
دانلود رایگان مقاله سیستم هوشمند طراحی چیدمان حفره برای قالب های تزریق
چکیده
این مقاله روش توسعهی یک سیستم هوشمند طراحی چیدمان حفره (ICLDS) برای قالبهای تزریق چند حفرهای را ارائه میکند. این سیستم برای کمک به طراحان قالب در طراحی چیدمان حفرهها در مرحلهی طراحی مفهومی، درنظر گرفته شده است. پیچیدگی و اهداف طراحی چیدمان حفره به همراه وابستگی های مختلف در طراحی قالب تزریق، معرفی شده اند. دانش موجود در طراحی چیدمان حفره خلاصه و دسته بندی شده است. کاربرد، ساختار کلی و فرایند عمومی ICLDS توضیح داده شده است. همچنین در این مقاله دربارهی برخی مسائل از جمله ارائه دانش و استدلال مورد-مبنا در توسعه این سیستم، مورد بحث قرار گرفته است. با یک مثال از مسائل طراحی چیدمان حفره، کاربرد این سیستم نشان داده شده است.
1. مقدمه
در تولید، ریخته گری تزریقی یکی از پرکاربردترین فرایندهای تولید می باشد که برای تولید قطعات پلاستیکی، با نرخ تولید بالا و با نیاز کم یا بدون نیاز به پلیسه بر روی محصول پلاستیکی، مورد استفاده قرار می گیرد. این فرایند، شامل ریخته گری ماده پلاستیکی ذوب شده از یک اتاق داغ به داخل یک قالب بسته، مهلت دادن به پلاستیک برای خنک شدن و منجمد شدن و سپس خروج محصول نهایی از درون قالب، می شود. برای هر محصول پلاستیکی جدید، ماشین ریخته گری تزریق به یک قالب تزریق جدید نیاز دارد. طراحی و تولید قالب یک فرایند زمانبر و پرهزینه به حساب می آید و به طور عمومی برای انجام این کار به سازندگان ابزار و قالب با مهارت بالا، احتیاج است. یک قالب تزریق از چندین جزء تشکیل شده است، که شامل شالوده قالب، پین های راهنما، یک اسپرو ، تزریقگر، ورودی ها، کانال ها آب خنک کننده، صفحات پشتیبان و مکانیزم های برش و خارج کننده، می شود [1]. همچنین طراحی قالب از عوامل متعددی از جمله هندسه قطعه، ماده قالب، خط جدایش و تعداد حفره ها در قالب، تأثیر می پذیرد.
با پیشرفت در تکنولوژی و هوش مصنوعی، تلاش ها برای کاهش زمان و هزینه طراحی و تولید قالب تزریق، جهت یافتند. طراحی قالب تزریق به موضوع اصلی بسیاری از تحقیقات تبدیل شده است، از آنجایی که شامل چندین زیر-طرح مربوط به قطعات قالب میشود و هرکدام نیازمند تجربه و دانش تخصصی هستند، یک فرایند پیچیده محسوب می شود. همچنین طراحی قالب بر روی موضوعاتی از قبیل بهرهوری، هزینه تعمیر و نگهداری قالب، قابلیت تولید قالب و کیفیت قطعات ریخته شده، اثرگذار می باشد. اکثر تحقیقات طراحی قالب بر روی سیستم های تخصصی، سیستم های دانش بنیان و هوش مصنوعی انجام شده اند تا مهارت انسانی مورد نیاز در فرایند طراحی سنتی را حذف و یا تکمیل کنند. کروث و ویلمز [2] یک سیستم هوشمند پشتیبان را برای طراحی قالب تزریق ادغام شده با CAD/CAM تجاری، یک پایگاه اطلاعات مرتبط و یک سیستم تخصصی، توسعه دادند. لی و همکاران [3] یک روش سیستمی و دانش بنیان برای طراحی قالب تزریق در یک محیط مهندسی همزمان، پیشنهاد کردند. راویوُنگس و آلادا [4] یک ابزار پیشتیبان طراحی عصبی تحت شبکه را توسعه دادند که آن را برای محاسبه شاخص پیچیدگی قالب و همچنین کمک به طراحان قالب در مورد ارزیابی قابلیت تولید طرح پیشنهادی خود، ارئه کردند. وونگ و اسمیث [5] یک سیستم محاسباتی برای فرایند طراحی قالب تزریق بر اساس سیستم تخصصی تختهسیاه-مبنا و روش استدلال مورد-مبنا توسعه دادند که این سیستم شامل طراحی قالب، برنامه تولید، تخمین هزینه و تعیین پارامترهای قالب تزریق، می باشد. بریتین و همکاران [6] در مورد طراحی قالب از یک دیدگاه کاربردی، با استفاده از دانش طراحی کاربردی و تعدادی از کتابخانه های طراحی، بحث کرده اند. موک و همکاران [7] یک سیستم CAD تعاملی و دانش بنیان برای ترکیب طراحی قالب با مدول های محاسباتی، دانشی و گرافیکی، توسعه دادند.
