
دانلود رایگان مقاله مسیریابی چند بخشی با تعادل بار در شبکه های مش بی سیم
چکیده:
با گسترش روزافزون خدمات چندرسانه ای و کاربردهای ارتباطی گروهی، نیاز به مسیریابی چند بخشی برای پاسخ به درخواست های چند بخشی در شبکه های مش بی سیم بیشتر از قبل احساس می شود. یکی از چالش های اصلی در شبکه های مش بی سیم چند رادیویی چند کانالی استفاده ی کارا از ظرفیت کانال ها و همچنین تعادل بار در شبکه است.در این مقاله، ما یک الگوریتم برای ایجاد یک درخت چند بخشی پیشنهاد کردیم، یعنی مسیریابی چند بخشی تعادلی بار با الگوریتم ژنتیک (LM-GA). هدف از این الگوریتم ایجاد یک درخت چند بخشی برای دوره های درخواست شده در شبکه های مش بی سیم چند کانالی چند رادیویی (MCMR WMN ها) در رابطه با تعادل بار در کانال ها از طریق به حداقل رساندن حداکثر مقدار استفاده از کانال ها است. نتایج کارایی LM-GA در توزیع بار در کانال های شبکه با پیدا کردن راه حل های نزدیک بهینه و همچنین افزایش عملکرد شبکه ضمن اجتناب از ایجاد گلوگاه ها نشان می دهند.
1-مقدمه
در طی تکامل شبکه های مختلف بی سیم در نسل بعدی برای ارائه خدمات بهتر، یک تکنولوژی کلیدی پدید آمده است که به عنوان شبکه های مش بی سیم شناخته می شود(WMN ها). این شبکه ها به دلیل هزینه پایین، تعمیر و نگهداری راحت، قابلیت اطمینان و استواری آنها محبوب و معروف هستند [1]. در WMN ها بسته ها از گره منبع به گره مقصد در یک روش چند هوبی ارسال می شوند. گره ها شامل روترهای مش و کلاینت های مش هستند. کلاینت های مش دستگاه های کاربر نهایی نامیده می شوند و در عین حال روترها نقش نقطه دسترسی گذر را برای تبادل اطلاعات بین کلاینتها یا کلاینت ها- اینترنت ایفا می کنند. برخی از روترهای مش دسترسی مستقیم به شبکه های سیمی دارند و به عنوان دروازه برای گره های دیگر به منظور دسترسی به اینترنت عمل می کنند.
در شبکه های بی سیم بر خلاف شبکه های سیمی، کاهش ظرفیت ناشی از تداخل به دلیل طبیعت پخش آنها یک چالش اساسی است. یک راه خوب برای غلبه بر این چالش تجهیز روترهای مش با چندین رادیو و تخصیص کانال های غیر همپوشانی را به رادیوهای آنها است. استفاده از چند رادیو باعث انتقال موازی در کانال های مختلف می شود؛ با این حال، روند مسیریابی را پیچیده خواهد کرد. همچنین نادیده گرفتن استفاده از کانال ها ممکن است منجر به تراکم در کانال های خاص شود. در نتیجه یک تنگنا ممکن است ایجاد شود یا یک بار اضافه اولیه ی کانال ممکن است رخ دهد. همه این ها باعث کاهش توان عملیاتی شبکه خواهد شد.
مسیریابی چند بخشی به عنوان روشی برای برقراری ارتباط بین چندین گیرنده در نظر گرفته شده است؛ به این معنی است که داده ها از یک منبع به گروهی از مقصد ها ارسال می شوند. هدف از مسیریابی چند بخشی، یافتن یک درخت چند بخشی است که ریشه آن گره منبع است و تمام گیرنده ها را پوشش می دهد.
