
دانلود رایگان مقاله الگوریتم مسیریابی مبتنی بر بهینه سازی کلنی مورچه
چکیده
کاهش مصرف انرژی گره های شبکه یکی از مهمترین مشکلات بمنظور مسیر یابی در شبکه های حسگر بی سیم بدلیل محدودیت باطری در هر حسگر بشمار می رود. این مقاله یک الگوریتم مسیر یابی مبتنی بر بهینه سازی جدید کلنی مورچه که از پارامترهای ویژه ای در تابع صلاحیت بمنظور کاهش مصرف انرژی گره های شبکه استفاده می کند. در این الگوریتم پیشنهادی جدید بنام الگوریتم مسیر یابی آگاه طولانی مدت برای شبکه های حسگر بی سیم LTAWSN))، اپراتور بروز فرمون بمنظور یکپارچه کردن مصرف انرژی و پرش ها در انتخاب مسیر یابی طراحی گردید. با نتایج شبیه سازی چند گانه توانستیم LTAWSN را نشان دهیم، در مقایسه با الگوریتم مسیر یابی مبتنی بر بهینه سازی جدید کلنی مورچه پیشین، الگوریتم مسیر یابی کلنی مورچه آگاه از انرژی برای مسیر یابی شبکه های حسگر بی سیم، الگوریتم مسیر یابی آگاه از مکان و مبتنی بر بهینه سازی کلنی مورچه برای شبکه های حسگر بی سیم و الگوریتم کلنی مورچه سنتی و افزایش کارایی سیستم انتقال متعادل تر در میان گره ها بدست آورده و مصرف انرژی مسیر یابی را کاهش داده و طول عمر شبکه را افزایش می دهد.
1. مقدمه
یک شبکه حسگر بی سیم (WSN) متشکل از ده ها، صدها و هزاران گره های کوچک مرتبط می باشد که هر کدام مجهز به یک دستگاه سنجش می باشد. اکثر شبکه های حسگر از ارتباطات بی سیم استفاده می کنند، و گره ها با باطری کار می کنند. منابع محدود آنها، قابلیت های ارتباطی محدود و مصرف برق محدود ملزم می کند که در لیست معیارهای طراحی کارایی باید بالا باشد. در نتیجه پیشرفت در ارتباطات بیسیم و فن آوری های الکترونیکی، حسگر های بیسیم در حال کوچکتر ، ارزانتر و قدرتمند تر شدن هستند. بدلیل گسترش سریع ریز پردازنده ها، حسگر و فرستنده و گیرنده، برنامه های کاربردی پیش زمینه بسیار عالی در مورد WSNs وجود دارد. از آنجاییکه از این شبکه ها در محیط های دشوار و غیر قابل دسترس مانند میدان های جنگ، آتشفشان ها، جنگل ها و غیره استفاده می کنیم، احتمال ضعیفی در تغییر یا شارژ مجدد گره های ناقص یا از کار افتاده وجود دارد. از اینرو، تفاوت اصلی بین WSNs و دیگر شبکه های بیسیم کلاسیک اینست که WSNs دارای حساسیت فوق العاده و آسیب پذیر به انرژی هستند.
انرژی محدود مسئله اصلی تاثیر گزار بر عملکرد WSNs می باشد. بنابراین، چگونگی استفاده از انرژی محدود WSNs جهت افزایش حد اکثری طول عمر WSNs مشکل اصلی طراحی مسیر یابی بحساب می آید]3[. اکثر الگوریتم های مسیر یابی برای شبکه های حسگر نیازمند اطلاعات مکان برای گره های حسگر هستند. در بیشتر موارد، اطلاعات مکان بمنظور محاسبه فاصله بین دو گره ویژه مورد نیاز بوده تا بتوان مصرف انرژی را ارزیابی کرد. بنابراین اطلاعات مکان را می توان در داده های مسیر یابی بصورت انرژی کارآمد مورد استفاده قرار داد.
خانواده الگوریتم بهینه سازی کلنی مورچه (ACO) جهت حل برخی مشکلات مسیر یابی در WSN بطور موفقیت آمیزی بکار رفته است]5[. در دو دهه اخیر، بهینه سازی کلنی مورچه به عنوان متد اکتشافی پیشرو متا برای حل مشکلات بهینه سازی ترکیبی پدیدار گردید.
