
دانلود رایگان مقاله ارزیابی عوامل منابع انسانی در مطالعه موردی مدیریت ارتباط با مشتری
چکیده
مدیریت ارتباط با مشتری (CRM) در تمامی سازمان ها یک اصل اساسی به شمار می آید. برخلاف این امر، استفاده CRM همیشه به نتیاج مورد نظر سازمان ها دست نیافته است. از آنجا که دیدگاه اغلب سازمان ها به این اصل یک دیدگاه تکنولوژیکی بوده است، این مساله با شکست مواجه شده است. در کنار تکنولوژی، عوامل دیگر نیز مانند منابع انسانی باید به عنوان منابع مهمی که در موفقیت مدیریت ارتباط با مشتری نقش دارند در نظر گرفته شوند. از این رو، شناسایی و ارزیابی منابع انسانی موثر در مدیریت ارتباط با مشتری بسیار مهم است. جامعه اماری این پژوهش را کارمندان بانک های خصوصی شیراز تشکیل می دادند و داده ها نیز با استفاده از پرسشنامه جمع آوری شد. داده ها از طریق آزمون همبستگی پیرسون تحلیل شدند. ازمون فریدمن نیز برای اولویت بندی منابع انسانی مهم در مدیریت ارتباط با مشتری بکار برده شد. یافته های این پژوهش تاثیر مثبت عوامل انسانی بر مدیریت را با مشتری را نشان داد و علاوه بر این مشخص شد که از میان عوامل انسانی مختلف، خود-شناسایی منابع انسانی بیشترین تاثیر را در این زمینه دارد.
1. مقدمه
سازمان ها با تغییر مسیر از راهبرد کسب و کار تولید محور به سوی راهبرد تمرکز بر مشتری، نیاز به تغییر را درک کردند (آلشوای و همکاران 2011). آن ها برای باقی ماندن در صحنه رقابت کسب و کارهای امروز، نه تنها باید مشتریان جدید جذب کنند بلکه باید مشتریان قبلی خود را نیز نگه دارند و وفاداری آن ها را حفظ کنند (یانگ و همکاران 2008؛ مندوزا و همکاران 2007). مدیریت ارتباط با مشتری یکی از راهبردهای اساسی برای حفظ مشتری است که از سودمندترین راه های رقابت در دنیای کسب و کار نیز به شمار می آید. در سال های اخیر، واژه مدیریت در “مدیریت ارتباط با مشتری” در حوزه های مختلف مانند بازاریابی، تکنولوژی اطلاعات، و غیره توجه زیادی به خود جلب کرده است. سازمان های بیش از پیش متوجه شده اند که مشتریان، دارایی مهم آن ها هستند و از این رو، ارتباط با آن ها را به عنوان یک راه حفظ سود شرکت در نظر مر گیرند (پلاکویناکی 2005). CRM یک تکنولوژی است و فرایندهای کسب و کار را که باید با یکدیگر همکاری کنند تا نیازهای مشتریان رفع شود با یکدیگر یکپارچه می کند؛ برای رسیدن به این هدف، تمام مولفه های یک سیستم باید به دقت در نظر گرفته شوند و تمامی انتظارات مدیریت شود تا نیازهای مشتریان تامین شود (کینگ و بورگس، 2008). در واقع، CRM یک دیدگاه کاملا مشتری محور است و ارتباط داشتن با مشتری که دیدگاه ان است، باید تمام چرخه کسب و کار را در بر گیرد. در واقع، نه تنها تمام دپارتمان های یک سازمان مانند بخش بازاریابی، حسابداری، تولید باید به مشتری و تامین نیازهای او توجه داشته باشند، و اطلاعات را با یکدیگر به اشتراک بگذارند، بلکه تمام نکات بدست آمده از ارتباط با مشتری و جزئی ترین اطلاعات در مورد او باید به شکل داده های مفید درآمده و در اختیار دپارتمان ها و مردم قرار گیرد (چو و همکاران 2002). اگرچه سیستم های CRM در سازمانئها بیش از گذشته به کار برده می شوند اما موفقیت اجرای آن ها نیازمند توجه به عوامل مختلفی است (مندوزا و همکاران 2007). CRM باید یه مفهوم راهبردی در نظر گرفته شود که از عوامل مهمی مانند منابع انسانی، تکنولوژی و فرایندهای کسب و کار تشکیل شده است. این بررسی که روی 202 سازمانی که CRM را اجرا می کردند نشان داد که تنها 30.7% از سازمان ها در اجرای آن موفق بودند و در ابعادی چون فروش، جذب مشتری جدید و حفظ مشتری های پیشین، پیشرفت کرده بودند. در واقع، 70% از سازمان هایی که CRM را از دید تکنولوژیکی مینگریستند نتوانسته بودند از آن به درستی استفاده کنند و اجرای CRM در آن ها با شکست مواجه شده بود. نرخ بالای شکیت در اجرای پروژه های CRM حاکی از این است که توجه و تمرکز کامل روی قسمت های سخت افزاری این پروژه ها و عدم درک دقیق اینکه سازمان ها از بخش های یکپارچه فرهنگ، فرایندهای مختلف، منابع انسانی، و تکنولوژی ساخته شده اند، یکی از مهم ترین عواملی است که استفاده از CRM را در سازمان ها با شکست مواجه می کند (جی.