
دانلود رایگان مقاله روتر انحراف بدون بافر تعادل بار برای شبکه روی تراشه
چکیده
روتر بدون بافر به عنوان یک گزینه جالب به منظور مقرون به صرفه بودن طراحی شبکه روی تراشه (NoC) پدید می آید. با این حال، روتر بدون بافر فقط تحت بار شبکه کم عمل می کند زیرا انحراف راحتر رخ می دهد در حالی که نرخ و سرعت تزریق افزایش می یابد. در این مقاله، ما یک روتر انحراف بدون بافر تعادل بار (LBBDR) برای شبکه روی تراشه که اثر انحراف را در شبکه روی تراشه بدون بافر کاهش می دهد،پیشنهاد می دهیم. LBBDR پیشنهاد شده یک شناسه تعادل تعویض را در روتر منبع برای کنترل جهت مسیریابی اولیه X یا Y برای یک رله در شبکه استفاده می کند. بر اساس این مکانیزم،نقل مکان مطابق مسیر XY یا YX در شبکه پس از آن،مسیریابی می شود. هنگامی که دو یا چند فلیت یک پورت خروجی مورد نظر مشابه را مطرح می کنند، یک روش اولویت به نام نزدیکتر-اولین برای حل مغایرت تخصیص پورت های خروجی مورد استفاده قرار می گیرد. نتایج شبیه سازی نشان می دهد که LBBDRمنجر به بهبود عملکرد مسیریابی در سرتاسر مسیریابی بدون بافر گزارش شده در نرخ انحراف فلیت، متوسط تاخیر بسته و توان عملیاتی به ترتیب 13٪، 10٪ و 6٪ می شود. مساحت طرح و مصرف انرژی در مقایسه با طرح های گزارش شده به ترتیب 12 و 7 درصد کمتر است.
1. مقدمه
با کاهش اندازه های ترانزیستور، هسته های مالکیت معنوی (IP) بیشتری در یک تراشه یکپارچه می شوند تا توابع سیستم پیچیده تری را اجرا کنند. همانطور که تعداد هسته های مالکیت معنوی در سیستم روی تراشه (SoC) همچنان به مقیاس بندی ادامه می دهند، معماری ارتباطات مبتنی بر باس و اتصالات متقاطع اغلب تنگنای عملکرد به علت افزایش نیاز به پهنای باند و تاخیر غیر قابل پیش بینی سیم است. راه حل رفع خواسته های ارتباطی سیستم چند هسته ای آینده، شبکه روی تراشه به دلیل مزایای قابل توجه آن مانند قابلیت استفاده مجدد، مقیاس پذیری و هم افزایی در زیرساخت ارتباطات تبدیل به یک راه حل در حال ظهور شده است.
روش مسیریابی یکی از مهمترین ملاحظات در طراحی شبکه روی تراشه است. این روش تأثیر مهمی بر برخی از معیارهای عملکردی نظیر متوسط تاخیر و توان عملیاتی سیستم در شبکه دارد. یک روتر لانه کرمی معمولی یا کانال مجازی برای شبکه روی تراشه معمولا شامل پورت های ورودی / خروجی، بافر ها، منطق مسیریابی و سوئیچ میله عرضی است که پورت های ورودی را به پورت خروجی متصل می کند. استفاده از بافر در روتر می تواند راندمان پهنای باند را افزایش دهد و از سقوط بسته جلوگیری کند. با این حال،بافر در روتر منجر به سربار بالای اجرای سخت افزاری می شود و پیچیدگی طراحی را افزایش می دهد. همانطور که در مرجع [6] اشاره شده است، بافر در روتر مسئول 46 درصد از مصرف برق روتر و 30 درصد ناحیه روتراست. با حذف بافرها، مسیریابی بدون بافر به عنوان یک راه حل بالقوه برای صرفه جویی در هزینه درطراحی شبکه روی تراشه پدیدار می شود.
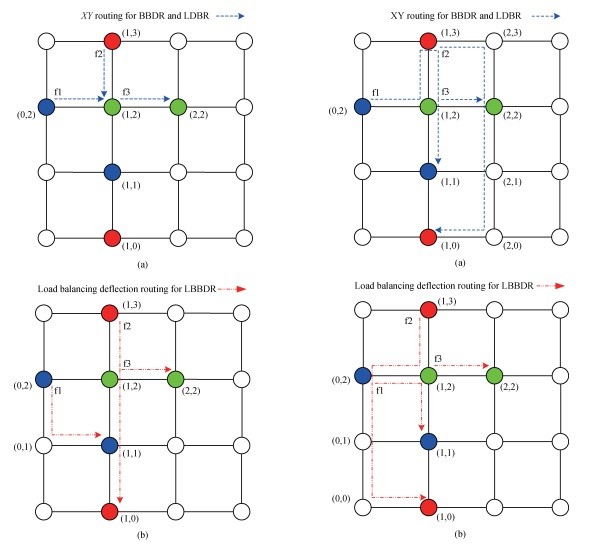
اصل اساسی مسیر بدون بافر برای شبکه روی تراشه این است که تمام بسته های ورودی به روتر باید بلافاصله به روتر مجاور فرستاده شوند. همانطور که هیچ بافری وجود ندارد، مغایرت پورت خروجی در روتر عمدتا توسط بسته ی انحراف، که' مسیریابی انحراف بدون بافر نامیده می شود، رفع می شود. برای مسیریابی انحراف بدون بافر، انحراف در بیشتر موارد دربار شبکه رخ می دهد،زیرا بسته های بیشتر ممکن است با یک پورت خروجی مشابه درگیر باشند.
