
دانلود رایگان مقاله یک کنترلر جریان باند پسماند تطبیقی
چکیده
در این مقاله یک کنترلر جریان باند پسماند تطبیقی برای فیلتر توان موثر به منظور از بین بردن هارمونی ها و جبران سازی توان موثرِ یکسو ساز سه فاز مطرح می شود. کنترلر جریان باند پسماند تطبیقی که بوسیله ی Bose برای پیش ران های ماشین های الکتریکی مطرح شده (روش کنترل جریان باند پسماند تطبیقیِ مبدل PWM خوراک ولتاژ برای سیستم پیشران ماشین) برای فیلتر توان موثر (APF) تطبیق داده می شود. کنترل کننده ی جریان باند پسماند تطبیقی، پهنای باند پسماند را بر اساس فرکانس مدولاسیون، منبع تغذیه، ولتاژ خازن dc و لبریزی موج جریان جبران ساز منبع تغییر می دهد. کنترل کننده ی جریان باند پسماند، سیگنال کلیدزنی APF را مشخص می کند و الگوریتمی بر مبنای بسطی از تئوری چارچوب منبع همگام برای شناسایی سیگنال های منبع جریان مطلوب استفاده می شود. نتایج مطالعه ی شبیه سازی از روش کنترل APF جدید که در این مقاله ارائه شده، در جهت حذف هارمونیک ها و مولفه های توان رآکتیو از جریان کاربردی، کاملا رضایت بخش یافته می شود. همه ی مطالعات از طریق شبیه سازی پویای دیجیتالی و با استفاده از جعبه ابزار سیستم توان شبیه سازی MATLAB انجام داده شده است. APF برای محقق کردن استاندارد IEEE 519 پیشنهاد شده برای سطوح هارمونیک ها، رضایت بخش یافته می شود.
1. دیباچه
انتشار گسترده ی تجهیزات الکترونیکی توان باعث افزایش اغتشاش هارمونیک در سیستم های توان شده است. بارهای غیرخطی، مولفه های توان رآکتیو و هارمونیکِ جریان را از خطوط اصلی ac می کشد. هارمونیک های جریان بوسیله ی بارهای غیر خطی مانند پیش ران های سرعت قابل تنظیم، تغذیه های توان استاتیک و UPS تولید شده است. هارمونیک ها باعث مشکلاتی در سیستم های توان و در محصولات مصرف کننده مانند بیش ا حد گرم شدن تجهیزات، انفجار خازن، لرزش موتور، جریان های نول بیش از حد و فاکتور توان کم می شوند. مرسوما، فیلترها و خازن های LC غیرفعال و برای حذف هارمونیک های جریان خط نیرو و جبران سازی توان رآکتیو بوسیله ی افزایش فاکتور توان استعمال شده اند. اما این فیلترها دارای معایب اندازه ی بزرگ، تشدید و رفتار جبران سازی ثابت شده هستند، از این رو راه حل مرسوم ناکارآمد می شود.
مفهوم استفاده از فیلترهای توان موثر در جهت کاهش مشکلات هارمونیک و جبران سازی توان رآکتیو بیش از دههه ی پیش مطرح شده بود. از آن به بعد تئوری ها و کاربردهای فیلترهای هارمونیک غیرفعال بسیار محبوب شدند و توجه بسیاری را جلب کردند. فیلتر توان موثر بدون نقطه ضعف های فیلترهای هارمونیک غیرفعال مانند فرسوده سازی مولفه ها و مسائل تشدید، راه حلی قابل اطمینان برای جبران سازی توان رآکتیو و نیز حذف جریان های هارمونیک به نظر می رسد.
