
دانلود رایگان مقاله به سوی ارزیابی عملکرد ارائه دهندگان سرویس ابر جهت امنیت داده های آن
چکیده
دادههای امروزی بدلیل حفظ حریم شخصی و امنیت، هم از طرف تأمین کنندگان خدمات ابری و هم کاربران ، در همه ی سطوح شامل: سطح ذخیره شده، انتقال ، تقاضا و پردازش دادهها حساس هستند. پردازش ابری در حوزه سلامت، امنیت ملی، خدمات، بانکداری و زمینههای دیگر استفاده شده است و همانطور که در چندسال اخیر دیده ایم تعدادی از کمپانی ها اطلاعات محرمانه را در ابر (سرورهای خدمات ابری) ذخیره کرده اند. بنابراین اطلاعات و حفظ امنیت دادهها یک بحث حساس و حیاتی است که باید بصورت کامل و جامع در حوزه ی محاسبات ابری پیگیری شود. این پژوهش بر روی تحلیل عملکرد مدلهای امنیت داده در محاسبات ابری تمرکز دارد .این مقاله مدلهای امنیت دادههای ابری را مبتنی بر فرایند کاری مدلسازی با نماد (BPMN) پیشنهاد کرده و با شبیه سازی نتایج، کارایی مباحث مربوط به امنیت دادهها را بعنوان بخشی از هرگونه ابتکار عمل سازمانی در زمینه ی مدیریت اجرایی کسب وکار (BPM) نشان داده است.
1. مقدمه
محاسبات ابری در سالهای اخیر بعنوان یک زمینه ی بسیار تأثیر گذار و مهم در حوزه ی فناوری اطلاعات تلقی شده و توجه زیادی را به خود بدلیل کاهش هزینههای مدیریتی اش جلب کرده است. هزینه ای را که ایالات متحده آمریکا جهت محاسبات ابری قرار داده ، برای مدت ۵سال گذشته برآورد رشد ۴۰ درصدی را تا پایان سال و رسیدن به نرخ ۷ بیلیونی را داشته است(کافمن ۲۰۰۹). همچنین طبق گزارش ها این تخصیص هزینه تاعبور از مرز ۹۵بیلیون دلار در سال ۲۰۱۸ رسیده است(سوباشینی و کاویتا،۲۰۱۱) . همچنین، پیشبینی میشد که دوازده درصد از بازار نرم افزار به سمت محاسبات ابری حرکت کند(آلزین، ساه،و پارادی ۲۰۱۳). با وجود رشد کنونی زمینه ی محسابات ابری و روند بازار نرم افزار، بنظر میرسد که این بازار از طریق محاسبات ابری از رشد دوازده درصدی خود هم عبور کرده بعلاوه، استفاده از ذخیره سازی و شبکههای اجتماعی از طریق ابر، انقلابی را در عرصهی تعاملات اجتماعی فناوری اطلاعات و برقراری ارتباطات در میان مردم، به وجود آورده است.
در میان تعاریف مختلف از رایانش ابری، مشهورترین و شناخته شده ترین تعریف که بشکلی جامع راجع به اجزای آن توضیح میدهد، همان تعریف مؤسسه ی ملی فناوری استانداردها (NIST) است(مل و گرانس،۲۰۱۱).برطبق این تعریف، محاسبات ابری یک مدل از فناوری اطلاعات برای استفاده آسان از منابع رایانشی مبتنی بر تقاضای کاربر، ذخیره سازی و خود تطبیق دهنده، چه نرم افزاری و چه سخت افزاری ، از طریق اینترنت بدون دردسرهایاحتیاج به منابع مدیریتی و تعامل بین تولید کننده و کاربر است. در این تعریف محاسبات ابری ۵ جزء اصلی از آن دیده میشود دسترسی از طریق شبکه، سلف سرویس براساس نیاز کاربر، مخزنی از منابع محاسباتی، محاسبه هزینه خدمات با توجه به اندازه استفاده و قابلیت ارتجاع خدمات با سرعت بالا(رونتری و کاستریلو ۲۰۱۴).همچنین تعریف NIST بصورت عمومی شامل سه مدل خدماتی:IaaS ( زیرساخت بعنوان خدمات)، PaaS( بستر بعنوان خدمات) و SaaS( نرمافزار بعنوان خدمات) و چهار مدل گسترش یا استقرار (خصوصی،عمومی، انجمنی و ترکیبی) است.