هر انحراف یک فلیت دیگر از مقصد خود ارسال می کند، که باعث تحمیل هزینه های اضافی برای زمان تاخیر و مصرف انرژی می شود. علاوه بر این، مسیریابی انحراف بدون بافر با نرخ انحراف بالا می تواند به شدت عملکرد را به دلیل پردازش یک بسته درگیر درلایو لاک تضعیف کند. بنابراین، کاهش انحراف یک کلید برای بهبود عملکرد مسیریابی انحراف بدون بافر است.
دو طرح اغلب برای رفع این مسئله برای روتر انحراف بدون بافر مورد بحث قرار می گیرد. یکی از این دو طرح کاهش انحراف از بسته ها با اضافه کردن چند بافر، مانند رویکرد ذکر شده در مرجع [10] است. با این حال، این استراتژی، مزیت اصلی روتر بدون بافر را در کارایی هزینه ضعیف می کند. طرح دیگر کاهش انحرافات با استفاده از استراتژی اولویت یا مکانیزم کنترل است. بر اساس این ایده، اولویت مبتنی بر موقعیت و یک مکانیزم کنترل تراکم منبع خفانشی توزیع شده، به ترتیب در منابع [11، 12]، برای کاهش انحراف و رفع تراکم برای روتر انحراف بدون بافر ارائه شده بود. نتایج آزمایش نشان داده است که توان عملیاتی را می توان تا حدود 12٪ در مقایسه با روتور انحراف بدون بافر پایه بهبود داد، همانطور که در منبع [12] ذکر شده است. برای تجزیه و تحلیل علل انحراف، سه مدل انحراف ایجاد شد و یک روتر بدون بافر دارای انحراف کم (LDBR) در منبع [13] پیشنهاد شد که یک اینترفیس شبکه چند کاناله و مکانیزم کنترل برای حل مغایرت را اتخاذ کرد.با این حال،روترهای بالا عملکرد را توسط یک مکانیزم پیچیده بهبود می دهند.
در این مقاله ، ما یک روتر انحراف بدون بافر تعادل بار به نام LBBDR برای شبکه روی تراشه پیشنهاد می دهیم. برای توضیح مکانیسم کار، دو روتر بدون بافر معمولی معرفی می شوند. نقص عمومی پیچیدگی طراحی برای آن روترها تجزیه و تحلیل می شود که با مزایای اولیه روتر بدون بافر مخالف است. بر اساس نتایج بررسی مجدد ، LBBDR پیشنهادی استراتژی تعادل بار را برای مسیریابی اولیه فلیت همراه با روش اولویت بهبود یافته برای ساده سازی طراحی روتور انحراف به کار می گیرد. برای ارزیابی اثربخشی LBBDR، عملکرد مسیریابی انحراف و سربار سخت افزاری توسط یک پلت فرم شبیه سازی با استفاده از سیستم C و Design Complier of Synopsys با تکنولوژی HPMC 28 نانومتری TSMC ارزیابی می شود. نتایج نشان دهنده برتری آن دربار شبکه پایین تا متوسط در مقایسه با طرح های گزارش شده هستند.
باقی این مقاله به شرح زیر سازمان دهی می شود. دو روتر انحراف بدون بافر معمولی برای توضیح مکانیسم کار و نقص نتایج تحقیقات کنونی در بخش 2 توضیح داده می شوند. معماری LBBDR پیشنهادی و الگوریتم آن در بخش 3 ارائه می شوند. مقایسه مغایرت پورت خروجی بین LBBDR پیشنهادی و روترهای انحراف بدون بافر گزارش شده برای تشریح برتری اولی در بخش 4 ارائه می شوند. نتایج شبیه سازی در بخش 5 ارائه می شوند. نتیجه گیری های این مقاله در بخش 6 ترسیم می شوند.
