
دانلود رایگان مقاله نسل سوم شبکه های موبایل (3G) در درمان از راه دور
چکیده
تکامل در زمینه های تکنولوژی ارتباطات از راه دور ، با قدرت و توانایی ای که سیستم ها ی جدید ایجاد کرده اند، به طور موثری در پیشرفت و توسعه در زمینه پزشکی تاثیر گذار بوده است ؛ همچنین این پیشرفت ها باعث به وجود آمدن نیاز برای استفاده از آن ها در بخش مراقبت های پزشکی شده است، بخشی که نسبت به اطلاعات حساس بوده و نیازمند آگاهی و اطلاعات است.ازین رو، راه حل های الکترونیکی برای مراقبت های پزشکی دارای اهمیت بسیاری است؛مراقبت های پزشکی الکترونیکی و درمان از راه دور موضوعاتی هستند که به طور واضح ، برای اجرا و توسعه های عملیاتی بسیار مهم شده اند و دارای آینده ای روشن در زمینه بازار تجاری هستند.با در نظر داشتن این ویژگی، اهمیت این موضوع در زندگی شهروندان در تمام دنیا و سهم آن در مراقبت های پزشکی روزانه توسط تمام عوامل درگیر در این روند ، نویسندگان این قسمت تلاش دارند تا خوانندگان را با تاثیری که شبکه های بیسیم با پهنای باند بالا ، روی خدمات درمان از راه دور دارند، آشنا کنند و نشان دهند که چگونه این شبکه ها ، انتقال امن اطلاعات مهم را ممکن میسازد که از برنامه هایی نیازمند پهنای باند بالا، منتشر میشوند.بعد از اینکه خوانندگان را با موضوعات مربوط با درمان از راه دور آشنا کنیم و نشان دهیم که چگونه میتوانند به روش های مراقبتی فعلی، ارزش بیفزایند، سپس تحلیلی روی ساختار بیسیم انجام میدهند که خدمات درمان از راه دور را در طول سالها، آسان تر کرده است، و نقش مهم که سیستم های ارتباط از راه دور نسل سوم در این زمنیه ایفا میکنند را نشان خواهیم داد.بعد از آن ، تحلیلی از گستره کاربرد های جدید را خواهیم داشت که میتوانند توسط ساختار های ارتباط از راه دور نسل سوم پشتیبانی شوند، و تحقیقات مرتبط با ان ها را که در سطح اروپایی در مورد استفاده از شبکه های نسل سوم برای کارایی های درمان از راه دور است را نیز معرفی میکنیم.در هر صورت، شبکه های نسل سوم دارویی جادویی نیستند ؛ به همین دلیل محدودیت های این شبکه نیز بیان شده است.نویسنده میخواهد به این نتیجه برسد که آیا شبکه های نسل سوم میتوانند راه حلی مناسب برای خدمات درمان از راه دور باشند یا نه.
مقدمه
تکامل در زمینه های تکنولوژی ارتباطات از راه دور ، با قدرت و توانایی ای که سیستم ها ی جدید ایجاد کرده اند، به طور موثری در پیشرفت و توسعه در زمینه پزشکی تاثیر گذار بوده است ؛ همچنین این پیشرفت ها باعث به وجود آمدن نیاز برای استفاده از آن ها در بخش مراقبت های پزشکی شده است، بخشی که نسبت به اطلاعات حساس بوده و نیازمند آگاهی و اطلاعات است.ازین رو، راه حل های الکترونیکی برای مراقبت های پزشکی دارای اهمیت بسیاری است؛مراقبت های پزشکی الکترونیکی و درمان از راه دور موضوعاتی هستند که به طور واضح ، برای اجرا و توسعه های عملیاتی بسیار مهم شده اند و دارای آینده ای روشن در زمینه بازار تجاری هستند.همانطور که در یک دهه قبل انتظار میرفت، موسسات مراقبت های پزشکی از شبکه های کامپیوتری ، دستگاه های ذخیره کننده انبوه اطلاعات، و ایستگاه های کاری پیچیده ، بسیار استفاده میکنند که در ان ها انسان ها و ماشین ها با هم تعامل داشته و با استفاده از ابزار پیچیده پردازش اطلاعات و تکنیک های مهندسی اطلاعات، کار میکنند تا به یک یکپارچگی در رسانه های چند حالتی، اطلاعات تشخیصی و اطلاعات تخصصی پزشکی دست پیدا کنند.در هر صورت، درمان از راه دور یک ایده کاملا جدید نیست و در مقابل، این ایده به نوعی در سال 1906، هنگامی که W.Einthoven احتمال ارسال اطلاعات کاردیوگرام ها را با استفاده از خطور تلفن بیان کرد، توصیف شد.این توصیف به نوعی در سال 1910 ، هنگامی که S.G. Brown واقعا صداهای شنیداری را انتقال داد، به واقعیت پیوست.به علاوه، چند سال بعد، مخصوصا در سال 1920، ارتباطات بی سیم برای فراهم کردن توصیه های پزشکی در قایق ها از بیمارستان نروژی هاوکلند، مورد استفاده قرار گرفت.
