
دانلود رایگان مقاله اندازه گیری یادگیری سازمانی و اثرات آن بر نوآوری شرکت
چکیده
هدف - هدف از این مقاله پیشنهاد و تأیید مقیاس اندازه گیری است تا قابلیت یادگیری سازمانی (OLC) را تصرف کند و بررسی کند چگونه OLC بر نوآوری تاثیر می گذارد. مدل های متعددی در گزارش ها است که توسط داده های آماری از شرکت های تولیدی، تولید شده است. این مقاله یک مدل معادلات ساختاری به منظور اندازه گیری OLC در تولید کنندگان کاشی و سرامیک ایران ارائه می دهد. مدل ارائه شده پنج بعد دارد - یعنی تعهد مدیریتی و توانمند سازی، آزمایش، ریسک پذیری، تعامل با محیط خارجی و صداقت و انتقال دانش و یکپارچه سازی - و توسط 23 آیتم مورد بررسی قرار گرفت.
طرح / روش شناسی / رویکرد - داده ها از 18 تولید کنندگان کاشی و سرامیک ایران جمع آوری شد. پرسشنامه به کارکنان قسمت فروش از هر کارخانه فرستاده شد و در مجموع 173 پرسشنامه معتبر به دست آمد و برای آزمون مدل تحقیق مورد استفاده قرارگرفت، تحلیل عاملی تأییدی (CFA) ، یعنی تجزیه و تحلیل خاص از روش مدل سازی معادلات ساختاری را به کارگرفت.
یافته - درفرایند اعتبار، هر دو اجزای اصلی و تحلیل عاملی تأییدی به وضوح وجود پنج ابعاد مذکور را در کار نظری اثبات کردند. به همین ترتیب، مقیاس اطلاعاتی را ارئه داد که می تواند توسط آن مدیران استفاده شود که مایل به بهبود توانایی یادگیری در شرکت خود هستند. علاوه بر این، نتایج نشان می دهد که OLC تاثیر مثبتی بر نوآوری دارد.
اصالت / ارزش: این تحقیقات نشان می دهد که محیط های سازمانی که یادگیری را تسهیل می کنند، خلاقانه تر هستند. علاوه بر این، گزارش های OLC نشان می دهد که OLC یک تاثیر قابل توجهی در اثر بخشی و عملکرد سازمان دارد. بنابراین، ضروری است تا ارزیابی معتبری را پیدا کند که می تواند OLC در سازمان ها را ارزیابی کند. مدل پنج عامل معرفی شده در این مقاله یک شیوه عملی است تا OLC را ارزیابی کند. در نتیجه، مدیران می توانند تعیین کنند که مسائل یادگیری سازمانی که ضعیف هستند باید قوی باشند، این اشاره ای برای بهبود است.
1. مقدمه
بطورجهانی قبول می شود که نوآوری ابزار اصلی برای رشد آینده بیمه و نجات هرگونه موسسه ای است(ترن 2008). نوآوری به سازمانها اجازه می دهد تا خودشان را با محیط، بازار و تقاضای مشتری هماهنگ و وفق دهند. تاوتی متوجه شد که رابطه ای بین نوآوری های فرهنگ سازمانی و قبول سیستم اطلاعاتی وجود دارد (تاوتی و گمک، 2006). بونو نوآوری را به عنوان یک عامل اصلی در عملکرد سازمان و نجات موسسه ها در محیط رقابتی می داند (بونو و اردونز 2004). اهمیت نوآوری محصول برای نتایج شرکتهای خوب بلند مدت بطورقابل توجهی تشخیص داده می شود و بطورگسترده در گزارشات و متون گزارش می شود. درنتیجه، بخاطر اهمیت نوآوری، محققان زیادی سابقه و پیشینه خود را تجزیه و تحلیل کرده اند، امیدوارند آنچه که موسسه باید انجام دهد، تشخیص دهند اگر آن امیدوار است که بهتر نوآوری شود. (گردن و طرفدار 2007).
سابقه نزدیک نوآوری و توانایی های یادگیری سازمانی (OLC) موجب می شود که دانشمندان احتمال اثرات مهم OLC در نوآوری را در نظربگیرند (سنژ 1990، آلگرا و شیوا 2008). بانوتو گومز (2004) بیان می کند OLC نقش مهمی در اثرات سازمانها ایفا می کند و پتانسیل خود را برای نوآوری و رشد افزایش می دهد. شیوا تا جاییکه امکانش است یکی از دلایل اصلی برای رشد اهمیت OLC در مدت 5 سال گذشته را بیان می کند که نیازی برای نوآوری در تغیرات سریع محیط است. (شیوا و آلگرا 2009). اگرچه بیشتر دانشمندان در اثرات مثبت OLC در نوآوری موافق هستند ، چندین تحقیق تجربی هستند که آن را بررسی می کنند.
