
دانلود رایگان مقاله کوپن های الکترونیکی ایمن
چکیده
کوپن ها (اوراق بهادار) در بازار جهانی بسیار مشهورند وبطور گسترده ای بمنظور جذب مشتریان جدیدی که به دنبال معاملات هستند وهمچنین بمنظور حفظ مشتریان وفادار استفاده میشوند. بطور کلی، اوراق بهاداری که برای مشتریان وفادار هستند، تخفیف بیشتری نسبت به اوراق بهادار مشتریان جدید دارند. بمنظور فرق گذاشتن بین مشتریان جدید و وفادار، ما دو رویکرد متفاوت را ابداع کردیم که به شرکتها اجازه میدهد تا انواع مختلفی از کوپن های الکترونیکی را از طریق شبکه ی اینترنت بیسیم صادر نماید. رویکرد اول برای ایجاد اوراق الکترونیکیای که به مشتریان خاص اختصاص ندارد، استفاده شده است. بنابراین، یک کوپن الکترونیکی استفاده نشده، میتواند بوسیله هر مشتریای استفاده گردد. این روش برای جذب مشتریان جدید بسیار مناسب است. روش دیگر برای تولید کوپن الکترونیکیای که به مشتریان خاص اختصاص دارد، استفاده میشود. لذا کوپن های الکترونیکی استفاده نشده، نمیتواند توسط مشتریان دیگر مورد استفاده قرار گیرد. این روش ثانویه، بمنظور حفظ مشتریان وفادار بسیار مناسب است. هر دو طرح پیشنهادی برای تجارت الکترونیکی موبایل طراحی شده است وهزینه ی فرآوری وپردازش کوپن ها را کاهش میدهد.
1. مقدمه
با رشد سریع فن آوری شبکه های کامپیوتری، بسیاری از معاملات سنتی به صورت الکترونیکی انجام می شود. بیشتر وبیشتر برنامه های کامپیوتری، همانند حراج های الکترونیکی، رایگیری الکترونیکی، پرداختهای الکترونیکی وغیره برای اجرا روی شبکهی اینترنت توسعه یافتهاند. بعلاوه ی اینترنت، تحولات ارتباطات تلفن همراه، بهسرعت در حال تغییر است ومنافع تجاری فراواناند. ارتباطات موبایل، همچون خدمات ارتباط شخصی(PCS) و سیستم جهانی ارتباط موبایل(UMCS) توسعه یافتهاند و در سراسر دنیا بسیار محبوب شدهاند. تکنولوژیها برای فراهم کردن ارتباطات ومحاسبات، بطور پویا طراحی شدهاند. تاکنون، شبکههای موبایل بسیاری توسعه یافته شدهاند؛ همچون GSM، USDC، PDS وغیره. سیستم GSM در حال حاضر در بیش از 70 کشور در سراسر جهان اجرا شده است. علاوه براین، بسیاری از برنامههای کاربردی وخدمات، همچون پروتکل برنامهی بیسیم(WAP)، کنفرانس از راه دورِ امن، سیستم پرداخت موبایل، برنامه های کاربردی محل آگاهی وغیره فراهم آورده شده است. تجارت تلفن همراه بطور گستردهتری در کسب وکار در حال استفاده است و درحال تبدیل شدن به یک موضوع تحقیق بسیار مهم است.
