
دانلود رایگان مقاله تاثیر ویژگی های جامعه طرفداران برند آنلاین در تعامل با مشتری
چکیده
ظهور بسترهای دیجیتال تعاملی، موجب شده تا افراد به طور مداوم در این بسترها تعامل داشته باشند. از طرفی از سازمان ها برای ایجاد جوامع آنلاین برای تعامل مشتریان با آنها و با دیگران به منظور افزایش وفاداری به برند، دعوت به عمل آمده است. در این پژوهش، آنچه که مشتریان را درگیر این جوامع طرفداران برند می سازد، مورد بررسی قرار گرفته است. از طریق بررسی پرسشنامه 430 نفر از کاربران فیس بوک، این مطالعه به بررسی چگونگی تأثیر ویژگی های منحصر به فرد جوامع طرفداران برند آنلاین (کیفیت اطلاعات، کیفیت سیستم، تعامل مجازی و پاداش) بر تعامل با مشتری تاثیر می پردازد. اثر تعامل مشتری بر وفاداری به برند نیز بررسی شده است. این پژوهش، یک مدل تجربی برای تعهد مشتریان با جوامع طرفداران برند آنلاین در فیس بوک را با توجه به نقش تعدیل کننده جنسیت، بیان کرده و تایید می کند. پارادایم محرک – ارگانیسم – پاسخ برای توجیه زمینه نظری این مطالعه، مورد نیاز است. داده ها با استفاده از مدل سازی معادلات ساختاری مورد آنالیز قرار گرفتند. نتایج نشان می دهد که هر یک از ویژگی های مثبت، بر تعامل مشتری تاثیر می گذارد، که در این بین کیفیت اطلاعات و تعامل مجازی قوی ترین تاثیر را دارند. تعامل مشتری نیز تاثیر مثبتی بر وفاداری به برند دارد. این نتایج نشان می دهد که اختلاف جنسیتی در محیط آنلاین قابل چشم پوشی است، زیرا تأثیر کلیه چهار ویژگی جوامع طرفداران برند آنلاین بر روی تعامل مشتری در بین اعضای زن و مرد غیر قابل تغییر و ثابت است.
1. مقدمه
پیشرفت های اخیر در تکنولوژی های تعاملی (دیجیتال) موجب ایجاد بسترهای جدید برای به اشتراک گذاری اطلاعات و معرفی خود است. مردم به طور پیوسته در بسترهای دیجیتال به اهداف شخصی و همچنین اهداف متقابل دست می یابند. از آنجایی که بیشتر مردم با اینترنت سر و کار داشته و در استفاده از آن مهارت دارند، سازمانها جوامع آنلاین را به منظور تعامل مشتریان خود با یکدیگر و با دیگران، ایجاد می کنند. جوامع آنلاین به طور کلی دارای یک فعالیت مصرف یا یک برند به عنوان نقطه مرکزی هستند. هنگامی که یک فعالیت مصرف، نقطه مرکزی است، جامعه آنلاین به عنوان جامعه مصرف نامیده می شود، که به گروهی از افراد با "احساسات، سبک زندگی، اعتقادات اخلاقی جدید، احساس بی عدالتی و شیوه های مصرف مشترک" اشاره دارد، در حالی که زمانی که یک برند نقطه کانونی است، جامعه آنلاین به عنوان جامعه طرفداران برند نامگذاری می شود که عبارت است از "یک گروه پایدار و انتخاب شده از سوی مصرف کنندگان، که قرارداد عضویت با یکدیگر و برند را قبول کرده و به رسمیت می شناسد."
محبوبیت روزافزون جوامع طرفداران برند آنلاین، موجب ارائه یک پلتفرم اجتماعی برای مصرف کنندگان، برای دیدن و به اشتراک گذاشتن تجربه و اشتیاق خود در مورد برند های مورد علاقه شان شده است. جوامع طرفداران برند آنلاین، با استفاده از قابلیت های بی نظیر ارتباطی و تعاملی خود، افزایش آگاهی برند، افزایش اعتماد، ایجاد دید مثبت در مشتری و مصرف کننده، افزایش وفاداری مشتری به برند و دستیابی به مزایای رقابتی در هنگام بازاریابی پیشنهادات سازمان ها را تضمین می کند.