فینگان و لی.کوری 2010). در حقثیقت، ما باید CRM را بخشی از یک راهبرد در نظر گیریم که نه تنها به حمایت تکنولوژی بلکه به حمایت همه افرادی که در سازمان مشغول به کار هستند نیاز دارد (چو و همکاران 2002). راهبرد، منابع انسانی و فرایندهای کسب و کار، مه از مولفه های بسیار مهم CRM هستند. دشوارترین مرحله در اجرای این سیستم این است که به تکنولوژی توجه کنیم اما به منابع انسانی سازمان توجهی نداشته باشیم (فردریک و همکاران 2005). در حقیقت، این منابع انسانی سازمان است که مدیریت رابطه با مشتری را شکل می دهد (سعیدی و دیلمی معذی 2010؛ چن و پاپوویچ 2003). اجرای CRM نیازمند مشارکت منابع انسانی در تمامی بخش ها مانند بازاریابی، سرویس دهی، ضمانت، و مدیریت می باشد (جی.فینگان و ال.کوری 2010). از این رو، ما در این پژوهش اثرات عوامل انسانی بر مدیریت ارتباط با مشتری ارتباط با مشتری را بررسی می کنیم. تا جایی که ما می دانیم پژوهشی وجود ندارد که این تاثیر را به طور مستقیم مطالعه کرده باشد. البته در برخی از پژوهش ها، عواملی که در موفق بودن ارتباط با مشتری اهمیت دارند شناسایی شده اند و در میان این عوامل، منابع انسانی همواره از مهم ترین عوامل بوده اند. تعریفی که چن و یانگ از مدیریت ارتباط با مشتری ارائه دارند، ترکیبی از افراد، فرایندها و تکنولوژی را در بر می گیرد. آن ها نتیجه گرفتند که موفقیت در مدیریت ارتباط با مشتری فقط از طریق راه حل های تکنولوژییکی نیست بلکه در این زمینه باید به فرایند انسانی مدیریت، از جمله درک نیازهای مشتری، حفظ روابط دوستانه، و بازخورد گرفتن از مشتریان نیز توجه کرد (چن و شانگ 2007). کراتو و لی (2003) منابع انسانی، سیستم یکپارچه، و امادگی تکنولوژییکی را عوامل مهمی ذکر کردند که در مدیریت ارتباط با مشتری نقش دارند. دیب و میدوز (2004) ساختار سازمانی، استخدام نیرو و تحصیلات را مهم ترین عوامل موفقیت CRM گزارش کردند. مطمنی و جعفری (2009) اظهار کردند که استفاده از تکنولوژی، یکپارچگی سازمان ها در سازمان، شخصی سازی خدمات، و مدیریت کارمندان، و مدیریت ارشد از عوامل بسیار مهمی هستند که موفقیت CRM را افزایش می دهند. علاوه بر این، آن ها ذکر کردند که مدیریت ارشد در این عوامل نقش مهم تری دارد. شهرکی و همکاران (2010) نیز در پژوهش خود به این نتیجه رسیدند که اجرای موفقیت آمیز CRM به طراحی و استفاده صحیح از راهبردهای CRM و ایجاد تعادل میان ساختار، فرهنگ، و تکنولوژی سازمان بستگی دارد.کرامتی و شهریور (2008) شاخص ها و معیارها را از عوامل اصلی موفقیت در مدیریت ارتباط با مشتری در صنعت نساجی ذکر کرده و گزارش دادند که سه ویژگی اساسی یعنی عوامل انسانی، تکنولوژی و فرایندها نقش مهمی در موفقیت روابط فردی ایفا می کنند. با این وجود، هیچ پژوهشی نبوده است که ارتباط میان این متغیرها را به طور مستقیم بررسی کرده باشد و هر یک از موضوعات ارائه شده، یک یا دو متغیر را بررسی کرده اند. البته، ادبیات پژوهشی از دیدگاه ذهنی و بافتاری، پیش زمینه مناسبی برای درک بهتر این بررسی فراهم کرده اند. در این پژوهش ها، ابعاد مختلف عوامل منابع انسانی و مدیریت ارتباط با مشتری مطابق با پیش زمینه ها مطالعه شده اند.