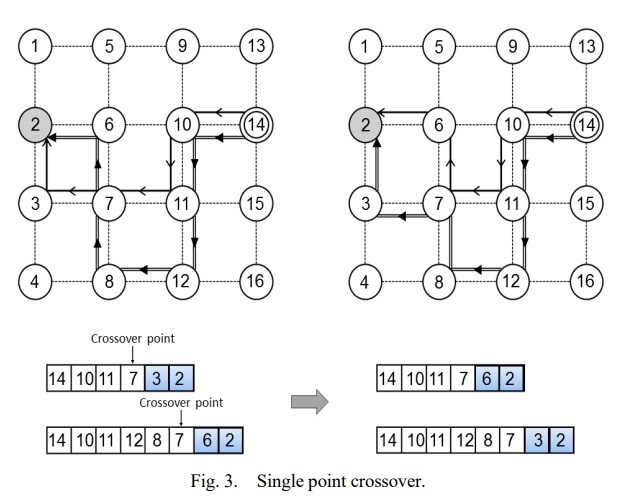
از آنجا که مشکل ایجاد یک درخت چند بخشی با کمترین هزینه (MCMT) یک مشکل NP سخت است [2]، یک الگوریتم به نام مسیریابی چند بخشی تعادلی بار با الگوریتم ژنتیک (LM-GA) برای یافتن جواب نزدیک بهینه استفاده شد. این الگوریتم فضای جواب ها را بررسی می کند و بهینه مکان را برای به دست آوردن بهترین راه حل و جواب برجای می گذارد.
این مقاله به شرح زیر سازمان دهی می شود: بخش 2 خلاصه ای از کارهای مرتبط ؛ بخش 3 مدل سیستم را معرفی می کند و مشکل را تعریف می کند. الگوریتم پیشنهادی ما در بخش 4 ارائه شده است؛ بخش 5 عملکرد الگوریتم را ارزیابی می کند؛ در نهایت بحث و نتیجه گیری در بخش 6 ارائه می شوند.
2- کارهای مرتبط
تعادل بار را می توان در دو سطح عمومی بررسی کرد: گره و کانال. بسیاری از مطالعات بر روی توازن بار در سطح گره انجام شده اند، یعنی روی روتر مش و مدخل. در اینجا تمرکز بر تعادل بار در کانال ها است. در حال حاضر برخی از تحقیقات در زمینه ساخت درخت چندپخشی انجام شده و تعادل بار در کانالها به طور خلاصه بررسی می شوند.در بقیه ی این مقاله، اصطلاحات مش و روتر ها به طور متناوب استفاده می شوند.
در [2]، لیو و لیائو مشکل ساخت یک درخت چندپخشی را با در نظر گرفتن دخالت بین درختان در مدل ترافیک پویا در شبکه های مش بی سیم چند کاناله چند رادیویی بررسی کردند (MCMR WMN). علاوه بر این، آنها در تحقیقات خود ثابت کردند که مشکل ساخت درخت چند بخشی با حداقل هزینه یک مشکل NP سخت است. علاوه بر این، آنها در ابتدا یک مدل بهینه برای ساخت یک درخت چن بخشی ارائه دادند و سپس یک الگوریتم نزدیک مطلوب به نام نزدیک ترین الگوریتم منشعب ترمینال بی سیم (WCTB) را پیشنهاد کردند. در هر مرحله از این الگوریتم، شاخه ای از منبع به مقصد به درخت اضافه می شود و این گره نزدیکترین مقصد بدون پوشش به منبع است.
اووک و میرجلیلی [3] یک الگوریتم ابتکاری برای ساخت یک درخت چند بخشی تعادلی - بار در MCMR WMN پیشنهاد کردند.آنها از یک تابع هزینه بارگیری آگاهانه برای وزن لینک ها استفاده کردند. در این تابع، دو عامل از مزایای پخش بی سیم (WBA) و توازن بار گره در نظر گرفته شد، که منجر به ساخت یک درخت چند بخشی با حداقل انتقال و توزیع منصفانه بار در شبکه و کاهش تداخل شد.