تا کنون، مطالعات بسیاری برای ارتقاء طراحی اجزاء خاص یک قالب تزریق انجام شده است. اونگ و همکاران [8] یک روش دانش بنیان و شیء گرا را برای طراحی سیستم تغذیه قالب های طراحی توسعه دادند که این سیستم می تواند به صورت کارآمد نوع، مکان و ابعاد یک سیستم ورودی قالب را طراحی کند. همچنین ایرانی و همکاران [9] یک سیستم نرمافزاری را برای طراحی خودکار سیستم های ورودی و تزریقگر قالب های تزریق، توسعه دادند که طرح ورودی را برمبنای پارامترهای عملکردی خاصی مورد ارزیابی قرار می دهد. نی و همکاران [10] یک روش برای تعیین بهینه جهات جدایش در طراحی قالب تزریق را پیشنهاد کردند که این روش بر مبنای شناسایی و استخراج خودکار ویژگی های زیربرش، عمل می کند. چن و چو [11] برای انتخاب خط جدایش در طراحی قالب با محاسبه مقدار زیربرش و به حداقل رساندن تعداد آن ها، الگوریتم هایی را ارائه کردند. پارک و وُن [12] بر روی سیستمهای خنک کننده قالب های تزریق کار کردند و برمبنای تحلیل گرمایی و تحلیل حساسیت طراحی به مرحله خنک سازی در فرایند ریخته گری تزریق، یک طرح بهینه پیشنهاد کردند. لین [13] بر روی استفاده از ابعاد و موقعیت ورودی به عنوان پارامترهای اصلی برای شبیهسازی پیش بینی عملکرد قالب تزریق، کار کرد.
موضوعی که در طراحی قالب تزریق کمتر به آن پرداخته شده است، طراحی چیدمان حفره در یک قالب تزریق چند حفرهای می باشد. به دلیل اینکه طرح چیدمان حفره یکی از مهمترین مراحل در فراین طراحی قالب می باشد، به طور مستقیم بر روی کل فرایند ریخته گری تزریق تأثیر می گذارد. توجه به طراحی چیدمان حفره در مرحله طراحی مفهومی، کیفیت محصولات ریخته شده ارتقاء خواهد یافت، زیرا این موضوع بسیاری از عوامل کلیدی را که بر روی طرح و کیفیت قالب اثر می گذارند، تعیین می کند. از جمله این عوامل می توان به تعداد حفره ها، خط جدایش، نوع قالب، نوع و موقعیت ورودی، سیستم تزریقگر، سیستم خنک کننده و سیستم خارج کننده، اشاره کرد. ایجاد مدل دقیق ریاضی برخی از این عوامل برای تحلیل و طراحی دشوار می باشد.
این مقاله بر مبنای روش های شیء گرا و دانش بنیان، توسعه یک سیستم پشتیبان طراحی به نام سیستم هوشمند طراحی چیدمان حفره (ICLDS) را برای قالب های تزریق چند حفرهای، ارائه می کند. در این مقاله از استدلال های مورد-مبنا و قانون-مبنا که در راه حل های طراحی چیدمان وارد شده است، استفاده می شود [14]. این کار براساس نرمافزار تجاری «RETE++» انجام گرفته است. این نرم افزار یک پلتفرم توسعه یکپارچه می باشد که برای مشتریان این امکان را فراهم می کند تا سیستم های دانش بنیان خود را توسعه دهند [15]. هدف این مقاله، استفاده کامل از تکنیکهای موجود در هوش مصنوعی برای کمک به طراحان در مرحله طراحی مفهومی، می باشد.