دهه گذشته، علاقه ی تحقیقاتی در رابطه با جوامع طرفداران برند آنلاین را تجربه کرده است. تحقیقات موجود در این حوزه بر نتایج مرتبط با برند مشارکت در یک جامعه طرفداران برند آنلاین یا بر تعاملات مصرف کنندگان و رفتار آنها در محیط آنلاین که در آن فعالیت می کنند، متمرکز شده است. نقش جوامع طرفداران برند آنلاین در جذب مشتریان و نیز توسعه و تقویت روابط مشتری، از اهمیت علمی قابل توجهی برخوردار است. بسیاری از بزرگترین برند های جهان در فیس بوک جوامع برند را به منظور تبلیغ، ترویج و ارائه خدمات خود به مشتریان و نیز مشارکت آنها به منظور ایجاد روابط بلند مدت مشتری-شرکت توسعه داده اند.
صرف نظر از پذیرش وسیع جوامع طرفداران برند آنلاین و تلاش سازمانی برای جذب مشتری در آن، اطلاعات ضعیفی در مورد انگیزه مشتریان برای پیوستن به این جوامع، در دسترس است. برای بالا بردن بازدهی سرمایه گذاری های انجام شده در ایجاد جوامع طرفداران برند آنلاین، بازاریاب ها نیاز به درک بهتر مشتری در مورد انگیزه آن ها برای شرکت در این جوامع برند و مزایای آن (نگرشی و مالی) برای برند، دارند. شناخت بهتر انگیزه های تعامل می تواند از طریق بهبود استانداردهای عملیاتی برای این پلتفرم پیشرفته جامعه برند، در دستیابی به بهترین مزیت کمک کند. از آنجایی که تعداد زیادی از مشتریان وقت خود را با جوامع طرفداران برند آنلاین می گذرانند، بررسی انگیزه مشتریان برای مشارکت و تعامل با آنها دارای اهمیت است.
انگیزه تحقیقات انجام شده توسط مصرف کنندگان در مورد جوامع طرفداران برند آنلاین، در مطالعات بازاریابی بسیار مورد توجه قرار گرفته است. موسسه علوم بازاریابی (MSI) همچنین توجه علمی و دانشمندانه به مشارکت مشتری را توصیه می کند. در چند سال اخیر، تحقیق در مورد مشارکت مشتری در زمینه جوامع طرفداران برند آنلاین، توجه زیادی به خود جلب کرده است اما اکتشاف تجربی در این حوزه هنوز توسعه نیافته است. هرچند این نیاز واقعی تحقیق در مورد انگیزه های مشارکت مشتری در جوامع طرفداران برند آنلاین، با سناریوی متغیر صنعت، هماهنگ نیست. مطالعات قبلی، بر نیاز به بررسی ویژگی های جامعه طرفداران برند و تاثیر آنها بر روی مشارکت مشتری تاکید کرده اند، زیرا این ویژگی ها منعکس کننده یک تصور کلی مشتری از یک جامعه طرفداران برند است. برخی مطالعات، ویژگی های جامعه طرفداران برند آنلاین و تاثیر آنها بر رضایت، تعهد و آگاهی برند را نشان داده اند. با این حال، مطالعات مربوط به ویژگی های جامعه طرفداران برند و مسیرهایی که از طریق این خصوصیات باعث ایجاد مشارکت مشتری می شوند، بسیار نادر هستند.