با SaaS کاربر به نرمافزار و برنامههای کاربردی از طریق مرورگرها یا رابطهای برنامه نویسی، بدون کنترل مستقیم بر زیرساختها دسترسی پیدا می کند.PaaS بستر زیرساخت را مانند سیستم عامل (OS)فراهم می کند که کاربر بتواند نرمافزار و برنامه ی کاربردی را روی آن اجرا و نصب نماید، اما کاربر نمیتواند به منابع سخت افزاری دسترسی داشته باشد. در IaaS، کاربر با یک سختافزار و شبکه ی زیرساختی تجهیز میشود که دسترسی فیزیکی به آنها ندارد اما میتواند از آنها برای اجرای سیستم عامل و برنامههای کاربردی خود بصورت مستقل استفاده نماید.
برطبق NIST، درمدل استقرار خصوصی رایانش ابری ،عرضه کننده خدمات ابری (CSP) یک مدل خدماتی را تنها برای یک سازمان بامدیرت خود سازمان یا CSP یا یک شخص ثالث ایجاد میکند. در حالی که مدل استقرار انجمنی یک سرویس خدمات ابری را تنها برای یک گروه مشخص از کاربران عرضه مینماید، مدل عمومی سرویس را برای عموم عرضه میکند و چهارمین مدل، مدل ترکیبی، ترکیبی است از دو یا تعداد بیشتری از از مدلهای استقرار قبلی.
سه مولفه کاربردی در رایانش ابری خدماتی یا تحویل دهنده می باشند، حول ارائه کننده سرویس(CSP) هستند،و اینکه کاربر مشتری یا مالک نامیده می شود، میباشند (سود،۲۰۱۲).مدیریت CSP بر روی ابر ، نقش بسیار مهمی در تأمین منابع ذخیره سازی و محاسباتی دارد. کاربر یا مالک بصورت انفرادی یا سازمانی می تواند خدمات رایانش ابری را برای ذخیره سازی داده و یا پردازش آنها خریداری و یا اجاره نماید.کاربر، شخصی است که از خدمات رایانش ابری بعنوان یک فرد ثبت نام شده، چه شخصی و چه از طریق یک سازمان استفاده می کند.
با این وجود رایانش ابری بدون چالش نیست. طبق گفته ی آرمبروست (۲۰۱۰) پردازش ابری مشکلات زیادی دارد. بعضی از آنها مربوط به بازبینی ،محرمانگی و انتقال دادههای قفل شده هستند. وسایر مشکلات شامل تدوام یا دردسترس بودن کسب وکار، عملکرد، غیر قابل پیشبینی بودن، مقیاس پذیری در امر ذخیره سازی، باگ و خطاهای موجود در سیستمهای توزیع شده بزرگ و وسیع، و مجوزهای نرمافزاری است.ریسکهای استفاده از رایانش ابری آنگونه که فوگارتی (۲۰۰۹) عنوان میکند ، شامل سازگاری، حفظ حریم خصوصی و قابلیت همکاری است. سازگاری به این معناست که دادهای ممکن است در یک CSP در CSP ی دیگر سازگار نباشد. سازمان مالک نمیتواند برروی حریم خصوصی اطلاعاتش کنترلی داشته باشد. همچنین آلزاین، پارادی، سوه و تام(۲۰۱۱)خاطر نشان کردند مسئله ی حفظ حریم خصوصی و امنیت به خطراتی درمورد محتوایات داده ها، نفوذ به آنها و در دسترس بودن خدمات مربوط برمیگردد.
بیشترین عیوب رایانش ابری که توسط تعداد زیادی از مولفین گفته شده و در بالا هم درموردشان بحث کردیم، و در جاهای دیگر هم می بینیم، مربوط به حفظ حریم شخصی و امنیت داده هاست. دادههای امروزی بدلیل حفظ حریم شخصی و امنیت، هم از طرف تأمین کنندگان خدمات ابری و هم کاربران ، در همه ی سطوح شامل: سطح ذخیره شده، انتقال ، تقاضا و پردازش دادهها حساس هستند.پردازش ابری در حوزه سلامت، امنیت ملی، خدمات، بانکداری و زمینههای دیگر استفاده شده است و تعدادی از کمپانی ها اطلاعات محرمانه را در ابر (سرورهای خدمات ابری) ذخیره کرده اند( به عنوان مثال فلیندرز،۲۰۱۴; گیل ،۲۰۱۳; تاکسن ،۲۰۱۴).بنابراین اطلاعات و حفظ امنیت دادهها یک بحث حساس و حیاتی است که باید بصورت کامل و جامع در حوزه ی محاسبات ابری پیگیری شود. این پژوهش بر روی تحلیل عملکرد مدلهای اخیر امنیت داده در محاسبات ابری تمرکز دارد.این مقاله در بخشهای مختلفی آمده است. بخش ۱: مقدمه و معرفی این مقاله بخش ۲: ارائه پیشینه و اصطلاحات مربوط به امنیت ابر و امنیت دادههای ابری است. بخش ۳: در مورد چگونگی تحقق امنیت در ابر بحث میکند. قسمت ۴: یک ارزیابی مهم را روی روشها و مدلهای ایجاد امنیت دادهها ارائه میدهد. قسمت ۵: مدل BPMN را برای عرضه کنندگان سرویسهای ابری (CSP-1 و CSP-3) ارائه میدهد و در نهایت در قسمت ۶: مراحل شبیه سازی BPMN را براساس تنظیم عملکرد پارامترها جهت شبیه سازی امنیت دادههای ابری موجود در فرایندهای تجاری توضیح میدهد.