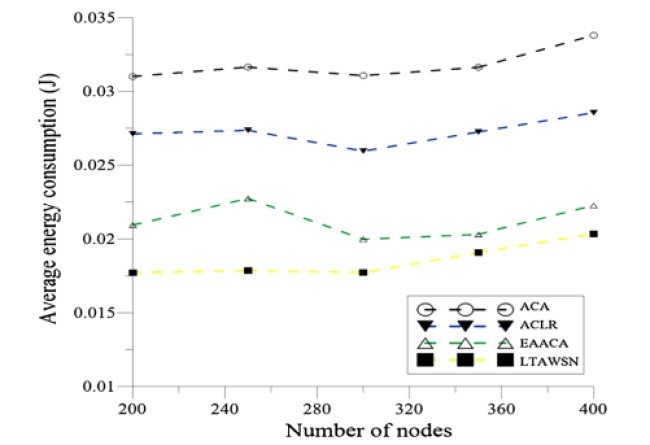
در این مقاله یک الگوریتم مسیر یابی برای شبکه های حسگر بیسیم بر اساس بهینه سازی کلنی مورچه با پارامترهای خاص ارائه دادیم. هدف اصلی الگوریتم افزایش حد اکثری طول عمر شبکه بوسیله تعریف هزینه لینک به عنوان تابع انرژی باقیمانده گره و انرژی انتقال مورد نیاز با استفاده از آن لینک می باشد. الگوریتم پیشنهادی را به عنوان الگوریتم مسیر یابی آگاه از طول عمر برای شبکه های حسگر بیسیم (LTAWSN) می نامیم و آنرا با انرژی الگوریتم مسیر یابی کلنی مورچه آگاه از انرژی برای مسیر یابی شبکه های حسگر بیسیم EAACA)) ارائه شده در قسمت 6، الگوریتم مسیر یابی آگاه از مکان مبتنی بر بهینه سازی کلنی مورچه برای شبکه های حسگر بیسیم ACLR)) ارائه شده در 5 و 7 و الگوریتم مسیر یابی کلنی مورچه سنتی ACA مقایسه می کنیم و مشاهده میشود که الگوریتم پیشنهادی مصرف انرژی در مقایسه با این الگوریتم های مسیر یابی را کاهش دهد و انتقال متعادل تری در میان گره بدست آمده و طول عمر شبکه را افزایش می دهد.
مابقی این مقاله بصورت زیر طبقه بندی شده است. در بخش 2، برخی از تحقیقات پیشین در مورد الگوریتم های مسیر یابی کلنی مورچه در شبکه های حسگر بیسیم ارائه شده است. در بخش 3 رویکرد پیشنهادی توضیح داده شده است. بخش 3 پارامترهای شبیه سازی را نشان می دهد. بخش 4 در مورد نتایج شبیه سازی بحث کرده و بخش 5 نتیجه گیری در مورد مقاله می باشد.
2. کارهای مرتبط
برخی از تحقیقات اخیر در مورد الگوریتم های مسیر یابی کلنی مورچه شبکه های حسگر بیسیم بصورت زیر ارائه شده است:
مولفان در بخش 5 یک الگوریتم مسیر یابی برای شبکه های حسگر بیسیم با استفاده از بهینه سازی کلنی مورچه ارائه داده که مقایسه دو الگوریتم مسیر یابی مبتنی بر کلنی مورچه با توجه به مقادیر مصرفی انرژی تحت سناریوهای مختلف و گزارش معیارهای معمول برای مسیر یابی در شبکه های حسگر بیسیم را نشان می دهد.
در قسمت 6 مولفان یک الگوریتم کلنی مورچه انرژی-آگاه برای مسیر یابی در شبکه های حسگر بیسیم ارائه دادند زمانیکه مورچه گره بعدی را انتخاب می کند، نه تنها فاصله گره حفره و مسیر انرژی میانگین در نظر گرفته می شوند. این الگوریتم با الگوریتم ACA سنتی مقایسه شده و در مصرف انرژی گره ها دارای بهبود در تعادل می گردد و طول عمر شبکه را افزایش می دهد.
در بخش 8 مولفان مقایسه عادلانه ای از سلسله مراتب خوشه تطبیقی انرژی کم (LEACH) و کلنی مورچه بکار رفته در LEACH بر اساس مرگ اولین گره در شبکه های حسگر بیسیم را ارائه داده و نشان داده شده زمانیکه الگوریتم کلنی مورچه در مورد پروتکل LEACH موجود بکار میرود، طول عمر شبکه بهبود یافته است.
در بخش 9 ابتدا یک جدول طبقه بندی ساخت شده و اشاره به ایجاد چندین فرمان مسیر یابی ممکن دارد. سپس ACO این مسیرها را کشف کرده تا مصرف توان گره ها را کاهش دهد.
در بخش 10 هر گره مقدار انرژی را محاسبه کرده و سطح انرژی شبکه باقیمانده را رویهمرفته بیان میکند. به کمک این مقایسه، گره تصمیم می گیرد که سر خوشه باشد یا خیر. احتمال سر خوشه شدن گره هایی با انرژی بالا بیشتر می باشد. عیب این رویکرد اینست که نیازمند ارتباط اضافه گره ها با ایستگاه پایه بوده و نیازمند انرژی بیشتر می باشد.
Abstract
Reducing the energy consumption of network nodes is one of the most important problems for routing in wireless sensor networks because of the battery limitation in each sensor. This paper presents a new ant colony optimization based routing algorithm that uses special parameters in its competency function for reducing energy consumption of network nodes. In this new proposed algorithm called life time aware routing algorithm for wireless sensor networks (LTAWSN), a new pheromone update operator was designed to integrate energy consumption and hops into routing choice. Finally, with the results of the multiple simulations we were able to show that LTAWSN, in comparison with the previous ant colony based routing algorithm, energy aware ant colony routing algorithms for the routing of wireless sensor networks, ant colony optimization-based location-aware routing algorithm for wireless sensor networks and traditional ant colony algorithm, increase the efficiency of the system, obtains more balanced transmission among the nodes and reduce the energy consumption of the routing and extends the network lifetime.
