
دانلود رایگان مقاله معماری SDN برای شبکه های رادیو شناختی
چکیده
بنا به حجم ترافیک خدمات متنوع و کمبود طیف، مفهوم ابر شبکه و رادیو شناختی میتواند ویژگیهای جدیدی در نسل بعدی تلفنهای همراه و شبکههای دسترسی بیسیم ایجاد کند. بهعنوانمثال، برای استقرار femtocells LTE و شبکههای Wi-Fi در فضاهای سفید تلویزیون راههای جدیدی برای تخلیهی ترافیک فراهم میکند که قادر به اشتراکگذاری طیف بهعنوان یک شبکهی رادیویی شناختی است. در این مقاله، ما یک نمونهی اولیه از شبکه با تعریف معماری نرمافزار و پروتکل OpenFlow برای بهاشتراکگذاری ناهمگن طیف شبکه در فضای سفید تلویزیون ارائه میکنیم. سپس، معماری کنترلر برای رادیو شناختی و زیرساخت معماری OpenFlow را مورد تجزیهوتحلیل قرار میدهیم. ما یک نمونهی اولیه از نرمافزار با تعریف شبکههای رادیو شناختی با کنترلر SDN و شبیهساز شبکه LTE / Wi-Fi پیادهسازی میکنیم. برخی از توابع کنترل ضروری از رادیو شناختی اجرا میشوند و حالات بالقوه جدید بر اساس شبکههای رادیو شناختی داده میشود.
1. مقدمه
بنا به روند طراحی شبکهی نشات گرفته از شبکه محور به مشتری محور، مفاهیم شبکه با تعریف نرمافزار (SDN) و عملکرد مجازیسازی شبکه (NFV) تکنیکهایی برای نسل بعدی اینترنت مانند ارتباطات تلفنهمراه G5 هستند. شبکهی سرویسگرا دسترسی مردم به اطلاعات درست مثل برق، آب و گاز در زندگی روزمره را پیشبینی میکند، بنابراین ما استدلال میکنیم که استفاده از طیف رادیویی یک سرویس است. متاسفانه، درحالحاضر دسترسی به فضای شبکههای رادیویی (RAN) کاملا ناهمگن است و آنها مانند LTE، Wi-Fi و WCDMA از یکدیگر جدا هستند. با این دیدگاه از رادیو شناختی، پارادایم استفاده از طیف جدید بهمنظور دسترسی کاربر تلفنهمراه به هر طیف ناهمگون قابل دسترس در اطراف آن لازم است. علاوهبراین، کیفیت تجربه کاربری (QoE) را میتوان تضمین کرد. از این رو، ما معتقدیم که معماری SDN/NFV حالت بالقوهای برای فعال کردن استفاده از طیف با تکنیکهای رادیویی شناختی در نسل بعدی اینترنت تلفنهمراه و یا G5 دارد.
حجم ترافیک برای آیندهی اینترنت تلفنهمراه در قالب دستورات در سال آینده افزایش خواهد یافت و منجر به آستانهی دادههای بزرگ در آینده خواهد شد. انتقال فیزیکی و کارایی طیفی برای ترویج بیشتر دشوار است، به این دلیل است که بهرهوری طیف LTE به بیست درصد رسیده است، که به مقدار شانون بسیار نزدیک است [1]. بهعنوان یک نتیجه، رادیو شناختی یک راه مهم برای فروش ترافیک برای شبکههای با سلول کلان به شبکههای Wi-Fi در G5 است. تراکم سلول کوچک با femtos LTE و Wi-Fi بدون برنامهریزی سلول ممکن است برای ارائهی طیف اشغال بیشتر برای هر کاربر با کاهش تعداد کاربران در هر سلول به نظر برسد. بااینحال، این مسئله منجر به یک مدیریت جامع شبکه، تحت معماری مشخص شبکه میشود. بنابراین، مفهوم جدیدی از SDN/NFV راه امیدوارکنندهای برای دخالت مدیریت و به اشتراکگذاری فعال طیف فراهم میکند.