این تحقیق تلاش می کند تا از طریق بررسی جامع و کامل انگیزه های مشتری برای مشارکت با جوامع طرفداران برند آنلاین در فیس بوک و تأثیر مشارکت مشتری در وفاداری به برند به این شکاف تحقیقاتی بپردازد. مطالعه فعلی اولین نوع مطالعه ای است که به طور جدی بررسی می کند که چگونه ویژگی های منحصر به فرد جوامع طرفداران برند آنلاین (بلوک های ساختمان) مشارکت مشتری را پیش بینی می کند. علاوه بر این، تحقیقات پیشین بررسی تاثیر تفاوت های جنسیتی در مشارکت مشتری در جوامع طرفداران برند آنلاین را نشان می دهد که به این معنا است که رفتار مصرف کننده در بین جنسیت های مختلف، متفاوت است. در زمینه رسانه های اجتماعی، مطالعات آنالیز جنسیتی در مرحله اولیه قرار دارد. بنابراین، با توجه به فقدان درک در مورد نقش تعدیل کننده جنسیت در ارتباط با جوامع طرفداران برند آنلاین، این مطالعه بیشتر به بررسی چگونگی تاثیر جنسیت های مختلف (مرد و زن) بر رابطه بین ویژگی های کلیدی جوامع طرفداران برند آنلاین و تعامل با مشتری می پردازد.
با توجه به شکاف فوق ذکر، این مقاله سهم قابل توجهی در ادبیات بازاریابی دارد، زیرا مطالعات قبلی به این موضوع نپرداخته اند که چگونه ویژگی های اصلی جوامع طرفداران برند آنلاین بر تعامل مشتری تاثیر می گذارد. از آنجایی که تعامل مشتری در زمینه آنلاین در برنامه های کاربردی رسانه های اجتماعی از طریق یک وب سایت آغاز می شود، این مطالعه به طور خاص به بررسی برخی از سازه هایی که اغلب در وب سایت و ادبیات طراحی جامعه طرفداران برند ذکر شده اند، می پردازد. ویژگی هایی مانند کیفیت اطلاعات و کیفیت سیستم در هنگام طراحی یک وب سایت شرکت موثر، مورد توجه قرار گرفته است، در حالی که تعامل و پاداش هایی برای افزایش رضایت و آگاهی از برند و همچنین ایجاد گرایش مطلوب مشتری به جوامع طرفداران برند آنلاین، پیشنهاد شده است. بنابراین، این مطالعه به بررسی تاثیرات جمعی این چهار ویژگی کلیدی (کیفیت اطلاعات، کیفیت سیستم، تعامل مجازی و پاداش) جوامع طرفداران برند آنلاین بر روی مشارکت مشتریان می پردازد. درخواست پارادایم محرک – ارگانیسم – پاسخ و اعتبار تجربی مدل مفهومی در زمینه فیس بوک با توجه به تفاوت های جنسیتی نیز به سهم این مطالعه می افزاید به این ترتیب که یافته های این مطالعه را می توان در رسانه های مختلف اجتماعی مانند توییتر، لینکدین و یوتیوب و غیره که مناسب تحقیقات دانشگاهی هستند، به کار گرفت.
بخش زیر اطلاعات قبلی مربوط به ساختارهای این مطالعه را به طور خلاصه بیان می کند و چارچوب مفهومی و فرضیه ها را ایجاد می کند. پس از آن، متدلوژی و آنالیز داده ها برای تأیید چارچوب مفهومی ارائه می شود. این مقاله با ارائه نتایج، بحث و محدودیت های مطالعه به پایان می رسد.
Abstract
The advent of interactive digital platforms has led people to progressively interact on such platforms, urging organizations to create online communities to engage customers with them and with each other to enhance brand loyalty. This study attempts to investigate what motivates customers to engage in these brand communities. Through a questionnaire survey of 430 Facebook users, this study investigates whether and how the unique characteristics (information quality, system quality, virtual interactivity, and rewards) of online brand communities affect customer engagement. The consequent effect of customer engagement on brand loyalty is also examined. This study frames and empirically validates a model for engaging customers with online brand communities on Facebook, considering the moderating role of gender. The Stimulus-Organism-Response paradigm is solicited to justify the theoretical background of this study. The data were analyzed using structure equation modelling. Results reveal that each of the characteristics positively influences customer engagement, with information quality and virtual interactivity bearing the strongest influence. Customer engagement also exhibits a strong positive impact on brand loyalty. This results further reveal that gender gap in the online environment is declining as the impact of all the four characteristics of online brand communities on customer engagement was invariable across male and female members.
