
دانلود رایگان مقاله تشخیص خطای اولیه سنسور مبتنی بر مشاهده گر مد لغزشی
چکیده
موضوعی که در این مقاله به آن پرداخته میشود، مسائل تشخیص خطای اولیه سنسور برای گروهی از سیستمهای غیرخطی با عدمقطعیت مشاهدهگر غیرمنطبق است. تشخیص خطای منحصر به فرد مبتنی بر مشاهدهگر مد لغزشی برای سیستم تکمیلی طراحی شده است که به همراه سیستم اصلی و خطای اولیه سنسور تشکیل است. پارامترهای طراحی شده با استفاده از تکنیکهای فیلتر خط و LMI استفاده میشود تا این اطمینان حاصل شود که باقی ماندههای تولیدی در برابر عدم قطعیتها مقاوم، و حرکت لغزان با خطا از بین نمیرود. سپس سه سطح از آستانههای تطبیقی براساس دینامیکهای مد لغزان مرتبه کاهش یافته پیشنهاد شده است که به طور موثر قابلیت شناسایی خطاهای اولیه سنسور را بهبود میبخشد. همچنین مطالعه موردی بر سیستم کششی در خط راه آهن سرعت بالا در چین ارائه شده است و اثربخشی طرح تشخیصی خطای اولیه سنسور را نشان خواهد داد.
1. مقدمه
سیستمهای کنترل مدرن به منظور اینکه الزامات روز افزون سطح بالایی از عملکرد را برآورده سازند، پیچیدهتر شده اند. مهندسین کنترل به صورت فزاینده با سیستمهای پیچیدهای روبرو هستند که در آن هر دو قابلیت اطمینان و ایمنی بسیار مهم هستند. با اینحال، خطاهای اولیه جز مولفه، همچون اثربخشی تلفات الکترولیت در خازن الکترولیتی، فرسودگی مکانیکی و غیره باعث ایجاد تغییراتی میشوند و علل ایجاد عملکرد نامطلوب و حتی ناپایداری هستند. این موارد امری مهم برای سیستمهای حیاتی واقعی و ایمنی مانند هواپیما، فضاپیماها، نیروگاههای هسته ای، کارخانههای شیمیایی با فرایند مواد خطرناک و خط راهآهنهای سریع تلقی میشوند. بنابراین تشخیص خطای اولیه و توسعه تکنیکهای تشخیصی از اهمیت عملی زیادی برخوردار هستند. همچنین مهمترین مسئله عملیات سیستم اطمینانپذیر، عمل تشخیص و تاحد امکان جداسازی خطاهای اولیه است، که در واقع میتواند اطلاعات کافی به اپراتورها بدهد تا زمان مناسبی برای جلوگیری از حوادث جدی در سیستم مهیا شود.
به طور معمول، خطاهای ناگهانی، ایمنی مربوط به سیستمها را تحت تاثیر قرار میدهد، که باید خیلی زود تشخیص داده شوند به اینگونه که با تنظیم مجدد اولیه بتوانیم از حوادث فاجعه بار اجتناب کنیم. چنین خطاهایی اثرات بیشتری بر باقیماندههای تشخیصی نسبت به عدم قطعیت مدلسازی میگذارند، که با انتخاب آستانههای مناسب آنها را میتوانیم تشخیص دهیم. در نهایت، خطاهای اولیه رابطه نزدیکی با مسائل تعمیر ونگهداری دارند و تشخیص زودهنگام تجهیزات فرسوده ضروری است. دراین مورد، دامنه خطاهای آغازین به طور معمول کوچک است. بنابراین در تشخیص با چالشهایی در زمینه تکنیکهای FDI مبتنی بر مدل با توجه به ترکیب تفکیک ناپذیر بین خطای اولیه و عدم اطمینان مدل سازی روبرو هستیم که در این مقاله ارائه میشود. بنابراین مهم است که رباستنس مانده را برای عدم قطعیت سیستم بهبود بخشیم و آستانه بسیار مناسبی انتخاب کنیم تا قابلیت شناسایی مکانیزم تشخیص خطا نیز بهبود یابد.
