
دانلود رایگان مقاله ارزیابی ارزش مدل کسب و کار تجارت الکترونیک
چکیده
بررسی مدلهای کسب و کار موضوع مهمی در زمینه کارآفرینی و هدف سازمان است، زیرا مدلهای کسب و کار بر احتمالات شرکت در خلق ارزش و ارزش گذاری تاثیر میگذارد. مطالعه حاضر شکافی را برای پر کردن باقی گذاشته و این شکاف نشان دهنده یک مسئله تحقیقاتی مهم است که باید حل شود، یعنی، چگونه این فعالیتهای معامله مجسم شده و به این ترتیب درآمد محاسبه میشود. بنابراين، اين مقاله، از مدل e3 براي بررسی ارزش شرکت تجارت الکترونیک تولید شده در این فرآیند استفاده کرده که میتواند برای انتخاب یا بهینه سازی فعالیتهای ارزش استفاده شود که تحقیق و عمل در زمینه تجارت الکترونیک را به پیش میبرد. نتیجه نشان میدهد که 1) اوراق سودآوری قادر به ضبط رفتارهای مشتریان است که به آنها بینش تازهای برای درک بهتر تجارب و انتظارات مشتریان آنلاین را داده تا تصمیمات منطقی را اتخاذ کنند، 2) این مدل فعالیتهای اصلی مدل کسب و کار را نشان داده و راههای بهینه سازی فعالیتهای ارزش را مورد بهره برداری قرار میدهد و 3) این رویکرد مدل سازی راه فعالیتهای حرفه ای را برای آزمایش واقعی مدلهای کسب و کار جایگزین، با شبیه سازی احتمالات مختلف قبل از تعهد به سرمایه گذاری خاص در واقعیت ارائه میکند.
1. مقدمه
در دهههای گذشته، علم و فن آوری تغییری چشمگیر و بنیادین داشته است که فرصت های کسب و کار جدید بسیاری را برای ایجاد شرکت های تجارت الکترونیکی فراهم می کند، به عنوان مثال شرکت های Alibaba Group Holding Ltd و Suning Commerce Group Co Ltd در mainland و ایده آل برای مطالعه توسعه مدل کسب و کار. اگرچه پرسش چه چیزی (یعنی تعریف، عملکرد و طبقه بندی مدل کسب و کار) در بسیاری از مطالعات بررسی شده است، پرسش چگونه (یعنی روش ارزیابی مدل کسب و کار) تا به حال بررسی نشده است.
چندین محقق این مسئله را شناسایی کرده و تلاش کرده اند تا منطق خلق ارزش و فرآیند مدل کسب و کار را از طریق ترکیبی از مضامین متنی، کلامی و آگهی گرافیکی نشان دهند ویل و ویتل (2001) سه گروه اشیاء – شرکت کنندگان (شرکت، مشتریان، تامین کنندگان و متحدان)، روابط و جریان (پول، اطلاعات، محصول یا جریان خدمات) را به منظور ارائه ابزار برای تجزیه و تحلیل و طراحی ابتکارات کسب و کار الکترونیکی معرفی کرده اند. Chesbrough and Rosenbloom (2002) مدل کسب و کار را به عنوان مکانیسم تبدیل ورودی / خروجی در نظر گرفته که از منابع داخلی شرکت تامین می شود. Osterwalder (2004) هستی شناسی مدل کسب و کار(BMO) را برای مفهوم سازی و رسمی سازی اجزای ضروری به عناصر، روابط، واژگان و معناشناسی اعمال می کند. بر اساس دیدگاه Penrosian شرکت، دیمیل و لکوک (2010) طبق RCOV (منبع R، شایستگیC و سازمانO و V ارزش) چارچوب گزاره ها را برای نشان دادن خلق و تکامل ارزش ارائه کردند. Casadesus-Masanell and Ricart (2010) مدل کسب و کار را با استفاده از یک نمودار حلقه علیت نشان می دهند که در آن انتخاب ها و عواقب با فلش بر اساس نظریه های علیت به یکدیگر مرتبط هستند. لی و وانگ (2010) قوانین را بر اساس مدل container توسعه داده که به طور سیستماتیک اجزای اساسی و بلوک های ساختمانی را نشان می دهد و عملکرد و ارزش فعالیت های مدل کسب و کار را تبیین می کند. Teece (2010) یک مدل کسب و کار را به عنوان راهی تعریف می کند که در آن شرکت بازرگانی ارزش را برای مشتریان فراهم می کند، مشتریان را برای پرداخت هزینه ها جذب می کند و این پرداخت ها به سود تبدیل می شود. با وجود تفاوت های مفهومی در ادبیات فعلی، تصدیق گسترده ای در این مورد وجود دارد که مدل کسب و کار واحد جدید تجزیه و تحلیل علاوه بر محصول، شرکت، صنعت یا سطوح شبکه است و خلق ارزش تمرکز مدل کسب و کار است. به این ترتیب، این مطالعات شکافی را باقی گذاشته که نشان دهنده یک مسئله بسیار مهم تحقیق است که باید حل شود، یعنی چگونگی تجسم این فعالیت های معامله و محاسبه درآمد عوامل به ترتیب.