بر اساس این دو دیدگاه، برای معماری نرمافزاری با تعریف شبکههای بیسیم (SDWN) برای RANهای ناهمگن و پهنای باند و برای سادهسازی مدیریت شبکه با یک پارادایم از طیفگرایی به G5 یک تعریف اختصاص دادیم. بهعنوان مثال، همزیستی LTE femtocells و Wi-Fi در فضای سفید تلویزیون بررسی شده است [2] [3]. موضوع اصلی مقاله میتواند به دو صورت خلاصه شود. یکی معماری ابر چند لایه پیشنهادی برای SDWN است. نمونهی اولیه برای سناریوهای رادیو شناختی تعریف شده با معماری SDN برای رادیو شناختی اجرا شده است. دیگری نمایش طیف توسعه یافته و مدیر طیف تحت معماری SDWN ارائه شده است. طیف جدید سناریوهای دسترسی/تحویل در شبکههای رادیویی شناختی بر اساس SDWN پشتیبانی میشوند.
ساختار مقاله به صورت زیر بیان میشود: در بخش دوم، به مرور پیش زمینهای از SDWN و مفهوم توسعه یافتهی اخیر در G5 بر اساس رادیو شناختی میپردازیم. سپس، معماری چند لایه SDWN برای RAN های ناهمگن را در بخش سوم تعریف میکنیم، که قادر به اشتراکگذاری طیف در فضای سفید تلویزیون و جداسازی دادهها/نقشههای کنترل با رابطOpenFlow در زیرساختها است. بخش چهارم طراحی نمونه اولیه و اجرا با ویژگیهای جدید برای SDWN فعال با اشتراکگذاری طیف را معرفی میکند. در پایان، نتیجهگیری مقاله در بخش پنج ارائه میشود.
2. پیشزمینهی رادیو شناختی و SDWN
این مقاله بهمنظور توسعهی رادیو شناختی با استفادهی عملی در معماری نرمافزار با تعریف شبکه مصمم است، چون بحث ما، استفاده از طیف بهعنوان یک سرویس در شبکههای تلفن همراه G5 است و سیاست اشتراکگذاری طیف و برنامهریزی مجدد نرمافزار بهعنوان یک کنترلر SDWN میتواند تعریف شود. اندازهگیری گسترده در مناطق شهری در جهان نشان داده است که کارایی طیفی در محدودهی 300MHZ به 3GHz با تنوع بالای فضا-زمانی ضعیف است [4]. تحقیقات قبلی در رادیو شناختی تمرکز بر بهبود منابع استفاده از طیف رادیویی بهطورعمده در مدلهای کاربر اولیه-ثانویه در باند تلویزیون UHFدارد. بهعنوانمثال، سناریوی LTE femtocell و Wi- Fi مستقر در فضای سفید تلویزیون اجازه میدهد تا اپراتورهای تلفنهمراه، میزان و ظرفیت شبکه را بهبود دهند و بااینحال CAPEX و OPEX را کاهش دهند.
