
دانلود رایگان مقاله راه حل متمرکز برای انتقال الکترونیکی امن اطلاعات پرداخت به بانک ها
چکیده
تراکنش های مالی در یک سازمان، برای مثال پرداخت به تأمین کنندگان و حقوق کارمندان، از طریق برنامه های کاربردی چندگانه برنامه ریزی منابع سازمانی(ERP) تولید می شود و نیازمند انتقال امن به بانک ها می باشد. مدلهای پرداخت در طول سالها با تحولاتی در زمینه استفاده از روش های پرداخت دستی، چک، کارتها، انتقال صندوق الکترونیکی (EFT) به خانه های تصفیه خودکار (ACH) مواجه شده اند. مدلهای فعلی از روشهای زیرساخت کلید عمومی برای مراحل احراز هویت استفاده می کنند که نیاز به گواهی و تأیید مشتری و اطلاعات پرداختی دارد. مطالعه موردی حاضر یک مدل تلفیقی را پیشنهاد می کند که با استفاده از یک زیرساخت متمرکز که تبادل امن اطلاعات پرداخت از واحدهای کاری مختلف در یک سازمان را به بانک امکان پذیر می سازد، توسعه یافته است. این روش توسعه یافته از نظر مقیاس و دامنه به صرفه بوده و مجموعه ای از شیوه های استاندارد را فراهم می کند که برنامه های کاربردی چندگانه ERP توسعه یافته برای واحدهای کسب و کار مختلفی که در مناطق مختلف جغرافیایی روی یک بستر نرم افزاری امن توزیع شده اند را در حداقل زمان بازسازی و انتظار، با هم ادغام می کند. این مدل ثابت کرده که منجر به صرفه جویی در زمان و هزینه از 25% به 75% می شود و یک بستر نصب و اجرا برای واحدهای کسب و کار در یک سازمان فراهم می آورد تا بطور امن با بانکهای مختلف تبادل اطلاعات پرداخت داشته باشند.
1. مقدمه
برنامه های کاربردی ERPدر بخش های مختلف صنعتی گسترش یافته است همچون ساخت و تولید، رسانه، سازمانهای تجاری که از یک چارچوب پرداخت خودکار بواسطه ماژول های استاندارد حساب قابل پرداخت استفاده می کنند. این پرداخت ها یا برای فرایند حقوق و دستمزد کارمندان یا پرداخت به تأمین کنندگان اجرا می شوند. بااین حال، در بنگاه های اقتصادی بزرگتر، حجم تراکنش ها و در بیشتر موارد مبالغ درحال نقل و انتقال به میلیون ها دلار می رسد، از این رو ایمنی و امنیت مبادله داده های پرداخت با بانک، بسیار حساس می باشد. زمانی که سازمان دچار رشد ارگانی/ غیرارگانی می شود، تضمین امنیت انتقال پرداخت به بانک دچار پیچیدگی بیشتری می شود که منجر به تحول چشم انداز فناوری اطلاعات (IT) آن سازمان و حفظ زیرساخت پرداخت امن با بانک های طرف قرارداد می شود. این پیچیدگی در آنجایی چند برابر می شود که واحدهای کسب و کار متفاوت در یک سازمان، از برنامه های کاربردی ERP و IT مختلف برای تولید اطلاعات پرداخت که با بانک مبادله دارد استفاده می کنند.
تأکید این مقاله بر تضمین امنیت داده های پرداخت تولید شده از یک یا چند برنامه کاربردی ERP و به رسمیت شناختن دستورالعمل های مصوب خزانه داری و ساخت زیربناهای امن به بهترین شیوه است. این مدل امن متمرکز تلفیقی که در حال حاضر توسعه یافته و اجرا شده است، چندین برنامه کاربردی ERP را در سرتاسر واحدهای کسب و کار مختلف که در مناطق جغرافیایی متعدد پراکنده هستند را با هم ادغام می سازد تا تراکنش های بانکی را اجرا و اطلاعات پرداخت با بانک ها را بطور امن مبادله کند. این زیرساخت متمرکز از روشهای انتقال امن برای نیل به مقیاس و زمان بصرفه بهره می گیرد و می توان از آن در چارچوب های سراسری با حداقل زمان بازسازی و انتظار، استفاده کرد.
