
دانلود رایگان مقاله توازن بار آگاه در روش شناسی مسیریابی XY برای معماری ناک
چکیده
الگوریتم مسیریابی عملکرد اصلی را در داخل عملکرد کلی اجتماع در تراشه انجام می دهد. مسیریابی پویا با در نظر گرفتن تغییر قابل توجهی در پهنای باند ارتباطی و سازگاری با اتصالات ناقص و ترافیک سنگین جالب است. مسیریابی XY در توپولوژي (جانمایی) مش باعث ترافیک در قسمت مرکزی شبکه می شود که تاخیر را افزایش و منجر به کاهش عملکرد می شود. ترافیک شبکه به طور کلی در بخش مرکزی شبکه به دلیل افزایش ترافیک در همان گره ها به طور دوره ای توسط گره های همسایه افزایش می یابد. علاوه بر این، ترافیک سنگین به دلیل گره های همسایه قطعا عملکرد سیستم را کاهش می دهد و اثر مضری بر گره ها خواهد داشت. سپس تلاش می کنیم که تاخیر محلی به علت ترافیک را با استفاده از آدرس مشخص نزدیک اندازه مکان، بر اساس روش تقسیم و حل برای کشش مسیر ، کاهش دهیم. آن تاخیر در هر همسایه محلی با کمک کاهش فشار مسیریابی هر گره محلی به حداقل می رسد. در این مقاله جانمایی محبوب مش همرا با الگوریتم LBAR را اجرا کرده ایم و نتایج با مسیریابی XY-معمولی مقایسه می شود. مشاهده می شود که توازن بار و تاخیر در مورد LBAR نسبت به XY معمولی بهبود یافته و ترافیک کل شبکه برای LBAR در مقایسه با XY سنتی کاهش می یابد.
1.مقدمه
سیستم کنونی تراشه ها از شبکه های گسترده منطقه در اطراف همسایگی آنها مقایسه می شود و به این دلیل است که آنها کمتر غیرجبرگرایی را نشان می دهند. همسایگی ها، شبکه های مفیدی مانند آنهایی که برای مقیاس بزرگ چند پردازنده تولید می شوند، نیازهای مقایسه ای و همچنین ضروری ها را دارند. به عنوان مثال، ویژگی های چند مشخصه، به عنوان مثال، انرژی مورد نیاز علاوه بر طراحی تخصصی زمان، در شبکه های SoC خاص هستند [1] [2[ اثربخشی اتصال داخلی و برآورد اطلاعات پیش نیازهایی را تبادل می کند که برای چارچوب های NoC ضروری تر هستند، و همچنین شبکه در تراشه (NoC) به عنوان سازگاری، چند منظوره تبدیل شده اند و همچنین برای مسائل مربوط به این نوع قابل استفاده است [3[. در سیم کشی معمولی NoC ، مبادلات در میان هسته های تعبیه شده برای اکثر قسمتها وسیله سوئیچ های متعدد و اتصالات سیم هستند. این مکاتبات چند هاب می تواند عملیات محدودکننده قابل توجه ای در اجرای چارچوب باشد که افزایش برای دموکراسی بیشتر و انتشار حیاتی را ارائه می دهد. برای غلبه بر این محدودیت اجرایی، ما مدل معماری جدید از طریق فرضیه های سیستم پیچیده در ارتباط با عمدتا مجموعه اتصالات تراشه ها برای ایجاد عملکرد بالا و تاخیر اندک را پیشنهاد می دهیم NoCs [4]. بر فرض مثال، بسیاری از مرکز ها، ساختارهای یکپارچه اینتل به سمت چند هسته ای ژئون فی [5] [6] ، به عنوان شیوه ای برای اجرای مولد و اجرای بیشتر با تاخیر کم حرکت می کنند. در این مقاله ما مدل عملکردی را پیشنهاد می دهیم که بار را در سیستم مبتنی بر تراشه شبکه به حداقل می رساند. به طور کلی، مهندسان مدل عملکردی را طراحی، بعدا تکنولوژی های آینده بر اساس مدل عملکرد را تجزیه و تحلیل می کنند. با توجه به این نکته، اولین مدل معماری و برنامه های کاربردی به صورت جداگانه ایجاد می شوند. سپس کاربردها توسط مدل های عملکرد توسعه یافته و معماری برای ارزیابی ترکیب کاربرد معماری منتخب استفاده می شود [7] [8]. در همین حال مسیرهای متعددی از گره فعلی به گره هدف وجود دارد؛ شبکه در تراشه باید الگوریتم های فرماندهی را جهت مسیر بسته داده برای مقصد نهایی اجرا کند. آن بر توانایی و تأخیری که ترافیک را تجربه می کند تاثیر می گذارد.
