
دانلود رایگان مقاله چالش های امنیتی VANet و راه حل ها
چکیده
VANet یک فناوری نوظهور با آیندهای امیدوار است که با چالشهای بزرگی بهخصوص در حوزهی امنیت روبهرو است. در این مقاله، به چارچوب امنیتی VANet در سه قسمت متمرکز میشویم. ابتدا یک نمای گسترده از ویژگیهای امنیتی VANet و چالشها و همچنین نیازمندیها ارائه میکنیم. این الزامات باید برای پیادهسازی زیرساخت امن VANet با ارتباطات موثر بین بخشها در نظر گرفته شود. جزئیات معماری امنیتی بیان شده و پروتکل شناخته شده استانداردهای امنیتی بیان شده است. در مرحله دوم، طبقهبندی جدیدی از حملات مختلف شناخته شده در کارهای گذشته مربوط به VANet و راهحلهای مربوط به آنها، ارائه میشود. در مرحله سوم، یک مقایسه بین برخی از این معیارهای امنیتی شناخته شده در VANet انجام میگیرد. سپس به مسائل مختلف باز و چالشهای مرتبط با امنیت VANet میپردازیم، که میتواند برای استفاده محققان در کارهای آتی کمککننده باشد.
1. معرفی
هدف VANet، اطمینان از رانندگی امن با بهبود جریان ترافیک و در نتیجه کاهش قابل توجه حوادث رانندگی است. که اخیرا با ارائه اطلاعات مناسب به راننده و یا به وسیله نقلیه حل شده است. بااین حال، هر گونه تغییر این اطلاعات در زمان واقعی ممکن است به شکست سیستم تأثیر بگذارد و امنیت مردم در جادهها را به خطر بیاندازد. برای اطمینان از عملکرد بدون اشکال آن، تامین امنیت این اطلاعات باید جزء اهداف مهم محققان امنیتی قرار گیرد.
VANET یک کلاس خاص از شبکه تلفنهمراه Ad-hoc با مسیرهای از پیش تعریف شده (جاده) است. که به روشهای خاص مدیریتی، واحدهای کنار جادهای (RSUs) متکی است. RSU ها بر کنارههای جاده برای انجام خدمات خاص قرار گرفتهاند و OBU ها در وسایل نقلیه موجود در VANET نصب شدهاند. تمام وسایل نقلیه در حال حرکت آزادانه در شبکه جادهای و ارتباط با یکدیگر و یا با RSUs و وسایل خاص هستند.
با استفاده از DSRC (ارتباطات اختصاصی با بردکوتاه) در یک و یا چند هاپ، حالتهای ارتباطی، V2V (خودرو به خودرو)، V2I (خودرو به زیرساخت) و یا ترکیبی است.
در سالهای آینده، بسیاری از وسایل نقلیه در VANET با وایرلس (OBU)، جی پی اس (سیستم موقعیتیاب جهانی)، EDR (ثبت روند داده) و سنسور (رادار و ladar) ارتباط برقرار خواهند کرد، همانطور که در شکل 1 نشان داده شده است. این تجهیزات برای نظارت و ثبت ترافیک استفاده خواهند شد.سپس بهطور خودکار اقدامات مناسب بنا به اطلاعات V2V یا V2I در داخل شبکه وسایل نقلیه انجام خواهد گرفت.
کاربران VANET از بسیاری از برنامههای کاربردی که به ایمنی فعال جاده، سرگرمی، بهرهوری ترافیک و مدیریت طبقهبندی شدهاند بهره میبرند[1]؛ سپس به مدیریت سرعت و ناوبری میپردازند.
امنیت حالتی از مصون ماندن نسبت به خطر یا تهدید است. امنیت به معنی ایمنی، و همچنین اقدامات انجام شده برای ایمنی یا محافظت است.
در VANET، محافظت در برابر فعالیتهای سوء استفاده و تعریف معماری امنیتی بسیار مهم است چرا که برقراری ارتباط بیسیم امن سخت است. امنیت و سطح تضمین شده آن برای پیادهسازی ایمنی مردم است. چند سال پیش، بسیاری از محققان حملات امنیتی را بررسی کردهاند و سعی در یافتن راهحلهای مربوط به آنها داشتند. افراد دیگر در تلاش برای تعریف امنیت در زیرساخت یا رسمی کردن استانداردها و پروتکلها هستند. اما هنوز هم، روند اعتماد نسبت به یک گره و تشخیص بسیار مشکل است.
