:Mg,Cu,P and good fading characteristics, has been developed by Doh et al(5) in Korea, and sintered LiF:Mg,Cu,Na,Si pellets have recently been developed at the Korea Atomic Energy Research Institute (KAERI)(6). Because TL pellets have a totally different material structure and dosimetric characteristics from TL phosphors due to the high-temperature sintering process, research on the physical and dosimetric characteristics of these pellets is needed.
In the present work the physical and dosimetric characteristics of LiF:Mg,Cu,Na,Si TL pellets were investigated. The glow curves were separated by a peak analysis program, and the activation energy and frequency factor calculated for the main peak. The threedimensional emission spectrum was measured with the heating temperature and frequency. The energy response in the range of 20–662 keV, the dose response from 106 to 102 Gy and the fading rate for a storage period of 1 year were also investigated for application to a personal dosimetry system.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
LiF:Mg,Cu,Na,Si TL pellets were made from TL phosphors by pressing at room temperature followed by a sintering process. These pellets have a diameter of 4.5 mm, are 0.8 mm thick with a blue colour and have a mass of 28 mg each. After 400 pellets had been produced they were irradiated with 137Cs gamma radiation and samples having a sensitivity within a 5% standard deviation were selected for experimental use.
The TL glow curves and intensities of the LiF:Mg,Cu,Na,Si TL pellets were measured using a commercial TLD reader (system 310 TLD reader: Teledyne Brown Engineering) controlled by a personal computer. Measurements were carried out with a linear heating rate of 5°C.s1 in a nitrogen flow of 70 kPa.
These pellets were irradiated with 137Cs gamma and X ray radiation on the 10 10 2 mm PMMA phantom at KAERI to investigate the physical structure, energy response, dose response, reusability and fading characteristics. The irradiating energies were in the range of 20 to 662 keV.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Glow curve and TL sensitivity
Figure 1 shows the glow peak separated from the glow curve of LiF:Mg,Cu,Na,Si TL pellets using a TL analysis program. The heating rate was 5°C.s1 and the reading temperature was up to 320°C. The glow curve can be separated into five peaks at 104, 145, 189, 234 and 268°C. Of these peaks, the main peak which can be used for dose evaluation is the fourth peak (the 234°C peak), and the activation energy and the frequency factor of the main peak analysed by the TL analysis program are 2.34 eV and 1.00 1023 s1 respectively.
مقدمه
مواد و روش ها
نتایج و بررسی
منحنی درخشندگی و حساسیت TL
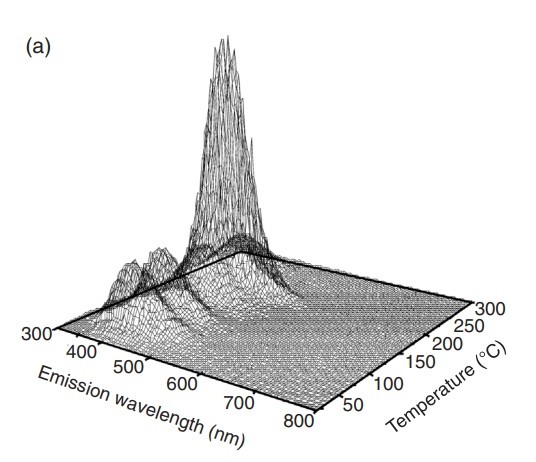
طیف انتشار TL
وابستگی انرژی
وابستگی به دوز
قابلیت استفاده مجدد
محو شدن
نتیجه گیری
Abstract
INTRODUCTION
MATERIALS AND METHODS
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Glow curve and TL sensitivity
TL emission spectrum
Energy dependence
Dose dependence
Reusability
Fading
CONCLUSIONS
