
دانلود رایگان مقاله بررسی اثر انباشت زباله در تیرچه بلوک در آب شستگی پل
چکیده
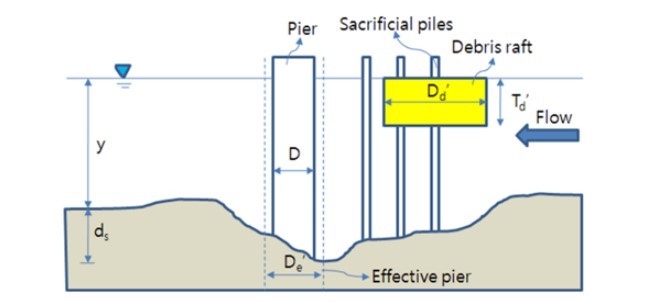
آسیب عمده پل در رودخانه در طول سیل رخ می دهد. آسیب به دلایل مختلف ایجاد می شود. دلیل اصلی آن وجود در بستر رودخانه در پایه های پل، یعنی اسکله و صیقلی شدن اباتمنت است. تجمع رسوب در پایه پل همراه با انسداد بزرگتر از پایه پل جدا شده می باشد. حضور بقایای آن باعث جابجایی بزرگتر و حذف رسوبات با توجه به عدم وجود رسوب باقی مانده است. رسوب باقی مانده در اثر پایه پل به صورت صیقلی موجود است و توسط چندین محقق مورد مطالعه قرار گرفت. اما اثرات تجمع باقی مانده در پل آبشستگی اسکله مورد مطالعه قرار گرفته نشده است. هدف از این مطالعه برآورد اثرات باقی مانده انباشته در آبشستگی اسکله و یک فرمول جدید برای پیش بینی عمق آبشستگی پل اسکله با باقی مانده انباشته در شمع می باشد. آزمایش برای درک تغییرات و تعامل عمق آبشستگی بیش از یک طیف از عمق جریان، y و جریان شدت، V / VC انجام شد. آزمایش در آبشستگی اسکله واحد انجام شد. وضعیت صیقل اسکله با آبشستگی باقی مانده و شمع با آبشستگی باقی مانده است. با مقایسه هر یک از نتایج تجربی یافت شده , اثرات باقی مانده به پل آبشستگی اسکله مربوط به اندازه و ضخامت آن بررسی می شود. روش های پیش بینی عمق آبشستگی با نتایج حاصل از این مطالعه تجربی مقایسه شده است. فرمول ملویل برای تغییر انتخاب شد. پیشنهاد فرمول عامل تابع عمق اندازه اصلاح ملویل، K '= 1.56D می باشد که در این مطالعه در نظر گرفته شد. یک رابطه جدید برای پیش بینی YB مطرح شده است. اثرات رسوب باقی مانده در شمع و در پایه پل با عمق نسبی بیان گر آبشستگی حداکثر صیقلی کردن موجود است . اسکله به صورت موثر با باقی مانده انباشته ارائه شده است. فرمول پیشنهادی جدید با نتایج تجربی همراه است. نتایج آزمایش ها طبق مقاله قبلی برای تجزیه و تحلیل و فرمول جدید ارائه شده است.
1. مقدمه
آبشستگی پل اسکله یک موضوع مورد علاقه از زمان اولین تمدن بوده است. دانش پیش بینی صیقلی عمق و اقدامات متقابل برای محافظت در برابر مشکل آبشستگی است و به سرعت در طول 50 سال گذشته پیشرفت کرده است. با این حال اثرات تجمع باقی مانده در پایه پل هنوز هم بسیار تحقیق شده است. (Breusers و همکاران، 1977) . این شامل رابطه بین عمق آبشستگی و رابطه V / VC توسط تجزیه و تحلیل ابعادی بررسی شده است، اما هیچ تجزیه و تحلیل دقیق طبق ماهیت وابستگی اعمال نمی شود. Hancu (1971) یک سری از آزمایش های آبشستگی را انجام داد و نتیجه گرفت که عمق آبشستگی موضعی وابسته به سرعت جریان است. این نتیجه گیری شبیه به نتیجه Breusers و همکاران، 1977 است . ریچاردسون و دیویس (1995) اظهار داشتند که تغییر بلند مدت مشخصات رودخانه معمولا برای ارزیابی دشوار خواهد بود. ملویل (1997) بسیاری از داده های آزمایشگاهی را توصیف و آب شستگی موضعی در دایره تحت شرایط آب زلال را بررسی می کند . در این وضعیت نشان داده شد که عمق آب شستگی موضعی در مقادیر پایین تر از V / VC کاهش می یابد. طراحی اسکله آبشستگی در حال حاضر در ایالات متحده آمریکا مطرح است که عمدتا در معادله CSU شرح داده شده در HEC-18 (CSU، 2001) بررسی می شود . شپرد و میلر (2006) وضعیت صیقلی را آزمایش و نتایج را با برخی از معادلات آبشستگی موضعی مقایسه می کند . معادلات پیش بینی موجود به طور گسترده ای متنوع برای جریان داده و شرایط رسوب است.
