
دانلود رایگان مقاله استفاده از تکنیک مبتنی بر خوشه K-میانگین
چکیده
گروه بندی اسناد متنی یکی از عرصههای پژوهشی در حال ظهور است، که در آن اسناد شناخته شده هستند، به صورت دستی یا لگاریتمی دسته بندی شده و یا متمایز شده اند. مقاله بر استفاده از گروه بندی خودکار اسناد متنی در دامنه تشخیص سرقت ادبی تمرکز میکند. در جهان امروزی سرقت ادبی، به خصوص در زمینه آموزشی و پژوهشی یک نگرانی اصلی است. هدف این مقاله مطالعه و مقایسه روشهای متفاوت گروه بندی اسناد در تشخیص سرقت ادبی خارجی است. در اینجا کانون اولیه کشف گروه بندی اسناد نظارت نشده / روشهای خوشه بندی با استفاده از تغییرات متفاوت الگوریتم K-میانگین و مقایسه آن با روش مبتنی بر N-gram عمومی و روش مبتنی بر مدل فضای بردار است. سرانجام تحلیل و ارزیابی با استفاده از مجموعه داده ای از PAN-2013 ارزیابی شده است و عملکرد بر اساس precision، recall و efficiency از نظر زمان اجرای الگوریتم مقایسه میشود.
1. مقدمه
دسته بندی خودکار اسناد متنی یا گروه بندی آنها فرآیند اختصاص اسناد به یک گروه خاص یا بیشتر به صورت الگوریتمی است. هیچ سوالی مربوط به ارزش تجاری دسته بندی اسناد با توجه به محتوا وجود ندارد چرا که به خودی خود دارای هزاران کاربرد بالقوه است. با رشد سریع تکنولوژی، سربار اطلاعاتی به یک مشکل اصلی تبدیل شده است و مرتب کردن و دسته بندی دقیق اسناد مربوطه به یک چالش تبدیل شده است. دسته بندی اسناد میتواند به صورت نظارت شده، نظارت نشده و نیمه نظارت شده گروه بندی شود. در دسته بندی سند نظارت شده، برخی از بازخوردهای خارجی برای ارائه اطلاعات دسته بندی صحیح در دسترس است. دسته بندی نظارت نشده، به عنوان خوشه بندی سند که دسته بندی را بدون هر ارجاعی به اطلاعات خارجی اجرا میکند اشاره دارد در حالی که بخش اصلی نیمه نظارت شده اسناد با استفاده از اطلاعات خارجی برچسب میخورند.
عرصه کاربردی دسته بندی اسناد، مانند شناسایی زبان، فیلتر کردن اسپم، دسته بندی ژانر، تحلیل احساسات، بازیابی اطلاعات (IR) و غیره بی شمار هستند. روشهای دسته بندی اسناد در این دامنه کمتر کشف میشوند. رشد سریع فناوری شبکه، از جمله تعداد زیادی موتور جستجو، مخازن سند، سیستمهای نرم افزاری ترجمه و غیره، نه تنها کانالهای کسب دانش گوناگونی را ارائه میدهند، بلکه دری را به سوی سرقت ادبی متون باز میکنند. سرقت ادبی معمولا به استفاده نامشروع از اطلاعات، متن، ایده شخص دیگر، بدون ارجاع مناسب به منبع اصلی داده، اشاره دارد.