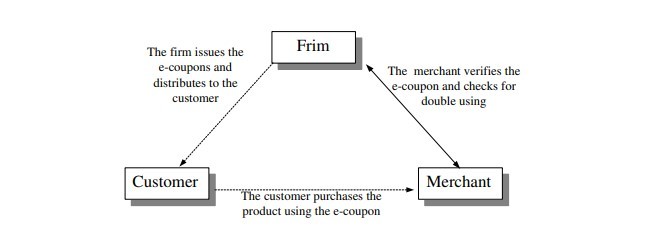
در بازار سنتی، صدور کوپن یک استراتژی مفید و شناخته شده برای افزایش فروش است. با توجه به خط سود، شرکت ها می توانند کوپن های تخفیف، برای رسیدن به مشتریان جدید صادر کنند. علاوه براین، شرکتها همچنین میتوانند کوپنهایی با تخفیف سنگین برای حفظ مشتریان وفادار صدور نمایند. نتایج حاصل از صدور کوپن های الکترونیکی در اینترنت بسیار آشکار است. علاوه براین، اگر ما بتوانیم مفهوم کوپنهای الکترونیکی را به محیط موبایل اعمال نماییم، میتوانیم انتظار داشته باشیم که این مهم مشتریان بیشتری را برای خریداری یک محصول جذب خواهد کرد. بنابراین، ایده استفاده از کوپن های الکترونیکی برای تجارت الکترونیکی تلفن همراه مطرح شده است. هدف اصلی استفاده از کوپنهای الکترونیکی بمنظور دریافت کردن واستفاده نمودن از کوپنهای موبایل برای مشتریان است. این فناوری به مشتری اجازه میدهد تا یک کوپنالکترونیکی را از طریق موبایل خود دریافت نماید. سپس مشتری هنگام تصمیم به خرید محصول، کوپن الکترونیکی را برای تاجر ارسال مینماید.
اگرچه در فضای الکترونیک، اطلاعات براحتی میتواند به سرقت رود یا دستکاری شود. از این رو، چگونگی ساخت یک کانال امن برای انجام معاملات، با استفاده از کوپنهای الکترونیکی یک موضوع کلیدی در چنین فن آوری است. بنابراین، برخی از نیازمندی های امنیتی برای این تکنولوژی ضروری است. ما خلاصه نیازمندی های امنیتی را برای استفاده از کوپن های الکترونیکی به شرح زیر خلاصه کردهایم:
1. احراز هویت: به منظور جلوگیری مشتری از جعل کوپن های الکترونیکی، منشاء کوپن های الکترونیکی باید معین شود. بنابراین یک تاجر باید توانایی تصدیق اعتبار تمامی کوپن های الکترونیکی دریافت شده را داشته باشد.
2. صداقت: به منظور جلوگیری مشتری از اصلاح کوپن های الکترونیکی، تمامیت الکترونیکی کوپن باید نگه داشته شود. بنابراین، یک تاجر باید اطمینان حاصل کند که کوپن های الکترونیکی دریافت شده است، اصلاح نشده است.
3. جلوگیری از استفاده مکرر: به منظور جلوگیری از استفاده نامحدود از کوپن های الکترونیکی، تعداد کوپن های الکترونیکی صادره باید محدود شود. بنابراین، سیستم باید مشتری را از استفاده دو باره از همان کوپن الکترونیکی بازدارد.
علاوه بر الزامات امنیتی، عملکرد کوپن های الکترونیکی نیز بسیار مهم است. با توجه به فضای حافظه کوچک و قابلیت های محاسباتی پایین تجهیزات الکترونیکی تلفن همراه، هزینه پردازش الکترونیکی کوپن، از جمله هزینه های محاسباتی، حافظه فضای بالای سر، و هزینه های ارتباطی، باید تا حد امکان کاهش یابد.
به منظور برآوردن این شرایط، برخی از تکنیک های رمزنگاری کارآمد مانند توابع هش می تواند ما را در طراحی چنین طرح الکترونیکی کوپن کمک نماید. به عنوان مثال، به منظور افزایش فروش و جذب مشتریان جدید، شرکت ها ممکن است آرزو کنندکه یک مشتری می تواند یک کوپن الکترونیکی استفاده نشده را به مشتری بالقوه دیگری فوروارد نماید، در صورتی که آن مشتری نخواهد از آن استفاده کند. از سوی دیگر، به منظور حفظ مشتریان وفادار، شرکت ممکن است ای-کوپن های ویژهای را به مشتریان وفادارصادر کند. ای-کوپن های ویژه معمولا تخفیف قیمت بیشتری دارند یا یک محصول را بصورت رایگان پیشنهاد میدهند.