در چند دهه گذشته، روشهای متعددی برای ارتقای رباستنس در تشخیص خطا مبتنی بر مشاهدهگر همچون جداسازی ورودی ناشناخته [1-4]، طرحهای H1و H2 بهینه [5–8]، اطلاعات مجموع خطای اندازهگیری باقیمانده [9] و روش پیش بینی [10] پیشنهاد شده است. تشخیص خطا برای طرحهای سوییچینگ [11،12] و فرایندهای تولید نیمه هادیها [13] نیز پیشنهاد شده است، از شرایط عمومی موجود در [2] مشخص شده است که یک ژنراتور باقیمانده کاملا از ورودی ناشناخته جدا شده است، واین مقوله تنها زمانی ممکن است که سیگنال خروجی کافی در دسترس باشد. غیر از رویکرد جداسازی، ژنراتورهای باقی مانده مقاوم در زمینه تعادل بین رباستنس در برابر اغتشاشات و حساسیت به خطاها طراحی شده اند [5]. هنگامی که جداسازی کامل امکان پذیرنیست، توابع تصمیمگیری که توسط باقی مانده تعیین شده اند بوسیله ورودیهای ناشناخته مخدوش خواهند شد. روش معمول برای ارزیابی توابع تصمیمگیری، تعریف آستانههای مناسب است، که توابع تصمیمگیری بوسیله این آستانهها مقایسه میشوند [1]. بنابراین، انتخاب باقیمانده های رباستنس و آستانههای مناسب دو عامل مهم برای بهبود قابلیت شناسایی مکانیزم تشخیص خطای اولیه است.
در طی دهههای گذشته، مشاهدهگرهای مدلغزان بصورت گسترده برای FDI استفاده میشود [14-22]. در رفرنس] 14 [ از یک مشاهدهگر لغزان برای تشخیص خطاها با ایجاد اغتشاش در حرکت لغزان استفاده کرد که یک مسئله دشوار است و انگیزههای زیادی برای تحقیق در این زمینه ایجادشد. مفهوم تزریق معادل خروجی در منابع ]15-19[، به منظور تشخیص و جداسازی خطا از جمله خطای سنسور و خطای محرک استفاده شد. در ]18[، عدم قطعیتها و اغتشاش مدنظر قرارگرفته شده است، که در فرض [23] ماتریسهای توزیع عدم قطعیتها و اغتشاشات مدلسازی نیازمند عدم قطعیت تطبیق یافته است. همچنین پژوهش مرجع [17] که در زمینه عدم قطعیت غیرتطبیقی بود، براساس مقوله مقاوم برای ارتقای رباستنس است. براساس ساختارهای مختلفی از ماتریس توزیع خطاها و عدم اطمینان، [20،22]، مشاهدهگر لئونبرگر با مشاهدهگر مدلغزشی به منظور تشخیص خطا ترکیب میشوند که دراین صورت به جداسازی کامل میان خطاها و عدم قطعیت ها نیاز وجود دارد. بنابراین چارچوب FDI مبتنی بر چارچوب مدلغزشی در مرجع ]17[، عمدتا بر طراحی ژنراتور باقی مانده مقاوم تمرکز کرده بود تا تعادلی میان رباستنس علیه اغتشاشات و حساسیت به خطا ایجاد شود. در واقع، با انتخاب آستانه مناسب، قابلیت شناسایی بهبود مییابد و آستانه تطبیقی نیز شهودی است(مرجع ] 24[ را مشاهده کنید). بنابراین طراحی آستانه تطبیقی مبتنی بر مشاهدهگرهای مد لغزشی در دسترس نیست.
در این مقاله، یک مشاهدهگر مدل لغزشی غیرخطی با سطح لغزان طراحی شده نوین برای تشخیص اولیه خطا پیشنهاد شده است. به طورخاص، پارامترهای مشاهدهگر براساس گین L2 طراحی شده اند، و رباستنس باقیمانده را نسبت به عدم قطعیت تضمین میکند. هم زمان، آستانههای تطبیقی مناسب، براساس حرکت لغزان مرتبه کاهش یافته حاصل میشود، که بهطور موثر قابلیت شناسایی خطای اولیه سنسور را بهبود میبخشد. علاوه براین، سطوح مختلف در طرحهای تصمیمگیری مبتنی بر تشخیص گسترش خطای اولیه سنسور پیشنهاد شده است. ساختار اصلی این مقاله به صورت زیر است:
• یک چارچوب مشاهدهگر مد لغزشی FDI نوین برای دستیابی به آستانههای تطبیقی مناسب به منظور بهبود قابلیت شناسایی خطای اولیه پیشنهاد شده است.