1. Introduction
Recent advances in interactive (digital) technologies have given rise to new platforms for information sharing and selfexpression (Jang et al., 2008). People are progressively interacting on digital platforms to achieve personal as well as mutual objectives (Dholakia et al., 2004). As more people are becoming proficient with the Internet, organizations are creating online communities to engage customers with them and with each other. The online communities generally have a consumption activity or a brand as focal point. When a consumption activity is the focal point, the online community is termed as consumption community, signifying a group of individuals ‘‘held together through shared emotions, styles of life, new moral beliefs, senses of injustice and consumption practices” (Cova, 1997, p. 301), while when a brand is the focal point, the online community is labeled as brand community and is ‘‘an enduring, self-selected group of consumers, who accept and recognize bonds of membership with each other and the brand” (Veloutsou and Moutinho, 2009, p. 316).
The rising popularity of online brand communities has offered a social platform for consumers to meet and share their experiences and enthusiasm regarding their preferred brands (Trusov et al., 2009; Zhu et al., 2016). With their unprecedented communicative and interactive capabilities, online brand communities warrant organizations to enhance brand awareness (Barreda et al., 2015), magnify trust (Nadeem et al., 2015), generate positive word of mouth (Wang et al., 2016), heighten customer brand loyalty (Zheng et al., 2015), and achieve competitive advantages while marketing their offerings (Jang et al., 2008).
The last decade has seen a thriving research interest with respect to online brand communities (Habibi et al., 2014; Islam and Rahman, 2016c; Zhang and Luo, 2016). The existing research in this domain has either focused on the brandrelated outcomes of participation in an online brand community or on the interactions of consumers and their behavior in the online environment they operate in. The role of online brand communities in engaging customers, developing and strengthening customer relationship has also been of significant academic interest (Dessart et al., 2015; Manchanda et al., 2015). Many of the world’s biggest brands have developed brand communities on Facebook to advertise, promote, and communicate their offerings to their customers, as well as engage them so as to build long-term customer-firm relationships (Zaglia, 2013).
Regardless of the extensive adoption of online brand communities and the organizational quest for engaging customers therein, scanty literature is available regarding what motivates customers to continuously interact on these communities (Baldus et al., 2015). To boost returns on the investments made in creating online brand communities, marketers require finer customer insights about the motivations to participate and engage in these brand communities and the resulting benefits (attitudinal and financial) to the brand. Better knowledge of the engagement motivations can help in achieving excellence by improving the operational standards for this advanced platform of brand communication. Because large number of customers spend time with online brand communities, it is worthwhile to explore customers’ motivation in participating and engaging with them (Brodie et al., 2013; Baldus et al., 2015).
The urge for customer engagement research in online brand communities is extensively conceded in the marketing literature (Brodie et al., 2013; Hollebeek et al., 2014; Dessart et al., 2015). Marketing Science Institute (MSI) also recommends scholarly attention towards customer engagement (MSI, 2014). In the recent few years, research on customer engagement in the context of online brand communities has gained a significant heed (Dessart et al., 2015) but the empirical exploration in this domain is still underdeveloped (Brodie et al., 2013). Albeit this realistic need, research on the motivations of customer engagement in online brand communities has not kept pace with the ever changing scenario of the industry (Brodie et al., 2013). Earlier studies have emphasized the need to examine brand community characteristics and their impact on customer engagement (e.g., Brodie et al., 2013; De Valck et al., 2009) because these characteristics reflect a customer’s overall impression of a brand community. A few studies have illustrated online brand community characteristics and their impact on satisfaction, commitment, and brand awareness (Barreda et al., 2015; Jang et al., 2008). However, studies exploring brand community characteristics and the paths through which these characteristics cause customer engagement are rare (Kang et al., 2016).
