
دانلود رایگان مقاله بررسی اجمالی طراحی IPsec VPN WAN
این راهنمای طراحی، اجزای کاربردی جامع و مورد نیاز برای ساخت یک شبکه اختصاصی مجازی سایت به سایت (VPN) را در زمینه اتصال شبکه گسترده منطقهای (WAN) تعریف میکند. این بررسی اجمالی درباره طراحی، در سطح بالا، انتخابهای طراحی دردسترس برای ساخت یک IPsec VPN WAN را تعریف میکند و عواملي را که بر انتخاب شما تأثير ميگذارند توصيف ميکند. راهنمای طراحی فردی، طراحی و اجرای دقیقتر برای هر یک از انواع طراحیهای اصلی را فراهم میکند.
بررسی اجمالی از طراحی، بخشی از راهحلهای VPN در حال انجام را با استفاده از آخرین فناوری VPN از سیسکو و براساس اصول طراحی عملی که برای مقیاسگذاری مورد آزمایش قرار گرفتهاند شناسایی میکند.
معرفی
این متن بهعنوان یک راهنمای طراحی برای کسانی است که قصد دارند یک VPN سایت به سایت براساس امنیت IP (IPsec) ارائه دهند. طرحهای ارائه شده در این متن بر پلتفرمهای روتر سیسکو IOS VPN تمرکز دارد.
توپولوژی اولیه که در این متن توضیح داده شده است، یک طراحی hub-and-spoke است که منابع اولیه در یک سایت مرکزی بزرگ، با تعدادی سایت کوچک و یا دفاتر شعبه با اتصال مستقیم به سایت مرکزی بر روی یک VPN واقع شدهاند. یک نمودار سطح بالا از این توپولوژی در شکل 1 نشان داده شده است.
مخاطب هدف
این راهنمای طراحی برای مهندسان سیستم طراحی شده است تا راهنماییها و بهترین شیوهها را برای استقرار مشتری ارائه دهند.
ساختار طراحی راهنمای
این راهنما بخشی از مجموعه راهنماهای طراحی است که هر کدام براساس فنآوریهای مختلف برای معماری IPsec VPN WAN هستند (به شکل 3 نگاه کنید). هر تکنولوژی از IPsec بهعنوان مکانیزم حمل و نقل برای هر VPN استفاده میکند. استفاده از IPsec در این راهنما به خوبی انتخاب معیارهای خاص VPN IPsec در تکنولوژی WAN مشخص شده است.
بررسی اجمالی IP امنیتی
هدف از این بررسی، معرفی امنیت IP (IPsec) و کاربرد آن در VPN ها است. برای درک عمیق IPsec، به آدرس زیر مراجعه کنید:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk583/tk372/technologies_tech_note09186a0080094203.shtml
معرفی IPsec
استاندارد IPsec یک روش برای مدیریت احراز هویت و حفاظت از دادهها بین جفتهای رمزنگاری شده در انتقال امن اطلاعات را فراهم میکند. IPsec شامل انجمن امنیت اینترنت و پروتکل مدیریت کلید (ISAKMP) / Oakley و دو پروتکلIPsec IP است: encapsulating پروتکل امنیتی (ESP) و سرآیند تایید (AH).
IPsec از الگوریتمهای رمزنگاری متقارن برای حفاظت از دادهها استفاده میکند. الگوریتمهای رمزنگاری متقارن برای پیادهسازی روی سختافزار کارآ و راحت هستند. این الگوریتمها نیاز به روش امن کلید تبادل برای اطمینان از حفاظت دادهها دارند. پروتکلهای ISAKMP / Oakley این قابلیت را فراهم میکنند.
این راهحل مستلزم یک روش مبتنی بر استاندارد برای محافظت از دادهها در مقابل استراق سمع و اصلاح است. IPsec چنین روشی را فراهم میکند. IPsec انتخاب مجموعههای تبدیل را فراهم میکند تا کاربر بتواند قدرت حفاظت از اطلاعات را داشته باشد. IPsec همچنین دارای چندین کد تایید هویت (HMAC) انتخابی است، که هر کدام دارای سطوح مختلف حفاظت از حملات مانند man-in-the-middle، جواب بسته (ضد جواب) و حملات یکپارچه اطلاعات هستند.
