
دانلود رایگان مقاله تشخیص عمق لبه با عملیات هموار کردن و مورفولوژیکی تصویر
چکیده
از آنجا که فنآوری اندازهگیری سه بعدی بهطورگسترده در صنایع تولیدی تشخیص لبه در یک تصویر عمق استفاده شدهاند بنابراین نقش مهمی در برنامههای کاربردی بینایی کامپیوتر دارند. در این مقاله، یک فرآیند تشخیص لبه در یک تصویر عمق براساس عملیات هموار کردن و مورفولوژیکی پیشنهاد شده است. در این روش از اصل فیلتر میانه، که دارای یکی از ویژگیهای مشهور برای حفظ خواص لبه است استفاده کردهایم. تشخیص لبه براساس اصل تشخیص لبه canny انجام شده است و با عملیات مورفولوژیکی به سرانجام رسیده است، که بهعنوان ترکیبی از erosion و dilation نشان داده شده است. سپس، نتایج حاصل را با برخی از روشهای موجود مقایسه کرده و نشان دادیم که این روش نتایج بهتری تولید میکند. اما، این روش در برنامههای کاربردی چند فریمی با نرخ فریم موثر کار میکند. بنابراین این روش به تشخیص عمق لبه در تصاویر و ترویج برنامههای کاربردی در تشخیص عمق تصاویر مانند تشخیص شی، تقسیمبندی جسم و غیره کمک خواهد کرد.
1. معرفی
همانگونه که عمق لبه نشاندهندهی خطوط شی است [1،2]، تشخیص مناسب لبه نیز نقش مهمی در مسائل مختلف بینایی کامپیوتر ارائه میکند. نگاشت لبه حاوی بخشی از اطلاعات هندسی از صحنههای طبیعی؛ بهخصوص در مورد عمق تصاویر است، ناپیوستگیهای عمق موجب میشود اشیاء پیشزمینه از پسزمینه جدا شود و برای کارهای پردازش تصویر مختلف از جمله تقسیمبندی و یا حذف نویز استفاده شود [3]. حتی اگر پیشرفت سریعی در زمینه طبقهبندی تصویر وجود داشته باشد [4-6] تشخیص جسم هنوز هم به عنوان یک موضوع تحقیقاتی فعال است.
فنآوری اندازهگیری سه بعدی بهطورکلی براساس محاسبه اطلاعات عمق اشیاء موجود در صحنه است. برخی مطالعات در زمینه فنآوریهای اندازهگیری سه بعدی وجود دارد، که در آن محققان در حال تلاش برای به دست آوردن اطلاعات در مورد عمق اشیاء موجود در یک صحنه با استفاده از دوربینهای استریو هستند [7-9]. با این حال، این روش محدود است، زیرا دوربینهای استریو قادر به عمل در صحنههای حاوی بافت فراوان هستند. برخی افراد از لیزر سه بعدی استفاده کردند [10،11] و موفق به تولید اطلاعات عمق دقیق شدند. اما آنها نمیتوانند از این دستگاه برای برنامههای کاربردی زمان واقعی با توجه به دستگاههای گران قیمت استفاده کنند. حتی برخی از روشهای مبتنی بر الگو [12-15] برای تولید یک نگاشت عمق استفاده شدند اما این روش با توجه به دوربینهای دیجیتال و موقعیت شی محدودیتهایی داشت. بنا به رشد سریع دسترسی به سنسور ارزان RGB-D مانند نخستین حسگر اپل، کینکت مایکروسافت، حسگر واقعی اینتل و غیره، پیشرفتهای بسیاری برای وظایفی نظیر مدلسازی سه بعدی[16]، تقسیمبندی [17] و برآورد طرح اتفاق افتاده است [18،19]. اگرچه این سنسورها برای رسیدن به نگاشت عمق به ما کمک میکنند اما تعداد کمی از روشها برای تجزیهوتحلیل این روش در تشخیص لبه استفاده شده است.