نوع و درجه سرقت ادبی از ساده ترین تا چالش برانگیزترین و پیچیده ترین محدوده بندی میشود. External/extrinsic و Internal/intrinsic دو روش تشخیص سرقت ادبی اصلی هستند. سرقت ادبی خارجی، سرقت ادبی را در تطبیق با یک سند اصلی یا بیشتر ارزیابی میکند در حالی که روش داخلی تغییر در سبک نوشتن منحصر یک نوشته را به عنوان شاخص سرقت ادبی بالقوه تحلیل میکند. این مقاله تشخیص سرقت ادبی خارجی را در جایی که اسناد منبع در فرم مجموعه داده/ وب منابع آنلاین در دسترس هستند توجیه میکند. در تشخیص سرقت ادبی خارجی، پنج وظیفه اصلی به صورت عمومی اجرا شدند. پیش پردازش مرحله اولیه ای است که اسناد منبع و مشکوک در معرض اصلاحات خاصی مانند حذف حرفهای اضافه پرکابرد، tokenization، lowercasing، تقسیم بندی جمله، حذف نقطه گذاری قرار میگیرند. این به کاهش اندازه داده واقعی با حذف اطلاعات مربوطه با توجه به رویکرد استفاده شده کمک میکند. مرحله بعدی بازیابی کاندید در مواردی است که زیر مجموعهای از اسناد مبنع بازیابی شدهاند که به صورت کلی با اسناد مشکوک مشابه هستند. در مرحله سوم، مقایسه دقیق اسناد مشکوک در برابر مجموعه اسناد کاندید است که برای بازیابی بخشهای سرقت ادبی شده انجام میشود. در اینجا تکنیک پردازش زبان طبیعی (NLP) مانند قطعه قطعه کردن؛ تجزیه، برچسب گذاری بخشی از گفتگو (POS) میتواند پذیرفته شود. مرحله چهارم، تشخیص مرزهای عبور با تحمین دقیق مرزهای متون مورد سرقا واقع شده در اسناد منبع و اسناد مشکوک با استفاده از معیار اصلی است. سرانجام ارزیابی سیستم با استفاده از برخی از معیارهای استاندارد، یا معیارهای PAN برای رتبه بندی عملکرد آن صورت میگیرد.
دسته بندی اسناد متنی میتواند در فاز اولیه روش تشخیص سرقت ادبی خارجی برای بازیابی اسنادی که مشابه با اسناد مشکوک هستند استفاده شود، مانند بازیابی کاندید. این تعداد مقایسه اسناد را در مرحله تحلیل دقیق و بنابراین پیچیدگی را کاهش میدهد. مقاله بر مطالعه جامع و تحلیل روشهای مبتنی بر N-gram، روشهای مبتنی بر مدل فضای برداری (VSM) و روشهای مبتنی بر خوشه بندی K میانگین در زمان استفاده از مراحل بازیابی کاندید تشخیص سرقت ادبی خارجی تمرکز میکند. روشها بر اساس تکنیکهای NLP مانند ریشه یابی، ریشه یابی و قطعه بندی مقایسه میشوند.
2. کارهای مربوطه
در تشخیص سرقت ادبی، بازیابی کاندید میتواند به عنوان کار بازیابی اطلاعات دیده شود. بر اساس این مفهوم، روشهای بازیابی کاندید متفاوت با استفاده از مدلهای IR توسط محققین برجسته بیان شده است. در این گروه، روشهای مبتنی بر اثر انگشت و N-gram، روشهای مبتنی بر هش و مدلهای فضای بردار محبوبیتی کسب کردند. S Schleimer یک روش مبتنی بر اثر انگشت را پیشنهاد داد که در آن سند به K-grams تقسیم میشود که در آن “K” یک مقدار مشخص شده توسط کاربر است. سپس هر K-gram هش میشود و برخی از آنها به عنوان اثر انگشت سند با استفاده از اندازه خاص پنجره انتخاب میشوند. نتایج با استفاده از Stanford Webbase ارزیابی شده اند. روش فقط میتواند تطبیق طول را تشخیص دهد. William B. Cavnar & John M. Trenkle یک روش گروه بندی متن مبتنی بر N-gram را ارائه میدهد که در ان اسناد اولیه به عنوان ویژگی N-gram ارائه شده است. سپس با استفاده از برخی از معیارهای فاصله تشابه بین اسناد محاسبه میشود و آنها دسته بندی میشوند. این فرکانس N-gram را با استفاده از قانون Zipf’ برای در نظر گرفتن N-grams برتر محاسبه میکند. برای تست، داده از پنج گروه تازه استفاده میشود و نتایج خوبی برای دسته بندی انواع مقالات جدید ارائه میشود. Peter Nather یک روش مشابه را پیشنهاد داد که در آن 1-gram تا 5- gram برای آزمایشات استفاده شدند. معیار تشابه دو پروفایل N-gram در مجموع تفاوت بین رتبه N-gramها در یک پروفایل و رتبه در دیگر پروفایل اتخاذ شده است. روش با استفاده از داده ای از Project Gutenberg ارزیابی شده است و دریافتیم که روش به خوبی با اسناد کوتاه اجرا شده است. با حجم بزرگ و دستکاریها د محتوا عملکرد روش کاهش مییابد.