نصب و راه اندازی شمع برای کاهش صیقلی در اسکله مورد توجه است. در بالادست, این به منظور کاهش رویکرد جریان فرسایش و تضعیف حرکت جریان گردابی مد نظر است . عمق آبشستگی در اسکله طبق عرض شمع اسکله را تحت تاثیر قرار می دهد . اگر شمع عرض کوچک با اثر کاهش آبشستگی داشته باشد, اثرات کاهش آبشستگی تنظیم و طول اسکله و توابع مختلف بررسی می شود . مطالعه تجربی اخیر شمع توسط هدفیلد (1997) انجام شد. هدفیلد (1997) پیشنهاد کرد که وضعیت شمع های موثر برای پنج شمع با قطر. 167 همراه با پارامترهای تنظیم شده X = 2.5D، E = D شکل می گیرد که در آن D قطر پایه پل استوانه ای است. X جابجایی شمع رو به جلو در اسکله را نشان می دهد. E فاصله بین شمع و α زاویه گوه است. برای تراز وسط, جریان یک آرایش جایگزین می تواند عمق آبشستگی 56 درصد را کاهش دهد. اثرات تجمع باقی مانده در شمع برای حالت صیقلی پل اسکله مورد مطالعه قرار گرفته است، لذا هدف از این مطالعه برآورد اثر انباشت نخاله در شمع برای آبشستگی اسکله و پیشنهاد یک فرمول جدید برای پیش بینی پایه پل طبق عمق آبشستگی با باقی مانده انباشته در شمع است . آزمایش برای درک تغییرات و عمق آبشستگی بیش از یک طیف از عمق جریان و شدت جریان انجام شد (پارک و همکاران، 2015).
2. فرمول تجربی برای انباشت زباله
2.1 تجزیه و تحلیل آب شستگی طبق عمق پیش بینی
عمق آبشستگی طبق فرمول پیش بینی برای مقایسه با این مطالعه نتایج تجربی انتخاب شد. روش مورد نظر در جدول 1 ارائه شده است. ارائه مقایسه اسکله صیقلی با توجه به نتایج مطالعه تجربی است (سوک و همکاران، 2014). نتایج گوناگون پیش بینی عمق آبشستگی در جدول 2 ارائه شده است.
آزمون (R.M.S.E) برای هر یک از نتایج پیش بینی در مقابل داده های آزمایشگاهی انجام می شود. از جمله نتایج روش گوناگون پیش بینی آبشستگی ملویل (1997) به معنای کمترین میزان خطا با ریشه مربع R.M.S.E = 0.020 است. بنابراین فرمول ملویل برای پیشنهاد یک روش جدید برای پیش بینی عمق آبشستگی در پایه پل با باقی مانده انباشته در شمع انتخاب شد.
Abstract
The major damage of bridges at river crossing occurs during floods. Damage is caused for various reasons, the main reason being riverbed scour at bridge foundations, namely pier and abutments. Debris accumulation at bridge pier provides larger obstruction to flow than an isolated bridge pier. The presence of debris causes larger scours and sediment removal compared to the absence of debris accumulation. Debris accumulation at bridge pier effects to bridge pier scour has been studied by several researchers. But the effects of debris accumulation at sacrificial piles on bridge pier scour have not been studied, yet. The aim of this study is to estimates the effects of debris accumulated at sacrificial piles to bridge pier scour and proposes a new formula for predicting bridge pier scour depth with debris accumulated at the sacrificial piles. Experiments were performed to understand the changes and interaction of scour depth over a range of flow depths, y and flow intensities, V/Vc. Experiments were conducted in single pier scour, sacrificial piles scour, single pier with debris scour and sacrificial piles with debris scour. By comparing each of the experimental results it has been found that debris effects to bridge pier scour related to its size and thickness. Several scour depth prediction methods were compared with the results of this experimental study results. Among those formulae Melville’s formula was chosen to modify. The proposed modified Melville’s formula depth-size factor, = 1.56D was defined in this study. A new relation has been proposed to predict the effects of debris accumulation at sacrificial piles on bridge pier scour in term of relative maximum scour depth. is proposed as effective pier with debris accumulated at sacrificial piles. The new proposed formula is well fitted with the experimental results. The results of experiments from the previous paper are used to analyze and the new formula is proposed.