بنابراین، این مقاله، از مدل ارزش e3 (مبادله اقتصادی، تبادل، توانمند) پیشنهاد شده به وسیله Gordijn and Akkermans (2001,2004) برای بررسی ارزش شرکت تجارت الکترونیک تولیدی در فرآیند استفاده می کند. تجزیه و تحلیل کمی مطالعه ما می تواند به عوامل درگیر در درک خلق و کسب ارزش و پیشرفت تحقیق و عمل در زمینه شرکت های تجارت الکترونیک کمک کند. بنابراین، مدیران باید با ویژگی های کلیدی هنگام طراحی مدل کسب و کار تجارت الکترونیک برای افزایش کارایی و اثربخشی آشنا باشند.
2. روش شناسی و ابزار
2.1. روش شناسی ارزش e3
مدل ارزش e3تعریف می کند که چگونه ارزش اقتصادی ایجاد و در داخل یک شبکه معامله با استفاده از مدل گرافیکی مفهومی و تفکر مبتنی بر سناریو مبادله می شود. علاوه بر این، می تواند یک تجزیه و تحلیل حساسیت مالی را انجام دهد. از طریق این مدل و اوراق سودآوری بعدی، می توانیم پایداری سازمانی را طبق پیش بینی و واکنش به محیط پویا پیدا کنیم در حالی که فعالیت های ارزش را بهینه می سازیم. این تکنیک مدل سازی دارای یک دیدگاه ارزش بر خلاف سایر ابزارهای مدل سازی سنتی است که یا دیدگاه فرآیند کسب و کار (خاص مدیریت عملیات) و یا معماری سیستم (خاص ادبیات سیستم های اطلاعاتی) را دارند. گوردین و اکرمس تعدادی مفاهیم، روابط و قوانین عمومی را به منظور ارتقا و افزایش درک عملیات و الزامات کسب و کار با استفاده از تجزیه و تحلیل سناریو و اندازه گیری شناسایی کردند. این مدل سازی به دنبال مفاهیم از ادبیات کسب و کار مانند عامل، شی ارزش، پورت ارزش، رابط ارزش، بخش بازار، عامل کامپوزیت، مسیر سناریو، محرک شروع، محرک پایان و ارتباط است. حالت ارزش e3 طبق قانون تقابل اقتصادی و روش «دادن و گرفتن» است: برای کالا یا خدماتی که به شبکه معامله ارائه شده است، در عوض شبکه های معامله باید کالا یا خدمات با ارزش برابر را ارائه کنند.
