
دانلود رایگان مقاله برنامه کاربردی مدل حمل و نقل برای برنامه ریزی شهر
چکیده
توسعهای که منجر به یک شهر با سطحپایین کربنشود، یک روند مهم در شهرسازی چینی است، و شکافی بین منابع زیربنایی حملونقل و تحمیل تقاضای سفر به مسائل حملونقل، مانند ازدحام، انرژی، و امنیت را بوجودمیآورد. یک ارتباط از دسترفته در برنامهریزی تقاضاگرا و برنامهریزی کم-کربن-گرا وجود دارد، چرا که اغلب بحثها در پیشرفت برنامهریزی جامع شهری برروی ازدحام رفتوآمد در ساعات اوج تمرکز میکند. این مقاله برروی سودها و مسائل سه راهحل حملنقل، براساس استراتژی الویت حملونقل در چین، شامل جستجوی سیاست حملونقل، جستجوی حملونقل هوشمند، و نیز جستجوی طراحی و برنامهریزی بحث میکند. مدل و برنامهکاربردی اکتشافی تکمیلی برای حملونقل هوشمند با سطح کربن پایین و سیستم حملونقل بدون موتور در ایجاد ساخت تصمیم استراتژیک مطرح شده بحثمیکند. نتایج نشانمیدهند که اگر حالت توسعه شهر با سطح کربن پایین را انتخاب کنیم، از حدود 30% مصرف انرژی و انتشار CO2 میتوان چشمپوشی کرد. راهحل و مطالعه موردی برای حالت شهر واحد و فناوری شبکه انرژی هوشمند شهری در برنامهریزیجامع شهر شینیگ برای پیداکردن شکل توسعه آینده شهرهای چین، بکارمیرود.
1. مقدمه
تقاضای شاخهای اجتماعی و اقتصادی، درخواست حرکت و مسافرت موجب ازدحام گسترده، مصرف انرژی و مسائل امنیتی در شهرهای کوچک و بزرگ چین میشود. چگونگی مدلکردن ازدحام حملونقل و مصرف انرژی در شهرها برای پشیبانی از توسعه آینده، یک مسئله بزرگ برای دولت شهری، بخصوص برای برنامهریزی اداری است. تصمیمات، فرآیندها را برای توسعه شهر با سطحپایینکربن در مواجهه با فاکتور مرتبط حمل ونقل، ایجاد میکند؛ این فاکتور شامل کاهش ازدحام ترافیک، افزایش امنیت سفر، و بهبود کیفیت سفر است. استراتژی توسعه حملونقلگرا یک راهحل بدیهی برای کاهش استفاده از ماشینهای شخصی، بخصوص در شهرهای پررفتوآمدچینی، باچگالی بالا استفاده از زمین، توسط انتقال و سفر با استفاده از خودرو، است.
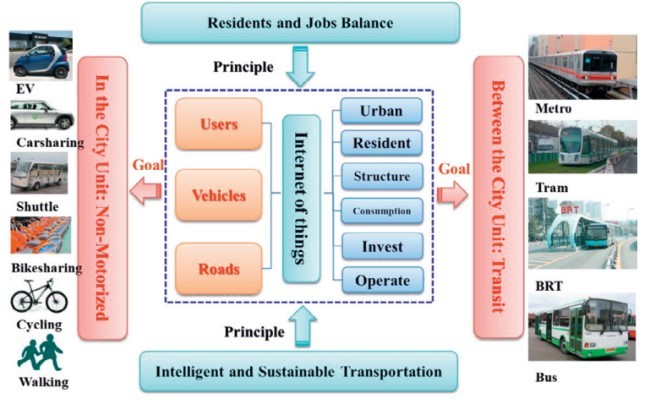
استراتژی توسعه حملونقلگرا با دو چالش اصلی در چین مواجهه میشود، یکی توسعه بازار ماشینهای شخصی با سرعت فزاینده 20% به ازای هر سال از سال 2008 تا سال 2012، که یک شکاف بین زیرساختها و گستردهشدن تقاضای ماشینهای مسافرتی ایجاد میکند، و چالش دیگر از دستدادن ارتباط متناسب با الگوی طبیعی توسعه شهری است، چرا که بیشتر شهرها ازقبل احداثشدهاند و ممکن است در همه شرایط برای حملونقل مناسب نباشند. لذا راهحل برای توسعههای آینده میتواند از دو طریق در چین انجام شود، زمانی که ما از حالت شهر واحد و فناوری شبکه انرژی هوشمند شهری، از نقطه شروع توسعه شهری استفاده میکنیم.