2. اصول نظری
یکی از مهم ترین عوامل در بقای سازمان، منایع انسانی کمی و مستقل است. در حقیقت، اهمیت منابع انسانی از منابع مالی و تکنولوژی نوین بسیار بیشتر است.نقش منابع انسانی شایسته، توانا و آموزش دیده در رسیدن سازمان به اهداف تعیین شده غیرقابل انکار است (تیمور نژاد و اصفهانی، 2010).
در مورد بکارگیری CRM، منابع انسانی عامل مهمی است که نادیده گرفتن آن به شکست این پروژه منجر می شود. مقاومت کردن منابع انسانی در مقابل CRM یک چالش جدید است. برای مقابله با این چالش و مدیریت موانع، همکاری منابع انسانی در اجرای پروژه های CRM، همراه کردن آن ها با تغییرات، و آموزش دادن آن ها بیشترین نتیجه را در پی خواهد داشت (مطمنی و جعفری، 2010). با توجه به انچه تا کنون گفته شد، توجه کردن به منابع انسانی یکی از مهم ترین عوامل موثر در مدیریت ارتباط با مشتری می باشد. از این رو، ما با بررسی ادبیات پژوهشی و مشورت کردن با متخصصان این حوزه تصمیم گرفتیم عوامل انسانی موثر در موفقیت مدیریت ارتباط با مشتری را مطالعه کنیم. در این راستا، آموزش، دانش، همگرایی مدیریتی، دیدگاه، درک و خود-شناختی، خلاقیت، فرهنگ و ارتباط درون سازمانی را به عنوان مولفه های مهم در ادامه برسی می کنیم.
2.1 آموزش منابع انسانی
وجود نیروهایی مانند جهانی سازی و تکنولوژی سرعت و پیچیدگی تغییرات را افزایش داده است و سبب شده است سازمان ها برای حفظ ثبات خود نکات بسیاری را بیاموزند (تیموری نژاد و اصفهانی، 2010).
به همین دلیل است که توسعه و بهبود منابع انسانی یکی از ضرورت های سازمان به شمار می آید. وقتی کسانی که در یک سازمان فعالیت می کنند، به طور حرفه ای آموزش دیده باشند، کار خود را به بهترین شل انجام می دهند و این سبب موفق شدن آن ها می شود.
پیشرفت انسانی در بعد حرفه ای آن ها را تشویق می کند از تکنولوژی و تجهیزات جدید با میل بیشتری استفاده کنند. علاوه بر این، آن ها را باانگیزه می کند تا از این ابزارها با دقت بیشتری بهره برند، و ظرفیت علمی و تکنولوژیکی خود را بالا برند تا زمینه برای انجام پژوهش، اختراع، و کشف کردن فراهم شود. به این ترتیب، آن ها با تغییرات پیوسته تکنولوژی و فرایندهای مرتبط با آن خو می گیرند. اگر منابع انسانی در سازمان به اندازه کافی و دقیق اموزش نبیند، ممکن است سیستم CRM جدید موفقیتی در آنجا نیابد. در واقع، اگر سازمان آموزش های صحیح به کارمندان ندهد، سرمایه گزاری آن روی راهبردها، و نرم افزارها و سخت افزارها نیز بی فایده خواهد بود (مطمنی و جعفری 2010). کارمندان یک سازمان در مورد ارتباط با مشتری نیز باید به طور حرفه ای آموزش ببینند تا بتوانند با مشتریان ارتباط موثری برقرار کنند.