پروتکلهای تونلزنی
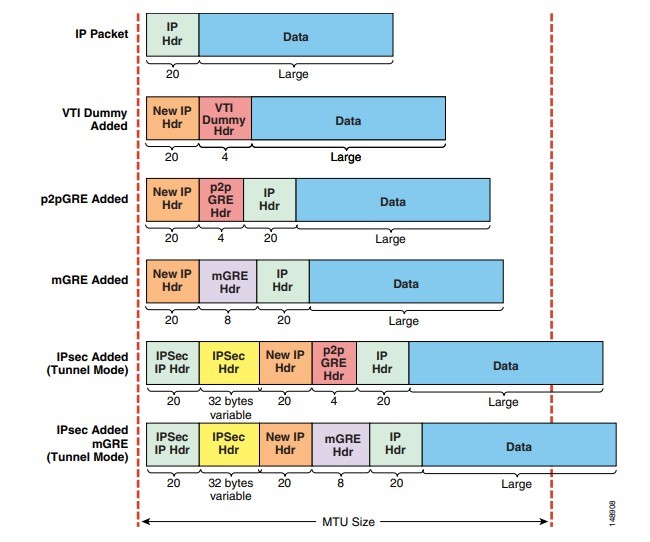
پروتکلهای تونلزنی در ویژگیهایی که پشتیبانی میکنند، مشکلاتی که برای حل آنها طراحی شدهاند و مقدار امنیتی که برای انتقال داده ارائه میکنند متفاوت هستند. طرحهای ارائه شده در این معماری براستفاده از IPsec بهعنوان پروتکل تونلزنی، IPsec مورد استفاده در ارتباط با Encapsulation مسیریابی عمومی(GRE) و رابطهای مجازی تونل (VTI) تمرکز دارند.
هنگامی که بهتنهایی استفاده میشود، IPsec یک شبکه خصوصی و انعطافپذیر برای یکپارچهسازی IP فراهم میکند، جایی که پشتیبانی برای چندپخشی IP، پروتکل مسیریابی IGP پویا، یا پروتکلهای غیر IP مورد نیاز نیست. هنگامی که از یکی یا تعداد زیادی از این ویژگیها مورد نیاز باشد، IPsec باید همراه با GRE یا VTI استفاده شود.
This design guide defines the comprehensive functional components that are required to build a site-to-site virtual private network (VPN) system in the context of enterprise wide area network (WAN) connectivity. This design overview defines, at a high level, the available design choices for building an IPsec VPN WAN, and describes the factors that influence the choice. Individual design guides provide more detailed design and implementation descriptions for each of the major design types.
This design overview is part of an ongoing series that addresses VPN solutions using the latest VPN technologies from Cisco, and based on practical design principles that have been tested to scale.
Introduction
This document serves as a design guide for those intending to deploy a site-to-site VPN based on IP Security (IPsec). The designs presented in this document focus on Cisco IOS VPN router platforms.
The primary topology described in this document is a hub-and-spoke design, where the primary enterprise resources are located in a large central site, with a number of smaller sites or branch offices connected directly to the central site over a VPN. A high-level diagram of this topology is shown in Figure 1.
Target Audience
This design guide is targeted at systems engineers to provide guidelines and best practices for customer deployments.
Design Guide Structure
This design overview is part of a series of design guides, each based on different technologies for the IPsec VPN WAN architecture. (See Figure 3.) Each technology uses IPsec as the underlying transport mechanism for each VPN.
IP Security Overview
The purpose of this overview is to introduce IP Security (IPsec) and its application in VPNs. For a more in-depth understanding of IPsec, see the following URL: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk583/tk372/technologies_tech_note09186a0080094203.shtml.
Introduction to IPsec
The IPsec standard provides a method to manage authentication and data protection between multiple crypto peers engaging in secure data transfer. IPsec includes the Internet Security Association and Key Management Protocol (ISAKMP)/Oakley and two IPsec IP protocols: Encapsulating Security Protocol (ESP) and Authentication Header (AH).
IPsec uses symmetrical encryption algorithms for data protection. Symmetrical encryption algorithms are more efficient and easier to implement in hardware. These algorithms need a secure method of key exchange to ensure data protection. Internet Key Exchange (IKE) ISAKMP/Oakley protocols provide this capability.