با توجه به دو استراتژی مختلف برای صدور کوپن، ما دو طرح متفاوت عملی را برای ای-کوپن ابداع کردیم که همهی الزامات را ارضا میکند. در طرح پیشنهادی اول، کوپنهای الکترونیکیای که صادر میشوند، به مشتری خاصی اختصاص ندارند. لذا، می تواند توسط هر مشتری استفاده شود. در طرح پیشنهادی دوم، ای-کوپنهایی که صادر میگردد به مشتریان خاصی اختصاص مییابد. بنابراین نمیتواند توسط هر مشتری استفاده شود. از دانش فعلی مان، ما هنوز هیچگونه طرح مشابهی برای بحث در مورد تمایز بین کوپنهای الکترونیکیای که به مشتریان خاص، اختصاص ندارد وکوپنهایی که به مشتریان وفادار خاصی اختصای مییابد، پیدا نکردهایم.
بقیه این مقاله به شرح زیر سازماندهی شده است: در بخش 2، فنآوری کد تایید هویت پیغام معرفی خواهد شد. این تکنولوژی بعدا در طرحهای پیشنهادی ما استفاده میشود. چارچوب سیستم و نمادهای مورد استفاده در سراسر بقیه مقاله در بخش 3 معرفی شده است. در بخش 4، ما طرح پیشنهادی اول را آوردهایم که برای صدور کوپنهای الکترونیکیای است که به مشتریان خاص اختصاص ندارد. در بخش 5، ما طرح پیشنهادی دوم را برای صدور ای-کوپنهایی که به مشتریان خاصی اختصاص دارد، آوردهایم. در بخش 6، خواص و عملکرد طرح های ما آزموده میشود. بخش 7 این مقاله را نتیجه گیری میکند.
Abstract
Coupons are well-known and widely used in the market place to attract new customers looking for deals and to keep loyal customers. Generally speaking, coupons for loyal customers have more discount than coupons for new customers. In order to differentiate between new and loyal customers, we invented two schemes that allow firms to issue different types of e-coupons through a wireless network. The first scheme is used to generate e-coupons that are not assigned to specific customers. Thus, an unused e-coupon can be used by any customer. This scheme is more suitable for attracting new customers. The other scheme is used to generate e-coupons that are assigned to specific customers. Thus, unused e-coupons cannot be used by other customers. This second scheme is more suitable for keeping loyal customers. Both of the proposed schemes are designed for mobile electronic commerce and reduces the cost for processing coupons.
I. INTRODUCTION
With the rapid growth of computer network technologies, many traditional transactions are conducted electronically. More and more applications such as electronic auction [11], electronic voting [3], electronic payments [10], [19], and others are developed to run over the Internet. In addition to the Internet, mobile communications revolutions are changing rapidly, and commercial interests abound. Mobile communications, such as Personal Communication Services (PCS) and Universal Mobile Communication System (UMCS), have been developed and have become very popular around the world. The technologies are designed for providing communications and computations with mobility. So far, there are many mobile networks that have been developed, such as GSM, USDC, PDC, and others [18]. The GSM system has now been implemented in more than 70 countries around the world. Furthermore, many applications and services are provided such as wireless application protocol (WAP) [7], secure teleconferencing [12], mobile payment system [9], location-awareness applications [14], and others. Mobile commerce is being used more widely in business and is becoming a very significant research topic.
In the traditional market place, issuing coupons is a useful and well-known strategy to increase sales. According to the profit line, firms can issue discount coupons to reach new customers. In addition, firms also can issue special coupons with heavy discounts to keep loyal customers. The results of issuing electronic coupons on the Internet are very obvious [2], [6]. Furthermore, if we can apply the concept of ecoupons to mobile environment, we can anticipate that this will attract more customers to purchase a product. Therefore, the idea of using e-coupons for mobile electronic commerce is raised. The main purpose of using electronic coupons is to make receiving and using coupons mobile for customers. The technology allows a customer to receive an e-coupon through his/her mobile phone. The customer can then forward the ecoupon to the merchant when he/she wants to buy the product.
