
دانلود رایگان مقاله تاثیر عدم قطعیت بر اطمینان پذیری خستگی عرشه پل بتن آرمه
چکیده
تخریب عرشه یک پل بتن آرمه که دچار آسیب ناشی از بار ترافیکی شده است میتواند بر دوام، ایمنی و عملکرد سازه تاثیر بگذارد. در مقاله پیش رو، آنچه انجام شده است آنالیز اطمینانپذیری به روی خستگی وابسته به زمان و بررسی اثر عدمقطعیت بر روی سرویسدهی عرشه پل بتن آرمه است. در این تحقیق از یک عرشه پل محافظت شده، با عرض 15 متر استفاده شده است. در این راستا مدل های ریاضی ارائه شده است و در موضوع عدمقطعیتها، استقامت سازه و بارهای اعمالی به عنوان اجزای سازه و با استفاده از روشهای احتمالاتی مورد اصلاح قرار گرفتهاند. توابع حالت حدی با استفاده از الگوریتم اطمینانپذیری درجه اول ارزیابی شده و کل فرایند نیز با استفاده از یک برنامه مطلب موسوم به ریزوست دات ام اجراء شده است. نتایج به دست آمده، بحرانیترین تاثیرات منجر به شکست را بیشتر در منطقه برشی عرشه و در بازه شاخص اطمینان پذیری از 6.95 تا 12.38- در مقایسه با منطقه خمشی با شاخص 8.85 تا 10.53- نشان داد.
1. مقدمه
پلهایی که نقش ارتباطی مهمی را در سیستم زیرساخت حمل و نقلی ایفا میکنند به شدت در معرض خستگی قرار دارند. خستگی میتواند منجر به بروز تهدیداتی برای ساختار ایمنی و در نتیجه خرابی فاجعهآمیز گردد. با افزایش بالقوه فرسایش و تردد وسایط نقلیه سنگین، ایمنی عرشه چنین پلهایی در چرخه بهرهبرداری پل اهمیت دو چندان پیدا میکند [15].
امکان برداشت میدانی برای همه نقاط مشکل دار دلخواه در یک پل وجود ندارد. در این راستا می توان از روش المان محدود (FEM) مبتنی بر آنالیز دینامیک سازه برای فراهم کردن دادهها و جزئیاتی در مورد گذشته تنشها و محدوده آنها برای سناریوهای مختلف استفاده نمود. [1] .
نه تنها فرسایش عرشه داخلی پل یک مشکل اقتصادی تلقی میشود بلکه برای کسانی که از آن برای تردد استفاده میکنند خطر محسوب میشود. محدوده و شکل فرسایش دارای طیف مختلفی است؛ از آسیب سطحی عرشه گرفته که نمای ناپسندی دارد و سرویس دهی عرشه پل را دچار ضعف میکند تا قلوهکن شدن تکه های بزرگ بتن که ضعف کارایی سازه را به ارمغان آورده و برای عموم خطر محسوب میشود. بنابرین، نیازمند درک رفتار عرشه پل تحت بار و بهبود فرایند به شکلی مطمئن هستیم و باید برای بهبود قابلیت سرویسدهی عرشه ارزیابی و تحلیل های لازم را صورت دهیم که این کار نیازمند ابزاری برای اصلاح یا رفع نواقص عرشه میباشد [2].
1.1. تاثیر خستگی بر روی پل
فرسایش و آسیب عرشه پل های بتنی که مستقیماً بر اثر بار ترافیک وسایل نقلیه به وجود آمده، بر دوام، ایمنی و عملکرد پل تاثیر میگذارد. ممکن است آسیبهای سازه ای افزایش پیدا کنند مثل تغییر شکل در عرشه و ایجاد ترک های متعدد که در نهایت باعث کاهش عمر عرشه و ظرفیت حمل بار پل میشود.
تقریبا اصلاح در مقاومت عرشه پل نسبت به خستگی کار دشواری است زیرا افت مقاومت برشی که بر اثر وجود بارهای مکرر به وجود آمده باید توسط بهبود در مقاومت خمشی جبران شود.