روش های کنترل جریان متنوعی برای چنین پیکربندی فیلتر توان موثر ارائه شده اما روش کنترل جریان، به لحاظ قابلیت سریع جریان و پیاده سازی باند پسماند دارای بالاترین نرخ در میان دیگر روش های کنترل مانند PWM سینوسی است. فاصله ی بین دو بخش کلیدزنی متوالی همانند اکثر کاربردهای PWM، به طور ثابت در یک چرخه ی فرکانسی توان تغییر می کند. این موضوع بدین معنا است که فرکانس کلید زنی ثابت نیست اما در زمان با اهداف و شرایط عملیات تغییر می کند. در اصل، افزایش فرکانس عملیات وارونگر به بهتر شدن شکل موج جبران سازی کمک می کند. بهر حال، محدودیت های دستگاه وجود دارد و افزایش فرکانس کلید زنی باعث افزایش اتلاف های کلید زنی می شود. محدوده ی فرکانس هایی که استفاده شده اند، بر مبنای مصالحه میان این دو فاکتور متفاوت هستند. در این مقاله، کنترلِ فرکانس کلیدزنی از طریق مطرح کردن الگوریتم کنترل جریان باد پسماند تطبیقی، مشخص می شوند.
هدف اصلی از این مطالعه، تحقیق در مورد اثرات پهنای باند پسماند در TDH منبع جریان و فرکانس کلید زنی است. کنترل کننده ی جریان باند پسماند تطبیقی، پهنای باند پسماند را به عنوان یک تابع از تغییر جریان جبران ساز منبع تغییر می دهد تا فرکانس کلیدزنی و منبع جریان THD را بهینه کند. در این مقاله، در ابتدا تئوری چارچوب d-q-0 همگام به طور مختصر مرور می شود. سپس، استراتژی جبران سازی برای فیلتر توان موثر سه فاز که بر مبنای کنترل جریان باند پسماند تطبیقی قرار داده شده، تشریح می شود. در ادامه، نتایج شبیه سازی و سپس نتیجه گیری ارائه می شوند.
2. فیلتر توان موثر موازی
فیلتر توان موثر موازی (APF) وسیله ای است که به صورت موازی متصل شده و جریان های هرمونیک و رآکتیو از یک بار غیرخطی را لغو می کند. جریان کل کشیده شده از خط اصلی ac به صورت سینوسی است. به طور ایده آل، APF نیاز دارد تا برای جبران سازی بارهای غیرخطی در خط، تنها جریان رآکتیو و هارمونیک کافی ایجاد کند.
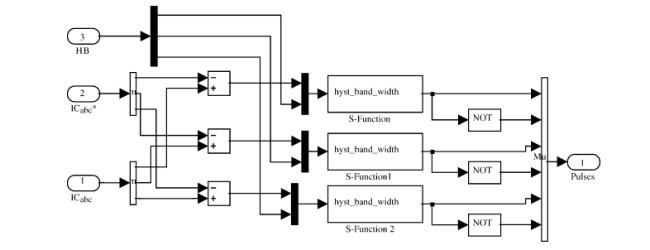
در APF نشان داده شده در شکل 1، یک وارونگر منبع ولتاژ کنترل شده ی جریان برای تولید جریان جبران ساز (ic) استفاده می شود و به شبکه ی منبع توان برق تزریق می گردد. این موضوع مولفه های هارمونیک کشیده شده بوسیله ی بار غیر خطی را لغو می کند و جریان خط برق (is) را به صورت سینوسی حفظ می کند. روش های متنوعی برای شناسایی هارمونیک های جریان لحظه ای در فیلتر توان موثر استفاده می شوند. می توان روش FFT (روش سرع فوریه)، تئوری p-q لحظه ای، تئوری چارچوب منبع d-q همگام و یا استفاده از فیلترهای الکترونیکی دیجیتالی یا آنالوگ مناسب را به عنوان مثال هایی از این روش ها نام برد. لازم به ذکر است که فیلترهای الکترونیکی یا دیجیتالی، مولفه های هارمونیک بیش از حد را جدا می کنند. در این مقاله، الگریتم بر مبنای تئوری چارچوب منبع d-q-0 همگام ارائه می شود.
