
دانلود رایگان مقاله اثر سطحی در ویژگی های پویا محرک نانو پرتو الکترواستاتیکی
چکیده
تجزیهوتحلیل رفتار کشش غیرخطی یک کنسول نانو محرک بیان شده و مدل پرتو اویلر-برنولی برای آزمون میدان حاشیه و سطح مورد استفاده قرار گرفته است و اثرات نیروی کازیمیر در این مطالعه انجام شده است. بهطورکلی، تجزیهوتحلیل یک دستگاه الکترواستاتیک دشوار است و معمولا توسط نیروهای الکترواستاتیک غیرخطی و نیروی کازیمیر در مقیاس نانو انجام میگیرد. معادلهی حاکم غیرخطی یک کنسول نانو پرتو میتواند با استفاده از یک طرح محاسباتی ترکیبی متشکل از تحول دیفرانسیل و تفاضل محدود برای غلبه بر پدیده جفت الکترواستاتیک غیرخطی حل شود. امکانسنجی روش ارائه شده در اینجا، که بهعنوان رفتار غیرخطی الکترواستاتیک از کنسول محرک نانو اعمال میشود، تجزیهوتحلیل شده است. نتایج عددی برای کشش ولتاژ در توافق با نتایج منتشر شده قبلی مشخص شده است. تجزیهوتحلیل نشان داد که اثر سطح تأثیر قابل توجهی در ویژگیهای پویا کنسول نانو محرک دارد.
1. معرفی
در سالهای اخیر، دستگاههای سیستم نانو الکترومکانیکی (NEMS) بهطور گستردهای در طیف متنوعی از برنامههای کاربردی، از جمله نانو سوئیچ، سنسور و ماژولهای ارتباطات] 3] و غیره استفاده شده است و این قطعا باعث میشود تا تحقیق ارزشمند گردد. هنگامی که یک ولتاژ محرک بین یک منقول و یک ساختار ثابت اعمال میشود، عوارض ناشی از نیروی الکترواستاتیکی در هر دو ساختار عمل میکند. بهعنوان ساختار متحرک نزدیک ساختار ثابت، نیروی الاستیک تمایل به بازگشت به موقعیت قبلی خود را دارد. در یک ولتاژ بحرانی، که بهعنوان ولتاژ جلو شناخته شده است، بیثباتی رخ میدهد و کنسول نانو پرتو بر روی ساختار ثابت فرو میریزد. این مسئله در طراحی دستگاههای مبتنی بر NEMS از اهمیت حیاتی برخوردار است.
فیزیک جدید با در نظر گرفتن NEMS پدید آمده است. بهعنوان مثال، اثر نیروهای بین مولکولی، مانند نیروهای کازیمیر و واندروالس I4]، که ممکن است نقش مهمی در مقیاس نانو بازی کنند. زمانیکه جداسازی کمتر از 20 نانومتر است نیروی بین دو سطح (جاذبه واندروالس)، متفاوت از جدایی مکعب معکوس است. زمانی که جداسازی بیشتر از 20 نانومتر است، نیروی بین دو سطح میتواند به عنوان اثر کوانتومی کازیمیر که متناسب با توان چهارم معکوس جداسازی است توصیف شود. Ke و همکارانش I6] اثر نیروی واندروالسی در کشش ولتاژ کربن بر اساس سوئیچ NEMSرا محاسبه کردند.] Rotkin 7] اثر نیروی واندروالسی در فاصله کشش را در نظر گرفته و عبارت تحلیلی برای هر دو شکاف کشش و ولتاژ در یک مدل کلی را به دست آورد. Soroush و همکارانش I4] اثر نیروی پراکندگی را در بیثباتیهای کنسول نانو فعالسازها با استفاده از روش تجزیهی Adomian (ADM) بررسی کردند. ADM یک تکنیک عملی برای حل مشکلات مقدار اولیه (IVP)، مشکلات مقدار مرزی (BVP)، خطی، غیرخطی و حتی سیستمهای پر هرجومرج است [8-11].
بااینحال، در عمل، سطح اثرات مانند سطح باقیمانده و کشش سطح باید به هنگام ارزیابی رفتار کشش دیسک NEMS از سطح بزرگ نسبت به حجم چنین ساختارهایی که موجب تغییر اندازه در بسیاری از خواص مواد محرک میشود گرفته شود. Ma و همکارانش [12] در مورد اثرات انرژی سطحی و کازیمیر اجرا شده در پارامترهای بیثبات کنسول سیلندر NEMS را بااستفاده از روش اختلال هموتوپی (HPM) مورد مطالعه قرار دادند. Wang و Feng [13] اثرات هر دو کشش سطح و سطح پسماند را در رفتار چرخشی و ارتعاشی از نانو پرتو مورد مطالع قرار دادند. Fu و Zhang [14[ از یک مدل زنجیرهای اصلاح شده برای بررسی رفتار کششی در یک نانو پرتو الکتریکی فعال و متصل و اثرات سطح ترکیب استفاده کردند. در این تحقیقات، تاثیر جاذبه کازیمیر و بهعنوان اثرات حاشیه نادیده گرفته شد. یک پارامتر کشش مهم وجود دارد که مشخص کننده طول جدا شدن در طراحی دیسک NEMS است. در صورت عدم وجود ولتاژ محرک، نیروی کازیمیر میتواند بر ترمیم الاستیک غلبه کند و منجر به سقوط از کنسول نانو پرتو شود. برای هر گونه شکاف اولیه ثابت بین الکترودها، حداکثر طول مجاز نانو پرتو کنسول که نمیخواهد به الکترود ثابت پایبند باشد طول جدا شدن [12] نامیده میشود.
