
دانلود رایگان مقاله ابزار پشتیبانی فعال برای نوآوری در عدم قطعیت عمیق - اجزای مدیریت استراتژیک
چکیده
این مقاله چارچوب نظری و کاربردی لازم را برای کاهش غیر قابل پیش بینی بودن پویایی نوآوری، سرعت انتقال فن آوری و سرعت پیکر بندی دوباره / تحول از طریق روش ادغام مهندسی سیستم، روش اختصاصی برای فرآیندهای تصمیم گیری استراتژیک و یکپارچه سازی اصول مدیریت نمونه کارها در گزینه های واقعی با یک عنصر تصادفی اضافی بیان شده توسط حرکت براونی هندسی (GBM) ایجاد می کند. این فلسفه جدید سعی در پیدا کردن یک تصمیم گیری بهینه در فرآیند نوآوری دارد، اما منجر به پیش بینی پویا ئی عمومی بر توسعه مکانیزم خاص بر اساس انعطاف پذیری به منظور ساخت راه حل های ویژه اختصاص داده شده در این زمینه و صنایع نوآورانه، مانند رباتیک و مکاترونیک می گردد. مواد تشکیل دهنده مدیریت استراتژیک باید تطبیق با شرایط معمولی از واکنش بازار و تغییر رفتار مصرف کننده را به چالش بکشند. فرایند تصمیم گیری درتکنولوژی صنعتی بالا مانند رباتیک و مکاترونیک بسیار پیچیده است چرا که این عنصر فنی باید در ارتباط اجتماعی و اقتصادی نوآوران، و عناصر مالی درک شود. چارچوب در واکنش های بازار پیچیده نسبت به پیشرفت های فن آوری مخرب و یک رقابت بسیار قوی جهانی شکل گرفته است. مواد تشکیل دهنده انعطاف پذیر در فرایند سازمانی توسط مفاهیمی چون تولید ناب و شش سیگما تنها در یک شیوه های فنی محقق ارائه شده ، اما مدیران صنعتی با تکنولوژی بالا نیاز به انعطاف پذیری بیشتر به منظور انطباق با یک پاسخ سریع به تغییرات در بازارهای تحت تاثیر قرارگرفته دارند.
1. مقدمه
رباتیک و مکاترونیک صنایع نوآورانه با نرخ موثر توسعه به منظور بدست آوردن خروجی حیاتی کسب و کار لازم هستن که دیدگاه جهانی درنظر می گیرند که فراتر از تکنولوژی و مدیریت استراتژیک است نوآوری عنصر مهم در این نوع از صنایع را ارائه می دهد اما تصویر جهانی باید تمام عناصر در تعاملات سینرژیک را درنظر بگیرد.
پارادایم تولید مشارکت چابک هم افزایی با یک چشم انداز استراتژیک بیان است و (قوی در مراحل تغییر) در زمینه رقابت قوی می باشد. پارادایم تولید ناب به منظور دست آوردن انعطاف پذیری و کیفیت معرفی شد. تولید ناب (روش های عملیاتی در استفاده بهینه از منابع متمرکز) پاسخ متعارف به رقابت با محدودیت در منابع، اما تولید چابک است ( استراتژی با عدم قطعیت کنار آمده است) و پاسخی به پیچیدگی است. چابکی در واقع پاسخ به تغییر بوده و نیاز به همکاری در منابع و انعطاف پذیری لازم برای انطباق سریع با بازار و مشتریان دارد.
شش سیگما مربوط به پیچیدگی بوده و به روش های مختلف، ابزارهای مبتنی بر تکنیک های مربوط به مدیریت کیفیت جامع (TQM) و بیان شده توسط DMAIC (تعریف - اندازه گیری - تجزیه و تحلیل) بستگی دارند. علاوه بر این حمایت از بهره وری سازمان بر اساس کیفیت (بالقوه و بالفعل)، کاهش ضایعات و استفاده فعال از روش برش هزینه دربهبود و کنترل تولید موثر است.
مشاهده جنبه های مهم در بازارهای مربوط به عنوان یک روش علمی، بر اساس شش سیگما (توسعه کسب و کار)، توسعه فرضیات سازگار مربوط به مشاهدات ساخت و آزمایش و پیش بینی با توجه به مفروضات و مشاهدات یک حلقه بازخورد است که تفاوت های بین مفروضات و نتایج واقعی کار را به حداقل رسانده است. نقش شش سیگما در مدیریت زنجیره تامین (SCM) باید با درموارد زیر در نظر گرفته شود: درسیاست تامین کنندگان، اهداف و تحویل، استراتژی های ارتباطی، جدول زمان بندی برای استقرار، روش ارزیابی کننده بهره وری شش سیگما و ادغام برنامه آن.
