
دانلود رایگان مقاله اقتباس منابع انسانی الکترونیک و نقش مدیریت منابع انسانی
چکیده
هدف – این مقاله تلاش میکند تحول نقش کارکردی منابع انسانی را که متاثر از استفاده از اینترنت و فنآوریها است را در شرکتها یونانی بررسی نماید.
طراحی/ روششناسی/ رویکرد – روششناسی این مقاله بر اساس هر دو روش کمی و کیفی بوده است. ما به منظور تحقق اهداف این تحقیق، گروههای پیمایش و کانونی تشکیل دادهایم.
یافتهها– این مقاله به بررسی و بحث در مورد توسعه منابع انسانی الکترونیک در کشور یونان و دلایل اقتباس روشهای منابع انسانی الکترونیک میپردازد و بر راهبردها، فرآیندها، و موضوعات مرتبط با مدیریت منابع انسانی تمرکز مینماید. یافتهها نشان میدهند که منابع انسانی الکترونیک، تبدیل و تحول نقش کارکردی منابع انسانی به داشتن نقشی راهبردی تسهیل میکند. عوامل محرک و عوامل حیاتی موفقیت در اقتباس و اجرای روشهای منابع انسانی الکترونیک در این تحقیق شناسایی شدهاند و مورد بحث قرار گرفتهاند.
محدودیتها / پیشنهادات تحقیق- کشورهایی نظیر یونان در اجرای روشهای حرفهای مدیریت منابع انسانی و نیز توسعه فنآوری با محدودیتهایی مواجه هستند.
پیشنهادات عملی- این بخش به شناسایی عوامل حیاتی موفقیت در اقتباس روشهای منابع انسانی الکترونیک و همچنین مسائل اصلی مرتبط با آن میپردازد.
نوآوری/ ارزش- نتایج کیفی که توسط گروههای کانونی بدست آمده است تصویری شرکتها مورد تحقیق ارائه میدهند.
مقدمه
پایان قرن بیستم موجب پدید آمدن بحثهای گستردهای راجع به واکنش مدیریت منابع انسانی نسبت به محیط متغیر داخلی و خارجی شرکتها شده است. در اواخر سالهای 1990 ادبیات تحقیق این موضوع در مورد لزوم مدیریت منابع انسانی راهبردی اتفاق آراء داشتند، ولی در مورد نقشهای جدیدی را که کارکرد منابع انسانی باید برای مقابله با چالشهای سازمانی معاصر اتخاذ کند نگرانیهایی داشتند (مثلا، کوچان، 1997؛ اولریچ، 1997الف، 1998). نقش راهبردی کارکرد منابع انسانی به معنای ورود به عرصه برنامهریزی راهبردی از ابتدای فعالیتهای سازمانی است و این اقدام صرفا به مرحله اجرا و تطابق منابع انسانی با نیازهای تجاری محدود نمیشود. انتظار میرود که این نقش در آینده تا حدود قابلتوجهی وقت مدیران و مجریان منابع انسانی را صرف خود کند (اندرسون، 1997). با این حال این بدان معنا نیست که نقشهای اداری از بین خواهند رفت، اگرچه یک تنش طبیعی بین چشمانداز مورد نیاز برای نقش راهبردی منابع انسانی و نقش سنتی متخصصان مدیریت منابع انسانی وجود دارد (بییر، 1997).
یکی از جنبههای مهم محیطهای متغیر که به ویژه با مدیریت ارتباط دارد انقلاب اطلاعاتی است. طبق نظر اولریچ (1997ب) یکی از موضوعات نوظهور مرتبط با مدیریت منابع انسانی که نیاز به سرمایهگذاری در زمان، استعداد، و منابع دارد، استفاده از ظرفیت فنآوریها است. فنآوریها در کاهش تنش بین نقشهای راهبردی و اداری به کمک ما میآیند، تا جایی که میتوانند بخشی از مسئولیتهای اداری را حذف کنند (اِلینگ، 1997). منابع انسانی الکترونیک به در جریان انداختن تعاملات تجاری (و به ویژه مدیریت منابع انسانی) با استفاده از اینترنت به همراه دیگر فنآوریها بازمیگردد (لِنگنیک- هال و موریتز، 2003).
