
دانلود رایگان مقاله ارزیابی عملکرد کارآمد برای خوشه های منابع در محیط ابری با استفاده از زنجیره مارکوف
چکیده
رایانش ابری به ما این امکان را می دهد تا برای پردازش کارها، کارها میان مراکز داده ابری مختلف را با اینترنت به عنوان ستون فقرات به اشتراک بگذاریم. انتخاب مراکز داده جهت پردازش کارها، مبتنی بر پتانسیل مراکز داده، نرخ ورود کارها و بهره برداری یا استفاده بهتر از منابع می باشد. مدلسازی عملکرد و ارزیابی سیستم های ابری، تصویری کامل از احتمال توزیع کارها میان مراکز داده، تعداد متوسط کارها در مراکز داده و زمان کل محیط ابری نشان می دهد. برای ارائه بهترین مدل ارزیابی عملکرد که به محیط ابری مساعد و موفق منتج می گردد، شیوه پیشنهادی نرخ ورود کارها را با استفاده از فرایند پواسن محاسبه می کند که نرخ ورود برای فواصل زمانی نامتناهی محاسبه شده و تعداد متوسط کارها و همچنین بهره برداری از منابع با استفاده از زنجیره مارکوف پیوسته مدلسازی شده اند. برای بهبود زمان بندی کارها با به حداقل رساندن زمان کل (زمان صرف شده ) محیط ابری، برنامه های مرتبط با محاسبه نرخ ورود و مدل بهره برداری از منابع شیوه های موجود حل شده اند.
1. مقدمه
رایانش ابری، به تامین کننده اجازه صدور و انتشار منابع محاسباتی نظیر فناوری های ذخیره سازی، نرم افزار و پلتفرم ها به عنوان سرویس مشترک برای کاربران به صورت اجاره ای و طبق تقاضا را می دهد. مفهوم مجازی سازی در اساس رایانش ابری نقش حیاتی ایفا نموده و امکان تشکیل گروه هایی از منابع محاسباتی از خوشه های سرور و تخصیص یا تخصیص مجدد منابع محاسباتی به اپلیکیشن به شیوه طبق تقاضا را فراهم می آورد [1]. یکی از چالش های اصلی در رایانش ابری، به حداقل رساندن زمان کل محیط ابری، با زمان بندی کارآمد منابع موجود برای کارهای ورودی می باشد. برخی از پارامترها نظیر نرخ ورود کارها، زمان پاسخ و زمان انتظار کار در خوشه های منابع، مورد توجه قرار گرفته و در عین حال، کارها برای منابع موجود در محیط ابری، زمان بندی شده اند. در این مقاله، برخی از مشکلات مشاهده شده با شیوه های موجود در رابطه با نرخ ورود و بهره برداری از دستگاه بررسی و حل شده است.
زمان اجرا یا تکمیل کارها در محیط ابری خاص، زمان کل (صرف شده) آن محیط ابری نامیده شده است [2]. منابع براساس پتانسیلشان خوشه بندی شده اند که این امر منجر به یک زمان بندی کارآمد در محیط ابری می گردد. در شیوه پیشنهادی، منابع با محاسبه پتانسیل هر منبع و با استفاده ازالگوریتم EPRNW خوشه بندی شده اند [3]. هدف اصلی شیوه پیشنهادی، توسعه یک مدل عملکرد و ارزیابی مناسب برای پارامترهایی نظیر نرخ ورود، نرخ تکمیل و بهره برداری از منابع محیط ابری است. زمان سرویس یا خدمات کارها عمدتاً به نرخ ورود کارها در منابع محاسباتی بستگی دارد. در شیوه پیشنهادی به دو دلیل نرخ ورود با فرایند پواسن محاسبه شده است: یکی اینکه فرایند پواسن ازخصوصیات زنجیره مارکوف پیروی می کند که از لحاظ سیستماتیکی قابل مدیریت است و دلیل دوم اینکه نرخ ورود کارها را می توان در فواصل زمانی مستقل محاسبه نمود و هیچ حدی برای فواصل زمانی وجود ندارد [4].