تعداد زیادی از پیشنهادات برای NoC ایجاد و توسط جانمایی های شبکه اجرا می شوند و الگوریتم های مسیریابی برای شبکه های ارتباطی در تراشه استفاده می شود. الگوریتم های مسیریابی را می توان به دو استراتژی خاص با توجه به نوع شبکه آبشاری کرد که کاملا متناسب با آن است. اگر راه مسیر یابی بسته داده ها ازقبل ثابت شود، این نوع از مسیریابی به عنوان مسیریابی منبع شناخته می شود. بخشی از آن اگر راه بسته داده ها گام به گام حل شود، این نوع از مسیریابی، مسیریابی منبع [5] [9] نامیده می شود. به طوری که NoC ها معمولا توسط بعد سفارش مسیریابی (DOR) اجرا می شوند که در ابتدا مسیر بسته ها را در جهت افقی (ابعاد X) و بعد در جهت عمودی ابعاد Y) ) به سمت دریافت کننده هدایت می کند [10]. اگرچه این الگوریتم زمان تاخیر را کاهش، آنها معمولا با سرعت بسیار پایین اجرا می شوند زیرا بار سنگینی در میان سیستم وجود دارد که باعث ترافیک در کل شبکه می شود [11[ الگوریتم مسیریابی توازن بار XY جانمایی شبکه از مختصات مشترک مختلفی استخراج می شود که این به کاهش ترافیک در شبکه کمک می کند، در نتیجه عملکرد کارآیی را نسبت به مسیریابی غیرفعال، یعنی، مسیر مرتب سازی بعدی انجام می دهد (DOR). این الگوریتم شامل کوتاهترین راه برای مسیریابی، اجرای پیشرفته و وزن سبک است.
2. کار مرتبط
الف) شرح مختصر NoC
تغیر رویکرد، جانمایی و الگوریتم مسیریابی، عنصر ضروری در طرح شبکه در تراشه است. جانمایی نشان دهنده اتصال داخلی شبکه است. در جانمایی مش، اتصالات در سیستم محدودیت های مقایسه ای دارند که باعث می شود طراحی فیزیکی اولیه نیز دامنه مستقیم به مقدار گره ها شود. اندازه در جانمایی فعلی از لحاظ خطوط و بخش ها اندازه گیری می شود [[12. طول های ثابت توسط بسیاری از شرکت های تحقیقاتی به دلیل خواص الکتریکی مناسب آن، توانایی طرح و سهولت در منابع در آدرس تراشه مورد نظر است [13[ ترجیح در کار با این جانمایی وجود دارد رفتار خاص خود را از نحوه فرمان به عنوان منبع هدایت شناخته می شو.د این عنصر در این جانمایی، رمزنگاری کارآمد مسیر داده های را تنها با چند بیت ارائه می دهد[12] . در حالی که یک هدر بسته بین گره ها وارد می شود، فرایند سوئیچینگ با آنچه که ابزار انتقال می دهد، حل می کند، یعنی کانال تزریق به کانال تخلیه متصل می شود [14] [12[.