تشخیص دقیق لبه از یک تصویر عمق در برخی از فرآیندهای تشخیص شی [20]، که وابسته به یک مدل خاص هستند ضروری است. روند تشخیص لبه مناسب، میتواند برای تجزیهوتحلیل اعمال مختلف افراد [21] در یک محیط واقعی مانند پیادهروی مورد استفاده قرار میگیرد. فرآیندهای تشخیص لبه موجود در تصاویر عمق، نمیتوانند در این نوع شرایط با توجه به برخی از محدودیتهای موجود اعمال شوند. اگر برخی از روشهای تشخیص لبه در تصاویر عمق [22] موفق به ارائه تصاویر عمق بدون نویز نشوند؛ در نتیجه تشخیص لبه مناسب نمیتواند حاصل شود.
برخی از روشهای دیگر نیز[22،23] در تشخیص لبه در تصاویر عمق مطالعه میکنند. با این حال، آنها فقط بر روی تک فریم کار میکنند. وقتی آن روشها در مسائلی که نیاز به پردازش چندفریمی دارند اعمال میشوند، ممکن است با شکست مواجه شوند و نمیتوانند با نویزهای تولید شده در هر فریم، مانند مشکلات مثل نور مقابله کنند.
در این مقاله، یک روش پیشنهاد دادیم که میتواند لبههای عمیق تر تصاویر عمق را تشخیص دهد. این روش میتواند لبههای پیوسته را تشخیص دهد چرا که تشخیص یک شیء بزرگ از یک تصویر مانند بدن انسان بسیار مهم است. برای تشخیص لبه پیوسته، روش تشخیص لبه Canny با عملیات مورفولوژیکی ترکیبی اصلاح شده است. عملیات مورفولوژیکی بهطورکلی با شکل ویژگیهای تصویر سروکار دارند. که برای حذف عیب و نقص از انواع مختلف شکل مانند مرزهای جسم، اسکلت، و غیره استفاده شده است. این عملیات به طورکلی شامل دو اپراتور ؛ فرسایش (erosion) و اتساع (dilation) هستند. اولین عمل، به باز کردن، هموار کردن شی کانتور، شکستن نوار باریک و حذف برآمدگیهای نازک اشاره دارد. عمل دوم، به بسته شدن، هموار کردن خطوط در مقایسه با باز کردن؛ ترکیب برآمدگیهای نازک، از بین بردن سوراخ و پر کردن شکاف اشاره دارد. این روش در چندفریم کار میکند، درحالیکه روش قبلی لبهها را در یک قاب تشخیص میدهد.
این مقاله به صورت زیر سازماندهی شده است: بخش 2 چارچوب کلی سیستم ارائه شده را توضیح میدهد. همچنین روشی که توسط آن یک تصویر عمق به دست میآید ارائه شده است. در بخش 3، یک فرایند صاف کردن تصویر عمق ارائه میکنیم. بخش 4 نشان دهنده یک روند تشخیص لبه در تصویر عمق است. بخش 5 نشاندهندهی نتایج تجربی برای صحنههای مختلف و مقایسه نتایج خود با یک روش موجود است. سرانجام بخش 6 نتیجهگیری این مقاله همراه با برخی از دستورالعملها برای کار در آینده را امکانپذیر میکند.