هدف ما در این تحقیق بطورعملی ارزیابی کردن روابط بین OLC و نوآوری است. بنابراین آن مهم است تا متوجه شوید که ارزیابی مناسب OLC در مورد گزارش یادگیری سازمان (OL) مقیاس می کند. مرورکردن گزارشات نشان می دهد که OLC نه تنها بر نوآوری بلکه بر مفاهیم سازمانی زیادی مانند رضایت شغلی، کیفیت محصولات، عملکرد، TQM ، مدیریت دانش، پذیرش سیستم اطلاعاتی و غیره تاثیر می گذارد. علاوه براین مقیاس ارزیابی OLC به مدیران کمک می کند تا عوامل تسهیل کننده یادگیری را شناسایی کند و OLC را در موسسه هایشان ارزیابی کند، سپس آنها می تواند یادگیری سازمانی را در شرکتهای خود توسعه دهند.
از آن زمان یادگیری سازمانی به عنوان یک عنصر اصلی شناخته شده است تا موسسه را نجات دهد، دانشمندان متفاوتی مفهوم مذکور را از دیدگاه های متفاوتی از قبیل روانشناسی، جامعه شناسی، نظریه سازمانی و اقتصاد صنعتی (بانوتو-گومز 2004) در نظر می گیرند. این حقیقت و مفهوم پیچیده OLC منجر به کمبود اتفاق آراء در این مفهوم می باشد. بررسی کردن OL نشان می دهد که محققان زیادی برای OLC کار می کنند تا مدلهای متنوع اصلی را ارزیابی کنند و توسعه دهند. مدلهای مذکور مشابه برخی از جنبه ها هستند و متفاوت از دیگران هستند یعنی مدلی وجو ندارد که توسط همه آنها قبول شود. در این مقاله،مدلهای متنوع زیادی در نظرگرفته شد تا مدل معادله ساختاری را برای ارزیابی OLC توسعه دهد که با ماهیت چند بعدی سازگار است سپس بخاطر اهمیت نوآوری بررسی شد که آیا OLC می تواند نوآوری در موسسه را توسعه دهد یا خیر. اطلاعات جمع آوری شده از پرسشنامه در 18 کارخانه کاشی سرامیک صنعتی انجام شد.
باقیمانده مقاله به شرح ذیل سازماندهی شد. این مقدمه با دوره کوتاهی از مفهوم OLC در بخش 2 همراهی می شود. در بخش 3 ابعاد ارزیابی OLC موجود دیگری در نظرگرفته شد تا مقیاس ارزیابی را بر اساس ماهیت پیچیده اش توسعه دهد. 3 مدل موجود یعنی گوه، شیوا و گومز استفاده شد تا مدل جدید در بخش 5 حاصل شود. پرداخت توجه خاص به کنترل کردن اعتبار مدل پیشنهادی ما، در بخش 6، روابط بین OLC و نوآوری تست شد و روش شناسی این تحقیق توضیح داده شد. سرانجام، بخش 7 از این مقاله نتیجه گرفت.
2. پیشینه تحقیق و فرضیه ها
2.1 گزارش یادگیری سازمانی
اهمیت عواملی که یادگیری سازمانی را تسهیل می کند (OL) بطورسنتی به گزارش و پیشینه یادگیری سازمانی مربوط شده است که اکثرا بر توسعه مدلهای قانونی برای ایجاد یادگیری سازمانی تمرکز می کند (ربلو و گومز 2011). بنابراین در این بخش، گزارش OL/LO دوره می شود.