این مقاله ویژگیهای امنیتی VANET و بسیاری از چالشهای امنیتی VANET و همچنین راهحلهای موجود را به شیوهای جامع بررسی میکند. پس از بررسی جزئیات معماری امنیتی و پروتکلهای استاندارد امنیتی شناخته شده، در مورد چارچوبهای اخیر و مسائل مرتبط بحث و بررسی انجام میدهیم. بنابراین بر طبقهبندی جدیدی از حملات مختلف شناخته شده در امنیت VANET و راهحلهای آن تمرکز میکنیم. در نهایت، با وجود تمام فرصتهای امیدوارکننده که همراه VANET است و پس از بحث در مورد آثار ارائه شده، به چالشهای پژوهشی خاص جهت تحقیقات آینده میپردازیم. بنابراین VANET به پیادهسازی یک سیستم برای وسایل نقلیه و گرههای مخرب میپردازد.
این مقاله به شرح زیر سازماندهی شده است. بخش 2 مدل VANET و نیازمندیهای امنیتی آن را بیان میکند. بخش 3 جزئیات و مدل حملات را بیان میکند. بخش 4 تلاشهای استانداردسازی را بیان میکند. بخش 5 راهحلهای طبقهبندی را به شیوهای منسجم بیان میکند. بخش 6 به تجزیهوتحلیل شکافها میپردازد. بخش 7 مسائل درحال ظهور و باز را بیان میکند و در بخش 8 نتیجهگیری بیان میشود.
2. ویژگیهای VANET، چالشهای امنیتی و محدودیتها
2.1 ویژگیهای VANET
VANET ها شبکههای ad hoc، بسیار پویا، با دسترسی کم به زیرساختهای شبکه و ارائه خدمات متعدد میباشند. حالتهای ارتباطی در VANET که در شکل 2 نشان داده شده است میتواند به کلاسهای خودرو به خودرو (V2V)، خودرو به زیرساخت (V2I) و ترکیبی طبقهبندی شود. در V2V، رسانههای ارتباطی استفاده شده، با زمان تاخیر کوتاه و نرخ انتقال بالا نشان داده شدهاند. این معماری در حالات مختلف هشدار (ترمز اضطراری، برخورد، کاهش سرعت، و غیره) و یا در رانندگی مشارکتی استفاده شده است. در V2I شبکه وسایل نقلیه، برنامههای کاربردی با استفاده از زیرساخت RSU و از طریق پورتال اینترنتی مشترک ارتباط برقرار میکنند. حالت ترکیبی، ترکیبی از دو روش قبلی است. ویژگیهای VANET بررسی شده در [1-6] را میتوان به دو گروه تقسیم کرد: 1) توپولوژی شبکه و روش ارتباطات یا 2) وسایل نقلیه و رانندگان.
Abstract
VANET is an emergent technology with promising future as well as great challenges especially in its security. In this paper, we focus on VANET security frameworks presented in three parts. The first presents an extensive overview of VANET security characteristics and challenges as well as requirements. These requirements should be taken into consideration to enable the implementation of secure VANET infrastructure with efficient communication between parties. We give the details of the recent security architectures and the well-known security standards protocols. The second focuses on a novel classification of the different attacks known in the VANET literature and their related solutions. The third is a comparison between some of these solutions based on well-known security criteria in VANET. Then we draw attention to different open issues and technical challenges related to VANET security, which can help researchers for future use.
1. Introduction
VANET aims to insure safe drive by improving the traffic flow and therefore significantly reducing the car accidents. The latter is solved by providing appropriate information to the driver or to the vehicle. Still, any alteration of this real-time information may lead to system failure impacting people safety on the road. To insure its smooth functioning, securing this information becomes a must and hence it is on the top outlook of security researchers.
VANET is a special class of mobile ad-hoc network with predefined routes (roads). It relies on specific authorities for registration and management, Roadside units (RSUs) and On-Board units (OBUs). RSUs are widespread on the road edges to fulfill specific services and OBUs are installed in the vehicles navigating in VANET. All vehicles are moving freely on road network and communicating with each other or with RSUs and specific authorities.
Using DSRC (Dedicated Short Range Communication) in a single or multi-hop, the communication mode is either V2V (Vehicle-toVehicle), V2I (Vehicle-to-Infrastructure) or hybrid.
In the coming years, most of the vehicles in VANET will be equipped with on-board wireless device (OBU), GPS (Global Positioning System), EDR (Event Data Recorder) and sensors (radar and ladar) as shown in Fig. 1. These equipments are used to sense traffic congestions and status. Then automatically take appropriate actions in vehicle and relay this information through V2V or V2I within the vehicular network.
VANET users profit from many applications that are classified into active road safety, infotainment, traffic efficiency and management [1]; the latter stands for speed management and cooperative navigation.
