
دانلود رایگان مقاله قیمت گذاری و زمان بندی پویای کیفیت خدمات آگاهانه در محاسبات ابری بی سیم
چکیده
این مقاله مسائل مربوط به به قیمتگذاری و زمانبندی کیفیت خدمات (QoS) آگاهانه را در محاسبات ابری بیسیم بررسی میکند که در آن تأمینکننده مجموعهای از خدمات را از طریق ارتباط بیسیم برای کاربران فراهم میکند. در این فرآیند، ارائهدهنده قیمت هر یک از خدمات را با توجه به وضعیت سیستم و طول صف اعلام میکند. با جمعآوری تقاضای خدمات از کاربران و مشاهده وضعیت سیستم، ارائهدهنده خدمات برخی منابع اختصاصی را برای برآورد تقاضا اختصاص میدهند. با توجه به پویایی تقاضا و وضعیت سیستم، برای ارائهدهندگان قیمتگذاری و تهیه منابع بهصورت بهینه دشوار است. این مقاله ابتدا مشکل را بهعنوان یک مدل ریاضی فرمولبندی میکند. سپس، قیمتگذاری پویای QoS آگاهانه و الگوریتم زمانبندی (QDPSA) را پیشنهاد میکند. الگوریتم QDPSA تنها به وضعیت سیستم فعلی و طول صف بستگی دارد و میتواند سود متوسط اپراتور را به حداکثر برساند. شبیهسازی نشان میدهد که میتوانیم از طریق تنظیم یک پارامتر کنترل، بین سود و طول صف از طریق اعمال عوامل کنترل مبادله و سبکسنگین کرد. علاوه بر این، نتایج ما همچنین نشان میدهد که خدمات باارزش بالاتر از ضریب QoS میتواند طول صف کوتاهی را به دست آورد، یعنی زمان پاسخ کوتاهتر خواهد بود.
1. مقدمه
دستگاههای موبایل در سالهای اخیر به بخش مهمی از زندگی انسان تبدیلشدهاند [1]. بهاینترتیب، برنامههای کاربردی موبایل و خدمات آن بهسرعت افزایش مییابد [2]. بااینوجود، با توجه به منابع محدود ارسال برنامههای کاربردی کافی در حد بالا روی ابزار موبایل بسیار چالشبرانگیز است، مواردی نظیر باطری، توان پردازش و پهنای باند شبکه. برای بهبود عملکرد برنامههای تلفن همراه، محاسبات ابر بیسیم برای غلبه بر برخی از این محدودیتها با تخلیه برنامههای تلفن همراه به ابر از راه دور و یا ارائه خدمات طراحیشده است [4]. در این نمونه، کاربران برای برنامههای کاربردی بهای آن را پرداخت میکنند و ارائهدهنده خدمات برخی منابع را برای خدمت به این خواستهها اختصاص میدهد و بهاینترتیب هزینههایی را به دست میآورد. مأموریت ارائهدهنده خدمات، طراحی الگوریتم قیمتگذاری و زمانبندی برای به حداکثر رساندن سود آن است.