However, in an electronic environment, information can be intercepted and tampered with easily. Hence, how to build a secure channel for transactions using e-coupons is a key issue in such technology. Therefore, some security requirements are essential to this technology. We summarize the security requirements for using e-coupons as follows:
1) Authentication: In order to prevent a customer from forging e-coupons, the origin of the e-coupons must be ascertained. Thus, a merchant must have the ability to authenticate the validity of all e-coupons received.
2) Integrity: In order to prevent a customer from modifying e-coupons, the integrity of e-coupons must be kept. Thus, a merchant has to ensure that a e-coupon that has been received has not been modified.
3) Preventing repeated use: In order to avoid unlimited use of e-coupons, the number of e-coupons issued should be limited. Therefore, the system must prevent a customer form using the same e-coupon twice.
In addition to the security requirements, the performance of e-coupons is also very important. Due to the small memory space and the low computational capability of mobile electronic equipments, the processing cost of e-coupons, including computational cost, memory space overhead, and communication cost, must be reduced to as low as possible. Therefore, a practical e-coupon system for mobile electronic commerce must be securely performed and efficiently managed with a low processing cost.
In order to satisfy these requirements, some efficient cryptographic techniques such as hash functions can help us to design such an e-coupon scheme. Furthermore, the strategies for issuing e-coupons for new customers or loyal customers may be different. For example, in order to increase sales and attract new customers, firms may wish that a customer can forward an unused e-coupon to another potential customer if the customer does not want to use it. On the other hand, in order to keep loyal customers, firms may issue special ecoupons to loyal customers. The special e-coupons usually have mush more price discounts or offer a product for free. Thus, firms may not wish that the special e-coupons be used by another customer.
According to the two different strategies for issuing coupons, we invented two types of practical e-coupon schemes that satisfy all the requirements. In the first proposed scheme, e-coupons that are issued are not assigned to specific customers. Thus, it can be used by any customer. In the second proposed scheme, e-coupons that are issued are assigned to specific customers. Thus, it cannot be used by other customers. From our knowledge so far, we have not yet found any related schemes for discussing the distinction between e-coupons that are not associated with specific customers, and e-coupons that are associated with specific loyal customers.
The rest of this paper is organized as follows. In Section 2, the technology of message authentication code will be introduced. The technology will be used later in our proposed schemes. The system framework and the notations used throughout the rest of the paper are introduced in Section 3. In Section 4, we present the first proposed scheme for issuing e-coupons which are not assigned to specific customers. In Section 5, we present the second proposed scheme for issuing e-coupons which are assigned to specific customers. In Section 6, the properties and the performance of our schemes are examined. Section 7 concludes this paper.
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. کد تایید پیام
3. چهارچوب سیستم ونمادها
4. طرح اول: کوپنهایی که به مشتریان خاص اختصاص ندارند
5. طرح2: کوپنهای الکترونیکی که به مشتریان خاص اختصاص دارند
6. بحث
A. تحلیل توابع امنیتی
B. آنالیز عملکرد
7 .نتیجهگیری
منابع
Abstract
1. INTRODUCTION
2. MESSAGE AUTHENTICATION CODE
3. SYSTEM FRAMEWORK AND NOTATIONS
4. SCHEME 1: ELECTRONIC COUPONS NOT ASSIGNED TO SPECIFIC CUSTOMERS
5. SCHEME 2: ELECTRONIC COUPONS ASSIGNED TO SPECIFIC CUSTOMERS
6. DISCUSSIONS
A. Analysis of Security Functions
B. Performance Analysis
7. CONCLUSIONS
REFERENCES