اگرچه رشته مدیریت منابع انسانی (به همراه رشته حسابداری) به دلیل پیچیدگیهای محاسباتی و کمّی در این حرفه و نیز مسئولیت آن برای ثبت حجم زیادی از اطلاعات تاریخچهای طولانی از تجربه استفاده از فنآوری اطلاعات در سازمانها دارد و هنوز به رهبری خود در اجرا و استفاده از فنآوری اطلاعات ادامه میدهد (تاونسِند و بِنِت، 2003)، مطالعات اندکی به بررسی میزان اقتباس فنآوری توسط مجریان منابع انسانی پرداختهاند (مثلا، بال، 2001؛ هندریکسون، 2003).
هدف این مطالعه بررسی استفاده از روشهای منابع انسانی الکترونیک در کشور یونان است تا بتوان از این طریق چارچوب تحلیلی از نظامهای منابع انسانی الکترونیک در کشورهای کوچکتر ارائه نمود. مشخصا اهداف این مطالعه عبارتند از:
بررسی دلایل اقتباس روشهای منابع انسانی الکترونیک. تاثیرات اقتباس منابع انسانی الکترونیک و نیز مسائل مرتبط با آن؛
شناسایی عوامل حیاتی موفقیت در اقتباس روشهای منابع انسانی الکترونیک؛
و بحث در مورد شیوههایی که منابع انسانی الکترونیک به نقش مدیریت منابع انسانی در اقتصاد جدید شکل میدهد، و نیز تاثیرات منابع انسانی الکترونیک بر آینده حرفه مدیریت منابع انسانی.
این مقاله با توضیح مختصری درباره مدیریت منابع انسانی در کشور یونان آغاز میشود و سپس مروری بر مفهوم منابع انسانی الکترونیک و کارکردهای آن در ادبیات مدیریت منابع انسانی خواهد داشت. سپس روششناسی، نتایج تحقیق کمّی و کیفی، و نیز مباحث مربوطه ارائه خواهند شد.
کارکردهای منابع انسانی الکترونیک:
این کارکردها چه مزایایی را به ارمغان میآورند؟
منابع انسانی الکترونیک میتواند بر هر یک از جنبههای مدیریت منابع انسانی تاثیرگذار باشد. در این بخش ما مختصرا به بیان تاثیرات فنآوری بر شش فرآیند کلیدی منابع انسانی میپردازیم که عبارتند از:
(1) برنامهریزی منابع انسانی؛
(2) جذب منابع انسانی (ثبت نام و گزینش)؛
(3) سنجش منابع انسانی (ارزیابی عملکرد)؛
(4) ارتباطات؛
(5) پاداش به منابع انسانی (سنجش عملکرد، جبران خدمات، و اعطای مزایا)؛
(6) [پرورش و] توسعه منابع انسانی (آموزش و پرورش، مدیریت مسیر شغلی).