اگرچه در دهه گذشته برنامه های تحقیقاتی بسیاری برای برداشت صحیح از خستگی و جایگزینی یک مدل خستگی مناسب برای پل های بتنی ارائه شده است، مشخصه های شکست و گسیختگی سازه های بتنی تقویت شده هنوز از به صورت سیستماتیک و بر پایه علمی جواب نداده است [9].
در حال حاضر روش تحلیل خطی المان محدود ارتجاعی به طور عمده برای طراحی عرشه پلهای بتن آرمه استفاده میشود. از آنجا که اثرات بار بر سازه پل تحت تاثیر انواع مختلفی از ترکیبها است، این رویکرد مناسب به نظر میآید. هرچند، چنین به خاطر این تحلیل خطاهایی نیز محتمل است.
1.2. خطای تخمینی
تحلیل و طراحی مهندسی سازه مملو از بیقطعیتی و عدم اطمینان است که بعضی از آن ها بدیهی و بعضی قابل اغماض است. این بیقطعیتیها را می توان به دو گروه تقسیم کرد که هر دو می تواند در نتیجه دانش اکتسابی یا در نتیجه شانس باشند که منشأ آنها از عوامل زیر است: زمان، محدودیت های آماری، محدودیت های مدل، تنوع در بار و خطااهای انسانی. قوانین طراحی تنش مجاز و طراحی فاکتور مقاومت در برابر بار تابع جنبه های مختلفی از جمله محدودیت آماری، تنوع در باز، زمان و مدلسازی است. موارد دیگر مثل خطاهای انسانی باید توسط روش های کنترل کیفی همچون بازدید و بررسی سازه ای برطرف شوند [14].
ABSTRACT
The deterioration of reinforced concrete bridge deck that has been damaged as a result of load action can affect the durability, safety and function of the structure. In this paper, a reliability time-variant fatigue analysis and uncertainty effect on the serviceability of reinforced concrete bridge deck was carried out. A simply supported 15m bridge deck was specifically used for the investigation. Mathematical models were developed and the uncertainties in structural resistance, applied loadings as well as the structural components were accommodated using probabilistic method. The limit state functions were evaluated using the First Order Reliability Algorithm and the entire process was implemented using a developed MATLAB program called Rayswit.m. Failure in the deck shear region gave the most critical effect with a reliability index range of 6.95 to -12.38 when compared to flexure region with an index of 8.58 to -10.53.
1. INTRODUCTION
Bridges which serve as a major link component in the infrastructure system, are extremely vulnerable to this action of fatigue. This action could possibly lead to major threats on structural safety and lead to catastrophic failure [10]. With increase in potential deterioration and much heavier vehicle loads, the safety of the existing deteriorating bridge decks in the later life cycle is more critical [15].
It is impossible to take on-site measurement for every concerned location of every bridge. As such, finite element method (FEM) based structural dynamic analysis can be used to provide reasonable stress range histories for bridge details in various scenarios [1].
Not only inbridge deck deterioration is an economic problem, it is also a risk to those who traverse the structure. Forms of deterioration can range from slightly damaged deck surfaces, causing unpleasant sights and decreasing bridge deck serviceability, up to spalling of large pieces of concrete that reduces the structural integrity and it can be a danger for the public. Therefore, there is a compelling need to understand the behavior of bridge decks under service load and develop a reliable procedure and analysis to assess the serviceability of the deck, which will then serve as a decision-making tool for the rehabilitation or the replacement of the decks [2].
1.1 Fatigue Effect on Bridge
The deterioration of concrete bridge decks that have been directly damaged by traffic loads affects their durability, safety, and function. Structural damage can increase, such as residual deformation and numerous cracks, which eventually decreases the life of the deck as well as its load carrying capacity [13]. It is fairly difficult to rehabilitate the fatigue resistance of a deck because the shear strength that has been decreased by repeated loads must be improved with the flexural strength.
Although numerous research programs over the past decade have attempted to understand fatigue response and to establish a fatigue model for concrete subjected to repeated loads, the fatigue failure characteristics of strengthened concrete structures are not yet systematically established on a scientific foundation [9].