مفهوم یادگیری سازمانی در سال 1900 شروع شد. وقتیکه تیلور اثرات مثبت بر انتقال دانش در عملکرد و توسعه قابلیت تولید در کارخانه کشف کرد. به هرحال، سیرت و مارچ اولین دانشمندانی بودند که یادگیری و سازمان را درکناریکدیگر قراردادند و عبارت یادگیری سازمانی را در گزارش های سازمان ایجاد کردند. قسمت در حال رشد تحقیق یادگیری سازمانی دیدگاهی معرفی می کند که یادگیری نه تنها توانایی افراد، یادگیری همچنین می تواند در سطح یک گروه رخ دهد و توسط سازمانی تسهیل شود که شرایط و انگیزه را برای یادگیری فراهم می کند (نمث 1997). از سال 1990،یادگیری تمایز اصلی بین سازمانها ایجاد کرده است و سپس آن موضوع اصلی می شود و بزودی پدیده یادگیری سازمانی بطورفزاینده ای منبع منافع و علاقه در میان محققان و پزشکان می شود (جوسی بابو و فروغ 2010).
Abstract
Purpose – The purpose of this paper is to propose and validate a measurement scale to capture organizational learning capabilities (OLC) and examine how OLC affects innovation. There are several models in the literature that have been generated by statistical data from manufacturing firms. This paper presents a structural equation model in order to measure OLC in Iranian ceramic tile manufacturers. The proposed model has five dimensions – i.e. managerial commitment and empowerment, experimentation, risk taking, interaction with the external environment and openness and knowledge transfer and integration – and is evaluated by 23 items.
Design/methodology/approach – Data were collected from 18 Iranian ceramic tile manufacturers. The survey was sent to employees of the business section of each factory and a total of 173 valid questionnaires were obtained and used to test the research model, employing confirmatory factor analysis (CFA), a particular analysis of structural equation modeling methods.
Findings – In the validation process, both the principal components and the confirmatory factor analyses clearly corroborate the existence of the five dimensions mentioned in the theoretical work. Likewise, the scale provides information that could be used by those managers wishing to improve learning capability in their firms. In addition, the results show that the OLC has a positive impact on innovation.
Originality/value – This research suggests that that organizational environments that facilitate learning are more innovative. In addition, the OLC literature shows that OLC has a significant impact on the effectiveness and performance of the organization. Therefore, it is essential to find a valid measurement that can evaluate OLC in an organization. The five-factor model introduced in this paper is a practical way to measure OLC. As a result, managers can determine which organizational learning issues are strong and which are weak; this is a hint for improvement.
1. Introduction
It is universally accepted that innovation is the key for the future growth insurance and survival of any firm (Tran, 2008). Innovation allows organizations to coordinate themselves with the changes of the environment, market and costumer demand. Twati found that there is a relationship between organizational culture innovations and the adoption of information system (Twati and Gammack, 2006). Bueno described the innovation as a critical factor in organization performance and survival of the firms in a competitive environment (Bueno and Ordonez, 2004). The importance of product innovation for good long-term company results is now widely recognized and has been extensively reported in the literature. In result, because of the importance of innovation, many researchers have analyzed its antecedents, hoping to determine what a firm must do if it hopes to become more innovative (Gordon and Tarafdar, 2007).
The close context of innovation and organizational learning capabilities (OLC) cause scholars to consider the possibility of the significant impact of OLC on innovation (Senge, 1990; Alegre and Chiva, 2008). Banutu-Gomez (2004) expressed that OLC plays a critical role on the effectiveness of organizations and enhances their potential to innovate and grow. Chiva goes as far as to state that one of the main reasons for the growing importance of the OLC during the past years is the need for innovation in the fast changing environment (Chiva and Alegre, 2009). Although most scholars agree on the positive effect of the OLC on innovation, there are a few empirical researches that investigate it.
Our aim in this paper is to practically evaluate the relationship between OLC and innovation. Thus it is important to find an appropriate OLC measurement scale regarding the organizational learning (OL) literature. Reviewing OL literature shows that OLC does not only affect on innovation but also influences on a lot of organizational concepts like job satisfaction, quality of products, performance, TQM, knowledge management, adoption of information system and etc. Furthermore, the OLC measurement scale helps the managers to recognize the facilitative factors of learning and evaluate the OLC in their firms; then they can develop the organizational learning in their companies.
Since the time that the organizational learning is known as an essential element to survive firms, different scholars consider this concept from different viewpoints such as psychological, sociological, organizational theory and industrial economy (Banutu-Gomez, 2004). This fact and the complex nature of OLC, lead to the lack of consensus on this concept. Studying the OL reveals that many researchers work towards OLC measuring and develop various normative models. These models are similar in some aspects and are different in others, i.e. there is no model that is accepted by all. In this paper, a lot of various models were considered to develop a structural equation model for measuring OLC that is compatible with its multidimensional nature, then because of the importance of the innovation was examined whether OLC could improve innovation in the firms. Data were obtained from a survey carried out in the 18 Industrial Ceramic tile manufactures.
