
دانلود رایگان مقاله یکپارچه سازی وسایل نقلیه برقی در شبکه هوشمند
چکیده
بحران انرژی و معضلات زیست محیطی موجب پذیرش وسایل نقلیه برقی به عنوان یک گزینه حمل و نقل جایگزین در وسایل نقلیه احتراق داخلی متداول شده است. اخیرا، ارائه مفهوم شبکه هوشمند در شبکه هوشمند موجب ارائه نقش وسایل نقلیه برقی به شکل تکنولوژی وسیله نقلیه به شبکه شده است. تکنولوژی وسیله نقلیه به شبکه موجب تبادل انرژی دو سویه بین وسایل نقلیه برقی و شبکه انرژی می شود که موجب ارائه خدمات متعدد در شبکه انرژی مانند تنظیم شبکه انرژی، ذخیره چرخان، اصلاح بیشینه بار، تعدیل بار و جبران توان راکتیو می شود. با توجه به این که پیاده سازی تکنولوژی وسیله نقلیه به شبکه به عنوان یک مسئله تعهد واحد پیچیده با اهداف و محدودیت های متناقض شناخته می شود، تکنیک های بهینه سازی به طور معمول مورد استفاده قرار می گیرند. این مقاله به بررسی این چارچوب، مزیت ها و چالش های تکنولوژی وسیله نقلیه به شبکه می پردازد. این مقاله همچنین تکنیک های اصلی بهینه سازی را جهت دستیابی به اهداف مختلف وسیله نقلیه به شبکه با حل محدودیت های مختلف ارائه می کند.
1- مقدمه
بخش حمل و نقل دارای بیشترین سهم از رشد مصرف کل انرژی در جهان می باشد. سهم عمده رشد مصرف انرژی در بخش حمل و نقل ناشی از رشد جمعیت و رشد بالای اقتصادی است. افزایش سریع تقاضای انرژی منجر به انتشار بیش از حد دی اکسید کربن و بحران انرژی خواهد شد. در بسیاری از کشور ها، طرح های تعدیلی جهت دستیابی به هدف کاهش مصرف انرژی و یکی از مهم ترین رویکرد ها در برقی کردن حمل و نقل ارائه شده اند.
وسیله نقلیه برقی به عنوان یک گزینه حمل و نقل جایگزین محسوب می شود که گاز های با خروجی صفر را منتشر کرده و حداقل صدا را ایجاد می کند. EV از موتور برقی و انرژی باتری برای نیروی محرکه استفاده می کند که دارای بهره وری بیشتر و هزینه عملیاتی کمتر در مقایسه با وسیله نقلیه موتوری احتراق داخلی معمول است. توسعه پیوسته باتری لیتیوم یونی و تکنولوژی شارژ دهی سریع به عنوان عوامل تسهیل کننده اصلی برای EV در آینده نزدیک به شمار می آید. با این حال، صنعت EV در حال حاضر مواجه با محدودیت های بسیار زیادی مانند قیمت اولیه بالا، تاسیسات شارژ کنندگی محدود، محدوده رانندگی کم و زمان شارژ دهی مجدد باتری به مدت زیاد است. علاوه براین، اتصال EV در شبکه انرژی جهت دریافت شارژ دارای پیامد های منفی بر روی عملیات شبکه انرژی است.
اخیرا، استفاده از مفهوم شبکه هوشمند موجب مدرنیزه شدن سیستم انرژی با خصوصیات ارتباطی اضافی شده است. مفهوم وسیله نقلیه به شبکه به عنوان یکی از تکنولوژی های شبکه هوشمند محسوب می شود که در برگیرنده EV جهت بهبود عملیات سیستم انرژی است. مفهوم V2G موجب تبادل انرژی بین EV و شبکه انرژی می شود که می تواند خدمات متعددی را به شبکه انرژی ارائه کند. با این حال، مالکان EV می توانند از درآمد های زیادی جهت مشارکت در سرویس های V2G بهره مند شوند.
می توان تکنولوژی V2G را به دو روش یک جهته و دو جهته تقسیم بندی نمود. در مورد V2G یک جهته، این روش از ارتباط بین اپراتور شبکه انرژی و EV جهت تنظیم نرخ شارژ دهی هر EV استفاده می کند. این عملیات می تواند موجب جلوگیری از اضافه بار شبکه، ناپایداری سیستم و افت ولتاژ شود. با توجه به شبکه انرژی، باتری EV به عنوان یک بار باتری محسوب می شود اما می توان آن را به عنوان ذخیره انرژی نیز در نظر گرفت. بنابراین، V2G دو جهته از این ایده جهت تبادل انرژی بین باتری EV و شبکه انرژی برای شارژ دهی EV و پشتیبانی از شبکه استفاده می کند. V2G دو جهته موجب انعطاف پذیری بیشتر در شبکه انرژی جهت کنترل انرژی باتری EV به منظور بهبود قابلیت اطمینان و پایداری سیستم انرژی می گردد.