تئوری تبدیل دیفرانسیل اولین بار توسط Pukhov ]15،16[ برای حل مسائل مقدار اولیه خطی و غیرخطی در فرآیندهای فیزیکی معرفی شد. ژائو از نظریه یکسانی باعنوان وسیلهای برای حل دامنه تجزیهوتحلیل مدار استفاده کرد. بااینحال، در سالهای اخیر، روش تحول دیفرانسیل (DTM) که شامل طیف گستردهای از مشکلات مهندسی است تمدید شده است. برای مثال، Chen و همکارانش [17[ و Liu و همکارانش [18،19] از DTM برای بررسی مشکل تولید آنتروپی در یک همرفت مخلوط با اثرات اتلاف در یک کانال موازی صفحه عمودی استفاده کردند. راهحل این معادله کسری توسط Biazar و Eslami [20] که DTM را مورد استفاده قرار میدهند بررسی شده است. DTM با موفقیت برای حل بسیاری از مسائل خطی و غیرخطی در ریاضیات [21،22] و مهندسی، از جمله هدایت حرارتی [23] و سیستمهای کنترل بهینه [24] بهکار برده شده است. DTM یک ابزار قدرتمند نیمه تحلیلی برای مهندسی عمومی و مسائل مکانیک است و به یک راهحل تحلیلی در قالب یک چندجملهای رسیده است [22].
در این مطالعه، پایه نانوفعالسازها دو مسئله تاثیر در شبیهسازی رفتار دینامیکی را ترکیب کرده و مورد بررسی قرار میدهد. اولین مسئله مشخص شده، فعالیت مولکولی مانند نیروی کازیمیر در مقیاس نانو است. دومی، سطح تاثیر است. ازاینرو، معادله حاکم براساس مدل پرتو اویلر-برنولی، ترکیب غیرخطی نیروهای الکترواستاتیک و مولکولی است که در مطالعه حاضر استفاده میشود. ساختار این مقاله به شرح زیر است: در بخش 2 استفاده از یک طرح محاسباتی ترکیبی برای تکمیل معادله حاکم غیرخطی از کنسول نانو پرتو و شرایط مرزی و اولیه مشخص توصیف میشود. بخش 3 روش پیشنهاد شده را بهکمک مقایسه نتایج عددی بهدست آمده برای جابجایی نوک و ولتاژ یک کنسول نانو پرتو با نتایج تحلیلی ارائه شده در کارهای گذشته تایید میکند. همچنین طرح محاسباتی ترکیبی برای تجزیهوتحلیل پاسخ دینامیکی پایه نانو پرتو بهعنوان یک تابع ولتاژ استفاده میشود. در نهایت، بخش 4 برخی نتایج ارائه شده است. در مقایسه با روشهای موجود از جمله روش تفاضل محدود، طرح ترکیبی عددی از مزایای بیشتری برخوردار است و همچنین بسیار سادهتر و سریع است.
Abstract
A nonlinear pull-in behavior analysis of a cantilever nano-actuator was carried out and an Euler–Bernoulli beam model was used in the examination of the fringing field and the surface and Casimir force effects in this study. In general, the analysis of an electrostatic device is difficult and usually complicated by nonlinear electrostatic forces and the Casimir force at the nanoscale. The nonlinear governing equation of a cantilever nano-beam can be solved using a hybrid computational scheme comprising differential transformation and finite difference to overcome the nonlinear electrostatic coupling phenomenon. The feasibility of the method presented here, as applied to the nonlinear electrostatic behavior of a cantilever nanoactuator, was analyzed. The numerical results for the pull-in voltage were found to be in good agreement with previously published results. The analysis showed that the surface effects had significant influence on the dynamic characteristics of the cantilever nano-actuator.
1. Introduction
In recent years, nano-electromechanical system (NEMS) devices have been widely applied in a diverse range of applications, including nano-switches [1], ultrasensitive sensor [2] and RF communication modules [3] and others, and this certainly makes NEMS research a worthwhile field. When a driving voltage is applied between a moveable and a fixed structure, charges are induced on each which causes an electrostatic force to act on both structures. As the movable structure approaches the fixed structure, an elastic force tends to make it return to its previous undeformed position. At a critical voltage, which is known as the pull-in voltage, instability occurs and the cantilever nano-beam collapses onto the fixed structure. This is of critical importance in the design of NEMS-based devices.