در [8]، 5 تا 6 N-grams برای نمایش پروفایلهای اسناد تشکیل شده اند. سپس شناسه سند به یک مجموعه از ارزشهای هش ساختار یافته نگاشت مییابد. یک شاخص معکوس شده، مقدار هش را به دنباله ای از شناسه سند نگاشت میکند که از آن محاسبه شده است. تشابه بیشتر با استفاده از ضریب جاکارد محاسبه میشود و سیستم با استفاده از مجموعه داده PAN-09 ارزیابی میشود. یک رویکرد بازیابی کاندید مبتنی بر N-gram در [9] پیشنهاد شده است که از رویکرد ضریب جاکارد و شینگل در مرحله بازیابی کاندید استفاده میکند. در اینجا بعد از اینکه پیش پردازش پروفایلهای N-gram با N= 3 یا 4 صورت گرفت سپس تشابه جاکارد محاسبه میشود. یک آستانه 0.1 برای بازیابی مجموعه اسناد کاندید استفاده میشود. ارزیابی سیستم نهایی با استفاده از مجموعه داده PAN-10 انجام شده است. Rajiv Yerra و Yiu --Kai Ng [10] یک روش تشخیص کپی مبتنی بر جمله را برای اسناد وب اجرا کردند. در اینجا تشابه بین جملات سند با استفاده از سه رویکرد 4-gram کمتر تکراری محاسبه شده است، در جایی که نشانههای اصلی در نظر گرفته شده اند. رویکرد IR فازی نیز بحث شده است، که بهتر از مورد اول اجرا میشود.
مدل یازیابی مشهور دیگری مدل فضای برداری (VSM) است که در وظیفه بازیابی کاندید استفاده شد. در [11] 16 grams ایجاد میشوند که سپس به عنوان بردارهای استفاده کنند از مقادیر tf-idf نمایش داده میشوند و فاصله سند بیشتر با استفاده از شباهت کسینوسی اندازه گرفته میشود. Muhr و همکاران [12] یک رویکرد مبتنی بر VSM را پیشنهاد کردند، در جایی که برداربندی اولیه اسناد منبع و مشکوک انجام شده است. سپس نزدیک ترین سندی که با سند مشکوک متناظر است از مجموعه مرجع با استفاده از شباهت کسینوسی یافت میشود. رویکرد تشابه در [13] و [14] برای بازیابی کاندید بحث شده است و سیستم با استفاده از مجموعه داده PAN ارزیابی شده است. در روشهای VSM زمان اجرا به سرعت با مجموعه داده بزرگ افزایش مییابد.