تکنولوژی V2G به عنوان یک مسئله تعهد واحد پیچیده همراه با اهداف و محدودیت های متناقض مختلف محسوب می شود. بنابراین، درک تکنولوژی V2G با استفاده از تکنیک های بهینه سازی حاصل می شود. تکنیک های مختلف بهینه سازی در مراجع مورد اشاره قرار گرفته اند، اما تکنیک های اصلی بهینه سازی جهت اجرای V2G شامل الگوریتم ژنتیک و بهینه سازی ازدحام ذرات است. با حل برخی از محدودیت های خاص، این تکنیک های بهینه سازی می توانند به اهداف و خدمات مختلف مانند اصلاح بیشینه بار، تعدیل بار، تنظیم ولتاژ و حداکثر شدن بهره مندی از فرآیند دست یابد.
این مقاله مروری بر مفهوم، چارچوب، مزیت ها، چالش ها و استراتژی های بهینه سازی V2G دارد. بخش های مهم این مقاله عبارتند از: (1) جهت بررسی مفهوم و چارچوب کلی V2G به ویژه در مورد V2G یک جهته و دو جهته (2) جهت بحث در مورد مزیت ها، خدمات و موانع موجد در اجرای تکنولوژی V2G (3) جهت تحلیل تکنیک های مختلف V2G با اهداف اجرایی و محدودیت ها و در نهایت (4) جهت ارائه نگرش های جدید در مورد V2G. در بخش 2، چارچوب و مفهوم V2G مورد بحث قرار خواهند گرفت. مقایسه V2G یک جهته و V2G دو جهته در بخش 3 مورد اشاره قرار خواهند گرفت. بخش 4 مزیت ها و چالش های پیش روی تکنولوژی V2G را ارائه می کند. استراتژی های بهینه سازی برای V2G در بخش 5 مورد بررسی قرار می گیرند. بخش 6 نتایج این تحقیق را ارائه می کند.
2- مفهوم و چارچوب وسیله نقلیه به شبکه
تکنولوژی EV موجب جلب توجه دولت و عموم با توجه به افزایش نگرانی ها در مورد محیط زیست و افزایش هزینه سوخت های فسیلی شده است. یکپارچه سازی بخش حمل و نقل و شبکه انرژی موجب بروز چالش های مختلف در سیستم انرژی خواهد شد. به طور مثال، نفوذ قابل توجه EV ها موجب افزایش بار شبکه انرژی در طی فرآیند شارژ دهی EV می شود. با این حال، نفوذ EV ها موجب ایجاد امکان اجرای V2G شده است.
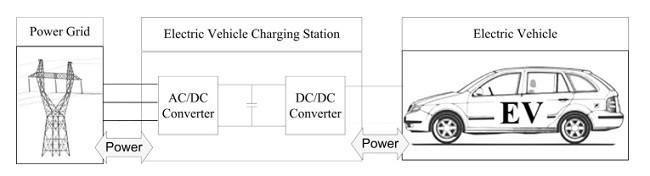
V2G در مورد کنترل و مدیریت بارهای EV توسط جمع آوری کننده های انرژی به وسیله ارتباط بین وسایل نقلیه و شبکه انرژی است. سه مفهوم رایج در مورد تکنولوژی های EV متصل به شبکه وجود دارند که شامل تکنولوژی های وسیله نقلیه به خانه (V2H)، وسیله نقلیه به وسیله نقلیه (V2V) و وسیله نقلیه به شبکه (V2G) است. V2G در مورد تبادل انرژی میان باتری EV و شبکه انرژی خانگی است. در این مورد، باتری EV می تواند به عنوان منبع ذخیره انرژی عمل کند که موجب ارائه انرژی پشتیبان در موارد استفاده از سیستم های برقی خانگی و در منابع انرژی تجدید پذیر خانگی می شود. V2V به عنوان یک سیستم EV محلی محسوب می شود که می تواند انرژی باتری EV را در میان آنها شارژ و یا تخلیه کند. V2G از انرژی حاصل از سیستم EV محلی استفاده کرده و آنها را به شبکه انرژی از طریق کنترل و مدیریت جمع آوری کننده محلی منتقل می کند.
به طور معمول، V2H، V2V و V2G شامل المان هایی همچون منابع انرژی، بارهای انرژی، جمع آوری کننده شبکه انرژی، سیستم انتقال انرژی، سیستم ارتباطی، وسایل نقلیه برقی و شارژر های وسیله نقلیه به شبکه می باشند. چارچوب یک سیستم V2G در شکل 1 نشان داده شده است.