مسیریابی لانه کرمی به طور گسترده ای برای سوئیچ کردن رویکرد با توجه به پیش نیازهای کمتر بافر آن و به طور قابل ملاحظه ای بسیار مهم مورد استفاده قرار می گیرد ، زیرا آن زمان انتقال بسته را در مورد عدم پیشقدر جدایی در میان هاب های منبع و مقصد تولید می کند. در لانه کرمی مسیریابی، بسته می تواند به پیشرفت موجودیت های طولی مقیم تقسیم شود، نقل مکان نامیده می شود. نقل مکان هدر (که حاوی اندازه گیری مسیریابی است) دوره ای از طریق سیستم را ایجاد می کند، در ضمن همانطورکه یک چرخش دقیق بدن، آن را در طراحی لوله ای دنبال می کند.
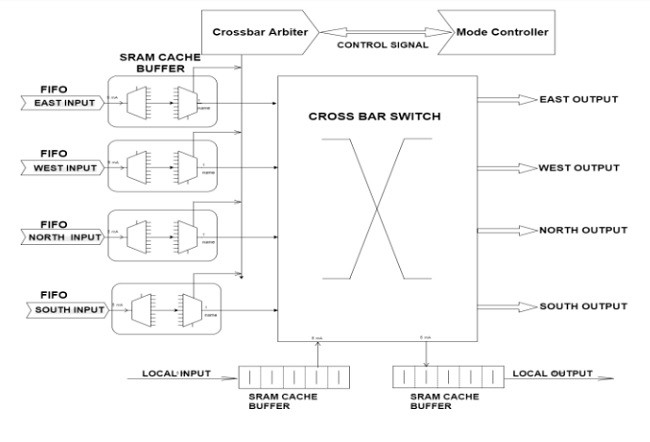
به طور متوالی به منظور اجرای کلی سیستم، هر کانال گروه می تواند بین چندین پشتیبانی، به ویژه کانال های مجازی، مخابره ترکیبی ساده ای داشته باشد. با اختصاص بسته های متمایز به هر یک از این پشتیبانی ها، از بسته های مختلف نقل مکان داده که ممکن است در هر یک از کانال های فیزیکی به صورت شیوه جاگذاری ارسال شود. این هر دو خروجی و نهفتگی با مجوز دادن به بسته های داده مسدود شده بهبود می یابد که نادیده گرفته می شود. [15 [. مسیر داده از بسته داده شامل بافرها و همچنین سوئیچ ماتریسی است. ماژول فرمان و تخصیص دهنده VC در مورد کانال مجازی و هاپ زیر تصمیم می گیرد و تخصیص دهنده سوئیچ مسئول درک نقل مکان ها برای حرکت به سوئیچ ماتریسی منتخب می باشد. در نقطه ای که بسته ی داده مسدود می شود به دلیل این واقعیت که هیچ فضای پشتیبانی در دسترس در سوئیچ مورد نیاز وجود ندارد، آن دارایی های بافر را در فورت مسیر خود اشغال خواهد کرد. بنابراین، ارسال پیام در سیستم های مبتنی بر سوئیچ لانه کرمی تمایل به توقف دارد [14] [16]. نقطه مبادله گرهی که در این رقم تعریف شده شامل 5 کانال شامل وقفه محلی برای برقراری ارتباط با مسیر مشخص ارتباطی هاب ها و دخالت در این نزدیکی برای وقفه محلی است همانطورکه نشان داده شده است.
در طول دوره، نقل مکان هدر پایگاه را در اطلاعات کانال مبادله (شامل هر دو گره های مجاور یا محور دسته همسایه مرتبط با سوئیچ غیر قابل تشخیص می باشد) لمس می کند، سوئیچ در مورد مسیر عبور بسته تصمیم می گیرد، به عنوان مثال در چهار جهت مختلف و یا کانال وقفه محلی یعنی کانال خروجی، بعدا، سوئیچ ماتریسی از طریق ارسال اطلاعات مرتبط به آن تنظیم می شود. تبادل ماتریسی کانال نزدیک نقل مکان را به کانال منتخب فعال ارتباط می دهد. به عنوان مثال، کانال مجازی آزاد، نقل مکان هدر ممکن است برای هاب مبادله شود و نقل مکان لبه پس از نقل مکان هدر شکل می گیرد. با بررسی برخی موارد دیگر، نقل مکان هدر نیاز به حفظ دارد تا زمانی که هر یک از کانال مجازی توسط کانال دیگر استفاده می شود مجموعه ای آزاد برای اشغال و استفاده از کانال است.