نگاشتهای خود سازمان ده (SOM) در [15] برای سازمان دهی و خوشه بندی داده استفاده شده است. این مقاله از یک SOM ساختار یافته با درخت چند لایه (MLSOM) استفاده میکند که در ان داده گره در سطوح متفاوت یک درخت در لایههای متفاوت MLSOM پردازش شده است. Liping Jing و همکاران [16] یک رویکرد خوشه بندی سند که از الگوریتم k-میانگین برای خوشه بندی داده پراکنده استفاده میکند، ارائه دادهاند. این به صورت خودکار وزن کلمات کلیدی را در هر خوشه برای شناسایی اهمیت آنها محاسبه میکند. آزمایشات با استفاده از دادههایی از 20 گروه خبری انجام شده است و نتایج امیدوار کننده است. کارهای متفاوت با استفاده از تکنیک خوشه بندی در IR و دامنه دسته بندی انجام شده است. اما زمانی که این دامنه تشخیص سرقت ادبی خارجی بوجود می آید، استفاده از تکنیک خوشه بندی بسیار محدود میشود. Duo Zuo و همکاران [17] یک روش تشخیص سرقت ادبی خارجی را پیشنهاد دادند که از خوشه بندی برای پردازش پست استفاده میکند. در اینجا در درجه اول مرحله پیش انتخاب برای کاستن از دامنه تشخیص با استفاده از اثرانگشتهای پی در پی انجام شده است. سپس همه بخشهایی بین دو سند یافت میشوند و ادغام میشوند. خوشه بندی بیشتر برای کاهش تاثیر متن مبهم استفاده میشود. سیستم در نهایت با استفاده از مجموعه داده PAN-10 ارزیابی شده است. بنابراین از بررسی ادبیات موضوعی انجام شده، مشاهده شده است که مدلهای IR، با روشهای مبتنی بر N-gram و VSM به صورت گسترده در تشخیص سرقت ادبی خارجی استفاده میشود در حالی که تکنیک خوشه بندی کمتر استفاده میشود. روش دسته بندی سند نظارت نشده و روش خوشه بندی سند پتانسیل خوبی در مرحله بازیابی کاندید تشخیص سرقت ادبی خارجی دارد. در این مقاله، خوشه بندی سند با استفاده از الگوریتم K میانگین برای وظیفه بازیابی کاندید کشف شده است. بسط متفاوتی از K-میانگین پایه با استفاده از تکنیک NLP و N-grams نیز بحث شده است. الگوریتمها با استفاده از مجموعه داده جزئی از مجموعه PAN-13 و مقایسه با روشهای مبتنی بر N-gram پایه و روش مبتنی بر VSM کلاسیک ارزیابی شدند. روشهای پیشنهاد شده و مقایسه شده در بخشهای زیر بحث شدند.
Abstract
Text document categorization is one of the rapidly emerging research fields, where documents are identified, differentiated and classified manually or algorithmically. The paper focuses on application of automatic text document categorization in plagiarism detection domain. In today’s world plagiarism has become a prime concern, especially in research and educational fields. This paper aims on the study and comparison of different methods of document categorization in external plagiarism detection. Here the primary focus is to explore the unsupervised document categorization/ clustering methods using different variations of K-means algorithm and compare it with the general N-gram based method and Vector Space Model based method. Finally the analysis and evaluation is done using data set from PAN-20131 and performance is compared based on precision, recall and efficiency in terms of time taken for algorithm execution.
1. INTRODUCTION
Automatic text document classification or categorization is the process of assigning documents to one or more specific categories algorithmically. There is no question concerning the commercial value of being able to classify documents automatically by content as it has myriad potential applications [1]. With the rapid development in technology, information overload has become a major problem and sorting out relevant documents and classifying them accurately has become a challenge. Document classification can be categorized as supervised, unsupervised and semi-supervised. In supervised document classification, some external feedback is available to provide the correct classification information. Unsupervised classification, also termed as document clustering performs classification without any reference to external information while in semi-supervised certain parts of document is labeled using external information [2].
Application areas of document classification are numerous, via language identification, spam filtering, genre classification, sentiment analysis, information retrieval (IR) and so on. Another such possible application area is plagiarism detection. Document classification methods are less explored in this domain. Rapid development of network technology, including large numbers of search engines, document repositories, translation software systems etc. not only provides people with the various knowledge acquisition channels, but also opens the door for text plagiarism. Plagiarism generally refers to the illegitimate use of someone else’s information, text, ideas, etc. without proper reference to the original source of these data [3].
The type and degree of plagiarism ranges from the simplest to the more challenging and complex one’s. External/extrinsic and Internal/intrinsic are the two main plagiarism detection methods. Extrinsic plagiarism evaluates plagiarism in accordance to one or more source documents while the intrinsic method analyze changes in the unique writing style of an author as an indicator for potential plagiarism[4]. This paper aligns on extrinsic plagiarism detection where the source documents are available in the form of some dataset/ the web/any online sources. In extrinsic plagiarism detection, five main tasks are generally performed [4]. Pre-processing is the initial step where the source and suspicious documents are subjected to certain refinements like stop-word removal, tokenization, lowercasing, sentence segmentation, punctuation removal etc. This helps to reduce the size of actual data by removing the irrelevant information with respect to the approach used. Next stage is candidate retrieval in which a subset of source document is retrieved that is globally similar to the suspicious document. In the third stage detailed comparison of each suspicious document against its candidate document set is done to retrieve the plagiarized fragments. Here different natural language processing (NLP) techniques like chunking, parsing, part of speech (POS) tagging etc can be adopted. Fourth stage, passage boundary detection deals with estimating the exact boundaries of plagiarized passages in both source and suspicious documents using certain criteria. Finally evaluation of the system is done using some standard measures, via PAN measures to rate its performance.