2. چارچوب کلی
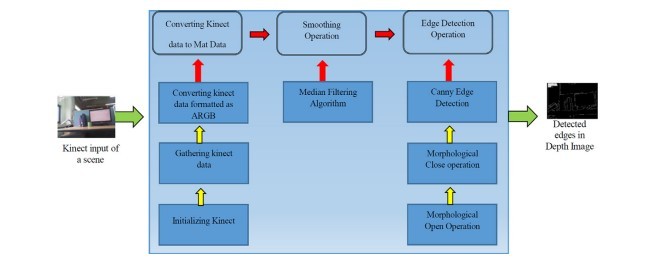
در شکل 1 چارچوب کلی سیستم پیشنهادی نشان داده شده است. در اینجا، یک تصویر عمق با استفاده از مایکروسافت کینکت به دست آمده است. دادههای به دست آمده از کینکت به یک روش خاص پردازش میشوند. پس از پردازش مناسب دادههای کینکت، تصویر عمق را برای کاهش سطح نویز با استفاده از اصل فیلتر میانه هموار میکنیم. سپس، در تلاش برای تشخیص لبه با هموار کردن تصویر عمق هستیم. در اینجا، از اصل تشخیص لبه canny استفاده میکنیم و آن را با عملیات مرفولوژی برای به دست آوردن عملکرد بهتر اصلاح میکنیم. عملیات مورفولوژیکی عملیات باز و بسته شدن هستند. در این بخش در مورد روش فنی برای به دست آوردن عمق تصویر از کینکت و پردازش آن را برای برنامههای اضافی بحث میکنیم. مایکروسافت برخی کتابخانهها را که در این کار برای دستیابی به عمق تصویر استفاده شده است فراهم میکند. بااینحال، برخی کارهای قبل از پردازش برای استفاده از مایکروسافت کینکت وجود دارد. تابع NuiGetSensorCount برای اطمینان از تعداد سنسورهای آماده استفاده، استفاده شده است. تابع NuiImageResolutionToSize برای اطمینان از تعداد سنسورهای آماده برای استفاده، استفاده شده است. تابع NuiImageResolutionToSize برای به دست آوردن عرض و ارتفاع قاب عمق و تابع INuiSensor NuiImageStreamOpen برای مقداردهی اولیه سنسور به جریان داده های عمق استفاده شده است. هنگامی که شروع به گرفتن جریان عمق کردیم دادهها را از فریم بعدی با استفاده از INuiSensor: NuiImageStreamGetNext و با استفاده از INuiSensor: NuiImageStreamRelease گرفتیم بنابراین هر فریم پس از ذخیره آن منتشر شده است.
Abstract
Since 3D measurement technologies have been widely used in manufacturing industries edge detection in a depth image plays an important role in computer vision applications. In this paper, we have proposed an edge detection process in a depth image based on the image based smoothing and morphological operations. In this method we have used the principle of Median filtering, which has a renowned feature for edge preservation properties. The edge detection was done based on Canny Edge detection principle and was improvised with morphological operations, which are represented as combinations of erosion and dilation. Later, we compared our results with some existing methods and exhibited that this method produced better results. However, this method works in multiframe applications with effective framerates. Thus this technique will aid to detect edges robustly from depth images and contribute to promote applications in depth images such as object detection, object segmentation, etc.
1. Introduction
As depth edges represent object contours [1,2], proper edge detection offers a significant role in various computer vision problems. Edge maps contain part of geometric information of natural scenes; especially in the case of depth images, depth discontinuities separate foreground objects from the background and can be used for various image processing tasks such as segmentation or denoising [3]. Even though there have been some rapid progresses in the field of image patch classification [4–6] object detection is still an active research topic.
The 3D measurement technology is generally based on calculating depth information of objects in a scene. There has been some work in 3D measurement technologies, where researchers tried to acquire the depth information of objects in a scene by using stereo cameras [7–9]. However, this approach is limited because stereo cameras are able to work in the scenes containing plentiful textures. Some people used three dimensional laser range finders [10,11]. They were successful to produce accurate depth data. But they cannot use this device to real-time applications due to their expensive apparatus. Even some patternbased methods [12–15] were used to produce a depth map but those methods also have some limitations with respect to the cameras and object positions. Since the rapid growth of the availability of inexpensive RGB-D sensors such as Apple Prime Sense, Microsoft Kinect, Intel Real Sense, etc., a lot of breakthroughs have been achieved for several tasks such as 3D modeling [16], segmentation [17] and body pose estimation [18,19]. Though these sensors helped us to achieve depth maps but very few methods have been applied to analyze such maps in terms of edge detection.