ب) الگوریتم مسیریابی
الگوریتم مسیریابی جزء مهمی است که اثر آن با مکاتبه بر NOC تأثیر می گذارد. محاسبه مسیریابی مسیر منتخب توسط بسته داده مشخص می شود که از منبع به مقصد هدایت می شود، یک دستور اولیه در NOC برای ساختن یک لایه شبکه است]17[. همانطور که مشخص شد گزینه های مسیریابی تعیین می شود، آن ممکن است منبع و توزیع مسیریابی را تحلیل کند. در مورد مسیریابی منبع، کل مسیر داده ها باید توسط گره منبع انتخاب شود، اگر چه در مسیر توزیع هر سوئیچ بسته داده ها را می گیرد و همچنین مسیر موثر برای بررسی داده ها انتخاب می شود. همانطور که نشان داده شد به چه شیوه ای مسیر برای ارسال بسته ها مشخص می شود، انتقال بسته های داده ها می تواند به صورت قطعی و یا چند منظوره مورد تجزیه و تحلیل قرار گیرد.به همین ترتیب آن با توجه به تطبیق پذیری آنها مشخص خواهد شد، ظرفیت تحمل خطا، کنترل کننده متمرکز، جریان داده ها را در یک چارچوب و بانک در مقدار مقصد خود کنترل می کند. هنوز هم به طور کلی همه کاره، قطعی و غیرفعال نامیده می شود. الگوریتم مسیریابی قطعی مسیر مشابهی را بین زوج های هاب تعیین می کند، تعادل بار به طور انحصاری برای شرایط فعلی بیان شده ضعیف و به هر حال آنها معمولا به دلیل کاربرد ساده استفاده می شود. در الگوریتم مسیریابی فراموشکار مسیربسته با توجه به حالت سیستم حذف می شود. الگوریتم مسیریابی سازگار داده ها در مورد حالت سیستم(مثلا محدودیت خطوط برای دارایی و غیره) برای تصمیم گیری مسیریابی استفاده می شود. روتر کاملا طراحی شده باید مسیر همه کاره را به سمت برنامه داده بسته در کانال ترافیک کم هدایت کند. در مسیر انطباق، هر سوئیچ اطلاعات مسدودی از محتویات محله خود دارد. متریک کانال انسداد را می توان بر اساس تعداد کانال های مجازی آزاد، تقاضا برای خروجی روتر ایجاد کرد، تعداد بافر های آزاد، ترکیب این پارامترها هستند [17] [21]. در رابطه با تراکم داده، سوئیچ بسته داده ای را برای اهداف خود با کانال های کم تراکم برنامه می کنند [18]. چند تجزیه و تحلیل امکان پذیر است مانند الگوریتم مسیریابی تحمل پذیر خطا که قطعه های شکسته را در زمان بسته های مسیریابی داده با قدرت تشخیص می دهد. بیشتر، مسیریابی از طریق تنظیم مجدد بدون تغیرعمده از سرتاسر ارتباط شکسته برای استفاده پیشرفته یک نوع مسیر به جای مسیر شکسته صورت می گیرد. نمودار جریان الگوریتم در شکل نشان داده شده است.