This solution requires a standards-based way to secure data from eavesdropping and modification. IPsec provides such a method. IPsec provides a choice of transform sets so that a user can choose the strength of their data protection. IPsec also has several Hashed Message Authentication Codes (HMAC) from which to choose, each giving different levels of protection for attacks such as man-in-the-middle, packet replay (anti-replay), and data integrity attacks.
Tunneling Protocols
Tunneling protocols vary in the features they support, the problems they are designed to solve, and the amount of security they provide to the data being transported. The designs presented in this architecture focus on the use of IPsec as a tunneling protocol alone, and IPsec used in conjunction with Generic Route Encapsulation (GRE) and Virtual Tunnel Interfaces (VTI).
When used alone, IPsec provides a private, resilient network for IP unicast only, where support is not required for IP multicast, dynamic IGP routing protocols, or non IP protocols. When support for one or more of these features is required, IPsec should be used in conjunction with either GRE or VTI.
معرفی
مخاطب هدف
محدوده کار
ساختار راهنمای طراحی
بررسی اجمالی IP امنیتی
معرفی IPsec
پروتکلهای تونل زنی
پروتکلهای IPsec
بسته شدن پروتکل امنیتی
سرصفحه تایید (AH)
استفاده همزمان از ESP و AH
حالتهای IPsec
حالت تونل
حالت حمل و نقل
تبادل کلید اینترنت
انجمن امنیتی
انجمن امنیتی ISAKMP
انجمن امنیت IPsec (تونل داده)
فاز اول IKE
روشهای تأیید اعتبار
کلیدهای پیش از اشتراک
زیرساخت کلید عمومی با استفاده از گواهینامههای دیجیتال X.509
الگوریتم های رمزگذاری
کدهای اعتبارسنجی پیام هشدار
توافقنامه کلید Diffie-Hellma
شفافیت NAT (تراکم NAT)
فاز دوم IKE
الگوریتمهای رمزگذاری
کدهای اعتباربخشی پیام هشدار
پنهان نگه داشتن کامل
مسائل قطعه بندی
تنظیم MTU بر روی کارتهای رابط مشتری و سرور
مسیر پوشش داده شده توسط MTU
رابط MTU
قطعهبندی Look Ahead
حداکثر اندازه بخش TCP
چرا مشتریان VPN IPsec را راه اندازی میکنند
افراد حاضر در کسب و کار
پهنای باند
کاهش هزینه
امنیت
توسعه انعطافپذیری
حالت ارتجاعی
الزامات مشتری
رمزگذاری
تأیید هویت IKE
کیفیت خدمات
سطح رابط
سطح اتصال یا جلسه
چندپخشی IP
پروتکلهای غیر IP
مسیریابی
کنترل از راه دور که به صورت پویا نشان داده میشود
دسترسپذیری بالا
شکست Headend
عدم موفقیت سایت
شکست دفتر شعبه
شکست Statefulدر مقابل Stateless
امنیت مجتمع
مشبک کردن پویا
مقیاسپذیری
تامین و مدیریت
درک تکنولوژی
دسترسی بدون تماس
مدیریت در حال اجرا
ارائهکننده خدمات
انتخاب طراحی
طراحی Encapsulation مستقیم IPsec
بررسی اجمالی طراحی
مزایا
معایب
بیشترین استفاده معمول
Point-to-Point GRE در طراحی IPsec
معماری Headend- یک Headend واحد در مقابل Headend دوگانه
معماری Headend تک لایه
معماری Headend دوگانه
عملکرد و ارزش
بررسی اجمالی طراحی
مزایا
معایب
بیشترین استفاده معمول
نقطه به نقطه GRE از طریق طراحی IPsec
معماری Headend- Headend تک لایه در مقابل Headend دوگانه
معماری headend تک لایه
معماری headend دوگانه
عملکرد و ارزش
بررسی اجمالی طراحی
مزایا
معایب
بیشترین استفاده معمول
VPN چندنقطه پویا - طراحی توپولوژی Spoke-to-Spoke
بررسی اجمالی طراحی
مزایا
معایب
بیشترین استفاده معمول
طراحی مجازی تونل مجازی
بررسی اجمالی طراحی
مزایا
معایب
بیشترین استفاده معمول
مقایسهی طراحیها
پشتیبانی از ویژگی های اصلی
پشتیبانی از پلتفرم
انتخاب طراحی
مقیاسپذیری یک طراحی
معیارهای بحرانی مقیاسپذیری
تعداد دفاتر شعبه
سرعت اتصال
بازده IPsec
بررسی انتقال دوجهته
تعداد بستهها در هر ثانویه (pps) دقیقتر است
