
دانلود رایگان مقاله ارزیابی قابلیت اطمینان خستگی عرشه پل متعامد تحت بارگیری احتمالی کامیون
رشد ثابت ترافیک تهدیدی برای ایمنی خستگی پل های بحساب می آید. بی ثباتی در جریان ترافیک باعث افزایش چالش ارزیابی دقیق ایمنی خستگی می گردد. این مقاله از نمونه بار ترافیک تصادفی بمنظور ارزیابی قابلیت اعتماد خستگی پل روگذر فلزی متعامد بهره برده است. نمونه بار ترافیک بوسیله اندازه گیری های مخصوص مکان-در حال-حرکت شبیه سازی می گردد. روش سطحی واکنش بمنظور حل مسئله زمان بر ایجاد شده بوسیله شبیه سازی های تنش نقطه حساس در نمونه مؤلفه محدود ارائه شده است. کاربردهای نمونه بار ترافیک اتفاقی برای ارزیابی شبیه سازی احتمالی و قابلیت اعتماد خستگی در مورد مطالعه پل تیر آهن فولادی نشان داده شده اند. نتایج عددی اشاره کرده که میزان رشد وزن ناخالص وسیله نقلیه منجر به کاهش سریع قابلیت اعتماد خستگی در مقایسه با رشد حجم ترافیک می گردد. با وجود رشد حجم ترافیک، کنترل کامیون های بارگیری شده در مقایسه با حجم ترافیک روشی موثر جهت اطمینان از قابلیت اعتماد خستگی پل-های فولادی می گردد.
1. مقدمه
تجمع خسارت خستگی یکی از مسائل مهم منجر به سقوط اکثر پل های فولادی می گردد. بر اساس مطالعه صورت گرفته توسط کمیته ASCE، حدود %80 تا %90 شکست پل های فولادی بدلیل مسائل خستگی یا شکستگی رخ می دهد. بطور کلی، مؤلفه مهم خستگی یک پل فولادی با مقاومت کافی در برابر خستگی و خستگی زندگی در برابر بار محوری چرخه ای طراحی شده است (4-2). بهرحال، افزایش مداوم در حجم ترافیک و وزن ناخالص وسیله نقلیه (GVW)، بدلیل رشد سریع و گسترش تحولات در حمل و نقل میان شهری و بین ایالتی، باعث ایجاد اطمینان خستگی پل های موجود گردیده است (5،6). بی ثباتی در جریان ترافیک، منجر به چالش ارزیابی صدمه خستگی دقیق می گردد. مؤلفه های بحران خستگی اکثر پل های فلزی بزرگراه اتصال جوش در صفحات عرشه هستند که ثابت قرار دادن سنسورهای کرنش مشکل می باشد. در نتیجه، ارزیابی قابلیت اعتماد خستگی عرشه های پل متعامد با توجه به بارهای ترافیکی واقعی هنوز به عنوان یک چالش محسوب می گردد.
یک گام حیاتی بمنظور ارزیابی قابلیت اعتماد خستگی پل ها نمونه سازی احتمالی محدوده تنش خستگی بشمار می شود. در این خصوص، اکثر پژوهشگران در سیستم نظارت سلامت ساختاری (SHM) بمنظور تجزیه و تحلیل آماری از سنجش فشار بهره بردند (9-7). بهرحال، کاربرد سیستم SHM بوسیله هزینه سنگین آن و اهداف مشخص شده محدود معین گردیده است. با توسعه تکنولوژی های سنسور، سیستم وزن-در-حرکت مختص مکان (WIM) که ابتدا برای مدیریت ترافیک مورد استفاده قرار گرفته، بمنظور تجزیه و تحلیل آماری بارهای ترافیکی مورد بهره برداری قرار گرفته است (10). بنابراین یکپارچه سازی سنجش WIM مختص مکان و روش مؤلفه محدود به یک رویکرد کاربردی برای ارزیابی قابلیت اعتماد خستگی پل های مورد استفاده تبدیل می گردد. رویکردهای تحلیلی متعدد در این مبحث ارائه شده است. مثلا، Wang و همکاران یک چارچوب محاسباتی بمنظور ارزیابی افزایش صدمه خستگی پل فولادی بوسیله ادغام محاسبات FE و داده های SHM ایجاد و توسعه دادند. GUO و همکاران (12) از یک نمونه FE احتمالی چند مقیاسی جهت ارزیابی قابلیت اعتماد خستگی پل روگذر فولادی متعامد بهره بردند. Zheng و همکاران (13) از یک رویکرد مواد متعامد برابر بمنظور شبیه سازی بار پویایی در نمونه FE بهره بردند. Ye و همکاران حساسیت اندازه و نوع مؤلفه را در محاسبات تنش ساختاری تحت بار وسیله نقلیه مورد مطالعه قرار دادند. Zhang و Au (15) یک نمونه بار احتمالی پیشرفته جهت شبیه سازی بار کامیون در پل بر اساس اندازه WIM ارائه داده و قابلیت اعتماد خستگی و خدمات باقیمانده عمر پل را ارزیابی می کنند. با توجه به توضیحات فوق، ادغام داده های ترافیکی بررسی شده و شبیه سازی عددی مبتنی بر FE رویکردی موثر در ارزیابی قابلیت اعتماد خستگی پل های فولادی بحساب می آید.