در مقایسه با روش های دیگر، مدل ارزش e3 به ایجاد یک مدل مفهومی برای تجارت الکترونیک مدل های کسب و کار فعلی و آینده کمک می کند و مدیران به سرعت می توانند بسیاری از پیامدهای احتمالی تغییرات را برآورده کنند. علاوه بر این، می تواند به طور خودکار محاسبات درآمد / سود برای هر عامل دخیل را ارائه و شرکت های تجارت الکترونیک را برای پایداری اقتصادی تجزیه و تحلیل کند. شایان ذکر است که مدل ارزش e3ساده سازی دنیای واقعی است و تمرکز این مدل بر این است که چه نوع اشیای ارزش باید با یکدیگر برای پوشش نیاز مشتری مبادله شود.
2.2. ابزار
انتقال ارزش را می توان با سازه های ارزش e3زیر (پر رنگ) مفهومی سازی کرد. عوامل، مانند خریدار و فروشنده، از لحاظ اقتصادی، مستقل است. عوامل اشیاء ارزش (کالا، خدمات، پرداخت یا تجربه) را با استفاده از انتقال ارزش نشان داده شده با فلش های علامت گذاری شده انتقال می دهند. با مبادله اشیای ارزش، آنها به سوددهی (در مورد تامین کننده) یا حداکثر سازی سود اقتصادی (در مورد مشتری) می پردازند. یک رابط ارزش اصل تقابل اقتصادی را مدل سازی می کند: عوتمل تنها مایل به انتقال ارزش در عوض مقدار دیگری از شی، و متشکل از پورت ارزش برای نشان دادن فعالیت های خروجی ورودی ارزش است. در مدل ارزش e3 مشتریان به عنوان نقطه شروع در نظر گرفته شده که دلیل ایجاد یک مدل کسب و کار است. چگونگی رفع نیاز مشتری به دنبال مسیر وابستگی است که نشان دهنده انتقال اشیاء ارزش است. مسیر وابستگی نشان می دهد که چقدر انتقال ارزش به عنوان یک نتیجه از نیاز مصرف کننده انجام می شود. مسیر وابستگی به عنوان مثال برای تجزیه و تحلیل جریان پول نقد خالص برای عامل دخیل استفاده می شود. بخش بازار مجموعه ای از عوامل را برای یک یا چند رابط ارزش، اشیاء ارزش از دیدگاه اقتصادی نشان می دهد. جدول 1 حالت ارزش e3 را نشان می دهد.
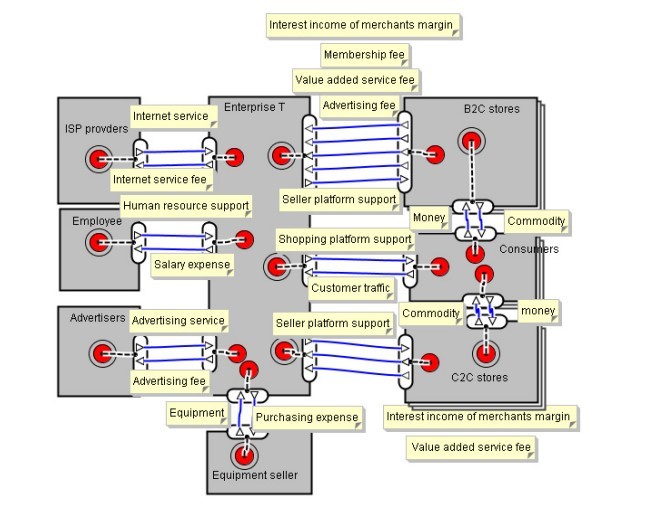
3. طرح مدل کسب و کار برای شرکت تجارت الکترونیک با استفاده از مدل ارزش e3
مدل کسب و کار یک قالب ساختاری است که سازمان معاملات شرکت کانونی را با تمام مشارکت کسب و کار خارجی توصیف می کند. شرکت تجارت الکترونیک، به عنوان یک شرکت تمرکز، فعالیت های ارزش را برای ارائه محصول یا خدمات انجام می دهد که می تواند به مشتریان ارائه شود و منابع را از عرضه کننده و دیگر شرکای کسب و کار تقاضا می کند. به منظور درک این رابطه انتقال ارزش به گونه ای ساختار یافته و دقیق تر از طریق تئوری کلامی امکان پذیر است، این مقاله از مدل ارزش e3 برای شرح تجارت الکترونیک استفاده کرده که مطابق با رویه و مقررات رفتار می کند. در ابتدا فرض این مدل کسب و کار تجارت الکترونیک این است که عمدتا شامل هشت عامل زیر است:
⦁ شرکت تجارت الکترونیکT طبق سیستم بازخورد و cogitation به شدت برای پیشگیری از تقلب یا اشتباهات عمدی، به عنوان مثال خریداران پرداخت کرده اند، اما فروشندگان کالاها یا خدمات را تحویل نمی دهند یا خریداران پرداخت نمی کنند، اما فروشندگان کالا یا خدمات را تحویل می دهند؛ یا فروشندگان محصولات تقلبی و جعلی را ارائه می دهند. به عنوان یک پلت فرم آنلاین، شرکت T باید کیفیت خدمات الکترونیکی را افزایش دهند، از جمله طراحی وب سایت، قابلیت اطمینان، امنیت و حریم خصوصی برای خریداران و فروشندگان.