بنابراین در ارتباطات بیسیم G5، برای مشاهدهی چالش مورد ظرفیت بزرگ، اتصال عظیم، قابلیت اطمینان بالا و زمان تاخیر کم، انتظار میرود رادیو شناختی نقش مهمی در دو جنبه بازی کند. ابتدا، طیف برای G5 را به 60GHz محدودهی موج میلیمتری تمدید خواهد کرد، استفاده از رادیو شناختی را میتوان بهمنظور بهبود استفاده از طیف در نوع جدیدی از به اشتراکگذاری مدل طیف، مانند طیف پویا توسعه داد [5]. ثانیا، G5 استفادهی مجدد فضایی تهاجمی از طیف را بهعنوان یک توانمندساز با روشهای جدید مانند MIMO و فوقالعاده متراکم را در بر خواهد گرفت. در این زمینه، رادیو شناخت را میتوان برای کنترل مسائل دخالت از فضا، فرکانس و دامنهی زمان با شیوهای بسیار هوشمندانه مورد استفاده قرار داد. ازسویدیگر، معماری SDWN مبتنی بر کنترل هماهنگی فرصتهایی برای مدیریت شبکههای بیسیم ناهمگن در طیف را فراهم میکند، که یک سرویس جدید در کنترل را تعریف میکند و بهعنوان یک جزء اساسی از سیستمعامل شبکه، بهعنوانمثال، نورافکن اجرا میکند. در این مقاله، یک معماری لایهبندی SDWN برای سناریو همزیستی در یک شبکه ناهمگن از LTE femtocell و شبکه Wi-Fi در فضای سفید تلویزیون با OpenFlow طراحی میکنیم. OpenFlow یک پروتکل است که، در دانشگاه استنفورد، برای فعال کردن سوئیچها در شبکه سیمی هوشمند و برنامهریزی از طریق یک رابط استاندارد آغاز شده است. پروتکل OpenFlow توسط ONF برای کاهش هزینه عملیات استاندارد استاندارد شده است درحالیکه مدیریت شبکه و نوآوری سرعت شبکه بهسادگی انجام میگیرد[6]. علاوهبراین، OpenFlow از شبکه سیمی به زیرساختهای بیسیم به عنوان OpenRoadتمدید شده است. OpenRoad برای حل مشکل تحرک با توپولوژی 5 سوئیچ، 30 Wi-Fi و یک وایمکس اختصاص داده شده است [7] [8]. کنترلر SDN از مشکل تحویل بدون درز بین Wi-Fi و وایمکس با موفقیت رد شده است. تا حال حاضر، OpenFlow در شبکههای مش بیسیم [9]، شبکههای حسگر [10] و شبکههای تلفن همراه استفاده شده است [11]. flowvisior یک تکنیک اولیه NFV برای SDWN است[12].
3. مسائل مربوط به معماری در شبکههای رادیو شناختی براساس SDN
A) معماری SDN برای شبکههای رادیو شناختی
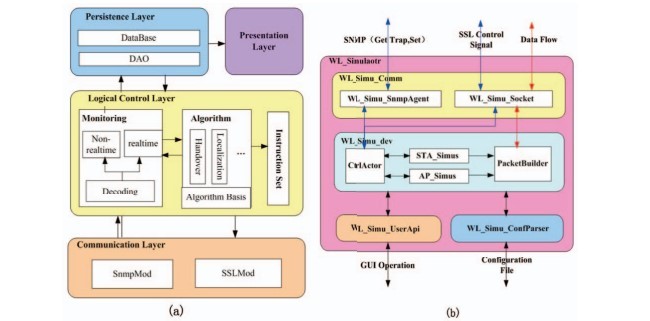
با نگاه به رادیو شناختی برای نسل بعدی ارتباطات تلفنهمراه، فرض میکنیم که هر eNodeB یا STA میتواند در بخشی از باند و رادیو در یک طیف وسیعی با نرمافزار تکنیکهای رادیویی مجددا پیکربندی شود، که پشتیبانی ضروری برای اجرای رادیو شناختی در این مقاله است. ما در تلاش برای تجزیهوتحلیل نیازمندیهای طراحی با چشمانداز و مفروضات هستیم. طرح کنترل جدید و پیشنهاد شده انتظار میرود که برای مدیریت تداخل و کنترل در همزیستی شبکههای بیسیم ناهمگن پاسخگو باشد. مکانیسم ارزیابی تداخل و تشخیص رویداد باید با عملکرد نظارت شبکه ارائه شده باشد. هنگامی که کنترلر تشخیص اتفاق میافتد، کنترلر برای ارسال تحویل طیف به مشتریان دستور خواهد داد. این نوع روش برای تحرک طیف باید برای مشتریان آشکار شود و QoE باید در آن در نظر گرفته شود.