مدلسازی بار ترافیکی یک رویه بسیار مهم برای ترکیب کردن اندازه گیری و سنجش WIM و روش FE ارزیابی قابلیت اعتماد خستگی پل های فولادی بشمار می رود. نمونه خستگی با کامیون که در مشخصات طراحی ملی تعیین گردیده و چندین نمونه بار کامیون پیشرفته در شروع توضیحات مرسوم می باشد. در این رابطه، Laman و Nowak (17) یک نمونه بار کامیون سه محوری بر اساس اندازه گیری و سنجش WIM توسعه دادند. Chotickai و Bowman (18) یک نمونه بار کامیون چهار محوری توسعه بخشیده و اشاره کردند که نمونه بار کامیون AASHTO را می توان در پل های با فاصله کوتاه زیاد برآورد کرد. Lan و همکاران (19) طیف بار ترافیکی و پیش بینی حجم ترافیک را برای تغییر شکل صدمه خستگی پل ها با هم ترکیب کردند. Chen و همکاران (20) از بارهای ترافیکی جهت ارزیابی عملکرد خستگی طاق پل بهره بردند. علاوه بر پیکربندی کامیون نشان داده شده در بالا، تأثیر پویا بدلیل تعامل وسیله نقلیه و پل بر طیف تنش خستگی تأثیر می گذارد (21). از آنجاییکه پارامترهای ترافیکی (مثلا نوع وسیله نقلیه، سرعت رانندگی، فاصله گذاری وسیله نقلیه و GVWs) بصورت تصادفی در طبیعت وجود دارند، اطلاعات آماری تمام کامیون ها در نمونه های بار کامیون مذبور قرار ندارد. بنابراین یک نمونه بار ترافیکی اتفاقی برای ارزیابی دقیق تجمع آسیب خستگی ضروری می باشد. بهرحال، با توجه به اطلاعات نویسندگان، اکثر تلاش های پژوهشی مرتبط راجع به نمونه بار ترافیکی اتفاقی بر تجزیه و تحلیل تعامل پل-وسیله نقلیه تمرکز نموده (22،23)، در حالیکه تحقیق در مورد کاربرد نمونه بار ترافیکی اتفاقی برای ارزیابی قابلیت اعتماد خستگی پل های فولادی ناکافی بنظر می-رسد.
هدف از این مطالعه توسعه نمونه بار ترافیکی اتفاقی بر اساس سنجش WIM مختص مکان جهت ارزیابی قابلیت اعتماد خستگی پل روگذرفولادی تصادفی می باشد. چارچوب محاسباتی که شبیه سازی تنش نقاط حساس قطعی مبتنی بر FE و مدلسازی احتمالی محدوده تنش را با هم ترکیب نموده در اینجا ارائه شده است. در مطالعه موردی، یک پل فولادی با جعبه تیر آهن به عنوان نمونه اصلی جهت نشان دادن اثر کاربرد نمونه بار کامیون خستگی اتفاقی انتخاب شده است. تأثیر پارامترها نمونه بار کامیون اتفاقی در مورد شاخص قابلیت اعتماد خستگی مورد بررسی قرار گرفته است.
2. نمونه بار ترافیک اتفاقی
بطور کلی نمونه خستگی بار کامیون که شامل پیکربندی قطعی و بار محوری بوده، بمنظور ارائه بارگیری ترافیک مختص مکان استفاده شده است. نمونه خستگی بار کامیون از طریق طیف بار ترافیک واقعی بر اساس معیار تجمع آسیب خستگی هم ارز ارزیابی شده است. بهرحال، بدلیل ترکیب بندی قطعی و بار محور، نمونه بار خستگی جهت استفاده در مدلسازی احتمالی تجمع آسیب خستگی مناسب نمی باشد. از اینرو، نمونه بار ترافیک تصادفی بر اساس اندازه WIM جهت شبیه سازی جریان ترافیک واقعی و ارزیابی قابلیت اعتماد خستگی پل های فولادی ارائه می گردند.