Text document classification can be applied in the initial phases of external plagiarism detection method to retrieve documents which are almost similar to the given suspicious document, i.e. candidate retrieval. This reduces the number of document comparisons in the detailed analysis stage and hence the complexity. The paper focuses on the comparative study and analysis of N-gram based methods, Vector Space Model (VSM) based methods and K-means clustering based methods when used in the candidate retrieval stage of external plagiarism detection. The methods are also compared based on NLP techniques like stemming, lemmatization and chunking.
2. RELATED WORKS
In external plagiarism detection, candidate retrieval can be viewed as an information retrieval task. Based on this concept, different candidate retrieval methods using IR models are proposed by eminent researchers. In this category, finger print or N-gram based method, hash-based method and vector space models have gained popularity. S Schleimer [5] proposes a finger print based method in which the document is divided into K-grams where ‘K’ is a user specified value. Then each K-gram is hashed and some of them are selected as finger prints of the document using a specific window size. The results are evaluated using Stanford Webbase. The method could detect matches of certain length only. William B. Cavnar & John M. Trenkle [6] presents an N-gram based text categorization method where initially documents are represented as N-gram profiles. Then using some distance measure the similarity between documents are computed and they are classified. It also calculates the N-gram frequency using Zipf’s Law to take into account the top N-grams. For testing, the data from five newsgroups are used and it gives good results for classification of various news articles. Peter Nather [7] proposes a similar method in which 1-gram to 5- grams are used for experiments. The similarity measure of two N-gram profiles is taken as the sum of differences between the rank of the N-grams in one profile and the rank in the other profile. The method is evaluated using data from Project Gutenberg and it is found that the method performed well with short documents. With large volume and manipulations in content the method performance decreased.
In [8], 4 to 6 N-grams are formed to represent document profiles. Then the document ID is mapped to a set of hash values constructed. An inverted index, mapping the hash value to the sequence of document IDs is computed from it. Further similarity is calculated using Jaccard coefficient and the system is evaluated using PAN-09 dataset. An N-gram based candidate retrieval approach is proposed in [9] which uses shingling and Jaccard coefficient approach in candidate retrieval stage. Here after the required pre-processing N-gram profiles typically of N= 3 or 4 is made and then Jaccard similarity is calculated. A threshold of 0.1 is used to retrieve the candidate set of documents. The final system evaluation is done using PAN-10 dataset. Rajiv Yerra & Yiu --Kai Ng [10] performs a sentence-based copy detection method for web documents. Here the similarity between document sentences is calculated using the three least frequent 4-gram approaches where the rare tokens are taken into account. Fuzzy IR approach is also discussed, which outperformed the former one.
Another popular retrieval model is Vector Space Model (VSM) which is also used in candidate retrieval task. In [11] 16 grams are made which is then represented as vectors using tf-idf values and further document distance is measured using cosine similarity. Muhr.et.al [12] proposes a VSM based approach where initially vectorization of source and suspicious documents are done. Then the nearest documents corresponding to each suspicious document is found from the reference corpus using cosine similarity. Similar approach is carried in [13] and [14] for candidate retrieval and further the system is evaluated using PAN data sets. In VSM methods execution time increased rapidly with large datasets.