از سال 2004، واژه سلامت الکترونیکی، به وجود آمد که توسط آیزنباخ ه این صورت تعریف شد : " سلامت الکترونیکی یک زمینه در حال ظهور در رابطه با اطلاع رسانی های پزشکی، سلامت عمومی و تجارت است که به خدمات بهداشتی و اطلاعاتی اشاره دارد که از طریق اینترنت یا تکنولوژی های مرتبط با آن تحویل یا بهبود داده میشود.در دیدی کلی تر، این واژه، نه تنها یک توسعه فنی را توصیف میکند، بلکه نوعی حالت ذهنی، دیدگاه ، منش و تعهد به یکپارچگی را بیان میکند که برای بهبود سلامت منطقه ای، ناحیه ای یا جهانی است ." واژه سلامت الکترونیک، باید واژه ای کلی باشد، یا بهتر واژه ای چتر مانند باشد تا تمام جنبه های خدمات درمانی از راه دور را زیر سایه خود ، در بر بگیرد.
درمان از راه دور (Telemedicine) ، یکی از جنبه هایی است که مشمول معانی واژه سلامت الکترونیک است.این واژه از کلمات tele از زبان یونانی به معنی فاصله دار و واژه medicine مشتق شده است که خود واژه medicine از واژه لاتین mederi مشتق شده است که به معنی درمان کردن است.در هر صورت، اگر چه این خدمات باعث به وجود آمدن واژه های بسیار شده است، در واقع تعریف استاندارد شده ای از آن وجود ندارد.در مقابل، سازمان های مختلفی به معانی متفاوتی در مورد درمان از راه دور رسیده اند. ازین رو برای مثال، سازمان جهانی بهداشت ، درمان از راه دور را به عنوان تحویل خدمات پزشکی ، در زمانی که فاصله یک عامل مهم و تاثیر گذار است، تعریف میکند که توسط متخصصین پزشکی با استفاده از تکنولوژی های اطلاعات و ارتباطات از راه دور برای تبادل اطلاعات معتبر برای تشخیص ، درمان و یا پیشگیری از مریضی ها و آسیب ها، تحقیقات و بررسی ها، و برای ادامه تحصیل ارائه دهندگان خدمات پزشکی، انجام میپذیرد که همگی به منظور پیشرفت وضعیت سلامتی افراد و جامعه شان است.از طرف دیگر، مرکز درمان از راه دور نروژی، درمان از راه دو را به این صورت تعریف میکند : تحقیق، پیگیری و آموزش بیماران و پرسنل با استفاده از سیستم هایی که امکان دسترسی مستقیم به اطلاعات بیماران و سرویس های مشورتی متخصصین را در هر جایی که باشند، فراهم میکند .علاوه بر این، ژورنال درمان از راه دور و خدمات از راه دور ، این واژه را به عنوان خدمات پزشکی ای تعریف میکند که از راه دور انجام میشود، و به طور مشابه نه تنها تشخیص بلکه درمان را نیز شامل میشود، همچنین در آموزش های پزشکی نیز مورد استفاده قرار میگیرد.با وجود اینکه باز هم این واژه به طور کاملا واضح تعریف نشده است، هدف روش های درمان از راه دور، فراهم کردن خدمات به صورت کیفی برای تمام شهروندان است، با تلاشی برای کم کردن یا حذف تاثیر موقعیت های جغرافیایی و موانع اقتصادی.