تفاوت بین تولید ناب با سود کم (بر اساس سیستم تویوتا) و شش سیگما با قابلیت تولید ناب به بهبود بهره وری در مقابل تمرکز بر نقص در مورد کیفیت شش سیگما، به کاهش مودا (اتلاف) در هر محیط منجر می گردند. مفهوم ناب مجموعه ثابت از راه حل شش سیگما در درک مکانیسم ظرفیت مشکلات دیگری که در پویایی فرایندهای نوآورانه وجود دارند ارائه می دهد که در این مورد دو مفهوم مکمل و توام باهم هستند.
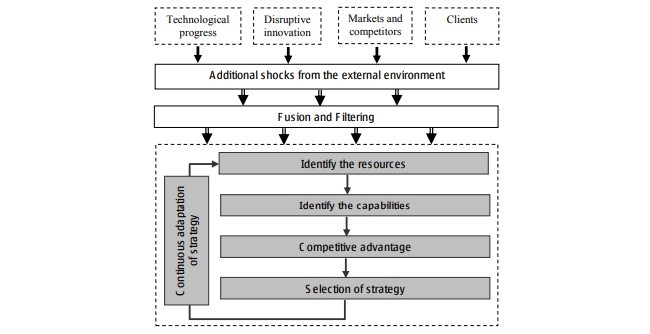
فرآیند نوآوری توسط مدیریت استراتژیک از عدم قطعیت به حداقل رساندن سازگاری با عدم قطعیت و ایجاد تعادل بین ثبات و انعطاف پذیری تحت تاثیر قرارمی دهد. تصمیم استراتژیک باید به تجزیه و تحلیل هزینه و مزایای کاهش / حفظ عدم قطعیت، اکتشاف بهینه از سیستم اعتقاد به شرکت وتجزیه و تحلیل اثر پیش بینی شده در معماری حلقه بازخورد بپردازد. از یک طرف، زیر سیستم ها نیاز به آزادی و انعطاف پذیری به منظور مقابله با عدم قطعیت به صورت محلی دارند و از سوی دیگر، اختلال می تواند به عنوان فرصت برای نوآوری سازمانی مشاهده شود.
در مورد مدیریت نوآوری در صنایع تکنولوژی بالا مانند رباتیک و مکاترونیک، اثرات ریسک و عدم اطمینان ممکن است با عدم تقارن اطلاعاتی تشدید شود. با توجه به عدم نوآوری معمولی از منابع معرفی بخش مهمی از عناصر مدیریت استراتژیک به منظور درک سازگاری با بازار و مشتریان در شیوه ای کارآمد ضروری است. اگر چه تصمیم گیرنده های استراتژیک مسئول و صاحب یک گستره وسیعی از ابزارهستند، قادر به ارائه یک تصویر یکپارچه از محیط پیچیده و اجتماعی و فنی از نظر دینامیک،هستندو یک دستور جهانی نمی تواند اعمال شود. فراست منحصر به فرد، به خصوص انعطاف پذیری و نیزتنظیم مجدد فرایند تصمیم گیری پیشرفتی به سوی چابکی است.
محدودیت های روش های فعلی از رشد مداوم از پیچیدگی، عدم توانایی پویا ئی دراستخراج سهمیه و اولویت های رتبه بندی (همه آنها مهم و مبرم بودند)، و همچنین روابط بین عامل انسان و فرایند اتوماسیون، از جمله ارتباطات نادرست بین انسان - ماشین آلات به شمار می روند.
Abstract
The paper creates the necessary theoretical and applied frame to reduce the unpredictability of the dynamics of innovation, the speed of technological transfer and the speed of reconfiguration/transformation through the integration of systems engineering techniques, dedicated methods for strategic decision making processes and the integration of portfolio management principles in real options with an additional stochastic ingredient expressed by Geometric Brownian Motion (GBM). This new philosophy does not try to find an optimum decision-making in the process of innovation, but contributes to a generalized dynamic prediction on the development of specific mechanism based on flexibility in order to build special dedicated solutions in the field of innovative industries, like robotics and mechatronics. Strategic management ingredients should respond to the challenge of adapting to the typical circumstances of market reactions and the change of the consumer behaviour. Decision making process in high tech industries like robotics and mechatronics is very complex because the technical element should be understand in the relationship with innovators, socio-economic and financial elements. The framework is even more complicated by the market reactions to disruptive technological progress and a very strong global competition. Flexible ingredients in the organizational process offered by concepts like lean manufacturing and Six Sigma are materialized only in a technical manner, but managers in high tech industries are influenced by the need of additional flexibility in order to adapt a quickly respond to changes in markets.