3- جریان انرژی از وسیله نقلیه به شبکه
V2G در مورد اثر متقابل بین وسیله نقلیه برقی و شبکه انرژی با کمک سیستم ارتباطی است. اپراتور شبکه انرژی از امکان ارتباطی جهت کنترل و مدیریت جریان انرژی بین باتری EV و شبکه انرژی به منظور دستیابی به مزیت های مطلوب بهره می گیرد. در بیشتر موارد، اهداف مدیریت V2G شامل حداکثر کردن مزیت ها، کاهش انتشار و بهبود کیفیت انرژی شبکه است.
3-1 V2G یک جهته
V2G یک جهته تکنولوژی است که نرخ کنترل باتری EV را در یک جهت جریان انرژی واحد بین EV و شبکه کنترل می کند. استفاده از V2G یک جهته با افزودن کنترل گر ساده جهت مدیریت نرخ شارژ دهی مقرون به صرفه خواهد بود.
V2G یک جهته موجب ارائه خدمات فرعی در شبکه انرژی مانند تنظیم شبکه انرژی و ذخیره چرخشی می شود. این موضوع می تواند موجب بهبود انعطاف پذیری عملیات شبکه انرژی شود. اجرای V2G یک جهته نیازمند وجود یک سیسات تبادل انرژی جذاب بین مالکان EV و سیستم انرژی است. به منظور تشویق و حمایت در مشارکت مالکان EV، باید این سیاست تبادل انرژی موجب تضمین درآمد های مالکان EV در صورتی که آنها EV ها را در طی ساعات غیر از اوج شارژ کنند و شارژ دهی EV را در طی دوره های اوج بار محدود کنند، شود. همچنین، سیستم انرژی می تواند از اضافه بارگذاری در طی ساعات اوج بار دوری کند. علاوه براین، V2G یک جهته می تواند به حداکثر شدن فایده و حداقل شدن انتشار با استفاده از تکنیک بهینه سازی دست یابد.
abstract
Energy crisis and environmental issues have encouraged the adoption of electric vehicle as an alternative transportation option to the conventional internal combustion engine vehicle. Recently, the development of smart grid concept in power grid has advanced the role of electric vehicles in the form of vehicle to grid technology. Vehicle to grid technology allows bidirectional energy exchange between electric vehicles and the power grid, which offers numerous services to the power grid, such as power grid regulation, spinning reserve, peak load shaving, load leveling and reactive power compensation. As the implementation of vehicle to grid technology is a complicated unit commitment problem with different conflicting objectives and constraints, optimization techniques are usually utilized. This paper reviews the framework, benefits and challenges of vehicle to grid technology. This paper also summarizes the main optimization techniques to achieve different vehicle to grid objectives while satisfying multiple constraints.
1. Introduction
The transportation sector has the largest share of total energy consumption growth in the world. Most of the energy consumption growth in transportation sector is due to the high economic and population growth [1]. The rapid increase of energy demand will result in excessive carbon dioxide emissions and energy crisis [2]. In many countries, mitigation plans have been undertaken to achieve a reduced emissions target and one of the promising solution is electrifying transportation.
Electric Vehicle (EV) is an alternative transportation option, which emits zero exhaust gases and generates minimal noises. EV uses electric motor and battery energy for propulsion, which has higher efficiency and lower operating cost compared to the conventional internal combustion engine vehicle. The continual development of lithium ion battery and fast charging technology will be the major facilitators for EV roll out in the near future [3,4]. However, the present EV industry encounters many technical limitations, such as high initial price, limited charging facilities, limited driving range and long battery recharge time [5]. Furthermore, the interconnection of EV on the power grid to receive charge has introduced negative impacts on the power grid operation.
Recently, the introduction of the smart grid concept has modernized the power system with additional communication features [6,7]. Vehicle to Grid (V2G) concept is one of the smart grid technologies, which involves the EV to improve the power system operation. V2G concept allows the energy exchange between EV and the power grid, which can provide numerous services to the power grid. Meanwhile, EV owners can also enjoy appealing revenues for their participations in the V2G services.
idirectional [8,9]. For unidirectional V2G, it utilizes the communication between the power grid operator and EV to throttle the charging rate of each EV. This action can prevent grid overloading, system instability and voltage drop issues [10,11]. From the perspective of the power grid, EV battery is an electric load but also can be considered as energy storage. Therefore, bidirectional V2G utilizes this idea to enable energy exchange between the EV battery and the power grid for EV charging or grid support. The bidirectional V2G provides greater flexibility for the power utility to control the EV battery energy to improve the reliability and sustainability of power system [12–14].