حالت شهر واحد برای توسعات آینده حالتی است که برروی تعادل کارها و مقدار حجم کار در سطح برنامهریزی استفاده از زمین تمرکز میکند. شبکه انرژی هوشمند شهری سیستمی است که از تکنولوژی IOT ( اینترنت وسایل) برای بررسی دادههای پویا و پیشبینی مدیریت گلوگاه برای دولت شهری استفاده میکند، و سیستم حملونقل هوشمند بخشعمده آن را تشکیلمیدهد. مدل حمل و نقل، درحالحاضر تست چگونگی اینکه حالت شهر واحد و فناوری شبکه انرژی هوشمند شهری، شهری را بخصوص در مواجهه باحملونقل تحت تاثیر قرار میدهد را توسعه میدهد. سرعت فزاینده ماشینهای خصوصی و تقاضای مسافرت به عنوان یکی از تحولات حرکت درون ساختار شهری، حالت استفاده از زمین، و منابع جادهای، درزمان بررسیهای گسترده حول چرخه عمر سیستم توسعه کربن در سطح پایین شامل سیستم آب، سیستم استفاده از انرژی، سیستم ضایعات، و سیستم اکولوژی و دیگر سیستم ها بررسیشدهاست[2].
این مقاله برروی سه راهحل حملونقل دهه گذشته در چین بحث میکند، و به مسئله عمده در زمان بررسی توسعه سطح پایینکربن اشاره میکند. استراتژی حملونقل هوشمند و سیستم طراحی شده بدونموتور ناشی از پشتیبانی از حالت شهر واحد و فناوری شبکه انرژی هوشمندشهری، در زمانی که کل مدل را برای شرح ازدحام و مصرف انرژی همزمان باهم بکارمیبریم، است. شهر شینگ به عنوان یک مطالعه موردی برای بررسی اینکه چگونه این فرآیند را انجام داده مورد مطالعه قرار گرفته است.
2. ادبیات نقد و بررسی
در اواخر سال 2011، نرخ شهرنشینی چین به 50% رسیده است[3]. مهم است که بدانید 18 گزارش در پنج سال، به نوع جدید صنعتیسازی که به انقلاب صنعتی پایبند بوده، برنامههای کاربردی فناوریاطلاعات و نوسازیکشاورزی اشاره کردهاند[4]. شهریسازی بارها و بارها به عنوان بزرگترین پتانسیل بر گسترش تقاضای داخلی تاکید میکند[5]. بهعنوان مثال در اتحادیه اروپا، در سال 2007 نرخ شهریسازی سراسری 72% بوده، درصورتیکه 85درصد GDP آن از شهر میآید [6].
بنابراین، دایره جدیدی از شهرنشینی آینده چینی، برروی شهرها با مقیاس متوسط و کوچک تمرکز میکند، که برروی ترکیب توسعات بیشتر در چهار مسئله چینی، در زمان تبدیل به زمینشهری، صنعتیسازی، فناوری اطلاعات و نوسازی کشاورزی فشار وارد میکند. این مسئله میتواند تغییر در این نوع شهرها و تغییرات چشمگیر رفتار سفر و حالت برای ساکنان جدید وقدیم را ، که به عنوان یک تجربه از شهرهای بزرگ و توسعه در چین است را، که از حالت سفر غیرآلوده اصلی مانند راهرفتن، دوچرخه سواری، به سرعت، حمل ونقل عمومی کارآمد، تاکسی و ماشینهای شخصی گذر میکند، افزایشدهد.
بهعنوان یک راهحل واقعی جلوگیری از ازدحام ترافیک، مصرف انرژی و مسئله امنیت در دور بعدی فرآیند شهرنشینی چینی، درسهایی از تجارب توسعه شهرهای بزرگ باید یادبگیریم، که در آنها ازدحام ترافیک و دیگر مسائل به طور گسترده به عنوان یک مسئله معمولی توسعه پذیرفته شدهاست. این یک ایده برای تغییر از راهحل مشخص به پذیرش مسئله است. چگونه شهرهای کوچک و بزرگ، بخصوص ساختارهای جدید شهری و طرحها به توسعه کربن سطح پایین منجر شوند، تحلیل مدل و بررسی استراتژیک در اطلاعات پایه حول طبیعت آنها میتواند راهی برای این کار باشد.