بهره برداری از منابع با تعیین تعداد متوسط کارهای مستقر در خوشه های منابع، محاسبه می شود. از مدل زنجیره مارکوف برای تعیین احتمال تعداد متوسط کارهای مستقر در خوشه های منبع استفاده شده و تضمین شده است که زمان های اجرا در خوشه منبع به صورت نمایی توزیع شده و نرخ ورود پیوسته کارها نیز از توزیع نمایی پیروی می کند. زنجیره مارکوف به دو نوع تقسیم شده است، زنجیره مارکوف با زمان گسسته و زنجیره مارکوف با زمان پیوسته. رویدادها تنها در پایان گام زمانی زنجیره مارکوف با زمان پیوسته، رخ می دهند، در صورتی که در زنجیره مارکوف با زمان پیوسته، رخداد رویدادها به فواصل زمانی مستقل بستگی دارد [5]. در شیوه پیشنهادی از زنجیره مارکوف بازمان پیوسته برای تعیین احتمال بهره برداری از منابع با محاسبه نرخ ورود کارها در فواصل زمانی مستقل با استفاده از فرایند پواسن استفاده شده است. برای تولید یک مدل ارزیابی عملکرد کارآمد، مقاله حاضر، بربرخی معایب شیوه های موجود غلبه کرده و راه حل نزدیک به حد بهینه ای حاصل می نماید.
2. کارهای مرتبط
پژوهشهای زیادی برای مدل ارزیابی عملکرد در مورد زمان بندی کارها روی محیط ابری وجود دارد. برای نیل به کارایی بالا، ارزیابی عملکرد مزارع منابع ابری، محاسبه توزیع تقریبی کارها و تعداد متوسط کارها در سیستم، یک مدل ریاضی پیاده گردید [6]. زمان بندی صف بازخورد چند سطحی توسط مدل زنجیره مارکوف و تحت برخی سیاست های زمان بندی مشترک بررسی گردید تا بدین طریق زمان پردازش CPU تعیین گردد [7]. از تحلیل زنجیره مارکوف برای ارزیابی Drum Buffer Rope و در کنار شیوه های متداول دیگر برای نشان دادن عملکرد بهبودیافته Drum Buffer Ropeدر محیط فروشگاه Job استفاده شده است [8]. مسئله پارتیشن بندی چند مکانی در ابرهای متحرک (موبایل) بررسی و با استفاده از طرح آفلودچندمکانی انرژی کارآمد، حل و برای دستیابی به مینیموم انرژی مصری ابرهای متحرک، با فرایند تصمیم گیری مارکوف مورد تجزیه و تحلیل قرار گرفت [9].
توان فوتوولتائیک گریدها (شبکه ها) با فرایند نیمه مارکوف نمایش داده شد تا بدین طریق توان فوتوولتائیک مطمئنی تولید و واحدهای ذخیره سازی انرژی به شیوه ای تصادفی و همزمان با منابع دیگر، زمان بندی شوند [10]. نتایج شبیه سازی الگوریتم LARAC توجیه می کند که طرح climb offloading برای کانال احتمالی مارکوفی مناسب بود و انرژی مصرفی دستگاههای موبایل را کاهش می دهد [11]. در ابرهای موبایل (متحرک)، با تعیین خصوصیت فراریت دستگاههای موبایل و پیش بینی حالتها با کمک مدل زنجیره مارکوف ، تحمل پذیری خطاحاصل می گردد [12]. با پیش بینی پهنای باند آتی کلیه ماشین های مجازی با کمک دانش پیشین راجع به حجم کار پهنای باند نیز زمان بندی کارآمدی از ماشین های مجازی در ابر، حاصل می گردد که این امر منجر به تغییرقدرتمندی در مدل مارکوف پنهان در راستای مدیریت سیستم تله هلث یا سلامت از راه دورمی گردد [13].
یکی از عوامل مهم برای شبیه سازیها و ارزیابی عملکرد، تولید حجم کار است. یک مولد حجم کار به نام BURSE به خاطر خصوصیات خودتشابهی و انفجاری بودن حجم کار در رایانش ابری مبتنی بر طبیعت ورفتار دو حالت فرایندهای پواسن مدوله شده مارکوف، پیشنهاد گردید [14]. دو پارامتر مهم آفلود یا تخلیه ابری موبایل عبارتنداز: مصرف انرژی اکسترم موبایل و زمان پاسخ روی داده با کاردستگاه موبایل. پارامترهایی نظیرجمع وزندار زمان پاسخ انرژی، حاصل ضرب زمان پاسخ انرژی و حاصل ضرب وزندار زمان پاسخ انرژی، بررسی و در استراتژیهای آفلود ابرموبایل استفاده شده اند تا بدین طریق مدل ارزیابی عملکرد به شیوه ای موثر، به نتیجه برسد [15]. زمان بندی کارها و پتانسیل حجم کارهای ناظر کانال پنهان ماشین مجازی متقابل با استفاده از مدل مارکوف پیوسته ارزیابی گردید. از تخصیص کارآمد ماشین مجازی برای به حداقل رساندن نرخ خطا در کانال مذکور استفاده گردید [16].