The security is the state of being free from danger or threat. Security means safety, as well as the measures taken to be safe or protected. For example, in order to provide adequate security for the parade, town officials often hire extra guards.
In VANET, it is critical to guard against misuse activities and to well define the security architecture because it is a wireless communication which is harder to secure. The security and its guaranteed level of implementation affect people safety. Few years ago, many researchers have explored the security attacks and tried to find their related solutions. Others tried to define security in frastructures, or formalize standards and protocols. But still, the trend of trustworthiness of a node and misbehaving detection is large to explore.
This paper presents VANET security characteristics and investigates most of the VANET security challenges as well as the existing solutions in a comprehensive manner. After detailing the recent security architectures and the well-known security standards protocols, we present and discuss the recent frameworks that address the related issues. We focus on a novel classification of the different attacks known in the literature of VANET security and their solutions. Finally, despite all the promising opportunities that accompany VANET and after discussing the presented works, we have specified certain research challenges and open questions which may be future research directions. Thus enabling VANET to efficiently implement a system for trusting vehicles and protect it from malicious nodes.
The remainder of this paper is organized as follows: Section 2 expands VANET model and its security requirements. Section 3 details the attacker model. Section 4 presents the standardization efforts. Section 5 presents the solutions classified in a coherent manner. Section 6 expands the gap analysis. Section 7 highlights the emerging and open issues and we conclude in Section 8.
2. Vanet characteristics, security challenges and constraints
2.1. VANET characteristics
VANETs are ad hoc networks, highly dynamic, with little access to the network infrastructure and offering multiple services. The communication modes in VANET shown in Fig. 2 can be categorized into Vehicle to Vehicle (V2V), Vehicle to Infrastructure (V2I) and Hybrid. In V2V, the used communication media is characterized by short latency and high transmission rate. This architecture is used in different scenarios of broadcasting alerts (emergency braking, collision, deceleration, etc.) or in a cooperative driving. In V2I, vehicular network takes into account the applications that use the infrastructure points RSUs which multiply the services through internet portals in common. Hybrid mode is a combination of the two previous techniques. VANET characteristics explored in [1–6] can be grouped related to: i) Network topology and communication mode or ii) Vehicles and drivers.
چکیده
1. معرفی
2. ویژگیهای VANET، چالشهای امنیتی و محدودیتها
2.1. ویژگیهای VANET
2.2. چالشهای امنیتی و محدودیتهای VANET
2.3. نیازمندیهای امنیتی (خدمات)
3. مدل مهاجم
3.1. حملات
3.2. مهاجمان
4. تلاشهای استانداردسازی شده
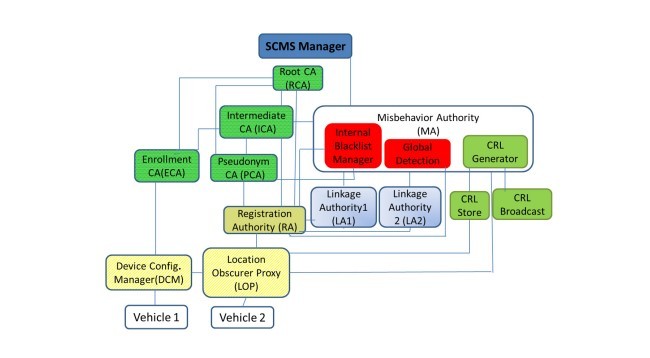
4.1. زیرساختهای امنیتی: PKI
4.2 معماری امنیت
4.3 استانداردهای امنیتی
5. راهحلهای پیشنهادی از کارهای گذشته برای حملات قبلا توضیح داده شده
5.1. حمله به رابطهای بیسیم:
5.2. حمله به سختافزار و نرمافزار
5.3. حمله به ورودی سنسور در خودرو
5.4. حمله به زیرساخت
6. تجزیهوتحلیل شکاف بین راهحلهای مختلف
7. مسائل باز و در حال ظهور
8. نتیجهگیری
منابع
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Vanet characteristics, security challenges and constraints
2.1. VANET characteristics
2.2. VANET security challenges and constraints
2.3. Security requirements (services)
3. Attacker model
3.1. Attacks
3.2. Attackers
4. Standardization efforts
4.1. Security infrastructure: PKI
4.2. Security architectures
4.3. Security standards
5. Proposed solutions from the literature to the previously described attacks
5.1. Attacks on wireless interface
5.2. Attacks on hardware and software
5.3. Attacks on Sensors input in vehicle
5.4. Attacks on Infrastructure
6. GAP analysis between different solutions
7. Emerging and open issues
8. Conclusion
References