2. طراحی چیدمان حفره در قالبهای تزریق
موضوع طراحی قالب تزریق (به خصوص طراحی چیدمان حفره)، به طور گسترده به تجربیات و دانش طراحان بستگی دارد. همچنین استفاده از دانش مهندسی، هوش مصنوعی و تکنیک های طرحی هوشمند در تولید یک طراحی چیدمان حفره قابل قبول برای دقت و کارآمدی در قالب تزریق، مطلوب به نظر می رسد. همچنین در طراحی قالب، اکثر الگوهای چیدمان حفره و قوانین و اهداف طراحی چیدمان حفره را به آسانی می توان به شکل دانشی که در بیشتر سیستم های طراحی دانش بنیان استفاده می شوند، ارائه نمود.
به طور مثال (برای الگوهای چیدمان نشان داده شده در شکل-1)، به طور کلی معیار انتخاب الگوی چیدمان مناسب در طراحی به محیط کاری، شرایط و نیازمندی های مشتری وابسته است و عموماً بر مبنای تجربه و مهارت طراح انجام می پذیرد. به طور حتم انتخاب عوامل متناقض به تجربه و دانش طراح وابسته است. همچنین برای سیستم هایی که برای این موقعیت ها طراحی شده اند (به خصوص طراحی های روزمره یا خلاقانه)، استفاده از تکنیک های طراحی هوشمند مناسب به نظر می رسد.
Abstract
This paper presents the development of an Intelligent Cavity Layout Design System (ICLDS) for multiple cavity injection moulds. The system is intended to assist mould designers in cavity layout design at concept design stage. The complexities and principles of cavity layout design as well as various dependencies in injection mould design are introduced. The knowledge in cavity layout design is summarized and classified. The functionality, the overall structure and general process of ICLDS are explained. The paper also discusses such issues as knowledge representation and case-based reasoning used in the development of the system. The functionality of the system is illustrated with an example of cavity layout design problem.
1. Introduction
In manufacturing, the injection moulding is one of the most widely used production processes for producing plastic parts with high production rate and little or no finishing required on plastic products. The process consists of injecting molten plastic material from a hot chamber into a closed mould, allowing the plastic to cool and solidify and ejecting the finished product from the mould. For each new plastic product, the injection moulding machine requires a new injection mould. Design and manufacture of injection mould is a time consuming and expensive process and traditionally requires highly skilled tool and mould makers. An injection mould consists of several components, which include mould base, cavities, guide pins, a sprue, runners, gates, cooling water channels, support plates, slides and ejector mechanism [1]. Design of mould is also affected by several other factors such as part geometry, mould material, parting line and number of cavities per mould.
With the advances in computer technology and artificial intelligence, efforts have been directed to reduce the cost and lead time in the design and manufacture of an injection mould. Injection mould design has been the main area of research since it is a complex process involving several sub-designs related to various components of the mould, each requiring expert knowledge and experience. Mould design also affects the productivity, mould maintenance cost, manufacturability of mould, and the quality of the moulded part. Most of the work in mould design has been directed to the application of expert systems, knowledge based systems and artificial intelligence to eliminate or supplement the vast amount of human expertise required in traditional design process. Kruth and Willems [2] developed an intelligent support system for the design of injection moulds integrating commercial CAD/CAM, a relational database and an expert system. Lee et. al. [3] proposed a systematic methodology and knowledge base for injection mould design in a concurrent engineering environment. Raviwongse and Allada [4] developed a neural networkbased design support tool to compute the mould complexity index to help mould designers to assess their proposed mould design on mould manufacturability. Kwong and Smith [5] developed a computational system for the process design of injection moulding based on the blackboard-based expert system and the case-based reasoning approach, which includes mould design, production scheduling, cost estimation and determination of injection moulding parameters. Britton et. al. [6] discussed the injection mould design from a functional perspective using functional design knowledge and a number of knowledge libraries. Mok et. al. [7] developed an interactive knowledge-based CAD system for injection mould design incorporating computational, knowledge and graphic modules.
