
دانلود رایگان مقاله ایجاد ظرفیت کارآفرینی در مناطق روستایی
چکیده
هدف - هدف این مقاله بررسی روند توسعه فعالیتهای اقتصادی در مناطق روستایی از نظر تجهیزات زیرساخت عمومی آنها است.
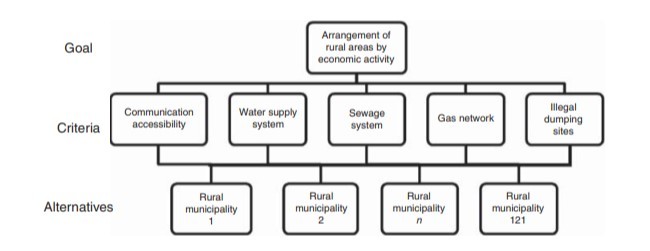
طراحی / روش شناسی / رویکرد - به عنوان یک مطالعه موردی، مناطق روستایی لهستان انتخاب شدند.یک نظرسنجی دو مرحلهایدر سال 2015 انجام شد. مرحله اول شامل کارآفرینان از مناطق روستایی بود.مرحله دوم نظرسنجی جمعآوری دادهها برای مناطق روستایی با توجه به فعالیتهای اقتصادی و تجهیزات زیرساخت بود.در مجموع 121 مورد انتخاب شدند.روش فرآیند سلسله مراتب تحلیلی چند متغيره AHP براي تجزیه و تحليل استفاده شد.
یافتهها - نتایج نشان میدهد که برای هر نوع کسب و کار، دسترسی به ارتباط مهمترین معیار است. در مقابل، آگاهی و دغدغه محیطی در مورد محیط زیست کم اهمیتترین عنصر برای پیگیری فعالیت اقتصادی در مناطق روستایی است.
محدودیت ها / پیامدهای تحقیق - محدودیت ها عمدتا با روش AHP مرتبط است. تعداد عناصر قابل مقایسه در یک سطح سلسله مراتب به دلیل اهداف عملی محدود شده است. علاوه بر این، یک فرضیه قابلیت مقایسه عناصر در مدل سلسله مراتب مورد بحث است. علاوه بر این، کیفیت دادهها و دسترسی به آن دامنه کار تجربی را محدود میکند.این مطالعه سادهسازی مدلسازی واقعیت است، اما از طریق سادهسازی روش حمایت از تصمیم، مزایای عملی را ارائه میکند.
مفاهیم عملی – یافتههای این مقاله به تئوری پیشرو در توسعه محلی با زیرساخت عمومی به عنوان یکی از عناصر اصلی آن کمک میکند. این مقاله به بررسی اهمیت زیرساخت فیزیکی برای فعالیتهای مختلف اقتصادی میپردازد و در نتیجه، بینش نظری را در دو حوزه ارائه میدهد.اول، این مقاله وزن نامناسب هر عنصر زیرساخت را برای بخشهای کسب و کارهای مختلف نشان میدهد. دوم، بر اساس دادههای جمعآوری شده، این مطالعه همچنین با استفاده از روش AHPبه ادبیات برای کشف روابط بین تجهیزات زیرساخت و فعالیت اقتصادی در مناطق روستایی کمک میکند. به عنوان مفهوم عملی برای سیاستهای توسعه محلی و منطقهای، این مطالعه نشان می دهد که مهمترین معیار برای هر نوع فعالیت اقتصادی دسترسی به ارتباطات است.این نوع سرمایهگذاری عمومی باید به طور عمده برای حمایت از کارآفرینی، به ویژه در مناطق روستایی انجام شود.
اصالت / ارزش - منحصر به فرد بودن این روش در فرضیه وزنهای نامنظم عناصر زیرساخت و در نتیجه تاثیر آنها بر روند ارزیابی مناطق روستایی تعبیه شده است. وزن عناصر مجزای زیرساخت بسته به نوع فعالیت اقتصادی متفاوت است؛بنابراین، نحوه ترتیب نیز برای هر نوع فعالیت اقتصادی متفاوت خواهد بود.
