
دانلود رایگان مقاله برنامه های کاربردی رباتیک به کمک اینترنت اشیا
چکیده
انقلاب مداوم اینترنت اشیا (IoT)، همراه با رشد انتشار روبات ها در فعالیت های بسیاری از زندگی روزمره، باعث میشود برنامه های کاربردی رباتیک بهکمک اینترنت اشیا یک واقعیت ملموس از آیندهی ما باشد. بر این اساس، خدمات جدید پیشرفته، براساس فعل و انفعال بین روبات ها و "اشیا"، تصور کمک به انسان را پیشرو دارد. با این وجود، در مسیر توسعهی برنامه های کاربردی رباتیک بهکمک اینترنت اشیا نیاز به حل چندین مسائلهی محوری میباشد، روش های طراحی به تثبیت برسند، و گزینه های قوی معماری به بحث گذاشته شوند. این مقاله به بررسی مفاهیم فنآوری، مسائل باز، و برنامه های کاربردی رباتیک بهکمک اینترنت اشیا میپردازد. بهطورخاص، در حال حاضر همکاری شامل چهار جنبه است. اول، حالت خالصی از هنر در موضوعات اصلی مربوط به اینترنت اشیا بهکمک خدمات رباتیک را فراهم میکند: شبکه های ارتباطی، برنامه های کاربردی رباتیک در محیط های توزیع و فراگیر، روش معناگرا به اجماع و امنیت شبکه. دوم، با برجستهترین چالش های مهم تحقیقات روبرو میشود. سوم، ابزار های فنآوری موجود درحال حاضر را توصیف میکند. چهارم، درس های آموخته شده به منظور بررسی ترویج مشترک علمی در میان تیم های تحقیقاتی با مهارت های مکمل را خلاصه میکند.
معرفی
تعدادی از دستگاه های درگیر در ارتباطات ماشین به ماشین (M2M) انتظار میرود که بهطور پیوسته تا سال 2020 رشد کند. درآن زمان، تعداد اشیاء هوشمند که قادر به صحبت کردن با یکدیگر هستند و با انسا کار میکنند باید حدود 50 میلیارد باشد، در نتیجه مقیاس اینترنت [1] - [17] و تحقق انقلاب با اینترنت اشیا (IoT) نامگذاری میشود، که در آن یکی از اهداف اصلی اعلام شده " اتصال به همه چیز و همهکس در همه جا و به همه چیز و هر کس دیگری" است [4] [16]. ازسوی دیگر، روبات، نقش مهمی در جامعه فردا بازی خواهد کرد، در ادامه کمک به انسان در انجام بسیاری از وظایف، عملیات کمکی به مونتاژ صنعتی، سیستم های مدیریت امداد و نجات با حمایت نظامی، مراقبت های بهداشتی با سیستم اتوماسیون [6]، [12] - [18].
روند تحقیق و کاربرد منجر به ظهور اینترنت روبات ها [19]، و به برنامه های کاربردی رباتیک بهکمک اینترنت اشیا شده است. هدف این مقاله، بررسی برخی از پیامد های تکنولوژیکی خود، مسائل باز، و هدف حوزه مستلزم است.
به نظر ما، برنامه های کاربردی رباتیک بهکمک اینترنت اشیا بر اکوسیستم های دیجیتال رشد خواهد کرد که در آن انسان، روبات ها و گره اینترنت اشیا بر اساس یک تعاونی تداخل میکنند. در این چارچوب، بازیگران درگیر باید در توافق مستقل اصول ارتباطات امن آزاد باشند، بر اساس معنای اطلاعات آنها میخواهند تغییر کنند و قصد ارائه/ دسترسی به تبادل خدمات آنها داشته باشند. بدین ترتیب، زمینه های تحقیقاتی مربوط به برنامه های کاربردی رباتیک بهکمک اینترنت اشیا از محدودهی فن آوری های ارتباطی به خدمات معناییگرا، از تئوری اجماع به طراحی پروتکل، از طراحی نرم افزار به محور اطلاعات شبکه، از امنیت به هرچیزی که برای ساخت یک هوشمند مفید، فراگیر و محیط امن است، قابل تغییر است.