خدمات درمان از راه دور
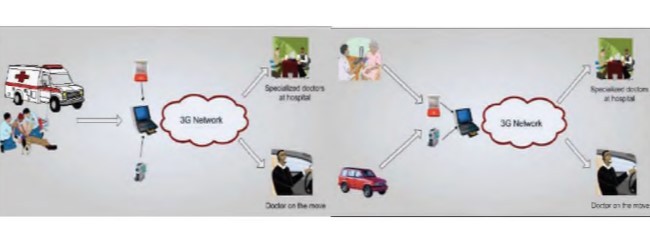
خدمات درمان از راه دور، اکنون برای پشتیبانی از تحویل خدمات پزشکی، مانند مشاوره های از راه دور( متخصص-متخصص یا متخصص –بیمار ) برای اهداف تشخیصی، راهنمایی از راه دور و اعمال روند های متنوع درمانی و جراحی است که ازین رو متخصصان را از راه های دور، در حوزه دسترسی می آورد ( مثلا محل تصادف، مکان های دور افتاده جغرافیایی، جزایر، میادین جنگی، کشتی ها و هواپیما ها، و محیط های خطرناک و غیره ) .همچنین دسترسی مستقیم به اطلاعات جهانی و استفاده مستقیم و راه دور از تسهیلات مکمل برای پردازش اطلاعات پزشکی را نیز ممکن ساخته است.علاوه بر این، یکی دیگر از اهداف درمان از راه دور، پیوستگی مراقبت های پزشکی و تحویل اماده ی اطلاعات بیمار ، به طور دقیق و شفاف در هر جا و هر زمان مورد نیاز ، است.درمان از راه دور ، شامل مجموعه ای از خدمات خودکار است که روی یک شبکه ارتباط از راه دور پیشرفته پیاده شده است و توسط تکنولوژی هی مختلف اطلاعاتی، پشتیبانی میشود.هدف آن ، فراهم کردن سطوح مختلف پشتیبانی برای نظارت از راه دور، پیشگیری و روند های درمانی و تشخیصی است.ازین رو، درمان از راه دور میتواند به عنوان یک مراقبت پزشکی گسترده واقعی در نظر گرفته شود که شامل منابع فیزیکی و انسانی موجود در یک گستره وسیع میشود تا روند های پزشکی و مدیریت بیماران را از راه دور، فراهم کند.
محیط نو ظهوری که در آن مراقبت های پزشکی خودکار از راه دور میتواند فراهم شود، دارای ساختاری لایه ای است.لایه بالایی مرتبط با خدماتی است که در واقع ارئه میشود، مانند تشخیص از راه دور، نظارت از راه دور، مشاوره از راه دور، مدیریت از راه دور، و دیگر خدمات با ارزش .لایه دوم، شامل تمام برنامه های کامپیوتری است که تمام ارتباطات لازم را ممکن میسازد و همکاری هایی که در محیط کامپیوتری برای تحقق خدمات درمان از راه دور انجام میشود.این چنین کارایی های کامپیوتری، شامل نامه های الکترونیکی، کنفرانس های چند رسانه ای، مشاوره های هماهنگ و ناهماهنگ ، تحلیل های تعاملی تصاویر، و مشاهده اطلاعات چند رسانه ای ، ابزاری برای بررسی اطلاعات پزشکی توزیع شده در محدوده های جغرافیایی، و تنوع بسیاری از کاربرد ها میشود که این خدمات با ارزش را تسهیل میسازد.لایه پایین هم مرتبط با سخت افزار و نرمافزار هایی میشود که این کاربرد هایی که ذکر کردیم را پشتیبانی میکند و شامل تجهیزات پزشکی، کارگاه ها ی توزیع شده، شبکه های ارتباط از راه دور و ابزاری برای مدیریت شبکه ها و دیگر منابع است.
هدف اولیه درمان از راه دور، فراهم کردن پشتیبانی برای مشاوره های متخصصین بر اساس اطلاعات پزشکی مورد نیاز به صورت منطقه ای، و راهنمایی از راه دور برای روند های پزشکی است که به صورت منطقه ای انجام میشود.ازین رو، درمان از راه دور میتواند گستره وسیعی از نیاز های درمانی را پوشش دهد، شامل فراهم کردن مراقبت های پزشکی در مناطق دور، در وسایل انتقال دهنده به بیمارستان، درمان های اورژانسی از راه دور، مراقبت های خانگی، تدریس از راه دور، همگون سازی خدمات پزشکی می باشد.خدمات مختلفی که در پایین توصیف میشود، بر اساس اهداف خاص هر بخش از درمان از راه دور هستند.