3. جبران سازی بر مبنای چارچوب منبع d-q-0 همگام
جریان های بار سه فاز نشان داده شده در شکل 2، پیش از این به چارچوب منبع همگام (تبدیلa-b-c به d-q-0) تبدیل شده است. فیلتر بالا گذر برای استخراج مولفه های dc نشان دهنده ی فرکانس بنیادی جریان ها اسفاده می شود. تبدیل مختصات از جریان های بار سه فاز (iLa, iLb, iLc) به جریان های بار بر مبنای چارچوب منبع همگام (iLd, iLq, iL0) به صورت پیش رو بدست می آید.
فیلتر بالا گذر برای حذف مولفه های dc از جریان بار تنها باید در جریان iLD به کار برده شود. جریان محور Q (iLq) برای معکوس کردن تبدیل به منظور جبران سازی توان رآکتیو به کار گرفته می شود. جریان محور صفر (iL0) باید در زمانی که ولتاژها معوج یا نامتوازن شده و جریان سینوسی نیاز باشد، استفاده شوند. در این مطالعه، این موضوع مورد بررسی قرار نگرفته است. ولتاژ طرف dc APF باید کنترل شوند و در مقداری ثابت نگه داشته شوند تا عملیات نرمال وارونگر را حفظ کند. چون اتلاف انرژی ناشی از رسانایی و اتلاف های توان کلیدزنی همراه با دیودها و IGBT های وارونگر در APF وجود دارد. لازم به ذکر است که IGBT ها معمولا مقدار Vdc در خازن Cdc را کاهش می دهند. مدار کنترل ولتاژ پسخورد نیاز دارد تا به همین دلیل در وارونگر در نظر گرفته شود. اختلاف بین مقدار منبع Vref و مقدار پسخورد Vdc، یک تابع خطا در ابتدا از یک تنظیم کننده ی PI عبور می کند و خروجی تنظیم کننده ی PI از مقدار محور d مولفه های جریان هارمونیک کسر می گردد. الگوریتم جبران سازی بر مبنای منبع d-q-0 همگام که در بالا تشریح شد، در شکل 2 نشان داده می شود. جریان های فیلتر منبع (i ∗ abc) منفی های خروجیِ ماتریس تبدیل معکوس (d-q-0 to a-b-c) مشخص شده اند. .
Abstract
In this paper, an adaptive hysteresis band current controller is proposed for active power filter to eliminate harmonics and to compensate the reactive power of three-phase rectifier. The adaptive hysteresis band current controller, proposed by Bose [An adaptive hysteresis band current control technique of a voltage feed PWM inverter for machine drive system, IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 37 (5) (1990) 402–406] for electrical machine drives, is adapted to active power filter (APF). The adaptive hysteresis band current controller changes the hysteresis bandwidth according to modulation frequency, supply voltage, dc capacitor voltage and slope of the i ∗ c reference compensator current wave. The hysteresis band current controller determines the switching signals of the APF, and the algorithm based on an extension of synchronous reference frame theory (d-q-0) is used to determine the suitable current reference signals. The results of simulation study of new APF control technique presented in this paper is found quite satisfactory to eliminate harmonics and reactive power components from utility current. All of the studies have been carried out through detail digital dynamic simulation using the MATLAB Simulink Power System Toolbox. The APF is found effective to meet IEEE 519 standard recommendations on harmonics levels. © 2004 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
1. Introduction
Recent wide spread of power electronic equipment has caused an increase of the harmonic disturbances in the power systems. The nonlinear loads draw harmonic and reactive power components of current from ac mains. Current harmonics generated by nonlinear loads such as adjustable speed drives, static power supplies and UPS. The harmonics causes problems in power systems and in consumer products such as equipment overheating, capacitor blowing, motor vibration, excessive neutral currents and low power factor. Conventionally, passive LC filters and capacitors have been used to eliminate line current harmonics and to compensate reactive power by increasing the power factor. But these filters have the disadvantages of large size, resonance and fixed compensation behavior so this conventional solution becomes ineffective.
The concept of using active power filters to mitigate harmonic problems and to compensate reactive power was proposed more than two decades ago [1,2]. Since then, the theories and applications of active power filters have become more popular and have attracted great attention [6–8]. Without the drawbacks of passive harmonic filters, such as component aging and resonant problems, the active power filter appears to be a viable solution for reactive power compensation as well as for eliminating harmonic currents.