Abstract
The routing algorithm performs a critical function inside the overall performance of the community on chip. Dynamic routing is attractive in view of its considerable change in communication bandwidth and keen adjustment to flawed connections and congested traffic. XY-Routing in the mesh topology creates congestion at the central part of the network which increases the latency and leads to decreased performance. Congestion in a network generally increases at the central part of the network due to increased traffic on the same nodes periodically by the neighbor nodes. Furthermore, congestion due to the neighboring nodes will certainly diminish the performance of the system and will have an adverse effect on the nodes. Then we strive to minimize the local latency due to congestion using address distinct nearby place size, based on Divide and Conquer method for routing strain. It minimizes latency in each local vicinity with the aid of decreasing the routing pressure of each local node. In this paper we have implemented the popular mesh topology along with LBAR algorithm and the results are compared with conventional XY-Routing. It is observed that Load balancing and latency is improved in case of LBAR as compared to Normal XY and Total Network Congestion is reduced for LBAR as compared to traditional XY.
1. Introduction
Current System on chip contrast from wide region networks in their neighbourhood proximity and on the grounds that they show less nondeterminism. Neighbourhood, elite networks such as those produced for large scale multi-processors will be having comparative necessities as well as imperatives. A few distinct attributes, for example, energy requirements furthermore, design time specialization, are particular in SoC networks [1] [2]. The effectiveness of interconnection and meeting information exchange prerequisite are more imperative for NoC frameworks, and also network on chip (NoC) have turned out as an adaptable, versatile, and likewise reusable for the issues concerning these kind [3]. In a conventional wired NoC, the interchanges among embedded cores are for the most part by means of numerous switches and wired connections. This multi hop correspondence gets to be a noteworthy bottleneck in framework execution, which offers ascend to high dormancy and vitality dissemination. To defeat this execution restriction we propose a new architectural models roused by complex system hypothesis in conjunction with deliberately set on-chip connections to make high performance and low-latency NoCs [4]. Many center outlines, for example, the Intel Integrated structures are moving towards multicore Xeon Phi[5] [6] , as a way to accomplish productive and higher execution with low latency. In this paper we are proposing a performance model that minimizes the load in network-on-chip based system. Generally, engineers design a performance model, later analyse forthcoming technologies based on performance model. Regarding this point, first architectural model and applications are established individually. Then the applications are developed by the performance models and architectures are used to evaluate the selected applicationarchitecture combination [7] [8]. Meanwhile there exists multiple directions from current node to targeted node, network on chip must carry out steering algorithms to route data packet for target destination. It influence the throughput and latency that experiences the traffic.
A large number of proposals have been made for NoC and are implemented by network topologies and the routing algorithms are utilized for the on-chip communication networks. Routing algorithms can be cascaded into two specific strategies in accordance to the network type which it firmly fits. If the routing path of the data packet is fixed in advance then this sort of routing is known as source routing. A part from that if the path of the data packet is resolved hop by hop then this type of routing is called source routing [5] [9]. Such that NoC’s are usually implemented by dimension ordered routing (DOR) which primarily routes the packets initially in the horizontal direction (X dimension) and later in the vertical direction(Y dimension) towards the receiver [10]. Although this algorithm reduces the latency, they generally perform very low because there is a heavy load amidst the system which causes traffic in whole network [11]. Load balance XY routing algorithm exploits the network topology into different co-ordinates this helps in reducing the traffic in network, thereby it provide efficient performance over oblivious routing i.e., dimension ordered routing (DOR). This algorithm contains shortest path routing technique, advanced implementation and a light weight.
2. Related Work
A. NoC Overview
Switching approach, topology and routing algorithm are essential element within the layout of network on-chip. The topology represents network interconnection. In mesh topology the connections in system have comparative limits which makes basic physical design also the range becomes direct to the quantity of nodes. Size in the present topology is measured in terms of lines and segments [12]. Constant lengths is desired by so many research companies because of its appropriate electrical properties, layout capability and ease in resource on chip address [13]. There is preference in work with this topology has got its individual specific manner of steering known as source directing. This element in this topology delivers a proficient encoding of way data with just few bits [12]. While a packet header arrives in between the nodes, the switching process resolves by what means the transfer is set, i.e. the injection channel is attached for the ejection channel [14] [12].