تشخیص از راه دور
عموما، این خدمات شامل ارتباط نقطه به نقطه غیر همزمان است و نیازمند برنامه های کاربردی نسبتا آسان و حداقل ساختار سازمانی است.با توجه به نیازی برای یک پایگاه راه دور، که تمام اطلاعات یا اطلاعات گزینش شده بررسی های تشخیصی را منتقل میکند، متخصصان در یک مرکز پزشکی ارجاعی این اطلاعات را بررسی میکنند و یک گزارش تشخیصی را به پایگاه درخواست دهنده منتقل میکنند.تشخیص از راه دور خصوصا برای منطقه های حومه شهر و جاهایی که دارای پرسنل متخصص پزشکی نیستند، مفید است.
ABSTRACT
The evolutions in the field o f telecommunications technologies, with the robustness and the fidelity these new systems provide, have significantly contributed in the advancement and development in the field o f medicine, and they have also brought forth the need for their utilisation in the healthcare sector. Thus, telemedicine and e-Health have clearly started to become an important issue for implementation, operational deployment o f services and apromising market for industry. Recognizing this trend, its importance in the lives o f citizens all around the globe and its contribution in the daily healthcare delivery by all actors involved in the procedure, the authors o f this chapter attempt to familiarize the readers with the impact that high broadband wireless networks have upon telemedicine services and with the way they facilitate the secure transmission o f vital information stemming from bandwidth demanding applications in real time. After providing the readers with an overview o f telemedical services and commenting on how they can offer added value to existing healthcare services, they provide an analysis o f the wireless infrastructure that has facilitated telemedical services over the years, and point out the significant role that the third generation telecommunications systems can play in the field. After that, follows an analysis o f the range ofnew applications that can be supported by the 3G telecommunications infrastructure, and the related research that has taken place in the European level regarding the utilization o f 3G networks for telemedical applications. However, 3G networks are not a panacea; for this reason the limitations o f this infrastructure is also stressed out. The authors conclude by discussing whether 3G networks can prove to be an attractive solution for telemedical services to healthcare providers.
INTRODUCTION
The evolutions in the field of telecommunications technologies, with the robustness and the fidelity these new systems provide, have significantly contributed in the advancement and development in the field of medicine; they have also brought forth the need for their utilisation in the healthcare sector, a sector that is information intensive and knowledge demanding. Thus, e-Health solutions are of crucial importance (Olsson & Lymberis & Whitehouse, 2004, p.312); telemedicine and eHealth have clearly started to become an important issue for implementation, operational deployment of services and a promising market for industry (Wooton, 1999) (“EU2004a”, 2004). As had been forecasted a decade ago, healthcare institutions make extensive use of computer networks, mass storage devices, and sophisticated workstations at which humans and machines interact, assisted by advanced information processing tools and techniques of knowledge engineering, to achieve integration of multimodality multimedia, diagnostic data and expert medical knowledge (Orphanoudakis & Kaldoudi & Tsiknakis, 1996, 210). However, telemedicine is not a brand new service. On the contrary, telemedicine has been described from as early as as 1906, when W.Einthoven described the possibility oftransmitting cardiogram information via telephone lines. This description became a reality in 1910 when S.G. Brown did actually transmit hearing sounds in London. In addition, a few years later, and more specifically in 1920, wireless communications were utilized in order to provide medical advice support in boats from the Norwegian hospital Haukeland.
Since 2004, the term eHealth aroused, defined by Eysenbach as: ‘‘eHealth is an emerging field in the intersection of medical informatics, public health and business, referring to health services and information delivered or enhanced through the Internet and related technologies. In a broader sense, the term characterises not only a technical development, but also a stateof-mind, a way of thinking, an attitude, and a commitment for networked, global thinking, to improve healthcare locally, regionally and worldwide by using information and communication technology’’(Eysenbach, 2001, e20), (Pagliari et al, 2005, e9). The term eHealth is supposed to be an overall term, or even better an “umbrella” term, including all aspects of Health Telematics.