1.2 سنجش WIM . سنجش ترافیک که در این مطالعه از آن استفاده شده است، از سیستم WIM پل بزرگراه در سیچوان چین برگرفته شده است. اطلاعات بیشتر در مورد سیستم WIM را می توان در مطالعه Liu (24)، Lu (25) و همکاران مشاهده نمود. فرآیند فیلترینگ بمنظور حذف داده های نامعتبر صورت گرفته است. معیار شناسایی داده های نامعتبر بدین صورت هستند: (1) GVW منحصر بفرد کمتر از 30kN است؛ (2) وزن محور بیشتر از 400 kN و کمتر از 5kN می باشد؛ (3) فاصله گذاری محور بیشتر از 20m می-باشد. مرور داده های تأثیر گذار در جدول 1 نشان داده شده است.
با توجه اندازه WIM، اولین گام تجزیه و تحلیل آماری طبقه بندی نوع وسیله نقلیه می باشد. بر اساس ترکیب بندی وسیله نقلیه، تمام وسایل نقلیه مانند آنچه در جدول 2 نشان داده شده به 6 نوع طبقه بندی می گردد. حدود %60 وسایل نقلیه فیلتر شده کامیون های 2 محور و اتومبیل های سبک هستند. بعلاوه %90 کامیون های سنگین در مسیر ترافیکی آهسته بکر گرفته شده، در حالیکه بیشتر کامیون های سبک مسیر ترافیک سریع بکار گرفته می شوند. پدیده ترکیب ترافیک بر قابلیت اعتماد خستگی پل های فولادی تأثیر می گذارد.
A steady traffic growth has posed a threat to the fatigue safety of existing bridges. Uncertainties in traffic flows add to the challenge of an accurate fatigue safety assessment. This article utilizes a stochastic traffic load model to evaluate the fatigue reliability of orthotropic steel bridge decks. The traffic load model is simulated by site-specific weigh-in-motion measurements. A response surface method is presented to solve the time-consuming problem caused by hotspot stress simulations in the finite element model. Applications of the stochastic traffic load model for probabilistic modeling and fatigue reliability assessment are demonstrated in the case study of a steel box-girder bridge. Numerical results indicate that the growth rate of the gross vehicle weight leads to a rapid decrease of the fatigue reliability in comparison to the traffic volume growth. Even though the traffic volume growth is rapid, the control of overloaded trucks in comparison to the traffic volume is an effective way to ensure the fatigue safety of the steel bridges.
1. Introduction
Fatigue damage accumulation is one of the crucial issues leading to collapse of most steel bridges. According to a study conducted by the ASCE committee [1], approximately 80– 90% of steel bridge failures are caused by fatigue and fracture issues. In general, a fatigue-critical component of a steel bridge is designed with enough fatigue resistance and fatigue life against the cyclic vehicular load [2–4]. However, a steady increase in both the traffic volume and gross vehicle weight (GVW), due to rapid growth and expansion of developments in intercity and interstate transportation, has posed a threat to the fatigue safety of existing bridges [5, 6]. Uncertainties in traffic flows lead to another challenge of an accurate fatigue damage evaluation. The fatigue-critical components of most highway steel bridges are welded joints in the deck plates, where strain sensors are difficult to be fixed. Consequently, fatigue reliability assessment of orthotropic bridge decks with consideration of real traffic loads is still a challenge.
A critical step for fatigue reliability assessment of bridges is the probabilistic modeling of fatigue stress ranges. In this regard, most researchers utilized strain measurements in structural health monitoring (SHM) system to conduct the statistical analysis [7–9]. However, application of the SHM system is limited by its expensive cost and limited specified objectives. With the development of sensor technologies, the site-specific weigh-in-motion (WIM) system, which is initially developed for traffic management, has been widely used for statistical analysis of traffic loads [10]. Therefore, integration of site-specific WIM measurements and the finite element (FE) method becomes a practical approach for fatigue reliability assessment of in-service bridges. Numerous analytical approaches have been presented on this topic. For instance, Wang et al. [11] developed a computational framework to evaluate the fatigue damage increment of the steel box-girder bridge by combining FE computations and SHM data. Guo et al. [12] utilized a multiscale probabilistic FE model to evaluate the fatigue reliability of an orthotropic steel bridge deck. Zhang et al. [13] utilized an equivalent orthotropic material approach to simulate the dynamic load in the FE model. Ye et al. [14] studied the sensitivity of the element size and the element type in calculating the structural stress under the vehicle load. Zhang and Au [15] presented an advanced probabilistic load model to simulate the truck-load on a bridge based on WIM measurements and then evaluated the fatigue reliability and the remaining service life of the bridge. As elaborated above, integrating the monitored traffic data and the FE-based numerical simulation is an effective approach for fatigue reliability assessment of steel bridges.