Several studies have also been made on improving the design of specific components of an injection mould. Ong et. al. [8] developed a knowledge-based and objectoriented approach for the design of the feed system for injection moulds, which can efficiently design the type, location and size of a gating system in the mould. Irani et. al. [9] also developed a software system for automatic design of gating and runner systems for injection moulds and provide evaluation of gating design based on specified performance parameters. Nee et. al. [10] proposed a methodology for determination of optimal parting directions in injection mould design based on automatic recognition and extraction of undercut features. Chen and Chou [11] developed algorithms for selecting a parting line in mould design by computing the undercut volumes and minimising the number of undercuts. Park and Kwon [12] worked on the design of cooling systems in injection moulds and proposed an optimal design based on thermal analysis and design sensitivity analysis of the cooling stage of the injection moulding process. Lin [13] worked on the use of gate size and gate position as the major parameters for simulated injection mould performance prediction.
One area in injection mould design, which has received little attention, is the design of cavity layout in a multiple cavity injection mould. Cavity layout design affects the whole process of injection moulding directly, since it is one of the most important phases in mould design process. Consideration of cavity layout design in injection mould at concept design stage will improve the quality of injection moulded products because it is associated with the determination of many key factors affecting the design and quality of mould. Such factors include number of cavities; parting line; type of mould; type and position of gate; runner system; cooling system and ejection system. Some of these factors are difficult to build as true mathematical models for analysis and design.
This paper presents the development of a design support system, called Intelligent Cavity Layout Design System (ICLDS), for multiple-cavity injection moulds based on knowledge based and object oriented approaches. It uses the case-based and ruled-based reasoning in arriving at the layout solution [14]. It is based on the commercial software system named “RETE++”, which is an integrated development platform for customers to develop their own knowledge-based systems [15]. The objective is to make full use of available techniques in artificial intelligence in assisting mould designers at concept design stage.
2. Cavity Layout Design in Injection Moulds
Current practice for injection mould design, especially cavity layout design, depends largely on designers’ experiences and knowledge. It would therefore be desirable to use knowledge engineering, artificial intelligence and intelligent design techniques in generating an acceptable cavity layout design in injection mould accurately and efficiently. In mould design, most of patterns of cavity layout and rules and principles of cavity layout design can also be easily represented in the form of knowledge, which can be used in most of knowledge-based design systems.
For example, for the layout patterns shown in Fig. 1, the criteria to select the suitable layout pattern for design are mainly dependent on working environments, conditions and requirements of customer and are mainly based on designer’s skill and experience. To make a choice of contradictory factors will rely obviously on designer’s knowledge and experiences. It is rather suitable for intelligent design techniques to be used in systems designed for such situations, especially for routine or innovation design.
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. طراحی چیدمان حفره در قالبهای تزریق
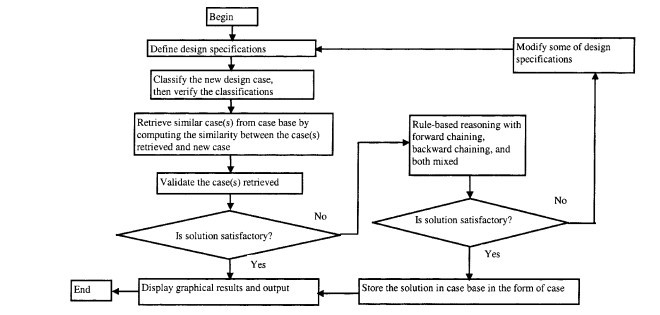
3. ساختار ICLDS و فرایند تولید
4.توسعه ICDLS
4.1 دسته بندی دانش
4.2 ارائه دانش
4.3 استدلال مورد-مبنا
4.3.1 فاصله ترتیبی
4.3.2 فاصله اسمی برای متن
4.3.3 فاصله اسمی برای نمادها
4.4 اعتبار مورد
4.5 معیار برای اعتبار کاهش هزینه
5. مثال کاربردی
6. نتیجه گیری
منابع
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Cavity Layout Design in Injection Moulds
3. Structure of ICLDS and the Design Process
4. Development of ICLDS
4.1. Classifications of Knowledge
4.2. Knowledge Representations
4.3. Case-based Reasoning
4.3.1. Ordinal Distance
4.3.2. Nominal Distance for Text
4.3.3. Nominal Distance for Symbols
4.4. Validation of Case
4.5. Criteria for Validity of Cost Reduction
5. Example of Application
6. Conclusion
References