Telemedicine is one ofthe areas canopied under the umbrella-term - eHealth. The term ‘telemedicine’ derives from the Greek ‘tele’ meaning ‘at a distance ’ and the present word ‘medicine’ which itself derives from the Latin ‘mederi’ meaning ‘healing’. However, even though this service has been attributed many terms, there is not actually a standardized definition of it. On the contrary, various organizations have come up with different definitions of the term telemedicine. Thus for example, the World Health Organisation defines telemedicine as the delivery of healthcare services, where distance is a critical factor, by healthcare professionals using information and communications technologies for the exchange of valid information for diagnosis, treatment and prevention of disease and injuries, research and evaluation, and for the continuing education of healthcare providers, all in the interest of advancing the health of individuals and their communities (W.H.O., 1998). The Norwegian Center of Telemedicine on the other hand defines telemedicine as the research, the follow-up and the management of patients, as well as the education of patients and personnel, making use of systems that allows the direct access in patient data and the advisory services of experts, anywhere they might be located (Norwegian Centre for Telemedicine 2007). Furthermore, the Journal of Telemedicine & Telecare defines telemedicine as the medicine practiced from a distance, and as such, encompasses not only the diagnosis but the treatment, as well and in addition the medical education (Journal of Telemedicine and Telecare 2007). Even though not clearly defined however, telemedicine targets towards the qualitative healthcare provision for all citizens, trying to diminish and if possible eliminate geographical and/or economical barriers.
TELEMEDICINE SERVICES
Telemedicine services are currently employed to support various aspects of healthcare delivery, such as remote consultation (physician-physician or patient-physician) for diagnostic purposes, remote guidance and performance of a variety of therapeutic and surgical procedures thus making expertise available at remote sites (e.g. site-ofan accident, geographically isolated places, on board ships and planes, sea-plants, battle-fields. hazardous environments, space stations, etc), real-time access to educational material and statistical information on a global basis and remote use of distributed complementary facilities for medical information processing. Furthermore, an important goal of telemedicine is to guarantee continuity of care, rendering the medical history of a patient readily, timely and transparently available wherever and whenever needed.
Telemedicine/telehealth consists of a set of added-value telematic services, implemented over an advanced telecommunications infrastructure and supported by different information technologies and related applications. Its main goal is to provide different levels of support for remote monitoring, preventive, diagnostic and therapeutic medical procedures. Therefore, telemedicine can be considered as an extended virtual healthcare institution that encompasses available physical and human resources over a wide region in order to support remote medical procedures and patient management.
The emerging environment in which healthcare telematics services can be provided has a layered structure (Orphanoudakis & Kaldoudi & Tsiknakis, 1996, 210). The top layer corresponds to the actual services provided, such as tele-diagnosis, tele-monitoring, tele-consultation, tele-management, and other added-value services. The second layer consists of all computer applications that provide the necessary communications and computer supported cooperative working environment for telemedicine services to be realized. Such applications include electronic mail, multimedia conferencing, synchronous and asynchronous consultation, immersive environments and tele-presence, interactive image analysis and visualization of multimedia medical data, tools for querying geographically distributed medical databases, and a variety of other applications that facilitate added-value information services. The bottom layer corresponds to the hardware and software infrastructure that supports the aforementioned applications and consists primarily of medical equipment, distributed workstations, the telecommunications network, and tools for the management of network and other resources.
The primary goal of telemedicine is to provide support for remote expert consultation based on locally acquired medical data and remote guidance for locally performed medical procedures. Thus, telemedicine can cover a wide variety of medical needs, including provision of healthcare in remote areas, in transportation means, emergency telemedicine, homecare, tele-education, homogenisation of medical services and others. Different services are described as follows, based on the specific objectives of each telemedicine session.
Tele-Diagnosis
Typically, this service involves asynchronous point-to-point communication and requires relatively simple applications and a minimum infrastructure. In response to a request by a remote site, which transmits all or selected data of a diagnostic examination, specialists at a referral medical center review these data and return a diagnostic report to the requesting site. Tele-diagnosis is particularly useful for rural and other areas that are not well served by specialized medical personnel.
چکیده
مقدمه
خدمات درمان از راه دور
تشخیص از راه دور
نظارت از راه دور
مشاوره از راه دور
مدیریت از راه دور
آموزش از راه دور
خدماتی با ارزش افزوده
زیرسازی های فنی
کاربرد ها
تحقیقات مربوطه
محدودیت ها
فواید
بحث
منابع
ABSTRACT
INTRODUCTION
TELEMEDICINE SERVICES
Tele-Diagnosis
Tele-Monitoring
Tele-Consultation
Tele-Management
Tele-Education
Added-Value Services
TECHNOLOGICAL INFRASTRUCTURE
APPLICATIONS
RELATED RESEARCH
LIMITATIONS
BENEFITS
DISCUSSION
REFERENCES