با شروع از این محل، و با اشاره به برنامه های کاربردی رباتیک بهکمک اینترنت اشیا، جایگاه این مقاله این چنین است:
_ پیشبینی سناریو های ممکن.
_ برجسته کردن نیاز به یک تعریف از مفاهیم کلیدی در امنیت، حفظ حریم خصوصی و اعتماد.
_ توصیف مزایا و معایب ارتباطات درحالحاضر اینترنت اشیا در سیستم [2]، و تلاش برای روش های جدید فراتر از چشمانداز میزبان محور [7].
_ روش های خود ساخته بر مبنای استراتژی اجماع معنایی به یک نقطه محوری تبدیل میشوند؛
_ خلاصه ای قابل تحسین با اشاره خاص به مباحث زیر فراهم میکند: شبکه های ارتباطی، امنیت شبکه، برنامه های کاربردی رباتیک در محیط های توزیع و فراگیر، طراحی سیستم معناگرا، و پروتکل توافقی بر اساس معنا.
به نظر ما، درس های آموخته شده از این مقاله ممکن است در تکمیل تحقیقات بسیاری از جوامع علمی کمک کند، که در حال حاضر بر روی جنبه های مختلف برنامه های کاربردی رباتیک بهکمک اینترنت اشیا کار میکنند.
ادامه ی مقاله به شرح زیر است: در بخش 2، یک مرور کلی از برنامه های کاربردی پیش بینی شده خواهیم داشت. در بخش 3، تحقیقات گذشته و پیشرفت های هدف در تمام زمینه های مرتبط از طریق بررسی کار های گذشته انجام خواهد شد. امکان سنجی از راه حل های آینده در بخش 4 بحث شده است. که ویژگی های اصلی از روبات های تجاری در دسترس را خلاصه میکند. در ن هایت، بخش 5 بحث را ادامه داده و درس های آموخته شده را نشان میدهد.
2. پیش بینی برنامه های کاربردی رباتیک به کمک اینترنت اشیا
هر دوی برنامه های کاربردی رباتیک و مبتنی بر اینترنت اشیا با موفقیت در چندین سناریو اعمال شدهاند. با این وجود، کار کمی در تعامل بین این دو رشته در تحقیقات شده است.
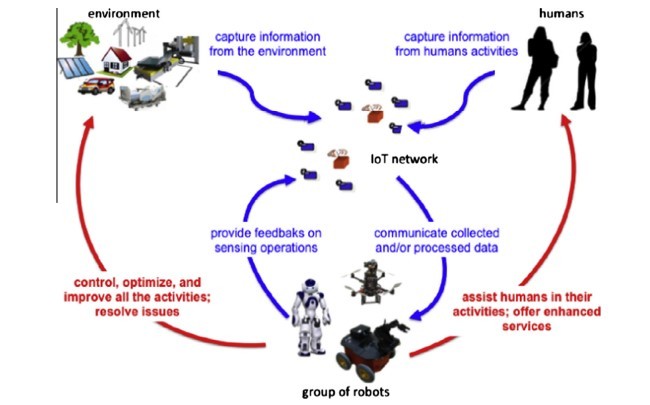
بسیاری از ربات های مدرن، در واقع، با سنجش، محاسبات مجهز و قابلیت های ارتباطی، قادر به اجرای پیچیده و هماهنگ عملیات هستند. در واقع، این ویژگیها بهطور موثری توسط اینترنت اشیا برای انجام نیازمندی های مورد نیاز توسط برنامه های کاربردی پیشرفته و مطرح در محیط های فراگیر و توزیع شده بهکار برده میشود. این ها مواردی هستند که در آن هدف، به تصرف درآوردن بزرگترین و وسیع ترین اطلاعات در فضای عملیاتی، به منظور تعامل اطلاعات فشرده در میان بازیگران آن است.از دید ما، چند نهاد باید آثار ربات را کامل کند، مانند اشیا هوشمند، سنسورها، سرورها، و دستگاه های شبکه از هر نوع، که از طریق زیر ساخت های شبکهی پیچیده و ناهمگن به هم متصل شدهاند. این اهداف چالشی را میتوان با بهره برداری از شبکهی متراکم اینترنت اشیا بدست آورد، دستگاه هایی که به طور مداوم با انسان، روبات ها و محیط زیست در تعامل هستند.