تعداد تونلها میتواند یک عامل باشد
خلاصه عملکرد
جفتهای مسیریابی
کیفیت خدمات
در دسترس بودن بالا
چندپخشی IP
استراتژی دسترسی به اینترنت
backhaul
تونل زنی تقسیم شده
سرویسهای یکپارچه
امنیت
VoIP
سایر خدمات یکپارچه
پیوست A-ارزیابی مقیاسپذیری طراحی
روش آزمایش
ترافیک ترکیبی
یافتن محدودیتها
نتایج
بسترهای ارزیابی شده سیسکو
پیوست B- منابع توصیه شده برای مطالعه
پیوست C-مخففها
Introduction
Target Audience
Scope of Work
Design Guide Structure
IP Security Overview
Introduction to IPsec
Tunneling Protocols
IPsec Protocols
Encapsulating Security Protocol
Authentication Header (AH)
Using ESP and AH Together
IPsec Modes
Tunnel Mode
Transport Mode
Internet Key Exchange
Security Association
ISAKMP Security Association
IPsec Security Associations (Data Tunnel)
IKE Phase One
Authentication Methods
Pre-Shared Keys
Public Key Infrastructure using X.509 Digital Certificates
Encryption Algorithms
Hashed Message Authentication Codes
Diffie-Hellman Key Agreement
NAT Transparency (NAT Traversal)
IKE Phase Two
Encryption Algorithms
Hashed Message Authentication Codes
Perfect Forward Secrecy
Fragmentation Issues
Setting MTU on Client and Server Network Interface Cards
Path MTU Discovery
Interface MTU
Look Ahead Fragmentation
TCP Maximum Segment Size
Why Customers Deploy IPsec VPNs
Business Drivers
Bandwidth
Cost Reduction
Security
Deployment Flexibility
Resiliency
Customer Requirements
Encryption
IKE Authentication
Quality of Service
Interface Level
Connection or Session Level
IP Multicast
Non-IP Protocols
Routing
Dynamically Addressed Remotes
High Availability
Headend Failure
Site Failure
Branch Office Failure
Stateful versus Stateless Failover
Integrated Security
Dynamic Meshing
Scalability
Provisioning and Management
Understanding the Technologies
Touchless Provisioning
Ongoing Management
Service Provider
Design Selection
IPsec Direct Encapsulation Design
Design Overview
Advantages
Disadvantages
Most Common Uses
Point-to-Point GRE over IPsec Design
Headend Architecture—Single Tier Headend versus Dual Tier Headend
Single Tier Headend Architecture
Dual Tier Headend Architecture
Performance and Value
Design Overview
Advantages
Disadvantages
Most Common Uses
Dynamic Multipoint VPN—Hub-and-Spoke Topology Design
Headend Architecture—Single Tier Headend versus Dual Tier Headend
Single Tier Headend Architecture
Dual Tier Headend Architecture
Performance and Value
Design Overview
Advantages
Disadvantages
Most Common Uses
Dynamic Multipoint VPN—Spoke-to-Spoke Topology Design
Design Overview
Advantages
Disadvantages
Most Common Uses
Virtual Tunnel Interface Design
Design Overview
Advantages
Disadvantages
Most Common Uses
Design Comparison
Major Feature Support
Platform Support
Selecting a Design
Scaling a Design
Critical Scalability Criteria
Number of Branch Offices
Connection Speeds
IPsec Throughput
Bi-directional Traffic Handling
Packets per Second (pps) is More Accurate
Number of Tunnels May be a Factor
Throughput Summary
Routing Peers
Quality of Service
High Availability
IP Multicast
Internet Access Strategy
Backhaul
Split Tunneling
Integrated Services
Security
VoIP
Other Integrated Service Types
Appendix A—Evaluating Design Scalability
Test Methodology
Traffic Mix
Finding Limits
Conservative Results
Cisco Platforms Evaluated
Appendix B—References and Recommended Reading
Appendix C—Acronyms