Wormhole routing is broadly utilized for switching approach on account of its less buffer prerequisites and high noteworthy critically, as it generates the packet conveyance time about unbiased of the separation amongst source and destination hubs. In wormhole routing, a packet can be divide into a progression of settled length entities, called flits. The header flit (which contain the routing measurements) sets up a course through the system in the meantime as a definitive body flit pursue it in a pipelined design.
Consecutively to surge the general execution of the system, each channel of the group can be convenient multiplexed between a few supports, in particular virtual channels. By assigning distinct packets to each of these supports, flits of data from different packets might be sent in an interleaved way over each physical channel. This improves both throughput and latency by permitting blocked data packets that are to be neglected [15]. The data path of the data packet includes buffers and also crossbar switch. The steering module and the VC allocator decides the following hop and the following virtual channel, and switch allocator is in charge of figuring out which flits are chosen to navigate into the crossbar switch. At the point when a data packet is blocked by the reason of the fact that there is no accessible support space in the required switch, it will occupy the buffer assets that are on forth its path. Hence, message directing in wormhole switch based systems is inclined to stop [14] [16]. The exchanging point of the node delineated in this figure comprises of 5 channels including the local interrupt to communicate with distinct direction connecting hubs, and the nearby interfere for the local interrupt as shown.
During the course, flit of the header touches base at the information channel of an exchange (including both a nearby nodes or the neighbourhood handling component associated with the indistinguishable switch) the switch decides packet take-off course e.g., in four different directions or the local interrupt channel i.e. ejection channel, later the switch arranges the crossbar switch through sending relevant data to it. Crossbar exchange associates the flit's approaching channel to the chose active one. Inside the instance of life of a free virtual channel, the header flit may be exchanged for the ensuing hub and the edge flits take after the header flit. Take some other case, the header flit needs to hold up until any of the virtual channel which was being used by other channel is set free to occupy and use the channel.
B. Routing Algorithm
Routing algorithm is an important component that influences effectiveness with correspondence to NOC .The routing calculation characterizes the direction chosen by the data packet starting from source directed towards the destination, is a primary errand in NOC to construct a network layer [17]. As indicated to locate routing choices are seized, it is conceivable to analyse source and distributed routing. In case of the source routing, entire data path has to be chosen by the source node, although in distributed routing every switch gets the data packet as well as chooses effective path to address data. As indicated by in what way the path will be characterized to send packets, data packet transfer can be analysed by deterministic or else versatile. Likewise it will be characterized depend upon their versatility, the fault-tolerant capacity, concentrated controller governs the flow of data in a framework and bank on their destination quantity. Still generally named versatile, deterministic and oblivious. Deterministic routing algorithm designate similar path between a couples of hobs, load balance is exceptionally impoverished for already stated situation, and however they are ordinarily utilized because of simple usage. In Oblivious routing algorithm packet course left out considering system's state. The Adaptive routing algorithm utilize data regarding the system's state (e.g. limit of lines for assets, and so on.) to compose routing decisions. A fully designed router has to give versatile routing directed towards program a data packet over the less congested channel. In adaptive routing, every switch has clog data of its encompassing neighbourhood. The channel clog metric can be founded on free virtual channels quantity, the demand for router output, the number of free buffers are blend of these parameters [17] [21]. In regards of congestion data, the switch programs the data packet for its goals with less congested channels [18]. A few analysis are conceivable like Fault Tolerance routing Algorithm in which powerfully distinguishes the broken segments at the time of routing data packets. What's more, Routing through the Reconfiguration without revolution form throughout the broken connection for utilizing the advanced one of a kind path rather than the broken path. The flow chart of the algorithm is shown in the fig.
چکیده
1.مقدمه
2. کار مرتبط
الف) شرح مختصر NoC
ب) الگوریتم مسیریابی
ج) روش شناسی
3. مدل شبیه ساز
4. نتایج
1. 4ارزیابی عملکرد LBAR در مسیریابی XY
5. نتیجه گیری
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
A. NoC Overview
B. Routing Algorithm
C. Methodology
3. Simulator Model
4. Results
1. Performance evaluation of LBAR over XYRouting
5. Conclusi