The remaining of the paper is organized as follows. This introduction is followed by a brief review of the concept of OLC in Section 2. In section 3 the dimensions of other exiting OLC measurements was considered to develop a measurement scale according to its complex nature. Section 4 sets out a theoretical review of innovation supporting the development of a measurement scale. The three existing models i.e. Goh, Chiva and Gomez are used to obtain a new model in section 5. Paying particular attention to checking the validity of our proposed model, in section 6, the relationship between OLC and innovation was tested and the methodology of this research was explained. Finally, section 7 concludes the paper.
2. Literature review and hypotheses
2.1 The organizational learning literature
The importance of the factors that facilitate organizational learning (OL) has traditionally related to the learning organization (LO) literature, which mainly focuses on the development of normative models for the creation of a learning organization (Rebelo and Gomes, 2011). So in this session OL/LO literature is reviewed.
The concept of learning organization was initiated in 1900, when Teylor discovered the positive effect of the knowledge transfer on the performance and productivity improvement in the factory. Nonetheless, Cyert and March were the first scholars who put learning and organization together and created organizational learning phrase in the organization literature. The growing body of organizational learning research introduces a perspective that learning is not only the capability of individuals; learning can also happen on a group level and is facilitated by an organizational climate that provides the conditions and motivations for learning (Nemeth, 1997). Since 1990, learning has made a critical distinction between organizations, and then it became an essential subject and soon the phenomenon of the organizational learning was increasingly becoming a source of interest among researchers and practitioners (Jyothibabu and Farooq, 2010).
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. پیشینه تحقیق و فرضیه ها
2.1 گزارش یادگیری سازمانی
3. ارزیابی توانایی یادگیری سازمانی
4. گزارش نوآوری سازمانی
4.1 ارزیابی نوآوری سازمان
4.2 اثرات یادگیری سازمانی در نوآوری سازمانی
5. ترکیب تحقیق
5.1 ارزیابی توانایی یادگیری سازمانی
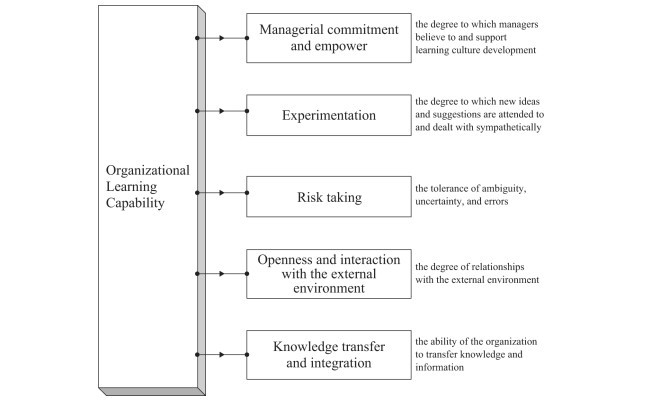
5.1.1 تعهد و قدرت مدیریتی
5.1.2 تجربه
5.1.3 ریسک پذیری
5.1.4 صداقت و تحمل با محیط خارجی
5.1.5 انتقال دانش و ادغام
5.2 ارزیابی نوآوری در سازمان
6. روش شناسی
6.1 جمع آوری داده
6.2 پایایی
6.3 روایی
6.3.1 روایی محتوایی
6.3.2 روایی همگرا و مشخص کننده
6.4 نتایج نظرسنجی
6.5 OLC و نوآوری موسسه
7. نتیجه گیری و اشارات
7.1 معنای عملی
منابع
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature review and hypotheses
2.1 The organizational learning literature
3. Organizational learning capability measurement
4. The organizational innovation literature
4.1 Measuring innovation in organization
4.2 Effect of organizational learning on organizational innovation
5. Research synthesis
5.1 Organizational learning capability measurement
5.1.1. Managerial commitment and empowerment
5.1.2 Experimentation
5.1.3 Risk taking
5.1.4 Openness and interaction with the external environment
5.1.5 Knowledge transfer and integration
5.2 Measuring innovation in organization
6. Methodology
6.1 Data collection
6.2 Reliability
6.3 Validity
6.3.1 Content validity
6.3.2 Discriminant and convergent validity
6.4 Survey results
6.5 OLC and firm innovation
7. Conclusion and implications
7.1 Practical implications
References