2.2 دانش منابع انسانی
با افزایش قدرت اقتصاد دانش محور، پارادایم جدیدی درمورد جایگاه منابع انسانی، به خصوص منابع انسانی دانش محور، ایجاد شده است. مهم ترین دارایی سازمان ها در قرن بیستم، تولید تجهیزات، و در قرن بیست و یکم، منابع انسانی دانش محور و کارایی آن ها است. منابع انسانی دانش محور و توسعه فعالیت های دانش محور در دهه های آینده، تغییرات اساسی در ساختار، ماهیت و متد ارزیابی سیستم اقتصادی ایجاد خواهد کرد. منابع انسانی دانش محور مهم ترین بخش یک سازمان در قرن بیست و یکم هستند. بیل گیتس در این باره می گوید که تمام دارایی های من بعد از پایان یافتن ساعت کاری کارمندانم، به پایان می رسد. در واقع، این منابع انسانی دانش محور هستند که در قرن بیست و یکم تایین می کنند چه سازمان هایی دوام میاورند و چ سازمان هایی از صحنه خارج می شوند. به همین دلیل است که مدیرانی دارای متد اقتصادی دانش محور می کوشند از این دارایی تاجایی که می توانند سود برند (فتحی، 2014). نظریه های جدید اقتصادی که بر اقتصاد دانش محور تاکید می کنند می دانند که اقتصاد موفق در اینده، دانش تولید و توزیع می کند و از آن استفاده تجاری می کند. از این رو، در نظریه های اقتصادی جدید، بیش از پیش به نقش سرمایه گزاری های انسانیی در توزیع دانش و پول درآوردن توجه می شود. در عصر دانش و خرد، سازمان ها به طور فزاینده ای بر دانش و کارمندان دانش محور تاکید می کنند (طهماسبی و گلی پور، 2012). در حقیقت، انچه به CRM جان می دهد، توانایی فف از این دانش در بهترین زمان و به بهترین شکل برای مشتری است (آلشوای و همکاران، 2010).
Abstract
Customer relationship management in all the organizations, has been represented as a fundamental and applicable principal. In spite of that, using CRM will not always realized the expected results of organizations. Because the view of most of the organizations to this principal was technological point of view so this view caused failure in most of the organizations that apply that principal. Besides technology, other factors including human resources should be recognized as one of the important and key sources in the success of customer relationship management. In this regard, recognizing and evaluating effective human resources in customer relationship management, is so important. The statistical community of this research is the employees of private banks of Shiraz city and data has been collected by means of questionnaire. In order to analysing data, we have used coefficient test of Pierson and in order to prioritizing effective human factors in customer relationship management, we have used Friedman test. The findings of this research show the positive effect of human factors on the customer relationship management and amongst these, factors such as view, understanding and self-recognition of human resources guaranteed the outmost effectiveness.
1. Introduction
By moving away from the strategy of production-based business toward the strategy of concentrating on customer, organizations find out the need of changing (Alshawi et.al, 2011). In order to compete in nowadays world of business and in order to be profitable for long term, we should not just concentrate on attracting new customers but we should keep the old customers they should also gain the persisting requisite which is the faith of customers (Young et.al, 2008 ,Mendoza et.al, 2007). Customer relationship management is one of the most fundamental strategies for keeping and preserving customers, especially the most profitable ones in the world of nowadays business. In recent years the word management of customer relationship management has attract lots of attention in different fields of marketing, information technology and etc. the organizations have extensively recognized that customers are their important possession and they consider communicating with customers as profitable trading (Plakoyiannaki, 2005). CRM is a technology and integrate process of business that should be coordinated to eliminate needs of customers and in order to performing that all the elements of the system should be considered carefully and all the expectations should be managed (King and Burgess, 2008). Actually CRM is a 360 degree customer based view and an advances and increasing communicating with customer that its point of view should cover all the cycle of business. Not just all the departments of organization such as marketing, accounting ,producing and etc. should pay attention to customer and his needs and participating in sharing information, but all the points of communicating with customer should be controlled and the most detailed information about customers should be transformed to useful data among departments and people (Chou et.al, 2002). Although CRM systems have been chosen for increased implementation in organizations, but success in its implementation requires paying attention to various factors (Mendoza et.al, 2007). CRM should be considered as a strategic concept that has consisted of important factors such as human resource, technology and business processes. This investigation of 202 implementing projects of CRM shows that only 30.7 percent of organizations were successful in implementing this system and could show successful function in selling, attracting and keeping customers. 