از مفهوم یادگیری تقویتی برای زمان بندی وظایف و از مفهوم نظریه صف بندی برای بهینه سازی زمان بندی وظایف براساس محدودیت های منابع استفاده گردید که نتیجه این امر نیز افشای رابطه بین نرخ ورود، بهره برداری از منابع و اندازه ذخیره سازی بود [17]. منابع به شکلی موثر و با پیش بینی مصرف CPU ماشین مجازی و همچنین با توجه به رفتارهای بلندمدت و کوتاه مدت VM با پیاده سازی نمای Hurst تخصیص داده شده اند که یکی از همراهان مدل انتقال مارکوف به حساب می آمد [18]. از فرایند تصمیم گیری مارکوفی به عنوان چارچوبی برای نیل به راه حل نزدیک بهینه جهت مسئله آفلود (تخلیه) دینامیکی در رایانش ابری موبایل استفاده گردید [19]. شیوه زمان بندی گره ها از تکنیک پیش بینی زنجیره مارکوف برای تجزیه وتحلیل داده های جریان سازی بزرگ وتضمین پردازش موثر آنها استفاده نمود [20]. روشهای پژوهشهای فوق برای ارزیابی عملکرد خوشه های منابع در رایانش ابری در صورت نرخ ورود بی نهایت و تعداد بزرگ خوشه های منابع کاملاً مناسب نیستند. به طور کلی در چنین موقعیت هایی، برخی مدلهای توزیع احتمال نظیر فرایند پواسن برای محاسبه نرخ ورود و زنجیره مارکوف برای برآورد بهره برداری از منابع و همچنین تعداد متوسط کارها در خوشه منبع، ارائه می گردد. هدف پنهان این کار، زمان بندی کارها موثر در محیط ابری را تعیین می نماید. از یک شیوه فراابتکاری بهبودیافته برای بهبود زمان بندی کارها در محیط ابری استفاده گردید [21]. از روش توزیع احتمال برای بهبود زمان بندی کارها در محیط ابری استفاده شده بود [22].
Abstract
Cloud computing enables us to share the jobs across various cloud data centers with the internet as a backbone in order to process the jobs. The selections of the data centers to process the jobs are based on the potential of the data centers, arrival rate of the jobs and better resource utilization. Performance modeling and evaluation of the cloud systems shows a perfect picture of probability of distribution of jobs among the datacenters, mean number of jobs in the datacenters and makespan of the cloud environment. In order to provide a best performance evaluation model which leads to a prosperous cloud environment the proposed approach calculates the arrival rate of jobs using Poisson process in which the arrival rate can be calculated for infinite time intervals and the mean number of jobs and also the resource utilization are modeled using continuous Markov chain. The problems related to the calculation of arrival rate and resource utilization model of the existing approaches are solved to enhance the job scheduling by minimizing the makespan of the cloud environment.
1 Introduction
Cloud computing allows the provider to issue the computing resources such as storage technologies, software and platforms as a common service to the users in a rental basis when it is on-demand. The concept of virtualization plays a vital role in the base of the cloud computing which enables to form the groups of computing resources from the server clusters and allocates or reallocates the computing resources to the application in an on demand manner [1]. One of the major challenge in cloud computing is to minimize the makespan of the cloud environment by efficiently scheduling the available resources to the incoming jobs. Some of the parameters such as arrival rate of the jobs, response time and waiting time of the job at the resource clusters are considered while scheduling the jobs to the available resources in a cloud environment. In this paper some of the difficulties faced by the existing approaches related to the arrival rate and device utilizations are addressed and solved.
The execution time or completion time of jobs at a particular cloud environment is called makespan of that cloud environment [2]. Resources are clustered based on their potentials which lead to an efficient scheduling in a cloud environment. In the proposed approach resources are clustered by calculating the potential of each and every resource by using the equivalence partitioning recurrent node weight algorithm [3]. The main objective of the proposed approach is to develop a suitable performance and evaluation model for the parameters such as arrival rate, completion time and resource utilization of a cloud environment. The service time of the jobs mainly depends on the arrival rate of the jobs at the computing resources. The arrival rate is calculated by Poisson process in the proposed approach due to two reasons: one is Poisson process obeys the properties of the Markov chain which is systematically manageable and second one is arrival rate of jobs can be calculated at independent time intervals and also no limit for the time intervals [4].
Resource Utilization can be calculated by identifying the mean number of jobs residing in the resource clusters. Markov chain model is used to identify the probability of mean number of jobs resides in the resource clusters by ensuring that execution times at the resource cluster are distributed exponentially and the continuous arrival rate of the jobs are also exponentially distributed. The Markov chain is divided into two types as discrete time Markov chain and continuous time Markov chain. The occurrence of the events are only at the end of the time step in discrete time Markov chain whereas in continuous time Markov chain the occurrence of events depends on independent time intervals [5]. Continuous time Markov chain is used in the proposed approach to identify the probability of resource utilization by calculating the arrival rate of the jobs at independent time interval using Poisson process. To produce an efficient performance evaluation model this paper overcomes some of the disadvantages in the existing approaches and produces the near optimal solution.