ارزیابی منابع انسانی
منابع انسانی الکترونیک به ما این اجازه را میدهد که کل فرآیند ارزیابی عملکرد را از طریق اینترنت شرکت به صورت آنلاین انجام دهیم. این بدان معناست که مدیر و کارمندان سازمان میتوانند مستقیما دادههای عملکرد افراد را در قالب فرمهای الکترونیک به معاونت منابع انسانی ارسال کنند. این روش اگرچه به دلیل اینکه به شکل مکتوب به اسناد رسمی تبدیل نمیشود مورد انتقاد قرار گرفته است، تشریفات کاغذی اداری را کاهش میدهد و اگر تعاملات اداری بین سرپرستان و کارمندانی که مورد نظارت قرار میگیرند به درستی ثبت شوند، میتواند به شکل قابلتوجهی موجب صرفهجویی در زمان و هزینههای معاونت منابع انسانی شود. نرمافزار خودمدیریتی به مدیران اجازه میدهد نتایج مربوط به ارزیابی عملکرد را بلافاصله وارد سیستم کنند و کارمندان نیز میتوانند اهداف و نتایج عملکردشان را مدیریت کنند و بر اساس صفحه منابع انسانی شخصیشان برای عملکردشان برنامهریزی نمایند. همچنین این نرمافزار میتواند اطلاعاتی را درباره چگونگی ارزیابی عملکرد، معیارهای خاص و ارزیابی پُستها و نقشهای سازمانی خاص، علاوه بر مدلها و الگوهای موثر برای ارزیابی عملکرد در اختیار مدیران قرار دهد (آدامسون و زامپتی، 2001).
ارتباطات. مزایای بسیاری در استفاده از منابع انسانی الکترونیک از لحاظ ارتباطی وجود دارد. منابع انسانی الکترونیک به سادهترین شکل آن، شامل استفاده از پُست الکترونیک [ایمیل] برای برقراری ارتباط با کارمندان است. ضریب نفوذ ارتباطات کامپیوتری در شرکتها، عمدتا ایمیل از طریق، بیش از 75% است و ایمیل به عنوان یک رسانه برگزیده برای برقراری ارتباطات ظهور نموده است (بونتیس و همکاران، 2003).
Abstract
Purpose – This paper attempts to investigate the transformation in the role of the HR function in Greek firms, as a result of the use of internet and technology.
Design/methodology/approach – The paper is based on both quantitative and qualitative methodology. A survey and focus groups took place in order to meet research objectives.
Findings – This paper examines and discusses the development of e-HR use in Greece and the reasons for adoption of e-HR practices focusing on strategy, process and HRM issues. Findings show that e-HR facilitates the transformation of HRM role into a more strategic one. Driving forces and critical success factors of e-HR adoption and implementation are identified and discussed.
Research limitations/implications – Limits its usefulness to countries that experience a stage of HRM professionalisation and technological development similar to that of Greece.
Practical implications – Identifies critical success factors in e-HR adoption as well as main problems associated with it.
Originality/value – Qualitative results provided by the focus groups give an illustrative picture of the companies presented.
Introduction
The closing of the twentieth century has given rise to a vast debate concerning the response of human resource management to the changing external and internal environment of the firm. The late 1990s found the literature somehow settled on the necessity of strategic HRM, but concerned about the new roles that the HR function should adopt in order to meet contemporary organizational challenges (e.g. Kochan, 1997; Ulrich, 1997a, 1998). The strategic role of the HR function means being involved in strategic planning from the outset and not only during the implementation phase and matching employee resources with business needs. This role is expected to occupy significantly more of the HR practitioner’s time in the future (Anderson, 1997). However, this does not mean that the administrative role will cease to exist, although there is an inherent tension between the outlook required for a strategic HR role and that of the HR specialist in a traditional role (Beer, 1997).
One of the important aspects of the changing environment especially relevant to management is the information revolution. According to Ulrich (1997b), an emerging HR practice area that will require investment of time, talent and resources is leveraging technology. Technology comes to the rescue in reducing the tension between the strategic and administrative role, as it has advanced to the point where it can remove part of the administrative responsibility (Ellig, 1997). E-HR refers to conducting business transactions (and in particular HRM) using the internet along with other technologies (Lengnick-Hall and Moritz, 2003).
Although HRM (along with accounting), due to the quantitative complexity of the profession, coupled with its responsibility for enormous record-keeping, has a very long history of information technology experience in organizations and continues to be a leader in the implementation and use of IT (Townsend and Bennett, 2003), few studies have looked at the level of technology adoption from HR specialists (e.g. Ball, 2001; Hendrickson, 2003).