New physics has emerged in the consideration of NEMS. For example, the effect of intermolecular forces, such as the Casimir and van der Waals forces [4], may play an important role at the nano-scale. For separations below 20 nm the force between two surfaces (van der Waals attraction), varies as the inverse cube of the separation. When the separation is greater than 20 nm, the force between two surfaces can be described as the quantum Casimir effect, which is proportional to the inverse fourth power of the separation [5]. Ke et al. [6] calculated the effect of van der Waals force on the pull-in voltage of carbon-nanotubes based NEMS switches. Rotkin [7] considered the effect of the van der Waals force on the pull-in gap and obtained analytical expressions for both the pull-in gap and voltage of a general model. Soroush et al. [4] investigated the effect of dispersion forces on the pull-in instability of cantilever nano-actuators using the Adomian decomposition method (ADM). ADM is a practical technique for solving initial value problems (IVP), boundary value problems (BVP), linear, nonlinear and even chaotic systems [8–11].
However, in practice, surface effects such as the residual surface stress and surface elasticity must be taken into account when evaluating the pull-in behavior of NEMs actuators since the large surface area to volume ratio of such structures induces a sizedependent change in many actuator material properties. Ma et al. [12] studied the effects of surface energies and the Casimir force on the instability parameters of cantilever NEMS actuators using the Homotopy perturbation method (HPM). Wang and Feng [13] addressed the effects of both surface elasticity and surface residual stress on the buckling and vibrational behaviur of nanobeams. Fu and Zhang [14] used a modified continuum model to investigate the pull-in behavior of an electrically actuated double-clamped nano-beam incorporating surface effects. In these investigations, the influence of the Casimir attraction as well as fringing field effects was neglected. There is an important pull-in parameter which is the detachment length in the design of NEMS actuators. In the absence of a driving voltage, the Casimir force could overcome elastic restoration and lead to collapse of the cantilever nano-beam. For any fixed initial gap between electrodes, the maximum allowable length of the cantilever nanobeam that will not adhere to the fixed electrode is called the detachment length [12].
Differential transformation theory was first introduced by Pukhov [15,16] to solve linear and nonlinear initial value problems in physical processes. Zhao used the same theory as a means of solving the circuit analysis domain. However, in recent years, the differential transformation method (DTM) has been extended to include a wide range of engineering problems. For example, Chen et al. [17] and Liu et al. [18,19] used DTM to investigate the problem of entropy generation within a mixed convection flow with viscous dissipation effects in a parallel-plate vertical channel. The solution of the fractional telegraph equation has been discussed by Biazar and Eslami [20] who also used DTM. DTM also has been successfully employed to solve many types of linear and nonlinear problems in mathematics [21,22] and engineering, including thermal conduction [23] and optimal control systems [24]. DTM is a powerful semi-analytical tool for general engineering and mechanics problems and yields an analytical solution in the form of a polynomial [22].
In this study, cantilever nano-actuators incorporating two issue effects are investigated in a simulation of dynamic behavior. The first issue considered is that of intermolecular activity such as the Casimir force at the nano-scale. The second is the surface effect. Hence, a governing equation based on the Euler–Bernoulli beam model incorporating nonlinear electrostatic and intermolecular forces has been used in the present study. The rest of this paper has been arranged as follows: Section 2 describes the use of a hybrid computational scheme to complete the nonlinear governing equation of the cantilever nano-beam and specify initial and boundary conditions. Section 3 validates the proposed method by comparison of the numerical results obtained for tip displacement and pull-in voltage of a cantilever nano-beam with the analytical results presented in the literature. Also, the hybrid computational scheme is used to analyze the dynamic response of the cantilever nano-beam as a function of the applied voltage. Finally, Section 4 presents some brief concluding remarks. Compared to existing methods such as the finite difference method, the hybrid numerical scheme has the advantages of an explicit physical meaning and is also simpler and much faster.
چکیده
1. معرفی
2. مدلسازی پایه محرکهای نانو
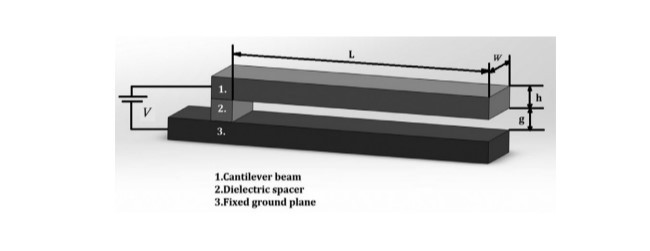
2.1. توضیحات مدل
2.2. معادله غیرخطی بدون ابعاد
3. نتایج عددی و بحثوگفتگو
4. نتیجهگیری
منابع
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The cantilever nano-actuator modeling
2.1. Model description
2.2. Dimensionless nonlinear governing equation
3. Numerical results and discussion
4. Conclusions
References