Abstract
The low carbon development is the important trend of Chinese urbanism, and the gap between transportation infrastructure resource and travel demand induces to the transportation problems, such as congestion, energy, and safety. There is a missing connection with the Demand-Oriented Planning and Low-Carbon-Oriented Planning, since most of our discussion in the Urban Comprehensive Planning Proceed is focusing on the commuting congestion in the peak hour. This paper discussed the benefits and problems of the three solutions of transportation, based on the Transit Priority Strategy in China, including the transportation policy research, smart transportation research, as well as planning and design research. A further Model exploration and application for the smart low-carbon transit and non-motorized transportation system construction strategic decision making is discussed. The result shows around 30% energy consumption and CO2 emission could be waived if we choose the low-carbon city development mode. The solution and case study apply the Unit City mode and City Intelligent Energy Network technology in Xining City Comprehensive Planning to find out how to form the future development in the cities in China.
1. Introduction
As the economic and social activity branch demand, travel and mobility request induce the widespread congestion, energy consumption and safety problems in the Middle and Small Scale cities in China. How to model our transportation congestion and energy consumption in cities to support our future development is the big issue for the City governments, especially for the planning bureau. The decision making process for the low carbon city development in transportation facet is connected with the factors, including traffic congestion reducing, travel safety increasing, and trip quality improving. Transit Oriented Development Strategy is an obviously solution to reduce the usage of private car, especially for the Chinese cites which have large amount of commuting residents and high density land-use mode, by transferring car use trips to transit.
The Transit Oriented Development Strategy face the two major challenges in China, one is the development of private car market with the rapid increasing almost 20% per year from 2008-2012[1], making the gap between infrastructure and car travel demand becoming wider; the other one is the missing connection with the nature pattern of urban development, since most of the city is constructed already and maybe not suitable for transit at all. So the solution for the future development could be two ways in China, when we use the Unit City mode and City Intelligent Energy Network technology, from the starting point of City development.
The Unit City mode for the future development is a mode which focuses on the balancing of Job and Work amounts in the land-use planning level. The City Intelligent Energy Network is a system which using the IOT (Internet of Things) technology to check the dynamic data and forecast the managing bottleneck for the city government, including the smart transportation system as the major part. A transportation model is developed already to test how this Unit City mode and City Intelligent Energy Network technology affecting our city, especially in transportation facet. The rapid increasing of the private car and travel demand is considered as one of the mobility change within the urban structure, landuse mode, and road resource, when widespread the considering about the low carbon development of the city life systems including the water system, energy using system, waste system, ecology system and other [2].
This paper is discussing the three solutions of the transportation last decades in China, and pointing out the major problems when they considering the low carbon developing. A strategic of the smart transit and well-designed non-motorized system is induced to support the Unit City mode and City Intelligent Energy Network technology, when we apply the whole model to describe the congestion and energy consumption together. Xining City is used as the case study to find out how the process done.
2. Literature Review
By the end of 2011, the urbanization rate of China has turned to the 50% limestone [3]. As the important 18th 5-years report pointed out, the new type of industrialization would adhere to industry revolution, information technology application and agricultural modernization [4]. Urbanization is repeatedly stressed as the greatest potential for expanding domestic demand [5]. Take the European Union as example, in 2007 the overall urbanization rate of 72%, while 85 per cent of its GDP came from the city [6].
Therefore, the new circle of the future Chinese urbanization, focusing on the Middle and Small Scaled cities, would push the further development combining the four issues of China, when city becomes the basement of urbanization, industrialization, information technology and agriculture modernization. That would raise the mobility in these kinds of cities and dramatically change the travel behavior and modes for the new and old residents, which could be concluded as the experiences from the big cities development in China, that the transition from original non-polluting travel modes such as walking, cycling, to the fast, efficient public transport, taxis, and private cars.
To really resolve and prevent traffic congestion, energy consumption and safety issues in next round of Chinese urbanization process, the lessons from the experience of the development of big cities should be learned, where traffic jams and other problems is now widely accepted as normal issues of the development. That is the change idea from the determinate solution to the acceptation of problems. How could Middle and Small Scaled cities, especially the new town construction and planning lead the low carbon development, model analysis and strategic consideration within the basic information about its nature will be the way to go.
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. ادبیات نقد و بررسی
3. تئوری و حالت حملونقل با سطح پایین کربن
4. مدل حملوتقل ترکیبی از سیاست، برنامه و فناوری
4.1 مدل مبتنیبر حالتشهری
4.2 مدل مبتنیبر دادههای پویا
4.3 مدل ترکیبشده
5. نتایج و نتیجهگیری
منابع
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Theory and Mode of Low-carbon Transportation
4. Transportation Model Combining Policy, Plan and Technology
4.1. Urban Mode Based Model
4.2. Dynamic Data Based Model
4.3. Combined Model
5. Results and Conclusion
References