2. بررسی ادبیات این حوزه
بررسی ادبیات گسترده در این حوزه، نیاز به انتقال پرداخت امن و کارآمدکردن رویه های مختلف مربوطه را به روشنی نشان می دهد. ناکارآمدی های شایع در برنامه های پرداخت موجود و تکامل اقدامات برای کاهش خطرات قبل از پرداخت مجاز، بطور گسترده ای در این مطالعه بحث شده است. پرداخت حقوق و دستمزد شامل تراکنش های محرمانه، باید رمزگذاری شوند تا از فعالیت های کلاهبرداری جلوگیری شود. جوریک [1]، عوامل خطر بالقوه را که در پردازش پرداخت دخیل است تجزیه و تحلیل کرده و بکارگیری فنون رمزنگاری را ضروری دانسته است. دارایا و همکاران [2] بر نیاز به رمزگذاری داده ها از طریق رمزنگاری برای تضمین امنیت بالا، اصرار دارند. عثمان و شاه [3] بر ضرورتهای کنترل داخلی به منظور جلوگیری از وقوع تقلب و همچنین تقویت سیستم های احراز هویت، تأکید می ورزند. کورنادو- گارسیا و همکاران [4] و بابو و همکاران [5] از مدل زیرساخت کلید عمومی برای تضمین امنیت تراکنش ها استفاده کرده اند.
دارایا و همکاران [2]، سیستم های ERP را تجزیه و تحلیل کردند که با داده های حساس درارتباط است و نیازمند اقدامات امنیتی اضافه می باشد و اطلاعات از چنین سیستم هایی را برای امنیت بالاتر باید رمزگذاری کرد. همچنین تشخیص تقلب و نفوذ در زمان مناسب در چنین سیستم هایی ضروری است. امنیت این داده ها، از طریق بکارگیری فنون رمزنگاری تقویت شده است. این مطالعه بیشتر سعی کرده تا تشخیص فعالیت های متقلبانه را از طریق جداول ورودی رویداد ، تعریف کند. محدودیت های احرازهویت معامله و تخصیص نقش ها به شکل تفکیک وظایف می تواند خطر فعالیت های متقلبانه را محدود سازد.
ماسوچا و همکاران [6]، چند مسئله فرهنگی و اجتماعی که مانع توسعه تراکنش های الکترونیکی می باشد را شناسایی کردند مثل مانع زبان، موانع قانونی کشور با فرهنگی متقابل، موانع لجستیکی، دسترسی محدود به اینترنت، و بعضی مسائل امنیتی. علاوه بر این، اجرای یک سیستم ERP یکپارچه برای یک انتقال امن، مستلزم تغییرات در فرهنگ سازمانی موجود [7] است زیرا امکان دارد روش معامله سنتی در جغرافیای اجرارایج باشد.
عثمان و شاه [3] راه حل هایی را برای کلاهبرداری بانکداری الکترونیکی ارائه و تحلیل کردند. تقلب در خدمات بانکداری الکترونیکی در نتیجه سازش های مختلف در امنیت از سیستم های ضعیف احراز هویت گرفته تا کنترل های درونی ناکارآمد، رخ می دهد.
هدف این مقاله شناخت عواملی است که می تواند در تقویت سیستم های جلوگیری از تقلب در بانکداری الکترونیکی، مهم باشند. یافته های این مطالعه نشان می دهد که فراتر از فناوری، عوامل دیگری مثل تقویت کنترل های درونی، استفاده مجدد از زیرساخت های فناوری و استاندارد کردن چارچوب خزانه داری برای تأیید پرداخت ها، می تواند اطلاعات پرداخت امن به بانک ها را امن سازد.