چارچوب کاربردی از بحث قبلی در شکل 1نشان داده شده است، که در آن اشیاء و ربات با همکاری برای رسیدن به یک هدف مشترک طراحی شدهاند.
در ادامهی این بخش، انواع مختلفی از برنامه های کاربردی، با توجه به [4] و [20]، طبق بندی شدهاند: مانند مراقبت های بهداشتی، صنعتی و ساخت و ساز، نظامی و مدیریت امداد و نجات. برای هر یک از آنها، خلاصه ای از ویژگی ها و قابلیت های پشتیبانی شده توسط هر دوی اینترنت اشیا و یا سیستم های رباتیک، به عنوان فنآوری جداگانه ارائه شده است. علاوه بر این، راهحل پیشنهادی رباتیک بهکمک اینترنت اشیا (مربوط به آینده) توصیف شده است.
Abstract
The ongoing revolution of Internet of Things (IoT), together with the growing diffusion of robots in many activities of every day life, makes IoT-aided robotics applications a tangible reality of our upcoming future. Accordingly, new advanced services, based on the interplay between robots and ‘‘things’’, are being conceived in assisting humans. Nevertheless, the path to a mature development of IoT-aided robotics applications requires several pivotal issues to be solved, design methodologies to be consolidated, and strong architectural choices to be discussed. This paper discusses technological implications, open issues, and target applications in the IoT-aided robotics domain. In particular, the present contribution is four-folded. First, it provides a solid state of the art on the main topics related to IoT-aided robotics services: communication networks, robotics applications in distributed and pervasive environments, semantic-oriented approaches to consensus, and network security. Second, it highlights the most important research challenges to be faced. Third, it describes the technological tools available nowadays. Fourth, it summarizes lessons learned to foster a joint scientific investigation among research teams with complementary skills.
1. Introduction
The number of devices involved in Machine-to-Machine (M2M) communications is expected to steadily grow till 2020. At that time, the number of smart objects able to talk to each other and to inter-operate with humans should be around 50 billions, thus inflating the scale of the Internet up to three orders of magnitude [1–17] and realizing the envisioned revolution called Internet of Things (IoT), in which one of the main proclaimed goal is ‘‘to connect everything and everyone everywhere to everything and everyone else’’ [4,16]. On the other hand, robots will play a major role in tomorrow’s society, continuing to help humans in accomplishing many duties, spanning from assistive operations to industrial assembly, from rescue management systems to military support, from health care to automation systems [6,12–15,18].
Research and application trends are leading to the appearance of the Internet of Robots [19], and to IoT-aided robotics applications. This position paper aims at shading some light on their technological implications, open issues, and entailed target domains.
In our view, IoT-aided robotics applications will grow upon a digital eco-system where humans, robots, and IoT nodes interact on a cooperative basis. In this framework, the actors involved should be free to autonomously agree on secure communication principles, based on the meaning of the information they want to exchange and on the services they intend to provide/access. Thus, the research areas related to IoT-aided robotics applications span from short range communication technologies to semanticoriented services, from consensus theory to protocol design, from application design to information centric networking, from security to whatever is useful to build a smart, pervasive, and secure environment.