2. پیش زمینه
امروزه رایانش ابری را میتوان بر اساس به اشتراک گذاری منابع (اجاره ی چندگانه)، قابلیت ارتجاع، مقیاس پذیری ، و پرداخت هزینه زمانی که از آن استفاده میکنید، شناخت ( بعنوان مثال مل و گرانس،۲۰۱۱ و وینکلر،۲۰۱۱) .یکی از ویژگیهای مدرن رایانش ابری مدل کسب وکار آن است که منابع مشابه در میان کاربران زیادی در شبکه میزبان و سطح برنامه ی کاربری به اشتراک گذاشته می شود. قابلیت ارتجاع به این موضوع اشاره دارد که کاربران رایانش ابری میتوانند نیازهای محاسباتی خود را تغییر داده و زمانی که نیازی به آنها ندارند منابعی را به دیگران عرضه کنند . فناوری حاضر در مجاسبات ابری به مشتریان این امکان را میدهد تا سیستمها ، پهنای باند و ظرفیت ذخیره سازی را با توجه به ویژگیهای قابل قیاس در ابر اندازهگیری کرده و بسنجند. ویژگیهای مهم دیگر در رایانش ابری بحث خودسازی و خود تأمینی توسط کاربر برای ظرفیتهای محاسباتی، نرم افزاری، و فضای دیسک و شبکه است. بیشترین عرضه کنندگان خدمات رایانش ابری ، کاربر را تنها برای زمان و منابع استفاده شده شارژ میکنند که همان پرداخت به اندازه مصرف است.
Abstract
Today’s data is sensitive that requires privacy and security both from the cloud service providers (CSP) as well as from users in its all the form of data states: data at rest, while transferring data, enquiring data, and processing the data. Cloud computing has been applied in the health sector, national security services, banking and other business and companies that store confidential data into the cloud as we have seen in recent years. Therefore, information and data security is a crucial issue that needs to be addressed thoroughly in the cloud computing business. This research deals with the performance analysis of recent cloud data security models. This paper proposes cloud data security models based on Business Process ModelingNotations (BPMN) andsimulationresults canrevealperformances issues relatedtodata security as part of any organizations initiative on Business process management (BPM).
1. Introduction
Cloud computing has become the influencing IT landscape and gained amplified attention in recent years as benefits of reduced IT costs and is management. The US spending on cloud computing for the last five years was estimated to grow at annual growth rate of 40% and was expected to reach $7 billion by the end of the year (Kaufman, 2009). It was reported that this speeding on cloud computing was expected to pass $95 billion in 2018 (Subashini & Kavitha, 2011). Moreover, it was estimated that 12% of the software market would shifttowards the cloud (AlZain, Soh, & Pardede, 2013). However, based on the current growth rate ofthe cloud business and the trend of software market, itlooks like thatthe software market in the cloud has already surpassed 12%. In addition, the use of cloud storage and social networks has revolutionized IT social interactions and communications of the people.
Among the variety of definitions of cloud computing, the most popular and commonly used definition that encapsulates the main constituents of cloud computing is the one by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) (Mell & Grance, 2011). Accordingly, cloud computing is an IT model for using on-demand, shared, measured and self adjustable computing resources, both software and hardware, conveniently via the Internet without the hassle of heavy management requirements and interaction between the client and the provider. There are five core components in the definition of cloud computing; network access, on-demand selfservice, resource pooling, measured service and rapid elasticity (Rountree & Castrillo, 2014). NIST definition also includes generally three service models; IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service), PaaS (Platform as a Service) and SaaS (Software as a Service) and four deployment models (private, public, community and hybrid) of cloud computing.
With SaaS the user accesses software and applications through browsers or programming interfaces without direct control over the infrastructure. PaaS provides platform infrastructure such as operating system (OS) where the user can run and configure software and applications but the user does not have control over the hardware. In IaaS, the user is provided with a hardware and network infrastructure where the user does not have physical access but can use for running OS and applications independently.
According to NIST, in private cloud deployment model the cloud service provider (CSP) provides one of the service models for an organization managed by the organization itself or by the CSP or by a third party. While the community deployment model provides cloud service to a certain classified group of users, the public model provides service to the general public. The fourth service model,the hybrid, is a combination oftwo or more ofthe previous deployment models.