1. Introduction
Robotics and mechatronics are innovative industries with an impressive rate of development and in order to obtain the critical output of business is necessary to consider the global view that is beyond the technology and takes into account elements from strategic management. Innovation offers the critical element in this type of industries, but the global picture should include all the elements in their synergic interactions.
The agile manufacturing paradigm is expressed by cooperativeness and synergism by a strategic vision (robust in the processes of change) in the context of strong competition. The paradigm of lean production1 was introduced in order to obtain flexibility and quality. Lean manufacturing (operational procedures focused on efficient use of resources) is the conventional response to competition with constraints on resources, but agile manufacturing (a strategy that cope with uncertainties) is the response to complexity. Agility is in fact the response to change and it requires cooperation on resources and the flexibility to adapt quickly to markets and clients.
Six sigma takes into account the experience related to complexity and it is based on different methods, tools and techniques associated to Total Quality Management (TQM) and expressed by DMAIC (define – measure – analyze – improve – control). The interest is to support organization’s efficiency based on quality (potential and actual), reducing waste, and the active use of cost-cut-in procedures.
As a scientific method, Six Sigma is based on: the observation of critical aspects in markets (related to the business), the development of consistent assumptions related to observation build and test the predictions according the assumptions and observations and a feedback loop that work until the differences between assumptions and real results is minimized2 . The role of Six Sigma in Supply Chain Management (SCM) should taking into account: the policies on suppliers, the goals and deliverables, the communication strategy, the time table for deployment, the methods of assessing supplier Six Sigma efficiency and the integration of the program.
The difference between Lean Production (based on Toyota system) and Six Sigma is expressed by capability of lean production to improve productivity versus the focus on defects in the case of Six Sigma quality, oriented to reduce muda (waste) in any environment. Lean concept offers a proven set of solutions but Six Sigma has the capacity to understand the mechanisms of other problems that appears in the dynamics of innovative processes. In this case the two concepts are complementary and synergic.
The process of innovation is influenced by the strategic management of uncertainties (minimizing versus copping with uncertainties and the balancing between stability and flexibility). The strategic decision should analyze the cost and benefits of reducing/maintaining uncertainties, the optimal exploration of belief system in the firm and the analysis of the anticipated effect in feedback loop architecture. On one hand, the sub-systems need freedom and flexibility in order to cope with uncertainties locally, and on the other hand, the disturbance could be view as opportunities for organizational innovation and change3,4.
Autonomy (self-determination on goals and rules) should be careful balanced with control (goals determined either autonomously or by other entities). In the literature5 the interest is to maximize the local control in the context of autonomy distribution according to task correlations and goals. Van de Ven (1976) analyzed the relationship between task uncertainty6 , task interdependence and coordination and Eisenharth (1985) introduced the cost of behavior with outcome measurements7 . Sitkin (1994) considered that total quality learning is essential in the context of manufacturing flexibility8 . Orton and Weick (1990) introduced the concept of loose coupling to express the dualism between the technical level, closed to external forces and the institutional level open to external forces9 . There are different approaches of loose coupling like: motivation through task orientation, the concept of higher order autonomy10, the possibility of switching between different organizational models11 and the role of culture in coordination/integration between decentralization autonomy and centralization of values.
In the case of innovation management in high technology industries like robotics and mechatronics, the effects of risk and uncertainty could be exacerbated by the informational asymmetry. Regarding the typical lack of resources in innovation, it is essential to introduce a strong component of strategic management elements in order to understand the adaptability to markets and clients in an efficient manner. Although the strategic deciding responsible owns an extended portfolio of instruments, able to give an integrated image of the complex and social-technical environment in the dynamics view, a universal recipe cannot be applied, since one takes into account the crisis physiognomy unique, the microscopic issues related to the specific actions that need intuition, but also the experience, and especially the flexibility of reconfiguring the decisional process and the progress towards agility.
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. اهداف فوری برای پروژه های تحقیقات آینده در زمینه رباتیک و مکاترونیک
3. ادغام گزینه های واقعی در روند تصمیم گیری در صنایع نوآورانه
4. راه به سمت انعطاف پذیری - ادغام ROA در فرآیندهای نوآوری
5. مجموعه گزینه های واقعی - یک گام دیگر برای بهبود انعطاف پذیری
6. اصول تصادفی برای نمایش انعطاف پذیری ارائه شده توسط گزینه ادغام
7. نتیجه گیری
منابع
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Emergent objectives for the future research projects in the field of robotics and mechatronics
3. The integration of Real Options in Decision Making Process in Innovative Industries
4. The way toward flexibility – the integration of ROA in the processes of innovation
5. Portfolios of Real Options – another step for improving flexibility
6. A stochastic ingredient for representing the flexibility offered by options
7. Conclusions
References