⦁ مصرف کنندگان: خرید آنلاین در زندگی روزمره ما محبوب شده است و T مجموعه محصولات غنی را ارائه می کند، مانند بهداشتی و سلامت، هدایا، ورزش و اسباب بازی، تلفن همراه و لوازم جانبی، رومیزی، لپ تاپ.
⦁ فروشگاه های B2C و فروشگاه های C2C نه تنها انواع وسیعی از کالاها را ارائه می دهند بلکه منابع درآمد قابل توجهی نیز برای شرکت T دارد. T هزینه تبلیغاتی (مانند هزینه فدرال، پیشنهاد قیمت و کلمات کلیدی رتبه بندی)، هزینه عضویت (از قبیل هزینه خدمات فنی و کالا)، هزینه ارزش افزوده خدمات (مانند محصولات در طرح مشخصات و لجستیک) را دریافت می کند.
⦁ ارائه دهنده خدمات اینترنت (ISP) کسب و کار اصلی شرکت تجارت الکترونیک T خرید آنلاین پلت فرم است و آنها علاقه زیادی به تمام فعالیت های فنی، مانند ارائه دسترسی به IP ندارند از این رو، آنها این فعالیت ها را به شرکت های مخابراتی اعطا می کنند.
⦁ تبلیغ کننده: پیام تبلیغاتی می تواند به طور موثر احتمال خرید مشتریان را افزایش دهد و تصویر محصول و خدمات، سپس فروشگاه های بیشتری را برای فروش محصولات جذب می کند.
⦁ کارمند: حقوق کارکنان به خوبی تا حد زیادی بر نوآوری شرکت تجارت الکترونیک تاثیر می گذارد.
⦁ فروشنده تجهیزات: شرکت تجارت الکترونیک T فعالیت های غیر رسمی مانند تولید، به روز رسانی و حفظ تجهیزات شبکه را به تولیدکنندگان حرفه ای می سپارند.
Abstract
The study of business models is an important topic for entrepreneurship and organizational purpose because business models affect firms’ possibilities for value creation and value capture. The present study leaves a gap to be bridged, and the gap reveals a critically important research problem to be resolved, that is, how to visualize these transaction activities and calculate revenue respectively. This paper, therefore, adopts e3 model for investigations of E-commerce enterprise value generating in the process, and can be used to select or optimize value activities that advance both research and practice in the field of E-commerce enterprises. The result indicates that: c Profitability sheet is able to capture customers’ behaviors, which gives them insights to better understanding online customers’ experiences and expectations, and make reasonable decisions. d This model illustrates the main activities of business model and exploits the ways to optimize value activities.e This modeling approach provides pro-activities way to actually experiment with alternative business models, by making enterprise to simulate various possibilities before committing to specific investments in reality.