Abstract
By an increasing expansion of multimedia services and group communication applications, the need for multicast routing to respond to multicast requests in wireless mesh networks is felt more than before. One of the main challenges in multi-channel multi-radio wireless mesh networks is the efficient use of the capacity of channels as well as load balance in network. In this paper, we proposed an algorithm for building a multicast tree, namely, Load balanced Multicast routing with Genetic Algorithm (LM-GA). The purpose of this algorithm is to construct a multicast tree for requested sessions in Multi-Radio Multi-Channel Wireless Mesh Networks (MCMR WMNs) regarding load balance in channels through minimizing the maximum amount of channels utilization. The results show the efficiency of LM-GA in distribution of load in the channels of the network with finding near-optimal solutions, and also an increase in the network performance while avoiding creation of bottlenecks.
I. INTRODUCTION
During the evolution of various wireless networks in the next generation for providing better service, a key technology has emerged which is known as wireless mesh networks (WMNs). These networks are popular for their low cost, convenient maintenance, robustness and reliability [1].
In WMNs packets are sent from the source node to the destination node in a multi-hop manner. Nodes consist of mesh routers and mesh clients. Mesh clients are called end user devices and at the same time routers play the role of transit access point for exchanging information either between clients or clients- internet. Some mesh routers have direct access to wired networks and they serve as gateway for other nodes for access to internet.
In wireless networks unlike the wired ones, owing to their broadcast nature, capacity reduction caused by interference is a basic challenge. A good way to overcome this challenge is to equip the mesh routers with several radios and to assign nonoverlapping channels to their radios. Using multi-radios causes a parallel transmission in different channels; however, it will complicate the routing process. Also, ignoring the channels usage may lead to congestion in specific channels; as a result, a bottleneck may be created or an early overload of a channel may occur. All these will lead to a decrease in the network throughput.
Multicast routing has been considered as a way for communication between several receivers; it means that data will be transmitted / sent from one source to a group of destinations. The aim of multicast routing is to find a multicast tree whose root is the source node and that it covers all the receivers.
Since the problem of constructing a Minimum Cost Multicast Tree (MCMT) is a NP-hard problem [2], an algorithm named Load balanced Multicast routing with Genetic Algorithm (LM-GA) was used to find the near optimal solution. This algorithm explores the space of solutions and leaves the local optimum in order to get to the best solution.
This paper is organized as follows. Section 2 provides a summary of related works; Section 3 presents the system model and defines the problem; our proposed algorithm is presented in Section 4; Section 5 evaluates the algorithm operation; finally, the discussion and the conclusion are provided in Section 6.
II. RELATED WORKS
The load balance may be studied at two general levels: the node and the channel. Many studies have been carried out on load balance at node level, namely, on the mesh router and gateway. Here the focus is on load balance in channels. Now some research carried out on the construction of the multicast tree and the load balancing on channels are briefly reviewed. For the rest of this paper, the terms mesh routers and nodes are used interchangeably.
In [2], Liu and Liao studied the problem of building a multicast tree by considering the interference between trees in dynamic traffic model in Multi-Radio Multi-Channel Wireless Mesh Networks (MCMR WMN). Moreover, in their research they proved that the problem of building multicast tree with the minimum cost is a NP-hard problem. Besides, in order to build a multicast tree, first they presented an optimal model and then proposed a near optimal algorithm called Wireless Closest Terminal Branching (WCTB) algorithm. In each stage of this algorithm, a branch from source to destination is added to the tree and this node is the closest uncovered destination to the source.
Avokh and Mirjalili [3] proposed an innovative algorithm for building a load-balanced multicast tree in MCMR WMN. They used a load-aware cost function to weight the links. In this function, two factors of Wireless Broadcast Advantage (WBA) and node load balance were considered, which resulted in building a multicast tree with the minimum transmission and fair distribution of load in the network and decreasing the interference.