Abstract
The bufferless router emerges as an interesting option for cost-efficient in network-on-chip (NoC) design. However, the bufferless router only works well under low network load because deflection more easily occurs as the injection rate increases. In this paper, we propose a load balancing bufferless deflection router (LBBDR) for NoC that relieves the effect of deflection in bufferless NoC. The proposed LBBDR employs a balance toggle identifier in the source router to control the initial routing direction of X or Y for a flit in the network. Based on this mechanism, the flit is routed according to XY or YX routing in the network afterward. When two or more flits contend the same one desired output port a priority policy called nearer-first is used to address output ports allocation contention. Simulation results show that the proposed LBBDR yields an improvement of routing performance over the reported bufferless routing in the flit deflection rate, average packet latency and throughput by up to 13%, 10% and 6% respectively. The layout area and power consumption compared with the reported schemes are 12% and 7% less respectively.
1. Introduction
With the shrinking of transistor sizes more intellectual property (IP) cores are being integrated onto a single chip to implement more complicated system functionsŒ1. As the number of IP cores continue to scale in system-on-chip (SoC) the architecture of bus-based communication and crossbar interconnections is often the performance bottleneck due to the growing of bandwidth requirement and non-predictable wire delayŒ2. Solution to address the communication demands of future multicore system, NoC has become an emerging solution due to its considerable advantages such as reusability, scalability, and parallelism in communication infrastructureŒ3 .
The routing policy is among the most important considerations in NoC designŒ4. It has an important impact on some performance criteria such as the average latency and system throughput in the networkŒ5. A typical wormhole or virtual channel router for NoC is commonly comprised of input/output ports, buffers, routing logic and a crossbar switch connecting input ports to output ports. The use of buffers in the router can improve the bandwidth efficiency and prevent the packet being dropped. However, buffers in the router lead to a high hardware implementation overhead and increase design complexity. As mentioned in Reference [6], buffers in the router are responsible for 46% of router power consumption and 30% of router area. With buffers elimination, bufferless routing emerges as a potential solution for cost-efficient in NoC design.
The basic principle of bufferless routing for NoC is that all packets arriving at a router must immediately be forwarded to an adjacent router. As there are no buffers, output port contention in the router is mostly resolved by the deflection packet, which is called bufferless deflection routingŒ8. For bufferless deflection routing, deflections occur more frequently at a high network load because more packets may contend the same output port. Each deflection sends a flit further from its destination, which causes extra cost for latency and power consumption. In addition, the bufferless deflection routing with a high deflection rate may severely degrade the performance due to the processing of a packet involved in livelockŒ9. Thus, to reduce deflection is a key for improving the performance of bufferless deflection routing.
Two schemes are mostly discussed to address this issue for the bufferless deflection router. One is to reduce the deflections of packets by adding a few buffers, such as the approach mentioned in Reference [10]. However, this strategy weakens the primary advantage of the bufferless router in cost-efficiency. The other is to reduce deflections by using a priority strategy or control mechanism. Based on this idea, a location based priority and a distributed source-throttling congestion control mechanism were proposed in References [11,12] respectively to reduce deflection and relieve congestion for a bufferless deflection router. The experiment results have shown that throughput can be improved by 12% compared with the baseline bufferless deflection router as mentioned in Reference [12]. To analyze the causes of deflections, three deflection models were constructed and a low-deflection bufferless router (LDBR) was proposed in Reference [13] which adopted a multi-channel network interface and control mechanism to address contention. However, the routers above yield performance improvement by a complex mechanism.
In this paper, we propose a load balancing bufferless deflection router called LBBDR for NoC. To explain the working mechanism, two typical bufferless deflection routers are introduced. The common deficiency of design complexity for those routers is analyzed, which disagrees with the primary advantages of the bufferless router. Based on the current research results, the proposed LBBDR employs the strategy of load balancing for flit initial routing combined with an improved priority policy to simplify the design of the deflection router. To evaluate the effectiveness of LBBDR, the performance of deflection routing and hardware overhead are assessed by a simulation platform using System C and Design Complier of Synopsys with the TSMC 28 nm HPM technology. The results illustrate its superiority under low-to-medium network load compared with the reported schemes.
The remainder of this paper is organized as follows. Two typical bufferless deflection routers are described to explain its working mechanism and the deficiency of current research results in Section 2. The architecture of the proposed LBBDR and its algorithm are presented in Section 3. A comparison of output port contention between the proposed LBBDR and the reported bufferless deflection routers are given to illustrate the superiority of the former in Section 4. The simulation results are presented in Section 5. The conclusions of this paper are drawn in Section 6.
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. روتر انحراف بدون بافرمعمولی
3. روتر انحراف بدون بافر پیشنهاد شده
4. بحث و تجزیه و تحلیل
5. نتایج تجربی
6. نتیجه گیری
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Typical bufferless deflection router
3. The proposed bufferless deflection router
4. Discussion and analysis
5. Experimental results
6. Conclusion