The purpose of the present study is to examine the use of e-HR in Greece, thus proposing a framework of analysis of e-HR systems in smaller countries. More specifically it aims at:
. examining the reasons for adoption of e-HR practices. The effects of e-HR adoption as well as problems associated with it will also be discussed;
. identifying critical success factors in e-HR adoption; and
. discussing the manner in which e-HR shapes the role of HRM in the new economy, as well as the perceived effect of e-HR in the future of the HR profession.
The paper begins with a brief presentation of HRM in Greece, followed by a review of the notion of e-HR and its functions as they appear in the HRM literature. Then the methodology and the results of the quantitative and qualitative research are presented, as well as the relevant discussion.
Definition of e-HR
The term e-HR was first used in the 1990’s and refers to conducting Human Resource Management “transactions” using the internet or an internet (Lengnick-Hall and Moritz, 2003). The term was inspired by the popular term of e-commerce, and wrongfully adopted the “e-” prefix, signifying “electronic”, even if e-HR is very specific to the use of the Net, so that a more accurate term would be “online HRM”.
E-HR aims at making information available to managers and employees at any time and anywhere. Currently, an e-HR system may include enterprise resource planning software (ERP), HR service centres, interactive voice response, manager and employee portals and web applications. So, a modern e-HR system allows employees to control their own personal information by updating records and making decisions, and allows managers to access information and data, conduct analyses, make decisions and communicate with others, without consulting the HR department.
Three forms/levels of e-HR have been identified (Lengnick-Hall and Moritz, 2003; Walker, 2001), depending on the primary focus of e-HR
(1) Publishing of information: This involves one-way communication from the company to the employees or managers. In this form of e-HR, the company uses the intranet as the primary information delivery medium.
2) Automation of transactions, with integration of workflow: In this form of e-HR, paperwork is replaced by electronic input. Intranets and extranets are used, frequently combining several different application programmes.
(3) Transformation of the HR function: In this form, e-HR liberates the function from its operational focus and redirects it toward a strategic one. Under this form, HRM takes up the following tasks: partnering with the line, creating centres of expertise and service centre administration.
The latter (transformational) form of e-HR is rare even in countries like the USA, which are very advanced in HRM (Lengnick-Hall and Moritz, 2003; Walker, 2001). Therefore, for the scope of the current paper, the first two distinctions of e-HR will be mostly used.
چکیده
مقدمه
منابع انسانی الکترونیک و نقش مدیریت منابع انسانی
روششناسی
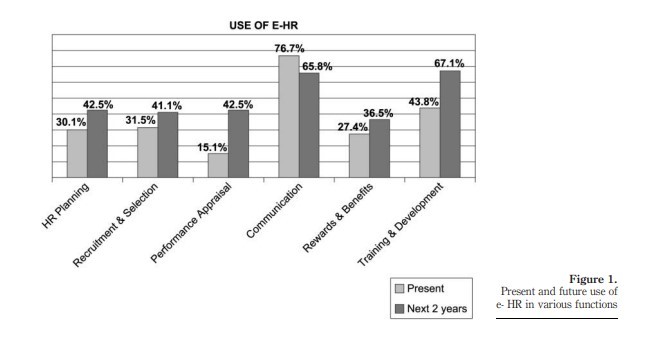
استفاده از روشهای منابع انسانی الکترونیک به منظور اقتباس آن
تاثیر منابع انسانی الکترونیک بر مدیریت منابع انسانی: حال و آینده
تحقیق کیفی
بخش تولیدی
بخش بانکداری
بخش مخابراتی [ارتباطات از راه دور]
نتیجهگیری
منابع
Abstract
Introduction
Definition of e-HR
E-HR and the role of HRM
Methodology
E-HR use and reasons for adoption
E-HR effect on the role of HRM: present and future
Qualitative research
Manufacturing sector
Banking sector
Telecommunications sector
Discussion
Level of e-HR use
Reasons for e-HR adoption
Critical success factors in e-HR
E-HR and the role of HRM
Conclusions
References