Starting from these premises, and with reference to IoT-aided robotics applications, this position paper:
envisions possible scenarios;
highlights the need for a (re) definition of the key concepts of security, privacy, and trust;
describes advantages and drawbacks of currently available IoT communication systems [2], and quest for novel approaches beyond the host-centric vision [7];
points out that self configuring approaches based on semantic consensus strategies become a pivotal point;
provides a solid summary of the state of the art, with particular reference to the following topics: communication networks, network security, robotics applications in distributed and pervasive environments, semantic-oriented systems design, and semantic-based agreement protocols.
It is our opinion that the lessons learned from this paper may help in complementing the research efforts of many scientific communities, which are currently working on the different facets of IoT-aided robotics applications.
The rest of the paper is organized as follows: in Section 2, we give an overview of envisaged applications. In Section 3, past research and aimed advances in all involved fields are investigated, through an exhaustive literature review. The feasibility of prospective solutions is discussed in Section 4, which sums up main features of commercially available robots. Finally, Section 5 wraps up the discussion and illustrates the lessons learned.
2. Envisaged IoT-aided robotics applications
Both IoT-based and robotics applications have been successfully applied in several scenarios. Nevertheless, little work has been carried out on the interaction between the two fields, which deserves more in depth investigation.
Most of modern robots, in fact, are equipped with sensing, computing, and communication capabilities, which make them able to execute complex and coordinated operations. Indeed, these features would be significantly magnified by IoT technology, toward the fulfillment of requirements posed by advanced applications in pervasive and distributed environments, especially those characterized by a high level of criticality. These are the cases, in fact, in which the objective is to capture the largest and broadest information in the operational space, in order to enable information-intensive interaction among its actors. In our vision, several entities should complement the robot works, such as smart objects, field sensors, servers, and network devices of any kind, connected through a complex and heterogeneous network infrastructure. These challenging goals can be achieved by exploiting a dense IoT network, whose devices continuously interact with humans, robots, and the environment.
The application framework inspired by the previous discussion is illustrated in Fig. 1, in which objects and robots are designed to collaborate to reach a common goal.
In the rest of this section, we consider different kinds of applications, classified according to [4,20], in the following fields: health-care, industrial and building, military, and rescue management. For each of them, a summary is provided about features and capabilities already supported by either IoT or robotics systems, applied as separate technologies. In addition, joint IoT-aided robotics prospected solutions (relevant for the upcoming future) are described.
چکیده
1. معرفی
2. پیش بینی برنامه های کاربردی رباتیک به کمک اینترنت اشیا
2.1. برنامه هایکاربردی بهداشتی درمانی
2.2. تاسیسات صنعتی و مناطق هوشمند
2.3.کاربردهای نظامی
2.4 . سیستمهای مدیریت امداد و نجات
3. بررسی اجمالی از پیشرفت به سمت پارادایم جدید
3.1 . معماری شبکه برای اینترنت اشیا
3.2. سیستمهای تصمیمگیری غیرمتمرکز در رباتیک بهکمک اینترنت اشیا
3.3 . روش معناگرا برای اجماع در کاربرد رباتیک بهکمک اینترنت اشیا
3.4 . امنیت اینترنت اشیا
4. امکان سنجی معماری ارائه شده
4.1 . رباتهای موجود
4.2. فنآوریهای اینترنت اشیا موجود
4.3. مرجع مورد استفاده: خدمات رباتیک اینترنت اشیا در فرودگاه
5 . نتیجهگیری
5.1 . پایان سخن
5.2 . درسهای آموخته شده
منابع
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Envisaged IoT-aided robotics applications
2.1. Health-care applications
2.2. Industrial plants and smart areas
2.3. Military applications
2.4. Rescue management systems
3. Overview of the state of the art and advances towards novel paradigms
3.1. Networking architectures for the IoT
3.2. Decentralized decision systems in IoT-aided robotics
3.3. Semantic oriented approaches for consensus in IoT-aided robotics applications
3.4. IoT security
4. Feasibility of the proposed architecture
4.1. Available robots
4.2. Available IoT technologies
4.3. A reference use-case: IoT-robotics services in the airport
5. Conclusion
5.1. Closing remarks
5.2. Lesson learned
References