70 percent of implementing the projects of customer relationship management that considered CRM from technological point of view, have failed. High rate of failure in CRM implementing projects show that complete attending and concentrating on hardware implementing projects and the lack of deep understanding of this issue that organizations are consist of integrated parts of culture, processes, human resources and technology is one of the most important factors of failure in CRM implementation (J.Finnegan and L.Currie, 2010). We should consider CRM as a participatory strategy that needs the support of all the people in organization not just technology and human resource (Chou et.al, 2002). Strategy, human resource and the processes of business are all vital elements of CRM. The most difficult phase in implementing this system is not paying attention to technology but it is paying attention to human resources of organization (Fredrick et.al, 2005). That’s the human resource of organization which are the constructing blocks of customer relationship management (Saeedi and Deylami Moazzi, 2010, Chen and Popovich, 2003). CRM implementation means extent involvement of human resource in all parts of organization such as marketing, service, guarantee and master management (J.Finnegan and L.Currie, 2010). According this in this research we will deal with investigating the effects of human factors on customer relationship management.in the literature of this subject, there is no research that has entered directly. In spite of that, in examining the literature, some factors have represented for the success of customer relationship management that human resource was the most important factor in implementing that. The definition that Chen and Young have represented from customer relationship management was the combination of people, processes and technology. They concluded that the success of customer relationship management is not just possible by means of technological solution but in implementing customer relationship management human process has the significant importance that includes activities such as understanding the needs of customer, controlling friendly relationships, integrating customer’s feedbacks and etc. (Chen and Shang 2007). Croteau and Li have introduced human resource, integrated system, and technology readiness as important factors in customer relationship management (Croteau and Li, 2003). Dibb and Meadows have introduced organizational structure, employment and education as the most important factor in the success of CRM in the under study organization (Dibb and Meadows, 2004). Motmeni and Jaafari in a research, recognized knowledge, using technology ,the integration of the system in the organization ,personalizing of services, personnel and master management as the most effective factors in implementing CRM that among all these the factor of master management has the outmost importance (Motmeni and Jaafari, 2009). Shahraki and his colleagues in a research considered the successful implementing of CRM in requirement of designing and correct use of CRM strategies and their balance with the structure, culture and technology of the organization (Shahraki et.al, 2010). Keramati and Shahrivar start recognizing indices and criterions as the key fundamentals of success in implementing customer relationship management in loom industry and three key characteristics such as human factors, technology and processes have been considered that has a significant importance for individual relations and processes (Keramati and Shahrivar, 2008). Although literature has no direct relation with under study subject, and each of the represented subjects have investigated one or several variables in the study. But the considered literature from subjective and contextual point of view have provided appropriate backgrounds and views for better performance of investigation. In the way that different dimensions of human resources factors and customer relationship management has been exploited according to represented back grounds.
2. Theoretical principals
One of the important factors of organization’s survival and durability is quantitative and authoritative human resources. Actually the importance of human resources is much more than new technology and financial sources. The role of competent, able and learned human resource in realization of organizational purposes is undeniable (Teymor Nejad and Esfastani, 2010).
In implementation project of CRM, human resource is the factor that its ignorance led to organizational failure. Human resource by resisting against CRM implementation is a new obstacle. In order to confronting these obstacles management and employment convergence, participating human resources in implementing the project of CRM, accommodating them with the changes and training them, has an outmost importance (Motmeni and Jaafari, 2010). According this paying attention to human resource is one of the important factors in the success of customer relationship management. That’s why, by considering the performed investigations in subject literature and holding the sessions of mental storm with the presence of geniuses and specializes, we dealt with recognizing effective human factors on the success of customer relationship management, that according this, training, knowledge, management convergence, view, understanding and self-recognition, talent creativity, culture and inter organizational communication potential have been considered that we will consider these factors in following.
2.1. Training human resources
Existence of forces such as globalization and technology has increased the speed and complexity of the changes that the organizations had to learn lots of more things in order to persistence and durability (Teymor Nejad and Esfastani, 2010).