کورنادو- گارسیا و همکاران [4]، زیرساخت کلید عمومی و ضرورت آن برای تضمین تراکنش های امن و قابلیت اطمینان بالای خدمات آن را تجزیه و تحلیل کردند. استفاده از رمزنگاری کلید عمومی، اولین شرط را برآورده می سازد، درحالیکه شرط دوم بطور سنتی با استفاده از معماری های توزیع شده ، برآورده می شود.به نظر بابو و همکاران [5]، بخاطر افزایش سریع در زیرساخت کلید عمومی (PKI) که برنامه های کاربردی در تراکنش های الکترونیکی متعدد را فعال کرده، ممیزی منظم سیستم گسترش یافته PKI و شناخت کارامدی این سیستم بسیار مهم است. این پژوهشگر یک رویکرد مبتنی بر عامل را برای ممیزی سیستم PKI پیشنهاد می دهد. این سیستم از یک گواهی چرخه عمر تولید شده برای شیوه های احراز هویت استفاده می کند. این رویکرد مبتنی بر عامل، گزارش های ممیزی مؤثری برای یک زیرساخت کلید عمومی ارائه می دهد که مؤثرتر از ممیزیهای دستی است.
Abstract
Financial transactions in an organization, for example payments to suppliers and employee salaries, are generated from Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) applications and require secure transmission to bank. The payment models have been evolving over the years which confronted transformations from the usage of manual payment methods, cheque, cards, Electronic Fund Transfer (EFT) to Automatic Clearing House (ACH). Current models utilize Public key infrastructure methods for authorization procedures which require certification and verification of customer and payment information. The present case study proposes a consolidated model that has been developed and deployed using a centralized infrastructure enabling secured payment information exchange from various business units in an organization to the bank. The developed method achieves economies of scale and scope, provides set of standardized procedures that integrate multiple ERP applications deployed for various business units distributed over multiple geographies on a secured platform at a minimum reconstruction and waiting time. The model has proven effective leading to cost and schedule saving from 25 % to 75% and provides a plug and play platform to business units in an organization to exchange payment information securely with various banks.
I. INTRODUCTION
ERP applications are deployed in various industry sectors such as manufacturing, media, trading houses that utilize an automated payment framework through standard account payable module. The payment runs are executed either to process employee salaries or to make supplier payments. However, in larger firms, the volume of transactions and often the amounts in play are encountered at millions of dollars, hence safety and security to exchange the payment data with the bank becomes crucial. An increased complexity is observed in ensuring secured payment transmission to bank when organization is going through organic/ inorganic growth, resulting in transformation of its Information Technology (IT) landscape and maintaining secured payment infrastructure with partner banks. The complexity is further multiplied where different business units in an organization deploy varied ERP and IT applications to generate payment information that is exchanged with the bank.
The paper emphasizes on securing the payment data generated from one or more than one ERP applications and formalizing treasury approvals guidelines and constructing secured infrastructure on best practices. The consolidated centralized secured model,already developed and implemented, integrates multiple ERP applications across various business units spread out in multiple geographies to carry out banking transactions and exchange payment information securely with banks. The centralized infrastructure uses secured transmission methods to achieves economies of scale and scope and can be utilized in global frameworks at a minimum reconstruction and waiting time.
II. LITERATURE REVIEW
The extensive literature review highlights the need for securing payment transmission and making various associated procedures efficient. The inefficiencies prevalent in present payment applications and the evolvement of measures to reduce risks before payment is authorized are discussed widely in this study. The payroll payment involving confidential transactions needs to be encrypted to avoid fraudulent activities. Djuric [1] analysed the potential risk factors involved in payment processing and necessities the usage of cryptography techniques. Dharaiya et al. [2] insisted the need for encryption of data through cryptography to ensure high security. Usman and Shah [3] emphasized the requisites of internal control to prevent fraud occurrences and also to enrich the authentication systems.Coronado-Garcia et al. [4] and Babu et al. [5]has utilized public key infrastructure model to secure transactions.
Dharaiya et al. [2] analyzed ERP systems, which deal with sensitive data, require additional security measures and information from such systems needs to be encrypted for higher security. It is also necessary to detect frauds and intrusions at the right time in such systems. The security of the data has been enriched through usage of cryptography techniques. The study further has tried to identify the detection of fraudulent activities through event log tables. The transaction authorization limits and roles assignment as per segregation of duties can limit the risk of fraudulent activities.