Abstract
Driven by the requirements from traffic volume versatile services and spectrum scarcity, the concept of cloud network and cognitive radio could become new features in the next generation mobile and wireless access networks. For example, to deploy LTE femtocells and Wi-Fi networks in the TV white spaces provides a new way for traffic offloading and enables spectrum sharing as a cognitive radio network. In this paper, we propose and prototype a software defined network architecture with the OpenFlow protocols for heterogeneous network spectrum sharing in the TV white space. Then, we analyze the controller architecture for cognitive radio and the OpenFlow enabled infrastructure architecture. We implement a prototype of software defined cognitive radio network with this SDN controller and LTE/Wi-Fi network simulator. Some essential control functions of cognitive radio are implemented and new potential scenarios based cognitive radio networks are given.
I. INTRODUCTION
With the trend of network design moving from the network centric to the client centric, the concepts of software defined network (SDN) and network function virtualization (NFV) are candidate techniques for the next generation Internet as well as the 5G mobile communication. The service-oriented network envisions people access the information just like the electricity, water and gas in the daily life, so we argue that radio spectrum usage is also a service. Unfortunately, the current radio access networks(RAN) environment is fundamentally heterogeneous and they are isolated each other, such as LTE, Wi-Fi and WCDMA. With a view of cognitive radio, a new spectrum usage paradigm is required in order to allow the mobile user access any reachable heterogeneous spectrum around it. Furthermore, quality of user experience(QoE) can be guaranteed . Therefore, we believe SDN/NFV architecture is potential to enable novel spectrum usage with the cognitive radio techniques in the next generation mobile internet or 5G.
The traffic volume for the future mobile Internet increases in form of orders of magnitude in the coming year and leads the eve of big data coming. The physical transmission and spectral efficiency is difficult to get promoted further, because the spectrum efficiency of LTE has reached within the twenty percent, as is very close to the shannon capacity limit[1]. As a result, cognitive radio is an important way to offload traffic for the macro-cell networks to the dense deployed femtocells and Wi-Fi networks in the 5G. The dense small-cell deployment with LTE femtos and Wi-Fi without cell planning may appear to provide more spectrum occupancy per user by reducing the number of users per cell. However, this leads to a complex network management under the network architecture already defined. Therefore, the new concept of SDN/NFV provides us a promising way to manage interferences and enable dynamic spectrum sharing.
Based on the two observation, we are dedicated to define a software defined wireless network (SDWN) architecture for the heterogeneous and broadband RANs to simplify network management with a novel spectrum usage paradigm oriented to 5G. As an example, the coexistence of LTE femtocells and Wi-Fi has been investigated in TV white space[2][3]. The main contributions in the paper can be summarized as two. One is a multi-tiered cloud architecture proposed for the SDWN. A prototype for cognitive radio scenarios defined with this SDN architecture has been implemented for cognitive radios. The other is a developed spectrum monitor and spectrum manager are proposed under the SDWN architecture. New spectrum access/handover scenarios are supported in a SDWN based cognitive radio networks.
The organization of this paper is defined as as following: In the section II, we review the background of SDWN and the recent developed concept of 5G oriented cognitive radio. Then, we define a multi-tiered SDWN architecture for heterogeneous RANs in the section III, which enables the spectrum sharing in TV white space and decouples the data/control planes with an Openflow interface in the infrastructure. Section IV introduces an initial prototype design and implementation with the new features for the SDWN enabled spectrum sharing environment. In the end, we make conclusions for the paper in the section V.
II. BACKGROUND OF COGNITIVE RADIO AND SDWN
This paper is motivated to develop cognitive radio with a practical usage in the software defined network architecture, because our argument is spectrum usage is also a service in 5G mobile networks and spectrum sharing policy could be defined and reprogrammable by software as a SDWN controller. The extensive measurements carried out in the major urban areas in the world have shown that the spectral efficiency is poor in a range of 300MHz to 3GHz with a high spatio-temporal variation[4].The previous research on the cognitive radio was focusing on improving the radio spectrum utilization resources mainly within the primary-secondary user models in the UHF TV band. For example, the scenario of LTE femtocell and WiFi deployed in TV white space allows the mobile operators to improve coverage and capacity of their network and reduce their CapEx and OpEx.