There are various current control methods proposed for such active power filter configurations, but in terms of quick current controllability and easy implementation hysteresis band current control method has the highest rate among other current control methods such as sinusoidal PWM. As in most PWM applications the interval between two consecutive switching actions varies constantly within a power frequency cycle. It means that the switching frequency is not constant but varies in time with operation point and conditions. In principle increasing inverter operation frequency helps to get a better compensating waveform. However there are device limitations and increasing the switching frequency cause increasing switching losses, audible noise and EMF related problems. The range of frequencies used is based on a compromise between these two different factors. In this paper, the control of switching frequency is realized by introducing an adaptive hysteresis band current control algorithm.
The main aim of this study is to investigate the effects of hysteresis bandwidth to THD of supply current and switching frequency of APF. Adaptive hysteresis band current controller changes the hysteresis bandwidth as a function of reference compensator current variation to optimize switching frequency and THD of supply current. In this paper, the synchronous d-q-0 reference frame theory is first briefly reviewed. Next, the proposed adaptive hysteresis band current control based compensation strategy for the three-phase active power filter is described. Then, simulation results are presented followed by the conclusion.
2. Shunt active power filter
The shunt active power filter (APF) is a device that is connected in parallel to and cancels the reactive and harmonic currents from a nonlinear load. The resulting total current drawn from the ac main is sinusoidal. Ideally, the APF needs to generate just enough reactive and harmonic current to compensate the nonlinear loads in the line.
In an APF depicted in Fig. 1, a current controlled voltage source inverter is used to generate the compensating current (ic) and is injected into the utility power source grid. This cancels the harmonic components drawn by the nonlinear load and keeps the utility line current (is) sinusoidal. A variety of methods are used for instantaneous current harmonics detection in active power filter such as FFT (fast Fourier technique) technique, instantaneous p-q theory, synchronous d-q reference frame theory or by using suitable analog or digital electronic filters separating successive harmonic components. In this paper, the synchronous d-q-0 reference frame theory based algorithm is proposed.
3. Synchronous d-q-0 reference frame based compensation
The three phase load currents shown in Fig. 2, have already been transformed to the synchronous reference frame (a-b-c to d-q-0 transformation). A high pass filter is used to extract the dc component representing the fundamental frequency of the currents. The coordinate transformation from three-phase load currents (iLa, iLb, iLc) to the synchronous reference frame based load currents (iLd, iLq, iL0) is obtained as follows.
The high pass filter to remove the dc component of load current should only be applied to the iLd current. Q axis current (iLq) is applied to inverse transformation to compensate reactive power. Zero axis current (iL0) must be used when the voltages are distorted or unbalanced and sinusoidal current are desired. In this study, it is not investigated. The dc side voltage of APF should be controlled and kept at a constant value to maintain the normal operation of the inverter. Because there is energy loss due to conduction and switching power losses associated with the diodes and IGBTs of the inverter in APF, which tend to reduce the value of Vdc across capacitor Cdc. A feedback voltage control circuit needs to be incorporated into the inverter for this reason. The difference between the reference value, Vref and the feedback value (Vdc), an error function first passes a PI regulator and the output of the PI regulator is subtracted from the d axis value of the harmonic current components. Synchronous d-q-0 reference frame based compensation algorithm, described above, is depicted in Fig. 2. Reference filter currents (i ∗ abc) are determined negatives of the outputs of the inverse transformation matrix (d-q-0 to a-b-c).
چکیده
1. دیباچه
2. فیلتر توان موثر موازی
3. جبران سازی بر مبنای چارچوب منبع d-q-0 همگام
4. کنترل کننده ی جریان باند پسماند تطبیقی
5. نتایج شبیه سازی و مباحثات
6. نتیجه گیری
منابع
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Shunt active power filter
3. Synchronous d-q-0 reference frame based compensation
4. The adaptive hysteresis band current controller
5. Simulation results and discussions
6. Conclusion
References