1. Introduction
In the last decades science and technology have experienced an impressive and fundamental change, which provides many new business opportunities to establish E-commerce enterprises, e.g. Alibaba Group Holding Ltd,JD.com Inc and Suning Commerce Group Co Ltd in the mainland, and an ideal setting for studying business model development. Although the “what” question (i.e. business model’s definition, function, classification) has been investigated in many studies, the “how” question (i.e. business model’s representing method, evaluation) has yet to be explored.
Several scholars have recognized this problem and have attempted to represent value creation logic and process of business model through a mixture of textual, verbal, and ad graphic representations. Weill and Vitale (2001) have introduced three classes of objects ü participants (firm of interest, customers, suppliers, and allies), relationships, and flows (money, information, product, or service flows) ü intended to provide tools for the analysis and design of e-business initiatives. Chesbrough and Rosenbloom (2002) thought business model as input-output convert mechanism to be financed out of internal corporate resources. Osterwalder (2004) applies business model ontology (BMO) to conceptualization and formalization of the essential components into elements, relationships, vocabulary, and semantics. Based on a Penrosian view of firm, Demil and Lecocq (2010) build on the RCOV (R means resource, C means competences, O means organization, V means value) propositions framework to represent how value create and evolve. Casadesus-Masanell and Ricart (2010) represent business model by means of a causal loop diagram, where choices and consequences are linked by arrows based on causality theories. Li and Wang (2010) develop rules based on container model, systematically reveals fundamental components and building blocks, and explains function and value activities of business model. Teece (2010) defines a business model as the way in which the business enterprise delivers value to customers, entices customers to pay for value, and converts those payments to profit. Despite conceptual differences among current literature, there is widespread acknowledgement that business model is a new unit of analysis in addition to the product, firm, industry, or network levels, and value creation is the focus of business model. Thus, these studies leave a gap to be bridged and the gap reveals a critically important research problem to be resolved, that is, how to visualize these transaction activities and calculate actors revenue respectively? This paper, therefore, adopts e3 value model (i.e. economical, exchange, enabler), proposing by Gordijn and Akkermans (2001,2004), to investigations of E-commerce enterprise value generating in the process.The quantitative analysis of our study can help the actors involved to understand value creation and capture, and advance both research and practice in the field of E-commerce enterprises. Therefore, managers need to know the key attributes when designing E-commerce business model to increase efficiency and effectiveness.
This paper is structured as follows: Section 2 presents our method and tools. Section 3 is E-commerce modeling construction. Section 4 is devoted to the evaluation of results. Section 5 summarizes our main conclusions and indicates the suggestions.
2. Methodology and tools
2.1. The methodology of e3 value
The model of e3 value defines how economic value is created and exchanged within a transaction network by utilizing conceptual graphical model and scenario-based thinking. What’s more, it can perform a financial sensitivity analysis. Through this model and subsequent profitability sheet, we can find enterprise sustainability depends on anticipating and reacting to dynamic environment while optimizing value activities. This modeling technique takes a value viewpoint unlike other traditional modeling tools that take either a business process viewpoint (typical of operation management) or a system architecture view (typical of information systems literature). Gordijn and Akkermans identified a number of generic concepts, relationships and rules in order to enhance and sharpen the understanding of business operations and requirements using scenario analysis and quantification. This modeling borrows concepts from business literature such as actor, value object, value port, value interface, market segment, composite actor, scenario path, start stimulus, end stimulus, and connection. The e3 value mode respect the rule of economical reciprocity and “give and take” methodology: for goods or services delivered to the transaction network, the transaction networks should provide goods or services of equal value in return.
Comparing with other methodologies, the e3 value model helps in building a conceptual model for E-commerce of both current and prospective business models, managers can quickly surmise many of the likely implications of making possible change. What’s more, it can automatically generate revenue/profit calculations for each actor involved, and analyze E-commerce enterprises for its economic sustainability. It is worth noting that the e3 value model is a simplification of the real world, and the focus of the model is on what kind of value objects must exchange to each other in order to cover customer needs.