Modeling traffic load is a critical procedure for integrating WIM measurements and the FE method for fatigue reliability assessment of steel bridges. The typical fatigue truck-load model specified in national design specifications and several advanced truck-load models are conventional in the opening literatures [16]. In this regard, Laman and Nowak [17] developed a 3-axle truck-load model based on WIM measurements. Chotickai and Bowman [18] developed a 4-axle truck-load model and indicated that the AASHTO truck-load model can be notably overestimated in short-span bridges. Lan et al. [19] combined the traffic load spectrum and the traffic volume forecast for fatigue damage evolution of bridges. Chen et al. [20] utilized actual traffic loads to assess the fatigue performance of an arch bridge. In addition to the configuration of the truck illustrated above, the dynamic effect due to vehicle-bridge interaction will also affect the fatigue stress spectrum [21]. Since the traffic parameters (e.g., vehicle types, driving speeds, vehicle spacing, and GVWs) are random in nature, the statistical information of all trucks is not included in the aforementioned truck-load models. Therefore, a stochastic traffic load model is necessary for an accurate estimation of the fatigue damage accumulation. However, to the best of the authors’ knowledge, most of the relative research efforts with respect to the stochastic traffic load model have focused on the vehicle-bridge interaction analysis [22, 23], while research on application of stochastic traffic load model to for fatigue reliability assessment of steel bridges is relatively insufficient.
This study aims at developing a stochastic traffic load model based on site-specific WIM measurements to evaluate fatigue reliability of orthotropic steel bridge decks. A computational framework integrating the FE-based deterministic hotspot stress simulation and probabilistic modeling of stress ranges is presented. In the case study, a steel box-girder bridge is chosen as a prototype to demonstrate the effectiveness of the application of stochastic fatigue truck load mode. Influence of the parameters in the stochastic truck-load model on the fatigue reliability index is investigated.
2. Stochastic Traffic Load Model
In general, a fatigue truck-load model, which contains deterministic configurations and axle loads, is used to represent the site-specific traffic loading. The fatigue truck-load model is usually evaluated through the real traffic load spectrum based on the equivalent fatigue damage accumulation criterion. However, due to the deterministic configuration and axle load, the fatigue load model is unappropriated to be used for probabilistic modeling of fatigue damage accumulation. Herein, a stochastic traffic load model based on WIM measurements is present to simulate the real traffic flow and the subsequent fatigue reliability assessment of steel bridges.
2.1. WIM Measurements. The traffic measurement utilized in the present study stems from a WIM system of a highway bridge at Sichuan, China. More information of the WIM system can be found by Liu et al. [24] and Lu et al. [25]. Filtering processes were conducted to eliminate the invalid data. The criteria of identifying the invalid data are (1) the individual GVW is less than 30 kN; (2) the axle weight is larger than 400 kN or less than 5 kN; and (3) the axle spacing is greater than 20 m. Overview of the effective data is shown in Table 1.
With the WIM measurements, the first step of the statistical analysis is the vehicle type classification. According to the vehicle configuration, all vehicles are classified into 6 types as shown in Table 2. It is observed that about 60% of the filtered vehicles are 2-axle trucks and light cars. In addition, about 90% of heavy trucks are driving in the slow traffic lane, while more light trucks are prone to be driving in the fast traffic lane. This phenomenon of the traffic composition will impact the fatigue reliability of steel bridges.
1. مقدمه
2. نمونه بار ترافیک اتفاقی
2.1. سنجش WIM
2.2. شبیه سازی بار ترافیکی تصادفی
3. متدلوژی
3.1. مبانی نظری
3.2. چارچوب محاسباتی پیشنهادی
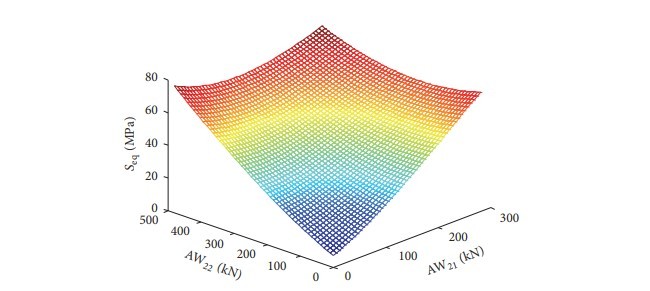
3.2.1. تخمین عملکرد سطح واکنش
3.2.2. مدلسازی احتمالی بر اساس GMM
4. مورد پژوهشی
4.1. پل نمونه اصلی
4.2. آمار متغیرها
4.3. مدلسازی احتمالی
4.4. ارزیابی قابل اعتماد خستگی
5. نتیجه گیری
منابع
1. Introduction
2. Stochastic Traffic Load Model
2.1. WIM Measurements
2.2. Stochastic Traffic Load Simulation
3. Methodology
3.1. Theoretical Basis
3.2. The Proposed Computational Framework
3.2.1. Approximating Response Surface Functions
3.2.2. Probabilistic Modeling Based on GMM
4. Case Study
4.1. Prototype Bridge
4.2. Statistics of Variables
4.3. Probabilistic Modeling
4.4. Fatigue Reliability Evaluation
5. Conclusions
References