That’s why improvement and development of human resources is one of the organizational necessities. When the people who work at organization have professionally trained in their job, they would do their job in the best way and that will lead to their success.
Human development in profession dimension will cause people to use advanced technology and equipment more eagerly in their productions and in implying them they will show more accuracy and on the other side they will increase and extend their scientifically and technologically capacity and view in order to perform applicable researches, inventing and exploring and that will cause, they adjust themselves with the continuous changes of technology and processes. If organization’s human resources do not train accurately, a new CRM system may not operate successfully. Actually if the organization does not act successfully in representing appropriate training to its employees all its investment in strategy, hardware and software will be useful (Motmeni and Jafri, 2010). The organization’s employees should be trained in the field of communicating and contacting with customers in professional and applicable semesters so they could make an effective contact with their customers.
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. اصول نظری
2.1 آموزش منابع انسانی
2.2 دانش منابع انسانی
2.3 همگرایی مدیریتی
2.4 دیدگاه، درک و خود-شناختی منابع انسانی
2.5 خلاقیت و استعداد منابع انسانی
2.6 پتانسیل ارتباط فرهنگی و میان سازمانی
3. روش پژوهش
3.1 پرسش اصلی پژوهش
3.2 پرسش های ثانوی
4. یافته ها
4.1 بررسی فرضیه های آزمون
4.1.1 فرضیه اصلی: آیا عوامل انسانی با مدیریت ارتباط با مشتری ارتباط دارد؟
4.1.2 آزمون فرضیه های ثانوی
4.1.2.1 فرضیه 1: آیا آموزش به منابع انسانی در مدیریت ارتباط با مشتری نقش دارد؟
4.1.2.2. فرضیه 2: آیا دانش منابع انسانی در مدیریت ارتباط با مشتری نقش دارد؟
4.1.2.3 فرضیه 3: همگرایی مدیریت در مدیریت ارتباط با مشتری نقش دارد
4.1.2.4 فرضیه4: آیا دیدگاه، درک، و خودشناختی در مدیریت ارتباط با مشتری نقش دارد؟
4.1.2.5 فرضیه 5: آیا خلاقیت و استعداد منابع انسانی در مدیریت ارتباط با مشتری نقش دارد؟
4.1.2.6 فرضیه 6: آیا فرهنگ و تونایی بالقوه ارتباط درون سازمانی در مدیریت ارتباط با مشتری نقش دارد؟
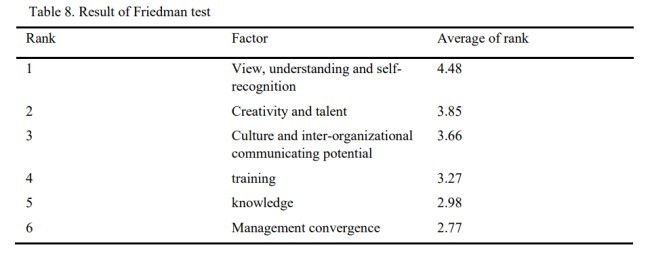
4.2 اولویت بندی عوامل
5. نتیجه گیری و پیشنهادات پژوهشی
منابع
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical principals
2.1. Training human resources
2.2. The knowledge of human resource
2.3. Management convergence
2.4. View, understanding and self-recognition of human resources
2.5. Creativity and talent of human resources
2.6. The culture and inter-organizational communicating potential
3. Research method
3.1. The main question of the research
3.2. Secondary questions
4. Findings
4.1. The test of research Hypotheses
4.1.1. Main Hypothesis: human resource factors has a role in customer relationship management
4.1.2. The test of detailed Hypotheses
4.1.2.1. Hypothesis 1: Training human resource has a role in customer relationship management
4.1.2.2 Hypothesis 2: The knowledge of human resource has a role in customer relationship management
4.1.2.3. Hypothesis 3: Management convergence has a role in customer relationship management
4.1.2.4. Hypothesis 4: View, understanding and self-recognition of human resource in customer relationship management
4.1.2.5 Hypothesis 5: Creativity and talent of human resource in customer relationship management
4.1.2.6 Hypothesis 6: Culture and inter-organizational communicating potential in customer relationship management
4.2. Determining prioritizing factors
5. Conclusion and research suggestions
References