مقدمه
به طور گستردهای به رسمیت شناخته شده است که زیرساخت در همه موارد برای رشد و توسعه سطوح محلی و منطقه ای مفید است.سرمایهگذاری در زیرساخت شبکه میتواند رشد اقتصادی بلند مدت را افزایش دهد (رسنزی و رودریگز، 2012) . سطح تجهیزات زیرساخت در یک منطقه نه تنها بر کیفیت زندگی تاثیر میگذارد، بلکه به طور قابل توجهی نیز خلاقیت و فرصت توسعه انواع مختلف کسب و کار را تعیین میکند. این وابستگی ظاهرا واضح همیشه برای تایید با مدلهای آماری یا طبقهبندی استاندارد امکانپذیر نیست. اکثریت مطالعات تجربی درباره رابطه بین زیرساخت و رشد منطقهای مطالعات اقتصادسنجی هستند (کاداکوا، 2012) . این مطالعه از ساختار سلسله مراتبی برای نشان دادن و ارزیابی روابط بین زیرساخت و نوع کسب و کار استفاده می کند.توجه خاص به زیرساخت فیزیکی صورت گرفته است که اساس تجهیزات ارضی / مکان است.همچنین زمینه روستایی در نظر گرفته شده است.
توسعه آهسته عنصر زیرساخت فیزیکی یا حتی فقدان آن برای فعالیت اقتصادی خاص (رشد) مهم است.به عنوان مثال، خدمات پذیرایی نیازمند مدیریت آب و فاضلاب تنظیم شده است.تغییر این وظیفه به سرمایه گذار، با توجه به هزینه های عملکرد، به طور موثر رشد کارآفرینی را محدود می کند. از سوی دیگر، یک شبکه جاده ای به خوبی توسعه یافته با دسترسی فضایی ضعیف واحد منطقه ای یا محلی، طرح های حمل و نقل را راه اندازی می کند (حامل های خصوصی).
کاداکوا (2012) اشاره کردند که نقش زیرساخت در صنایع متفاوت است چرا که صنایع مجزا از نظرالزامات محل،محصولات و شرایط بازار متفاوت است و هر یک از این عوامل می تواند بر نقش و مزایای زیرساخت در صنعت تأثیر بگذارد.
در هر جامعه، اگر شرایط مناسب باشدنهادهای کارآفرینی وجود دارداز جمله زیرساخت که باعث ایجاد فعالیت و آغاز خلق بسیاری از کسب و کارها و در نتیجه مشاغل یا خود اشتغالی می شود.وظایف مقامات محلی باید شامل تشویق چنین نگرش هایی، برای منافع مشترک همه ساکنان و افراد مسئول توسعه منطقه باشد.هدف توسعه اقتصادی محلی رفع نیازهای مهم، از جمله ایجاد محل کار است.این به خصوص در مناطق روستایی مهم است به طوری که کارآفرینی و محل کار و کسب و کار جدید برای توسعه اقتصادی بیشتر لازم است.در میان بسیاری از مسائل بالقوه در مورد زیرساخت محلی، تفاوت در تأثیر پشتیبانی زیرساخت در انواع مختلف کسب و کار و منطقه به خصوص برای برنامه ریزان سیاست بسیار مهم است.
توسعه کارآفرینی ممکن است همراه با توسعه زیرساخت باشد و وضعیت زیرساخت بهتر می تواند رشد شرکت را تعیین کند یعنیتوسعه تجهیزات زیرساخت اساسی و کسب و کار وابسته به یکدیگر است (کلدرون و سرور، 2014) .
علیرغم این اعتقاد که زیرساخت یک عنصر کلیدی در موفقیت اقتصاد کشور است، رابطه بین زیرساخت و رشد نامشخص است، اغلب برآورد آن دشوار است و اشتباه می شود.بنابراین، بررسی و ارزیابی رابطه ای که ممکن است بین سطح توسعه زیرساخت و انواع مختلف کسب و کار وجود داشته باشد، جالب است.
این تحقیق متمرکز بر توسعه فعالیت های اقتصادی در مناطق روستایی از نظر تجهیزات زیرساخت عمومی آنها است.از روش چند معیاره برای ترتیب خطی مناطق با توجه به سطح فعالیت های مختلف اقتصادی و نیز سطح توسعه زیرساخت استفاده شد.
بنابراین، پرسش های تحقیق زیر مطرح شدند:
RQ1آیا می توان چنین ارتباطی را بر اساس داده های آماری تعیین کرد؟
RQ2 آیا انواع مختلف کسب و کار به روش های مختلف نسبت به سطح کلی زیرساخت عمومی حساس است؟
RQ3در نهایت، آیا می توان تعیین کرد که عناصر زیرساخت متناظر با توسعه یک نوع خاص از کسب و کار است؟
چارچوب نظری
توسعه روستایی و فعالیت اقتصادی
اهمیت مناطق روستایی می تواند از طریق داده های آماری نشان داده شود.بیش از نیمی ازجمعیت اتحادیه اروپا EU در مناطق روستایی اولیه یا متوسط زندگی می کند. این مناطق 45 درصد از ارزش افزوده ناخالص را تشکیل می دهند و بیش از 50 درصد از اشتغال را در اتحادیه اروپا تامین می کنند. مناطق روستایی بیش از 90 درصد از قلمرو اتحادیه اروپا و بیش از 56 درصد از جمعیت را تشکیل می دهد.به طور سنتی، مناطق روستایی مرتبط با فعالیت های اقتصادی مبتنی بر منابع طبیعی، به ویژه کشاورزی و جنگلداری بوده است. با این حال، کاهش اهمیت نسبی کشاورزی و نیاز به اقتصاد روستایی متنوع تر منجر به ظهور فعالیت های جدید و حوزه های جدید کارآفرینی روستایی شده است.فضای روستایی دیگر محدود به فعالیت های کشاورزی و کاربری زمین نیست اما برای شمول فعالیت های چند بخشی گسترش یافته است(Labrianidis, 2006).