The three functional components that the cloud computing model, be it the service or delivery, rotates around are cloud service provider (CSP), client also called owner and user (Sood, 2012). The CSP manages the cloud playing a significant role in providingThe three functional components that the cloud computing model, be it the service or delivery, rotates around are cloud service provider (CSP), client also called owner and user (Sood, 2012). The CSP manages the cloud playing a significant role in providing storage space and computational resource. The client or the owner is individual or organization that rents or buys cloud-computing service for storing data and/or for computation. The user is the individual that utilizes the cloud service as a registered individual or registered through a customer organization.
However, cloud computing is not without a challenge. According to Armbrust et al. (2010) cloud computing has a number of challenges. Some of them are related to data such as lock-in, auditability, confidentiality and transfer problems. The rest include business continuity/availability, performance, unpredictability, storage scalability, bugs in big distributed systems and software licensing. Risks of adopting cloud computing as identified by Fogarty (2009) include compatibility, privacy and interoperability. Compatibility is related to the fact that data in one CSP may not be compatible in other CSP. The owner organization cannot control over the privacy of its data. Alzain, Pardede, Soh, and Thom (2011) also identified the issue of privacy and security related to the risks on data integrity, data intrusion and service availability.
Most of the drawbacks of cloud computing as mentioned by most of the authors as discussed above and others are related to privacy and security of data. Today’s data is sensitive that requires privacy andsecurity bothfromtheCSP side andfromtheuser side at its state of rest,transfer and processing. Cloud computing is applied in the health sector, national security services, banking and other business and companies that store confidential data into the cloud (e.g. Flinders, 2014; Gill, 2013; Toxen, 2014). Therefore, information and data security is a crucial issue that needs to be addressed thoroughly in the cloud computing business. This research deals with the performance analysis of recent cloud data security models. This paper outlined structure consists of Section 1 provides introduction to this article, Section 2 provides background and related literature on cloud security & cloud data security, Section 3 discusses approaches on cloud security, Section 4 provides critical evaluation of cloud data security approaches and models, Section 5 provides BPMN modesl for Cloud Service providers (CSP-1 & CSP3), and finally Section 6 provides BPMN simulation process steps on setting performance parameters for cloud data security simulation of the business processes.
2. Background
To date cloud computing can be defined based on resource sharing (multi-tenancy), elasticity, scalability, self-provisioning andpay when you use (e.g. Mell & Grance, 2011; Winkler, 2011). One of the modern cloud computing features is its business model where same resource is shared between multiple users at network, host and application level. Elasticity refers to the fact that cloud users can change their computing needs and provide resources to others when they do not need them any more. The current technology in cloud computing provides the customers to scale systems, bandwidth and storage size due to the scalability feature of cloud computing. Another important attribute in cloud computing is selfprovisioned by the user for computing capacity, software and disc space and network. Most cloud computing service providers charge the users only for the time and resource used, this is referred as pay as use.
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. پیش زمینه
3. امنیت برای رایانش ابری
4. امنیت دادهها در ابر
5. مدل فرایند کار(BPM)
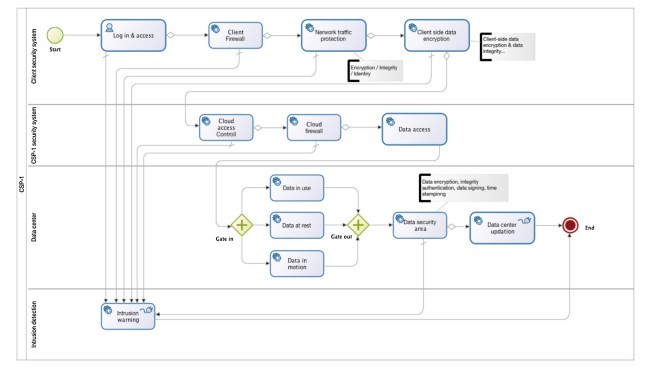
5.1. مدل امنیت داده CSP-1:
5.2. مدل امنیتی داده CSP-3
6. شبیه سازی BPMN برای امنیت
6.1. چگونه BPMN میتواند برای ایجاد امنیت مفید باشد.
7. نتیجه گیری
8. نتیجهگیری و چشم انداز آینده
منابع
ABSTRACT
1. Introduction
2. Background
3. Security for cloud computing
4. Cloud data security
5. Business process modelling (BPM)
5.1. CSP-1 data security model
5.2. CSP-3 data security model
6. BPMN simulations for security
6.1. How BPMN can be useful for enterprise security?
7. Discussion
8. Conclusion and future work
References