However, in the 5G wireless communications, to meet the challenge requirements of huge capacity, massive connectivity, high reliability and low latency, cognitive radio is expected to play an important role in two aspects. First, since the spectrum band for 5G will be extended to even 60GHz millimeter-wave range, the usage of cognitive radio can be extended to improve the spectrum utilization within new types of spectrum sharing models, such as dynamic licensed spectrum leasing[5]. Second, 5G will take aggressive spatial reuse of spectrum as a enabler with new techniques such as massive MIMO and Ultra-dense Deployment. In this context, cognitive radio can be used to control the interference issues from space, frequency and time domains with a very smart manner. On the other hand, the controller-based SDWN architecture provides the coordination opportunities for heterogeneous wireless network management on spectrum and interferences, which is defined a new service on controller and implemented as an essential component of the network operation system, e.g. Floodlight. In this paper, we design an layered SDWN based architecture for the coexistence scenario in a heterogeneous network of the LTE femtocell and Wi-Fi network in the TV white space with Openflow. Openflow is a protocol, initiated at Stanford, to enable switches on the wired network to be intelligent and programmable via a standardized interface. The Open-Flow protocol is standardized by the ONF to mitigate operation cost while simply network management and speed network innovation[6]. Furthermore, Openflow has been extended from wired network to wireless infrastructures as OpenRoad. The OpenRoad is dedicated to solve mobility problem with a topology with 5 switches, 30 Wi-Fi APs and a WiMax AP[7][8]. The SDN controller deals with the seamless handover problem between Wi-Fi and WiMax successfully. Till now, Openflow has been used in wireless mesh network[9], sensor networks[10], and cellular networks[11]. The flowvisior is an initial NFV techniques for SDWN[12].
III. ARCHITECTURE ISSUES IN SDN BASED COGNITIVE RADIO NETWORKS
A. SDN Architecture for Cognitive Radio Networks
With the vision of cognitive radio for the next generation mobile communication, we assume whatever eNodeB or STA can be reconfigurable on the part of baseband and radio in a large range with the software defined radio techniques, which is essential support to implement the cognitive radio defined in this paper. We attempt to analyze design requirement with the vision and assumptions. The new proposed control plane is expected to be responsible for interference management and control in the coexistence of heterogeneous wireless network. The mechanism of interference appraisal and event detection should be provided with the network state monitoring function. Once the controller detects the event happened, controller will decide to send clients the spectrum handover command. This kind of method for spectrum mobility should be apparent to clients, and the QoE should be considered within it.
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. پیشزمینهی رادیو شناختی و SDWN
3. مسائل مربوط به معماری در شبکههای رادیو شناختی براساس SDN
A) معماری SDN برای شبکههای رادیو شناختی
B) مدیریت شبکه با نظارت برای رادیو شناختی
C) طرح جداسازی داده/کنترل برای رادیو شناختی
4. نمونهی SDN برای رادیو شناختی
A) اجرای مجازیسازی کنترلر ابر
B) معماری کنترلر برای رادیو شناختی
C) شبیهساز شبکههای بیسیم جریان باز
D) سناریو: دسترسی/ اجاره طیف
E) سناریو: تحویل/ تحرک طیف
F) سناریو: برش/ مجازیسازی طیف
5. نتیجهگیری
منابع
Abstract
1. INTRODUCTION
2. BACKGROUND OF COGNITIVE RADIO AND SDWN
3. ARCHITECTURE ISSUES IN SDN BASED COGNITIVE RADIO NETWORKS
A. SDN Architecture for Cognitive Radio Networks
B. Network management with monitoring for cognitive radio
C. Data/Control plane decouple for cognitive radio
4. SDN PROTOTYPE FOR COGNITIVE RADIO
A. Cloud-controller virtualization implementation
B. Controller architecture for cognitive radio
C. Open-Flow Wireless Network Simulator
D. Scenario: Spectrum access/lease
E. Scenario: Spectrum handover/mobility
F. Scenario:Spectrum slicing/virtualization
5. CONCLUSION
REFERENCES