• طراحی توسعه یافته تشخیصی خطای اولیه سنسور مورد مطالعه قرار گرفته و سطوحی از تصمیمات تشخیصی پیشنهاد شده است.
ادامه مطالب این مقاله به صورت زیر است:در بخش دوم، مقدمات و فرضیه ها ارائه شده است، در بخش سه مشاهدهگر مد لغزشی FDE با پارامترهای مشاهدهگر براساس تکنیکهای فیلتر خطی و LMI طراحی شده است. در بخش چهارم، آستانههای تطبیقی خطای سنسور( برای خطا، خرابی) طراحی شدهاند، و تصمیمات تشخیصی برای خطاهای گسترش یافته سنسور بصورت پیوسته تکه ای انجام میشود. در بخش پنجم، مطالعه موردی برنامه مبتنی بر یک سیستم کششی در CRH( خط راه آهن سرعت بالا درچین) برای ارائه نتایج بررسی شده است. در بخش ششم نتیجه گیری انجام میشود.
Abstract
This paper considers incipient sensor fault detection issue for a class of nonlinear systems with “observer unmatched” uncertainties. A particular fault detection sliding mode observer is designed for the augmented system formed by the original system and incipient sensor faults. The designed parameters are obtained using LMI and line filter techniques to guarantee that the generated residuals are robust to uncertainties and that sliding motion is not destroyed by faults. Then, three levels of novel adaptive thresholds are proposed based on the reduced order sliding mode dynamics, which effectively improve incipient sensor faults detectability. Case study of on the traction system in China Railway High-speed is presented to demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed incipient senor faults detection schemes.
1. Introduction
Modern control systems have become more complex in order to meet the increasing requirement for high levels of performance. Control engineers are faced with increasingly complex systems for which both the reliability and safety are very important. However, component incipient faults, such as electrolyte loss effectiveness of electrolytic capacitor, mechanical wears and bears etc., may induce drastically changes and result in undesirable performance degradation, even instability. These are life-critical for safety and actuate critical systems such as aircrafts, spacecrafts, nuclear power plants, chemical plants processing hazardous materials and high-speed railways. Therefore, incipient fault detection and development detection techniques are of practical significance. And, the most important issue of reliable system operation is to detect and isolate incipient faults as early as possible, which can give operators enough information and time to take proper measures to prevent any serious consequences on systems.
Typically, abrupt faults affect safety-relevant systems, which have to be detected early enough so that catastrophic consequences can be avoided by early system reconfiguration. Such faults normally have larger effect on detection residuals than that of modeling uncertainties, which can be detected by choosing appropriate thresholds. At the other end, incipient faults are closely related to maintenance problems and early detection of worn equipment is necessary. In this case, the amplitude of incipient faults are typically small. Thus the detection presents challenges to model-based FDI techniques due to the inseparable mixture between incipient fault and modeling uncertainty. Therefore, it is important to improve the residual robustness to system uncertainties and select more proper thresholds to improve the detectability of fault detection mechanism.
There are many methods proposed in last few decades to enhance the robustness in observer based fault detection, such as perfect unknown input decoupling [1–4], optimal H2, H1 schemes [5–8], total measurable fault information residual [9], and projection method [10]. Fault detection schemes for switching systems [11,12] and semiconductor manufacturing processes [13] have also been proposed. It has been recognized from general existence condition in [2] that, for a residual generator perfectly decoupled from unknown input, it is only possible when enough output signals are available. Different from perfect decoupling approach, the robust residual generators are designed in the context of a trade-off between robustness against disturbances and sensitivity to faults [5]. When perfect decoupling is not possible, the decision functions determined by residuals will be corrupted by unknown inputs. The common practice to evaluate the decision functions is to define appropriate thresholds, with which the decision functions are compared [1]. Therefore, the robustness residuals and proper selected thresholds are two important factors to improve detectability of incipient fault detection mechanism.