Currently the linear elastic finite element analyses method is mainly used in the design of reinforced concrete bridge decks. Since the load effects on the bridge superstructure are sought for by a multitude of load combinations, this approach is suitable. However, some uncertainties relate to such an analysis [7].
1.2 Uncertainties
Structural engineering analysis and design is replete with uncertainties, some of which are obvious and some others may never have been considered. These uncertainties can be categorised into two, either as a result of acquired knowledge or by chance and they have their sources from some of the following: Time, Statistical Limits, Model Limits, Load Variation and Human Errors. The Allowable Stress Design and the Load Resistance Factor Design codes take some aspect of Statistical Limit, Load Variation, Time and Modelling. Others such as Human Errors must be dealt with using quality control methods such as review and construction inspection [14].
چکیده
1. مقدمه
1.1. تاثیر خستگی بر روی پل
1.2. خطای تخمینی
2. مصالح و روش ها
2.1. تخمین پارامترهای اطمینان پذیری عرشه پل
2.2. مدل پل
2.3. مصالح ساختمانی
2.4. ارزیابی حالت حدی
2.5. تابع حالت حدی برش در تیر داخلی
2.6. فرایند آنالیز کامپیوتری
3. نتایج و مباحثات
3.1. اثر ضریب تغییرات حاصل از عدم قطعیت در مدل بار ترافیکی
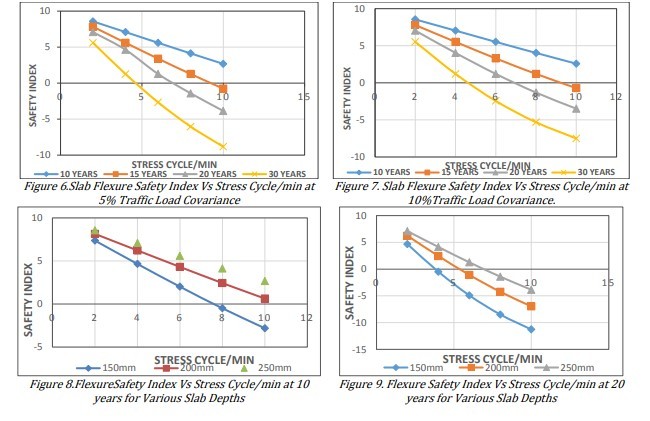
3.2. تاثیر تغییرات در عمق دال عرشه بر روی شاخص ایمنی بر حسب چرخه تنش تحت شرایط خمش
3.3. تاثیر تغییر عمق تیر بر شاخص ایمنی بر حسب چرخه تنش تحت شرایط تنش برشی
3.4. اثر عدم قطعیت استقامت بتن بر روی شاخص ایمنی برحسب چرخه تنش
3.5. اثر عدم قطعیت مدل استقامت بر شاخص ایمنی برحسب چرخه تنش تحت شرایط خمش
4. نتیجهگیری و توصیهها
منابع
ABSTRACT
1. INTRODUCTION
1.1 Fatigue Effect on Bridge
1.2 Uncertainties
2. MATERIALS AND METHOD
2.1 Estimation of Parameters for Reliability of Bridge Deck
2.2 Bridge Model
2.3 Structural Materials
2.4 Limit State Evaluation
2.5 Limit State Function for Shear in Interior Beam
2.6 Computer Analysis Procedure
3. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
3.1 Effect of Coefficient of Variation due to Traffic Load Model Uncertainty
3.2. Effect of Deck Slab Depth Variation on the Safety Index with Respect to Stress Cycle under Flexure Condition
3.3. Effect of Beam Depth Variation on the Safety Index with Respect to Stress Cycle under Condition of Shear Stress
3.4 Effect of Concrete Strength Uncertainty on the Safety Index with respect to the Stress Cycle
3.5 Effect of Strength Model Uncertainty on the Safety Index with respect to the Stress Cycle under Condition of Flexure
4. CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDATIONS
REFERENCES