نقش های قابل توجه کارآفرینی به عنوان یک محرک رشد وتنوع اقتصادی در مناطق روستایی در ادبیات و سطح سیاست اروپا شناخته شده است. ادبیات علمیع لاقه زیادی به وقوع و عوامل تعیین کننده فعالیت های اقتصادی روستایی را گزارش کرده است.بسیاری از مطالعات نیز متمرکز بر پلوراسیت و چند منظوره بودن در مناطق روستایی است به عنوان مثال Alsos et al., 2003.
به طور خاص، سیاست توسعه روستایی اتحادیه اروپا 2020 – 2014 به مناطق روستایی اتحادیه اروپا در مواجهه با طیف گسترده ای از چالش های زیست محیطی، اقتصادی و اجتماعی و استفاده از فرصت ها در قرن بیست و یکم کمک میکند.ستون دوم سیاست های کشاورزی مشترک CAP به این اهداف اختصاص دارد (کمیسیون اروپا، 2010). به طور خاص، افزایش جمعیت کارآفرین روستایی یکی از اولویت های سیاست توسعه کشاورزی و روستایی اتحادیه اروپا است.اشتغال و رشد بنگاه عناصر کلیدی استراتژی 2020 اروپا برای رشد هوشمند، پایدار و همه جانبه است (کمیسیون اروپا، 2011).
Abstract
Purpose – The purpose of this paper is to verify the development of economic activities in rural areas in terms of their public infrastructural equipment.
Design/methodology/approach – As a case study, the Polish rural areas were selected. A two-stage survey was conducted in 2015. The first stage involved entrepreneurs from rural areas. The second stage of survey was data collection for rural areas regarding economic activity and infrastructural equipment. In total, 121 objects (communes) were selected. The multicriteria analytic hierarchy process (AHP) method was used for the analysis.
Findings – The results demonstrate that for each kind of business, communication accessibility is the most important criterion. By contrast, environmental awareness and concern for the environment is the least important element for pursuit of the economic activity in rural areas.
Research limitations/implications – Limitations are connected mainly with the applied AHP method. The number of the comparable elements at the same hierarchy level is limited due to practical purposes. In addition, an assumption of full comparability of elements (criteria and alternatives) in the hierarchy model can be discussed. Furthermore, data quality and availability limit the scope of the empirical work. This study is a major simplification of reality modeling, but it gives practical benefits by simplifying the decision support procedure.
Practical implications – The findings of this paper contribute to the advancing theory of local development, with public infrastructure being one of its basic elements ( factor of production). This paper explores the importance of physical infrastructure for different economic activities, and thus offers theoretical insights in two areas. First, this paper indicates the uneven weight of each infrastructure element for the various business sectors. Second, based on the collected data, this study also contributes to the literature, by using the AHP method to explore the relationships between infrastructural equipment and economic activity in rural areas. As the practical implication for local and regional development policies, this study indicates, that the most important criterion for each kind of economic activity is communication accessibility. This kind of public investment should be undertaken primarily to support entrepreneurship, especially in rural areas.
Originality/value – The uniqueness of the method lies in assumption about the uneven weights of infrastructure elements and therefore their impact on the process of ranking the objects (rural areas). The weight of individual infrastructure elements will vary depending on the kind of economic activity; therefore, the way of ordering will also be different for each economic activity.
Introduction
It is widely recognized that infrastructure is beneficial to growth and development at all local and regional levels. Investment in network infrastructure can boost long-term economic growth (Crescenzi and Rodriguez-Pose, 2012; Égert et al., 2009). The level of infrastructural equipment in an area affects not only the quality of life, but also significantly determines creativity and the opportunity to develop different types of business. This seemingly obvious dependence is not always possible to verify with standard statistical or taxonomic models. The majority of empirical studies on the relationship between infrastructure and regional growth are econometric studies (Kadokawa, 2012). This study uses the hierarchic structure to show and evaluate relationships between infrastructure and business type. Particular attention has been paid to physical infrastructure, which is the basis of the territorial/location equipment. Also, the rural context is regarded.