This study attempts to address this research gap by comprehensively examining some customer motivations to engage with online brand communities on Facebook and the resulting effect of customer engagement on brand loyalty. The current study is the first of its kind to conclusively investigate whether and how the unique characteristics (the building blocks) of online brand communities predict customer engagement. Furthermore, prior research suggests the exploration of the effects of gender differences on customer engagement in online brand communities (Cambra-Fierro et al., 2015; Hammedi et al., 2015) as consumer behavior is likely to differ across genders (Ruane and Wallace, 2013). In the social media contexts, gender analysis studies are at an early stage (Verbraken et al., 2014; Zhang et al., 2014). Therefore, considering the dearth of understanding regarding the moderating role of gender in relation to online brand communities, this study further analyzes how different genders (male and female) influence the relationship between key characteristics of online brand communities and customer engagement.
By addressing the above mentioned gaps, this paper makes significant contribution to the marketing literature as prior studies have not considered how prime characteristics of online brand communities influence customer engagement following interactions on them. Because customer engagement in the online context is initiated within social media applications (e.g., Facebook) via a website, this study specifically looks at some constructs that have frequently been cited within the website and brand community design literature. Characteristics such as information quality and system quality have been considered as imperative to incorporate while designing an effective company website (Cao et al., 2005; Hung and Lin, 2015; Ou and Sia, 2010), whereas interaction and rewards have been suggested to enhance satisfaction and brand awareness as well as generate favorable customer attitude towards online brand communities (Barreda et al., 2015; Jang et al., 2008; Mollen and Wilson, 2010). This study, therefore, studies the collective impact of these four key characteristics (information quality, system quality, virtual interactivity, and rewards) of online brand communities on customer engagement. The solicitation of Stimulus-Organism-Response paradigm and the empirical validation of the conceptual model in the context of Facebook, taking into account the gender differences, also adds to the contribution of this study as the findings of this study can be applied to different social media platforms such as Twitter, Linkedin, and YouTube etc., which are appropriate for academic research.
The following section summarizes prior literature relevant to the constructs of this study and develops the conceptual framework and hypotheses. The methodology and data analysis to validate the conceptual framework is presented thereafter. The paper concludes by presenting the results, discussion and limitations of the study.
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. توسعه نظری
2.1 چارچوب محرک – ارگانیسم – پاسخ
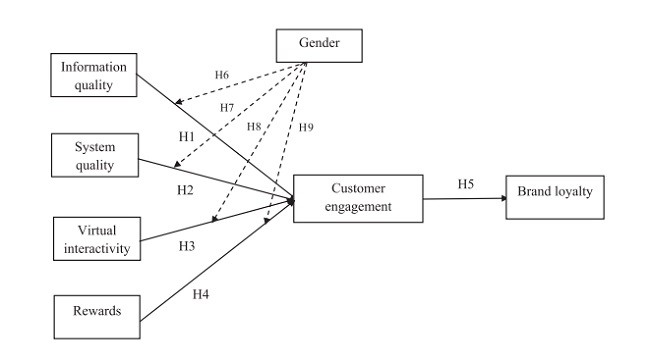
3. مدل تحقیق و فرضیه
3.1 تأثیر کیفیت اطلاعات در مشارکت مشتری
4. متدولوژی تحقیق
4.1 نمونه
4.2 معیارها
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical development
2.1. Stimulus-Organism-Response framework
2.2. Online brand communities and customer engagement
3. Research model and hypotheses
3.1. Influence of information quality on customer engagement
3.2. Influence of system quality on customer engagement
3.3. Influence of virtual interactivity on customer engagement
3.4. Influence of rewards on customer engagement
3.5. Customer engagement and brand loyalty
3.6. Gender as a moderator
4. Research methodology
4.1. Sample
4.2. Measures
5. Analysis and results
5.1. Structural model
6. Discussion and implications
7. Limitation and future research
References