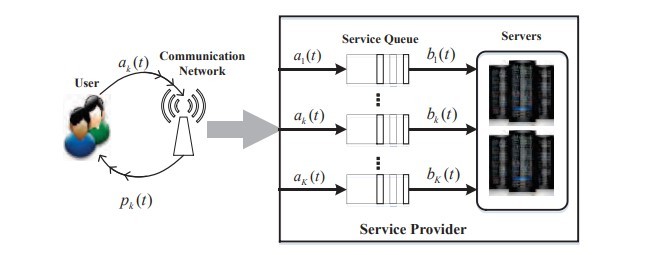
در این مقاله، الگوریتم پویای قیمتگذاری و زمانبندی باکیفیت خدمات (QoS) را در نظر میگیریم تا در سیستم محاسبات ابری بیسیم سود را به حداکثر برسانیم، همانطور که در شکل 1 نشان دادهشده است. این سیستم میتواند کاربر را با انواع برنامههای کاربردی مانند محاسبات علمی، جستجوی بصری و پردازش تصویر گروهی تأمین کند. در این مقاله، روی خدمات غیرفعال تأخیری تمرکز میکنیم که 70 درصد از کل کارهای سیستم را تشکیل میدهد [5]. فرض کنید که نوع K سرویسهای غیر حساس با نیازهای مختلف QoS برای کاربران وجود دارد و QoS به طول صف متوسط اشاره دارد. در هر زمان، ارائهدهنده خدمات، صف خدمات و وضعیت سیستم را مشاهده میکند و مجموعهای از قیمتها را انتخاب میکند و آنها را به همه کاربران اعلام میکند. کاربران به قیمت فعلی با تقاضای خاص واکنش نشان میدهند. سپس، ارائهدهنده خدمات منابع پشتیبان را برای برآورده کردن خواستههای بهدستآمده از صف خدمات K اختصاص میدهد. فرآیند فوق هزینهای را به ارمغان میآورد. در تلاش هستیم تا الگوریتم قیمتگذاری و زمانبندی را برای به حداکثر رساندن سود متوسط زمان ارائهدهنده خدمات بیابیم درحالیکه ثبات صف و نیاز به QoS اطمینان داریم.
مسائل مربوط به قیمتگذاری و زمانبندی در محدوده شبکه کامپیوتری [6] [7]، شبکه هوشمند [8] [9]، بازارهای وای فای [10] و محاسبات ابری [11] [12] [13] و غیره موردمطالعه قرارگرفته است. بهعنوانمثال، در [6] یک الگوریتم تخصیص منابع تکراری دوسطحی مبتنی بر قیمت در شبکههای تککاره بیسیم پیشنهادشده است. این الگوریتم به یک شبکه جهانی مطلوب نزدیک میشود. در [13]، نویسندگان به موضوع چگونگی مدیریت هوشمندانه منابع در یک سیستم پایگاه داده محاسبات ابری پرداختند و سیستم مدیریت منابع هزینه را ارائه دادند. بعضی از مطالعات سعی داشتند با قیمتگذاری پویا و زمانبندی مسئله در محیط بیسیم مقابله کنند. هنده و همکاران [14] با در نظر گرفتن قیمتگذاری و زمانبندی، بهطورکلی مدل توزیع نرخ بر مبنای حداکثر سازی ابزار شناختهشده را برای تعریف قیمتگذاری ارائهدهندگان محتوا تعمیم میدهند. هوانگ و نلی [15] یک الگوریتم آنلاین ساختند که بهطور مشترک قیمتگذاری و زمانبندی پویا برای یک نقطه دسترسی (AP) را در یک شبکه بیسیم حل میکند که میتواند به هر سود متوسطی که بهطور قراردادی نزدیک به مطلوب است دست یابد. رن و همکاران [16] بر زمانبندی و قیمتگذاری در محاسبات ابری تمرکز میکنند و الگوریتم زمانبندی و قیمتگذاری پویا (Dyn-SP) را میسازند. Dyn-SP یک سود متوسط نزدیک به مطلوب را ایجاد میکند درحالیکه طول صف سرویس را هم محدود میکند. تا آنجا که میدانیم، تمام تحقیقات فوق قواعد مختلف QoS را بررسی نمیکنند، الزامات خدمات مختلف برای قیمتگذاری پویا و زمانبندی در محاسبات ابری بیسیم هستند. برخی آثار [17] بر مسئله زمانبندی آگاهانه QoS در محیط ابری تمرکز دارند. بااینحال، آنها بهطور همزمان مشکلات قیمتگذاری و محیط پویای را در نظر نمیگیرند. در تلاشیم تا الگوریتم قیمتگذاری و زمانبندی QoS پویا را برای دستیابی به سود مطلوب ایجاد کنیم. کمک و همکاری اصلی این مقاله را میتوان به شرح زیر خلاصه کرد:
- این مقاله یک مدل زمان گسسته برای فرمولبندی قیمتگذاری و زمانبندی پویای مشکل در محاسبات ابری بیسیم ارائه میدهد و این مدل بسیار کلی است.