1 Introduction
A wireless sensor network (WSN) typically consists of tens to hundreds or thousands of relatively small nodes, each equipped with a sensing device. Most sensor networks use wireless communication, and the nodes are often battery powered. Their limited resources, restricted communication capabilities, and constrained power consumption demand that efficiency be high on the list of design criteria [1]. As a result of the advances in wireless communication and electronics technologies, wireless sensors are getting smaller, cheaper, and more powerful. Due to the fast development of the microprocessor, sensor and transceiver, there is great applications foreground about WSNs. Also since we often use these networks in rough and inaccessible environments such as battlefields, volcanoes, forests and so on, normally there is low possibility to change or recharge the defective or dead nodes. Hence, the main difference between WSNs and other classic wireless networks is that WSNs are hypersensitive and vulnerable to energy [2].
The limit energy is the key issue influencing WSNs performance. So, how to use the limit energy of WSNs to maximize the life of WSNs becomes the all-important problem of routing design [3]. Most of the routing algorithms for sensor networks require location information for sensor nodes. In most cases location information is needed in order to calculate the distance between two particular nodes so that energy consumption can be estimated [4]. Therefore, location information can be utilized in routing data in energy efficient way.
A family of ant colony optimization (ACO) algorithms has been successfully applied to solve some routing problems in WSN [5]. Over the last two decades, ant colony optimization has emerged as a leading Meta heuristic method for the solution of combinatorial optimization problems [4].
In this paper, we proposed a routing algorithm for wireless sensor network based on ant colony optimization with special parameters. The main objective of the algorithm is to maximize the network lifetime by carefully defining link cost as a function of node remaining energy and the required transmission energy using that link. We call the proposed algorithm as life time aware routing algorithm for wireless sensor networks (LTAWSN) and compare it with energy aware ant colony routing algorithms for the routing of wireless sensor networks (EAACA) that presented in [6], ant colony optimizationbased location-aware routing algorithm for wireless sensor networks (ACLR) that presented in [5, 7], and traditional ant colony routing algorithm ACA, and see that proposed algorithm reduce consumption of energy in comparison of these routing algorithms, obtains more balanced transmission among the node, therefore extends the network lifetime.
The rest of this paper is organized as follows. In Sect. 2, some of the recent researches about ant colony routing algorithm in wireless sensor networks are presented. In Sect. 3, the proposed approach is described. Section 3 represents the simulation parameters. Section 4 discusses about the simulation results and finally Sect. 5 concludes the paper.
2 Related work
Some of the recent researches about ant colony routing algorithm in wireless sensor networks are presented as follows:
The authors in [5] proposed a routing algorithm for wireless sensor networks using ant colony optimization that present a comparison of two ant colony-based routing algorithms, taking into account current amounts of energy consumption under different scenarios and reporting the usual metrics for routing in wireless sensor networks.
In [6], the authors proposed an energy aware ant colony algorithm for the routing of wireless sensor networks that when the ant chooses the next node, not only the distance of sink node, but also the residual energy of next node and the path of the average energy are taken into account. This algorithm was compared with traditional ACA algorithm and gets more improvement in balance the energy consumption of nodes and extends the network life time.
In [8], the authors proposed a fair comparison of low energy adaptive clustering hierarchy (LEACH) and ant colony applied on LEACH on the basis of the death of first node in the wireless sensor networks and is shown that when the ant colony algorithm is applied on existing LEACH protocol, the network lifetime has improved.
In [9] first, a grade table is build and referred to generate several possible routing paths. Then the ACO explores these paths to reduce the power consumption of the nodes.
In [10] each node calculates the amount of its own energy level and then sums up the energy level of the remaining network. With the help of this comparison the node decides whether to become the cluster head or not for that round. The nodes with higher energy are more likely to become cluster heads. The drawback of this approach is that it requires extra communication of nodes with base station which in turn needs more energy.
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. کارهای مرتبط
3 الگوریتم مسیر یابی پیشنهادی مبتنی بر ACO (LTAWSN)
1.3 مسیر یابی مبتنی بر ACO اولیه برای WSNs (ACA)
2.3 الگوریتم کلنی مورچه آگاه به انرژی برای مسیر یابی شبکه های حسگر بیسیم (EAACA)
3.3 الگوریتم مسیر یابی مبتنی بر بهینه سازی کلنی یک مورچه (LTAWSN)
4. نتایج شبیه سازی
5. نتیجه گیری
منابع
Abstract
1 Introduction
2 Related work
3 The proposed ACO based routing algorithm (LTAWSN)
3.1 Basic ACO based routing for WSNs (ACA)
3.2 An energy aware ant colony algorithm for routing of wireless sensor networks (EAACA)
3.3 An ant colony optimization based routing algorithm for extends network lifetime in wireless sensor networks (LTAWSN)
4 Simulation results
5 Conclusion
References