During the past decades, sliding mode observers have been used for FDI extensively [14–22]. Ref. [14] uses a sliding mode observer to detect faults by disruption of sliding motion which is a difficult problem and motivate much research in the area. In [15– 19], the “equivalent output injection” concept is used to explicitly construct fault signals to detect and isolate the faults, including sensor faults and actuator faults. In [18], uncertainties and disturbances are considered, which need the so called “matched uncertainty” in [23] assumption on the distribution matrices of the modeling uncertainties and disturbances. Also, [17] studies the so called “unmatched uncertainty” case based on the robust H1 to enhance the robustness. Based on different structures of distribution matrices of faults and uncertainties, [20,22] combine the Luenberger observer with sliding mode observer to detect faults, which needs perfect decoupling between faults and uncertainties. Therefore, sliding mode observer based FDI framework in [17,21] mainly focus on robust residual generator design to get a trade-off between robustness against disturbances and sensitivity to faults. In reality, fault detectability can also be improved by selecting proper thresholds and the adaptive threshold is intuitive (see, e.g. [24]). However, adaptive threshold design based on sliding mode observers has not been available.
In this paper, a nonlinear sliding mode observer with novel designed sliding surface is proposed for incipient sensor fault detection. The parameters of the observer are particular designed relying on L2 gain, guaranteeing residual robustness to uncertainties. At the same time, proper adaptive thresholds are obtained based on the reduced order sliding motion, which effectively improves incipient sensor fault detectability. Furthermore, different levels of detection decision schemes for incipient sensor fault development are proposed. The main contribution of this paper is as follows:
1. A novel FD sliding mode observer framework is proposed to get proper adaptive thresholds to improve incipient fault detectability.
2. Incipient sensor fault development detection schemes are studied and levels of detection decisions are proposed.
The remainder of this paper is organized as follows. In Section 2, preliminaries and assumptions are presented. In Section 3, the FDE sliding mode observer is proposed with parameters of observer being designed based on LMI and linear filter techniques. In Section 4, the sensor fault adaptive thresholds (for incipient fault, fault and failure) are designed and the continuous and piecewise continuous incipient sensor fault development detection decisions are made. In Section 5, case study of an application to the traction system in CRH (China Railway High-speed) is presented to demonstrate the obtained results. Section 6 concludes this paper.
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. فرمول بندی مسائل
2.1 توصیف سیستم و مدلسازی خطای سنسور
2.2 مقدمات و فرضیات
3. طراحی مشاهده گر مد لغزان FDE
4. طرح تصمیم تشخیص خطای سنسور
4.1 طرح تصمیمگیری مبتنی بر تشخیص خطا
4.1.1 طرح تصمیم گیری مبتنی بر تشخیص گسترش خطای اولیه سنسور
4.1.2 طرح تصمیم گیری مبنی بر تشخیص خطا
4.2 طرحهای قابلیت شناسایی خطا
4.2.1 طرح قابلیت شناسایی گسترش خطای اولیه به خطای سنسور
4.2.2 طرح قابلیت شناسایی گسترش خطای اولیه سنسور به شکست سنسور
5. مورد مطالعاتی
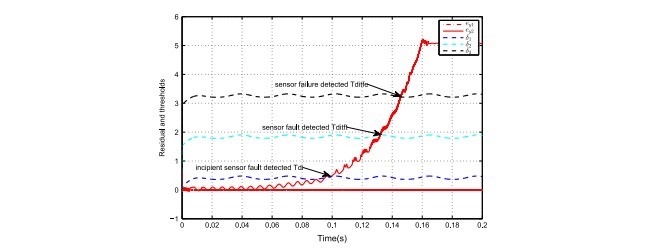
5.1 گسترش خطای اولیه سنسور بصورت پیوسته و تشخیص خطای سنسور
5.2 گسترش خطای اولیه سنسور بصورت پیوسته و تشخیص شکست سنسور
5.3 تشخیص خطای سنسور پیوسته تکهای
6. نتیجه گیری
منابع
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Problems formulation
2.1. System description and incipient sensor fault modeling
2.1. System description and incipient sensor fault modeling
3. FDE sliding mode observer design
4. Sensor fault detection decision schemes
4.1. Fault detection decision schemes
4.1.1. Incipient sensor fault developing detection decision schemes
4.1.2. Fault detection decision scheme
4.2. Fault detectability schemes
4.2.1. Incipient sensor fault developing to sensor fault detectability scheme
4.2.2. Incipient sensor fault developing to sensor failure detectability scheme
5. Case study: application to traction system
5.1. Continuous incipient sensor fault developing to sensor fault detection
5.2. Continuous incipient sensor fault developing to sensor failure detection
6. Conclusion
References