- این مقاله الگوریتم QDPSA را برای حل مشکل فوق پیشنهاد میکند. این الگوریتم را میتوان با استفاده از آمار سیستم ناشناخته قیاسی تکمیل کرد و سود مطلوب به دست آورد. مهمتر از همه، الگوریتم QDPSA میتواند نیازهای مختلف QoS را برآورده کند. این نتایج با شبیهسازیهای ما معتبر هستند.
بقیه مقاله به شرح زیر است: بخش دوم، فرمولبندی مدل سیستم را ارائه میدهد. الگوریتم QDPSA در بخش سوم ارائهشده است. عملکرد الگوریتم QDPSA با شبیهسازی در بخش 4 ارزیابی میشود. بخش V این مقاله نتیجهگیری است.
2. مدل سیستم
یک مدل زمان گسسته را در نظر میگیریم که اپراتور ارائهدهنده قیمت خدمات را اعلام میکند و منابع را برای ارائه به تقاضا در هر بخش زمانبندی میکند. نمادهای کلیدی مورداستفاده در این مقاله در جدول 1 فهرست شدهاند. توضیحات «در بخش t» را برای کوتاهی و خلاصه کردن مطلب حذف کردیم.
A. مدلسازی تقاضا
(pk (t را برای قیمت خدمات نوع k نشان میدهد که کاربران تلفن همراه را تبلیغ میکند. فرض کنید p k (t) متعلق به مجموعه جمعی P برای همه t است و با [0, pmax] محدود میشود. تقاضا، ai,k (t) برای خدمات دستهای نوع K کاربر i به قیمت فعلی (t) pk بستگی دارد و میتواند بهصورت تابع (t) pk مدلسازی شود.
Abstract
This paper considers the Quality-of-Service (QoS) aware pricing and scheduling problem in wireless cloud computing, where the service provider provides a set of services to users through wireless communication. In this process, the provider announces a price for each service according to the system state and queue length. By collecting the service demand from users and observing the system state, the provider allocates some resources to serve the demand. Due to the dynamic of both the demand and system state, it is hard for the provider to make price and schedule the resources optimally. This paper first formulates the problem as a mathematical model. Then, it proposes the QoS aware dynamic pricing and scheduling algorithm (QDPSA). The QDPSA algorithm only depends on the current system state and queue length and can maximize the average profit of the operator. Simulations show that we can get better tradeoff between the profit and queue length through setting a control parameter. In addition, our results also demonstrate that the service with higher value of QoS coefficient can achieve shorter queue length, i.e. shorter response time.
I. INTRODUCTION
Mobile devices have become an essential part of human life in recent years [1]. Correspondingly, the mobile applications and services increase rapidly [2]. However, it is very challenging to deliver highly sophisticated applications on mobile devices due to the limited resources, such as battery, processing power and network bandwidth [3]. To improve the performance of mobile applications, wireless cloud computing is designed to overcome some of these limitations by offloading the mobile applications to the remote cloud or service provider [4]. In this paradigm, users pay for executing applications and the service provider allocates some resources to serve these demands, thereby yielding some cost. The mission of the service provider is to design a pricing and scheduling algorithm to maximize its profit.
In this paper, we consider the Quality-of-Service(QoS) aware dynamic pricing and scheduling algorithm to maximize the profit in wireless cloud computing system, as shown in Fig.1. The system can provide users a variety of applications, such as scientific computing, visual search, and batch image processing. In this paper, we focus on the delay insensitive services, which account for 70% of all workloads of the system [5]. Suppose that there are K types of delay insensitive services with different QoS requirements available to the users, and QoS refers to average queueing length. At each time, the service provider observes the service queue and the system state and chooses a set of prices and announces them to all users. The users react to the current price with certain demand Next, the service provider allocates server resources to serve the demands, resulting in K service queues. The above process yields some cost. We are trying to explore the pricing and scheduling algorithm so as to maximize time average profit of the service provider while ensuring queue stability and QoS requirement.