2 Related works
Many literatures are available for performance evaluation model regarding to the job scheduling on a cloud environment. To achieve high efficiency, a mathematical model for performance evaluation of the cloud resource farms was implemented to calculate the approximate distribution of jobs and mean number of jobs in the system [6]. The multilevel feedback queue scheduling was examined by Markov chain model under some common scheduling policies to determine the CPU processing time [7]. Markov chain analysis had been used to evaluate the Drum Buffer Rope with the other conventional approaches to show the improved performance of the Drum Buffer Rope in the Job shop environment [8]. Multi site partitioning problem in mobile clouds had been addressed and solved using energy efficient multisite offloading scheme and analyzed by Markov decision process in order to achieve the minimum energy consumption of mobiles [9].
Photovoltaic power of grids was represented by a semi Markov process to produce a reliable Photovoltaic power and also schedules the energy storage units in stochastic manner in concurrence with other resources [10]. The simulation results of canonical LARAC algorithm justifies that one climb offloading scheme was well suited for Markovian probabilistic channel and reduces the energy consumed by the mobile devices [11]. In mobile clouds the fault tolerance can be achieved by declining the volatility property of mobile devices and prediction of prediction of states with the help of Markov chain model [12]. An efficient scheduling of virtual machines in cloud can also be attained by predicting the future bandwidth of all the virtual machines with the help of accumulating the prior knowledge of the bandwidth workload which leads to vigorous modification in Hidden Markov Model in order to manage the telehealth system [13].
One of the important factors for simulations and performance evaluation is workload generation. A workload generator called BURSE was proposed for both the characteristics of workloads bursty and self similar in cloud computing based on the nature and behavior of the matter of two states Markov Modulated Poisson processes [14]. The two important parameters of mobile cloud offloading are the utilization of energy by the mobile extreme and the response time incident by the job of the mobile device. The parameters such as energy response time weighted sum, energy response time product and the energy response time weighted product are examined and applied to the different offloading strategies of mobile cloud to conclude the performance evaluation model in an effective manner [15]. The job scheduling and potential of the bystander workloads of the cross virtual machine covert channel was evaluated using Continuous Markov model. An efficient virtual machine allocation was used to minimize the error rate in cross virtual machine covert channel [16].
The concept of reinforcement learning was used for task scheduling and the concept of queuing theory was used to optimize the task scheduling based on the resource constraints and it also results in disclose of relationship between the arrival rate, resource utilization and storage size [17]. The resources are allocated effectively by predicting the usage of virtual machine CPU as well as considering both long and short term behaviors of VM’s by implementing Hurst exponent which was an companion of Markov transition model [18]. Markovian decision process was used as a framework to achieve the near optimal solution for the dynamic offloading problem in mobile cloud computing [19]. Markov chain prediction technique was used by nodes scheduling approach to analyze the big streaming data and ensures that big streaming data can be effectively processed [20]. The methodologies of the above literatures are not perfectly suited for the performance evaluation of the resource clusters in cloud computing in the case of infinite arrival rate and large number of resource clusters. By generally speaking in such situations undergo the some of the probability distribution models as Poisson process for calculating the arrival rate and Markov chain for estimating the resource utilization as well as mean number of jobs in the resource cluster. The hidden objective of this work specifies the effective job scheduling in cloud environment. An improved metaheuristic approach was used to enhance the job scheduling in cloud environment [21]. Probability distri bution method had been used to improve the job scheduling in cloud environment [22].
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. کارهای مرتبط
3. روش پیشنهادی
3.1 فرایند ورود در هر خوشه منبع
3.2 توزیع کارها میان خوشه های منبع
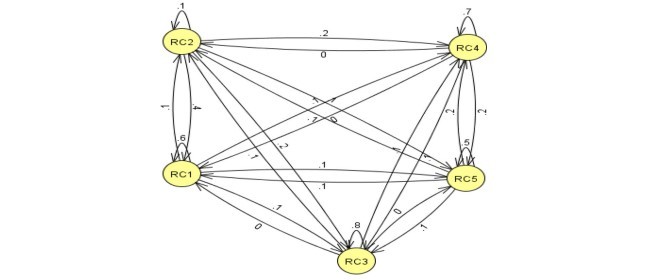
4. نتایج و بحث
5. نتیجه گیری
منابع
Abstract
1 Introduction
2 Related works
3 Proposed methodology
3.1 The arrival process into each resource cluster
3.2 Distribution of jobs among the resource clusters
4 Results and discussions
5 Conclusion
References