Masocha et al. [6] identified few social and cultural issues hindering the development of e-transactions such as language barrier, cross cultural country legislation barriers, logistical barriers, limited access to internet, and few security concerns. Moreover, implementation of an integrated ERP system for a secure transmission demands changes in existing organizational culture [7] since traditional transaction method may be prevalent in the geography of implementation.
Usman and Shah [3] analyzed and offered solutions for E-banking fraud. Frauds in e-banking services occur as a result of various compromises in security ranging from weak authentication systems to insufficient internal controls.
The purpose of this paper is to understand factors that could be critical in strengthening fraud prevention systems in electronic banking. The study findings show that beyond technology, other factors such as strengthening internal controls, reusing technology infrastructure and standardizing treasury framework to approve payments can secure payment information to bank.
Coronado-Garcia et al. [4] analyzed Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) and its essentiality to assure secure transactions and high reliability of its services. The use of public key cryptography satisfies the first requirement, while the second requirement has been traditionally satisfied by the use of distributed architectures. Babu et al. [5] considered rapid increase in Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) enabled applications in various electronic transactions, it has become very important to audit the deployed PKI System regularly and to understand the effectiveness of the system. The researcher proposed an agentbased approach to audit a PKI System. This system utilized a certificate generated life cycle on authorization procedures. The agent based approach offered effective audit reports for a public Key infrastructure that was more effective than the manual audits.
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. بررسی ادبیات این حوزه
3. چالش های رودر روی مدل موجود
الف. اقدام به کلاهبرداری در خلال تراکنش های پرداخت
ب. پردازش دستی ناکارآمد
پ. تراکنش های غیراستاندارد از طریق درگاه های پرداخت
ت. روابط و تراکنش های بانکداری چندگانه
4. حالت های مختلف پرداخت
الف. چک
ب. ACH
ج. EFT
5. امنیت در انتقال فایل
الف. روشهای اجتناب از ریسک های پرداخت
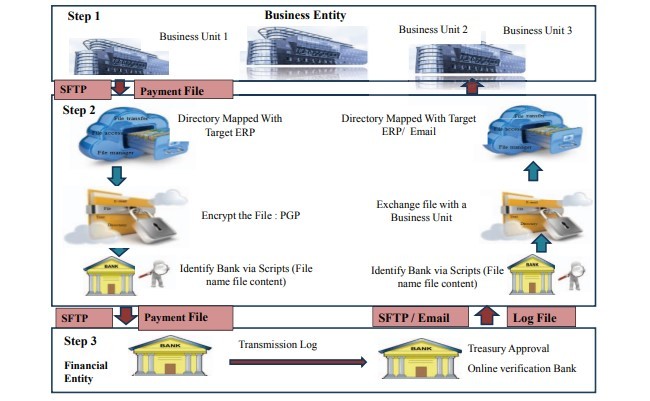
6. مدل پیشنهادی
الف. ویژگی های سیستم پرداخت خودکار
ب. زیرساخت پرداخت خودکار
پ. رعایت زمان اجرا برای این مدل
ت. مزایای اجرای این مدل
7. نتیجه گیری
منابع
Abstract
1. INTRODUCTION
2. LITERATURE REVIEW
3. CHALLENGES FACED BY EXISTING MODEL
A. Fraudulent Activities during Payment Transactions
B. Inefficient Manual Processing
C. Non Standardized Transactions through Payment Gateways
D. Multiple Banking Relationships and Transactions
4. VARIOUS PAYMENT MODES
A. Cheques
B. ACH
C. EFT
5. SECURITY IN FILE TRANSMISSION
A. Methods of Preventing Payment Risks
6. PROPOSED MODEL
A. Features of Automated Payment Systems
B. Automated Payment Infrastructure
C. Observance of implementation time for the model
D. Benefits observed with the implemented model
7. CONCLUSION
REFERENCES