Pricing and scheduling problem has been widely studied in the area of computer network [6][7], smart grid [8][9], WiFi Markets [10], and cloud computing[11][12][13], etc. For example, in [6], a new price-based two-tier iterative resource allocation algorithm in wireless ad hoc networks is proposed. The algorithm converges to a global network optimum. In [13], the authors address the issue of how to intelligently manage the resources in a shared cloud database system and present a cost aware resource management system. Some work tried to tackle the dynamic pricing and scheduling problem in wireless environment. By taking both pricing and scheduling into consideration, Hande et al [14] generalize the well-known utility maximization based rate allocation model to incorporate pricing of content providers. Huang and Neely [15] develop an online algorithm that jointly solves the dynamic pricing and scheduling problem for an Access Point (AP) in a wireless network, which can achieve any average profit that is arbitrarily close to the optimum. Ren et al [16] focus on scheduling and pricing in wireless cloud computing and develop a provably-efficient Dynamic Scheduling and Pricing (Dyn-SP) algorithm. DynSP produces a close-to-optimal average profit while bounding the service queue length. To our best knowledge all above works fail to consider different QoS, requirements of different services for the dynamic pricing and scheduling problem in wireless cloud computing. Some works [17] focus on the QoS aware scheduling problem in cloud environment. However, they do not consider the pricing problem and dynamic environment simultaneously. We are trying to develop a QoS aware dynamic pricing and scheduling algorithm to achieve optimal profit. The main contributions of this paper can be summarized as follows:
This paper proposes a discrete time model to formulate the dynamic pricing and scheduling problem in wireless cloud computing and this model is very general. This paper proposes the QDPSA algorithm for solving the above problem.
This algorithm can be implemented with unknown system statistics a priori and achieve optimal profit. More importantly, the QDPSA algorithm can satisfy different QoS requirements. These conclusions are validated by our simulations.
The rest of the paper is organized as follows. Section II presents the system model formulation. The QDPSA algorithm is developed in Section III. Performance of the QDPSA algorithm is evaluated with simulations in Section IV. Section V concludes this paper.
II. SYSTEM MODEL
We consider a discrete-time model in which the operator of the service provider announces the service price and schedules resources to serve the demand at each slot. Key notations used in this paper are listed in table I.
A. Demand Modelling
Let (t) k p t denotes the price for type-k service advertised to the mobile users. Assume that (t) k p t belongs to a compact P set for all t and is bounded by [0, pmax]. The demand ai,k(t) for type-k batch service of user i depends on the current price (t) k p t and it can be modelled as a function of (t) k p t.
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. مدل سیستم
A. مدلسازی تقاضا
B. فرمول نویسی نرخ خدمات
C. پویایی و پایداری صف
D. فرمول نویسی مسئله
E. شرایط آهستگی
3. الگوریتم قیمتگذاری و زمانبندی پویای QOS آگاهانه
A. پویایی صف QOS آگاهانه
B. الگوریتم قیمتگذاری و زمانبندی پویای QoS آگاهانه
C. تجزیه تحلیل اجرایی
4. شبیهسازی
5. نتیجهگیری
منابع
Abstract
1. INTRODUCTION
2. SYSTEM MODEL
A. Demand Modelling
B. Service Rate Formulation
C. Queue Dynamic and Stability
D. Formulation of the Problem
E. Slackness Condition
3. QOS AWARE DYNAMIC PRICING AND SCHEDULING ALGORITHM
A. QoS Aware Queue Dynamics
B. QoS Aware Dynamic Pricing and Scheduling Algorithm
C. Performance Analysis
4. SIMULATION
5. CONCLUSION
REFERENCES