1. Introduction
Bridge pier scour has been a subject of interest and importance to people from the time of the earliest civilizations. Knowledge of predicting scour depths and countermeasures for protecting against scour problem has progressed rapidly over the past 50 years. However the effects of debris accumulation at bridge pier still not have been researched much. (Breusers et al., 1977) has developed the relationship between the scour depth and the relation of V/Vc by dimensional analysis, but applied no detailed analysis into the nature of the dependency. Hancu (1971) conducted a series of scour experiments and concluded that the local scour depth is dependent of the flow velocity. This conclusion is similar to that of (Breusers et al., 1977). Richardson and Davis (1995) commented that long term streambed profile changes will usually be difficult to assess. Melville (1997) presented many laboratory data that describe the temporal development of local scour at circular bridge piers under clear-water conditions. It was shown that local scour depth were reduced at lower values of V/ Vc. The current pier scour design in the USA is mainly based on the CSU equation described in HEC-18 (CSU, 2001). Sheppard and Miller (2006) conducted pier scour experiments and compared their results with some of the local scour equations. Available prediction equations give widely varied results for a given flow and sediment conditions.
Sacrificial pile installation is the mechanism for reducing scour at bridge pier. Pile was installed at upstream of the pier to reduce flow approach of erosion and to weaken the eddy current motion. The scour depth at the pier was affected by sacrificial pile width upstream of the pier. If the pile width small the effect of scour reduction also small. The effects of scour reduction are number of sacrificial piles, its arrangement, pier length and various angle arrangement functions. The most recent experimental study of sacrificial piles was carried out by Hadfield (1997). Hadfield (1997) suggested that the most effective pile arrangement was found to consist of five sacrificial piles of diameter 0.167D with arrangement parameters X = 2.5D, e = D, and ∝= 300 ; where D is the diameter of the cylindrical bridge pier; X is the displacement of the forward most pile from the upstream face of the pier; e is the spacing between the piles and ∝ is the wedge angle. For aligned flows an alternative arrangement could reduce scour depths by 56%. The effects of debris accumulation at sacrificial piles to bridge pier scour has not been studied, recently. So the aim of this study is to estimate the effect of debris accumulation at sacrificial piles to bridge pier scour and to propose a new formula for predicting bridge pier scour depth with debris accumulated at the sacrificial piles. Experiments were performed to understand the changes and interaction of scour depth over a range of flow depths and flow intensities (Park et al., 2015).
2. Empirical Formula for Debris Accumulation
2.1 Analysis of Scour Depth Prediction Methods
Various scour depth prediction formulae were chosen to compare with this study experimental results. The most comment proposed methods are presented in Table 1. The comparison of single pier scour depth of this experimental study results (Sok et al., 2014) with various proposed scour depth prediction results are presented in Table 2.
The Root Mean Square Error (R.M.S.E) test has been performed for each prediction results versus the laboratory data. Among various proposed scour prediction method results Melville (1997) gave the lowest root mean square error rate, R.M.S.E = 0.020. So Melville formula was chosen to use for proposing a new method for predicting scour depth at bridge pier with debris accumulated at the sacrificial piles.
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. فرمول تجربی برای انباشت زباله
2.1 تجزیه و تحلیل آب شستگی طبق عمق پیش بینی
2.2 فرمول ملویل
2.3 فرمول اصلاح شده ملویل
3. فرمول جدید برای تیرچه بلوک با باقی مانده
3.1 اشتقاق فرمول جدید
3.2 دقت پیش بینی و فرمول کالیبراسیون
4. نتیجه گیری
منابع
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Empirical Formula for Debris Accumulation
2.1 Analysis of Scour Depth Prediction Methods
2.2 Melville’s Formula
2.3 Modified Melville’s Formula
3. New Formula for Sacrificial Piles with Debris
3.1 Derivation of New Formula
3.2 Prediction Accuracy and Formula Calibration
4. Conclusions
References