2.2. Tools
Value transfer can be conceptualized by the following e3 value constructs (in italic). Actors, such as the buyer, seller are economically independent entities. Actors transfer value objects (goods, service, payment, or experience) by means of value transfers depicted by labeled arrows. By exchanging value objects they rather aim for profitability (in the case of supplier) or maximum their economic utility (in the case of customer). A value interface models the principle of economical reciprocity: Actors only willing to transfer a value in return for some other value of object, and consists of value ports, to depict outgoing-ingoing value activities. In the e3 value model, customers are considered as the starting points and the reason why a business model must be generated. How to satisfy customer need follows dependency path, which indicates the transfer of value objects. The dependency path shows how many value transfers are executed as a result of a consumer need. The dependency path is e.g. used to analyze the net cash flow for each actor involved. A market segment shows a set of actors that for one or more of their value interfaces, value objects from an economical perspective. The Table 1 shows e3 value mode how to present.
3. Building the business model for E-commerce enterprise using e3 value model
The business model is a structural template that describes the organization of a focal firm’s transactions with all of its external business partnerships. E-commerce enterprise, as a focus firm, is performing value activities to provide product or service which can be offered to customers, and demand resources from suppliers and other business partners. In order to understand these value transfers relationship in a more structured and rigorous way than would be possible through verbal theorizing, this paper applies e3 value model to the description of Ecommerce enterprise that behaves in compliance with procedure and regulations. Initially, assuming this Ecommerce business model that mainly involves eight actors below:
⦁ E-commerce enterprise T. It adopts feedback system and cogitation system strictly to prevent committing fraud or making intentional errors, e.g. buyers have paid but sellers don’t deliver the (right) goods or services, or buyers will not pay but sellers have delivered goods or services; or sellers will deliver counterfeits and bogus products. As a online platform, enterprise T must enhance e-service quality, including website design, reliability, securing and privacy for both buyers and sellers.
⦁ Consumers. Online shopping has become popular in our daily life and T provides rich products portfolio, such as Heath & Beauty, Gifts, Sports & Toys, Mobile Phone & Accessories, Desktops, Laptops.
⦁ B2C stores and C2C stores. They not only provide the wide variety of commodities, but also important revenue resource for company T. T gathers advertising expense (such as federal fees, bidding fee, key words ranking fee), membership fee (such as technical service fee, merchandise helving fee), value-added service charge (such as (the products in characteristics display, logistics charge).
⦁ Internet service provider(ISP). The core business of e-commerce enterprise T is to provide online shopping platform, and they are not so much interest in all technical activities, such as IP access provisioning. Therefore, they outsource these activities to the telecommunication enterprises.
⦁ Advertiser. Advertising message could effectively increase customers’ purchasing probability and enhance the image of product and service, then attract more stores to sell products.
⦁ Employee. The salary of treating employees well is largely influencing innovation in the E-commerce enterprises.
⦁ Equipment seller. E-commerce enterprise T outsources activities such as manufacture, update and maintain network equipment to the professional manufactures.
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. روش شناسی و ابزار
2.1. روش شناسی ارزش e3
2.2. ابزار
3. طرح مدل کسب و کار برای شرکت تجارت الکترونیک با استفاده از مدل ارزش e3
4. شبیه سازی مدل
4.1. تنظیم پارامترهای مدل
4.2 اوراق سودآوری
4.3. تجریه و تحلیل حساسیت
5. نتایج اصلی و پیشنهادات
5.1. نتایج اصلی
5.2. پیشنهادات
5.2.1. در کنار منطق غالب جدید
5.2.2. در کنار فنآوری جدید
5.2.3. در کنار روندهای جدید مشتری
منابع
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology and tools
2.1. The methodology of e3 value
2.2. Tools
3. Building the business model for E-commerce enterprise using e3 value model
4. Simulation of the model
4.1. Model parameters setting
4.2. Profitability sheet
4.3ˊ Sensitivity analysis
5. Main conclusions and suggestions
5.1. Main conclusions
5.2. Suggestions
5.2.1. Keep abreast of new dominant logic
5.2.2. Keep abreast of new technology
5.2.3. Keep abreast of new customers trends
References