Accurate edge detection from a depth image is essential for some object detection processes [20], which are dependent on a model of particular shape. A proper edge detection process can be used for various Human action analysis [21] problems in a real environment such as walking, spotting and sitting. Existing edge detection processes in depth images, however, cannot be applied in these types of situations due to some limitations. Some methods of edge detection in depth images [22] failed to deliver noise-free depth images; thus proper edge detection cannot be achieved.
Some other methods [22,23] work in edge detection in depth images. However, they only work for a single frame. When they are applied to problems requiring processing multi-frames, these methods may fail as they cannot deal with newly generated noises in each frame, such as flickering problems.
In this paper, we proposed a method that can detect edges from depth images more profoundly. This method can detect continuous edges, which are very important when we try to detect a large object from an image such as a human body. To detect continuous edges, we modified the Canny edge detection method by incorporating morphological operation. The morphological operation generally deals with shape of features in an image. It has been used to remove imperfections from various types of shape such as object boundaries, skeletons, etc. This operation generally consists of two operators; erosion and dilation. The first operation, denoted as opening, smooths the contour object, breaks narrow strips and eliminates thin protrusions. The second operation, called closing, also smooths contours but in contrast with opening; it fuses thin discontinuities, eradicate trivial holes and fills gaps in the contour. This method also works in multi-frames, whereas the previous methods detect edges in a single frame.
This paper is structured as follows: Section 2 explains the overall framework of the proposed system. It also presents the way by which a depth image is acquired. In Section 3, we present a process for smoothing the depth image. Section 4 represents an edge detection process in the depth image. In Section 5 we show our experimental results for different scenes and compare our results with an existing method. Finally Section 6 concludes this paper along with some directions for possible future work.
2. Overall framework
In Fig. 1 we have illustrated the overall framework of the proposed system. Here, a depth image has been acquired by using Microsoft Kinect. The data captured from Kinect has to be processed in a certain way. After proper processing of the Kinect data we smooth the depth image for reducing the level of noises using the principle of Median filtering. Later, we move on to the edge detection process with the smoothed depth image. Here, we use the principle of Canny Edge Detection and modified it with Morphological operations for gaining better performance. The morphological operations are opening and closing operations. In this section we discuss the technical approaches for gaining the depth image from Kinect and process it for additional applications. Microsoft provides some built-in libraries which have been used in this work for acquiring the depth image. However, there are some preprocessing task for using Microsoft Kinect. NuiGetSensorCount function has been used to make sure the numbers of sensors ready for use. NuiImageResolutionToSize function has been used to make sure the numbers of sensors ready for use. NuiImageResolutionToSize function has been used to acquire the width and height of the depth frame and INuiSensor:: NuiImageStreamOpen function has used to initialize the sensor to stream out the depth data. Once we have started to get the depth stream we had started to capture the data from the next frames by using INuiSensor:NuiImageStreamGetNextFrame and by using INuiSensor:NuiImageStreamReleaseFrame each frame has been released after saving it.
چکیده
1. معرفی
2. چارچوب کلی
3. الگوریتم هموارسازی تصویر
4. الگوریتم تشخیص لبه در تصویر عمق
4.1. الگوریتم تشخیص لبه canny
4.1.1. روند الگوریتم تشخیص لبه canny
4.2. اصلاح الگوریتم تشخیص لبه canny
4.2.1. باز شدن
4.2.2. بسته شدن
5. نتایج و مقایسهها
6. نتیجهگیری
منابع
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Overall framework
3. Depth image smoothing algorithm
4. Edge detection algorithm in depth image
4.1. Canny Edge detection algorithm
4.1.1. Process of Canny Edge detection algorithm
4.2. Modification of Canny Edge detection algorithm
4.2.1. Opening
4.2.2. Closing
5. Results and comparison
6. Conclusion
References