The slow development of an element of the physical infrastructure, or even the lack of it, is significant for the specific economic activity (growth). For example, catering services require a regulated water and wastewater management. Shifting this obligation to the investor, due to the performance costs, effectively limits the growth of this entrepreneurship. Alternatively, a well-developed local roads network, by the poor spatial availability of the regional or local unit, triggers transport initiatives (private carriers).
Haughwout (1998) and Kadokawa (2012) noted that the role of infrastructure varies across industries, because individual industries vary in their location requirements, products, and market conditions, and each of these factors can influence the role and benefits of the infrastructure in the industry.
In every community, there are entrepreneurial entities, which, if appropriate conditions (including infrastructure) are created, spur to action, and initiate creation of many businesses and therefore jobs or self-employment. The tasks of the local authorities should include encouraging such attitudes, for common interests of all inhabitants and people responsible for the development of the area. The purpose of local economic development is to meet the important needs, inter alia, by creating workplaces. This is especially important in rural areas, where entrepreneurship and new work places and businesses are necessary for further economic development. Among the many potential issues regarding the local infrastructure, differences in the impact of infrastructure support across business types and regions are particularly important for policy planners.
The development of entrepreneurship may be accompanied by infrastructural development, and better infrastructural state may determine enterprise growth. This means that the basic infrastructure equipment and business development are interdependent (Calderón and Servén, 2014; Francois and Manchin, 2013).
Despite the conviction that infrastructure is a key ingredient in a country’s economic success, the relationship between infrastructure and growth is unclear, difficult to estimate and often misunderstood. It is interesting, therefore, to investigate and evaluate the relationship that may exist between the level of infrastructural development and different types of business.
This research focuses on the development of economic activities in rural areas in terms of their public infrastructural equipment. The multicriteria method was used for the linear ordering of areas regarding the level of various economic activities and the level of infrastructural development as well.
Therefore, the following research questions arise:
RQ1. Can such a relationship be determined based on statistical data?
RQ2. Are different types of business in various ways “sensitive” to the overall level of public infrastructure?
RQ3. Finally, is it possible to determine which infrastructure elements correspond closer to the development of a particular type of business?
Theoretical framework
Rural development and economic activity
The importance of rural areas can be shown through statistical data. More than half of the population of the European Union (EU) lives in predominantly or intermediate rural areas. These regions account for 45 percent of the gross value added and provide over 50 percent of the employment in the EU (Eurostat). Rural areas cover over 90 percent of the territory of the EU, and account for more than 56 percent of the population. Traditionally, rural areas have been associated with economic activities based on natural resources, notably agriculture and forestry. However, the decline in the relative importance of agriculture and the need for a more diversified rural economy has led to the emergence of new activities and new areas of rural entrepreneurship. Rural space is no longer confined to agricultural activities and land uses, but is extended to include multisectoral activities (Labrianidis, 2006).
The significant roles of entrepreneurship as a driver of economic growth and diversification in rural areas have long been recognized in literature and at European policy level (Clark et al., 2007; Erdiaw-Kwasie and Alam, 2016). The scientific literature reports great interest in the occurrence and the determinants of rural economic activities (Barbieri and Mahoney, 2009; Gorton et al., 2008; Grande, 2011; Hansson et al., 2013; Maye et al., 2009; Vik and McElwee, 2011). Many studies also focus on pluriactivity and multifuctionality in rural areas (e.g. Alsos et al., 2003; Blad, 2010; Jaafar et al., 2015; Lagerkvist et al., 2007; McNamara and Weiss, 2005).
Specifically, the EU Rural Development Policy 2014-2020 helps EU’s rural areas to meet and face the wide range of environmental, economic and social challenges and take advantage of the opportunities in the twenty-first century. The second pillar of the Common Agricultural Policy (CAP) is devoted to these objectives (European Commission, 2010). In particular, the rural population entrepreneurship increase is one of the priorities of the EU agricultural and rural development policy. Employment and firm growth are key elements of the EU’s Europe 2020 strategy for smart, sustainable and inclusive growth (European Commission, 2011a, b).
چکیده
مقدمه
چارچوب نظری
توسعه روستایی و فعالیت اقتصادی
اهمیت پشتیبانی از زیرساخت
داده و روش
داده
روش
نتایج
بحث
نتیجه گیری
مشارکت
محدودیت و تحقیق در آینده
منابع
Abstract
Introduction
Theoretical framework
Rural development and economic activity
Importance of the infrastructural support
Data and method
Data
Method
Results
Discussion
Conclusion
Contribution
Limitation and future research
References