Self-Organizing Maps (SOM) is used in [15] for data organization and clustering. It uses a multi-layer tree structured SOM (MLSOM) where node data in different levels of a tree are processed in different layers of the MLSOM. Liping Jing et al.[16] presents a document clustering approach using K-means algorithm to cluster sparse data. It also automatically calculates the weights of keywords in each cluster to identify their importance. Experiments are conducted using datas from 20-Newsgroups collection and the results are promising. Different works are done using clustering techniques in IR and classification domain. But when it comes to the external plagiarism detection domain, the use of clustering techniques is too limited. Duo Zuo et al. [17] proposes an external plagiarism detection method which uses clustering for post processing. Here initially a pre-selecting step is done to narrow the scope of detection using the successive same fingerprint. Then all fragments between two documents are found and merged. Further clustering is done to reduce the impact of obfuscated text. The system is finally evaluated using PAN-10 data set. Thus from the literature survey conducted, it is observed that IR models, via N-gram based and VSM based methods are widely used in external plagiarism detection while clustering techniques are less explored. Unsupervised document classification method/ document clustering method have good potential to be applied in the candidate retrieval stage of external plagiarism detection. In this paper, document clustering using K-means algorithm is explored for candidate retrieval task. Different extensions of basic K-means using NLP techniques and Ngrams are also discussed. The algorithms are evaluated using partial dataset from PAN-13 corpus and compared with the basic N-gram based methods and classical VSM based method. The methods proposed and compared are discussed in the following sections.
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. کارهای مربوطه
3. روشهای پیشنهاد شده و مقایسه شده
3.1 روش مبتنی بر N-gram
3.2 روش مدل فضای بردار (VSM)
3.3 روش مبتنی بر خوشه با روش پیشنهادی الگوریتم K-میانگین
3.4 تغییرات الگوریتم K-میانگین پیشنهادی
3.4.1 K-میانگین با Stemming (K-Stem)
3.4.2 K-میانگین با ریشه یابی (K-Lem)
3.4.3 K-میانگین با N-gram (K-Ng)
3.4.4 K-میانگین با قطعه بندی (K-Chk)
4. تنظیمات آزمایشی و تحلیل نتایج
4.1 آمارههای داده
4.2 ارزیابی
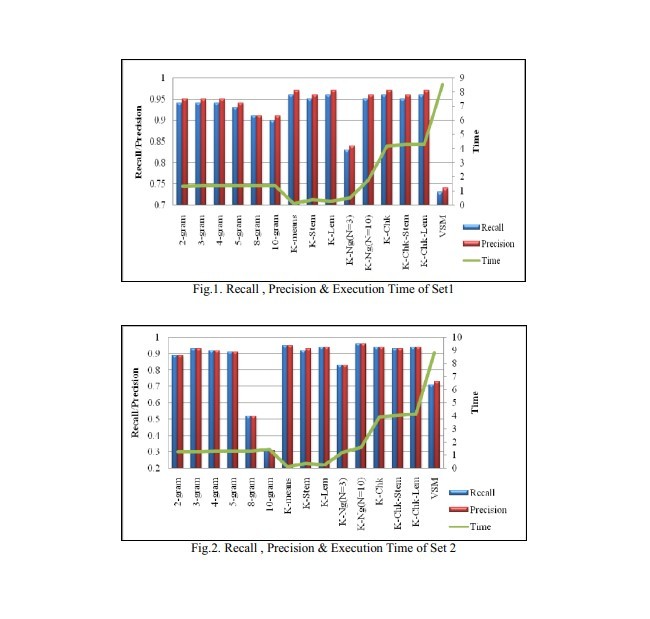
4.3 نتایج و بحثها
5. نتیجه گیری و تحقیقات آینده
منابع
Abstract
1. INTRODUCTION
2. RELATED WORKS
3. METHODS PROPOSED AND COMPARED
3.1. N-gram based Method
3.2. Vector Space Model (VSM) Method
3.3. Cluster based Method with K-means AlgorithmProposed Method
3.4. Variations of Proposed K-means algorithm
3.4.1. K-means with Stemming(K-Stem)
3.4.2. K-means with Lemmatization(K-Lem)
3.4.3. K-means with N-gram(K-Ng)
3.4.4. K-means with Chunking(K-Chk)
4. EXPERIMENTAL SETTINGS AND RESULT ANALYSIS
4.1. Data statistics
4.2. Evaluation
4.3. Results and Discussions
5. CONCLUSION AND FUTURE SCOPE
REFERENCES