V2G technology is a complicated unit commitment problem associated with different conflicting objectives and constraints. Therefore, the realization of the V2G technology is achieved by using optimization techniques. There are various optimization techniques in the literature, but the main optimization techniques for V2G implementation are Genetic Algorithm and Particle Swarm Optimization. By satisfying certain constraints, these optimization techniques can achieve different objectives and services, such as peak load shaving, load leveling, voltage regulation and maximization of profit.
This paper reviews the concept, framework, advantages, challenges and optimization strategies of V2G. The key contributions of this paper are: (1) to deliberate about the overall V2G concept and framework, specifically on the unidirectional and bidirectional V2G, (2) to discuss comprehensively on the benefits, services and potential barriers of the V2G technology implementation, (3) to analyze various V2G optimization techniques with practical objective functions and constraints, and lastly (4) to provide new insights into the prospects of V2G technology. Section 1 gives an introduction on the V2G background. In Section 2, V2G framework and concept will be discussed. The comparison of unidirectional V2G and bidirectional V2G will be explained in Section 3. Section 4 presents the advantages and challenges of V2G technology. The optimization strategies for V2G are reviewed in Section 5. Section 6 concludes the paper.
2. Vehicle to grid concept and framework
EV technology has attracted the attentions of government and public due to the growing concerns on the environment and rising cost of fossil fuel. The integration of transportation sector and power grid will lead to many challenging issues to the power system. For instance, a large penetration of EVs will increase the power grid load during the EV charging process. Nevertheless, the projected penetrations of EVs have also opened up the possibility of the V2G implementation.
V2G refers to the control and management of EV loads by the power utility or aggregators via the communication between vehicles and power grid. There are three emerging concepts of grid-connected EV technologies, which are the Vehicle to Home (V2H), Vehicle to Vehicle (V2V) and Vehicle to Grid (V2G) [15]. V2H refers to the power exchange between the EV battery and home power network. In this case, EV battery can work as energy storage, which provides the backup energy to the home electric appliances and to the home renewable energy sources [16]. V2V is a local EV community that can charge or discharge EV battery energy among them. V2G utilizes the energy from the local EV community and trades them to the power grid through the control and management of local aggregator [17].
3. Power flow from vehicle to grid
V2G refers to the interaction between electric vehicle and power grid with the assistance of the communication system. Power grid operator utilizes the communication facility to control and manage the power flow between the EV battery and the power grid in order to achieve desired benefits. In most cases, the objectives of the V2G management are to maximize profit, reduce emissions and improve power quality of the grid [18,19].
3.1. Unidirectional V2G
Unidirectional V2G is a technology that controls the charging rate of EV battery in a single power flow direction between the EV and grid [8,20]. The realization of the unidirectional V2G is inexpensive by adding the simple controller to manage the charge rate.
Unidirectional V2G can provide ancillary services to the power grid, such as power grid regulation and spinning reserve [21,22]. This can enhance the flexibility of the power grid operations. The implementation of unidirectional V2G needs the existence of an attractive energy trading policy between the EV owners and the power utility [23,24]. In order to encourage the participation of EV owners, this energy trading policy must guarantee revenues to the EV owners if they charge their EVs during off peak hours and limit the EV charging during on peak periods [25–27]. At the same time, the power utility can avoid overloading during on peak hours. In addition, unidirectional V2G can achieve maximization of profit and minimization of emission by using optimization technique [18,28].
1- مقدمه
2- مفهوم وسیله نقلیه به شبکه و چارچوب
3- جریان انرژی وسیله نقلیه به شبکه
3-1 V2G یک جهته
3-2 V2G دو جهته
4- مزیت ها و چالش های V2G
4-1 سرویس ها و مزیت های V2G
4-2 چالش های V2G
5- بهینه سازی الگوریتم V2G
5-1 روش های بهینه سازی
5-2 اهداف بهینه سازی
5-3 محدودیت ها و موانع بهینه سازی
6- نتیجه گیری
Abstract
Keywords
1. Introduction
2. Vehicle to grid concept and framework
3. Power flow from vehicle to grid
3.1. Unidirectional V2G
3.2. Bidirectional V2G
4. V2G advantages and challenges
4.1. V2G services and advantages
4.1.1. Ancillary services
4.1.2. Active power support
4.1.3. Reactive power compensation
4.1.4. Support for renewable energy resources
4.2. V2G challenges
4.2.1. Battery degradation
4.2.2. High investment cost
4.2.3. Social barriers
5. Optimization of V2G algorithm
5.1. Optimization approaches
5.1.1. Genetic Algorithm (GA)
5.1.2. Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO)
5.2. Optimization objectives
5.2.1. Operation cost
5.2.2. Carbon dioxide emission
5.2.3. Profit
5.2.4. Support for renewable energy generation
5.2.5. Target load curve and power losses
5.3. Optimization constraints
5.3.1. Power system
5.3.2. Electric vehicle
6. Conclusion
