
دانلود رایگان مقاله مدلسازی رویکرد هوشمند ارزیابی ریسک برای محیط رایانش ابری
چکیده
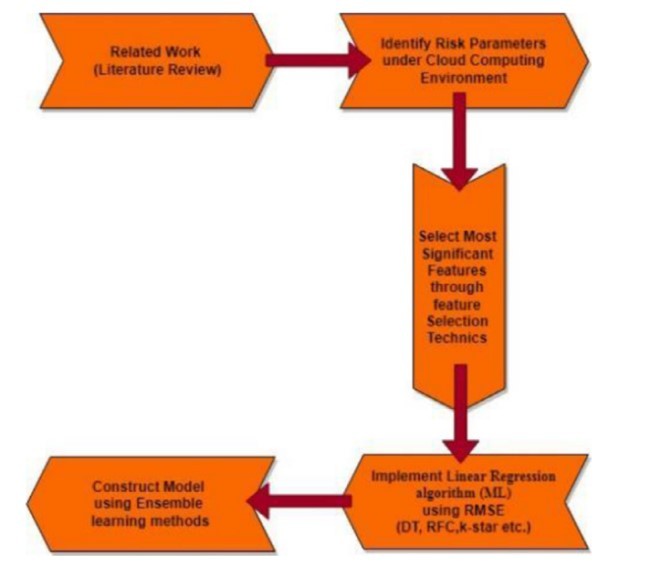
ستون اصلی بازار رقابتی و آتی امروز قطعا تبدیل شدن به رایانش ابری است و بنابراین شرکت ها از قابلیت های خدمات رایانش ابری استفاده می کنند. برای بهبود ابتکارات امنیتی توسط رایانش ابری سرویس یا CRP، انواع جدید ابزارها و پروتکل ها همیشه مورد تقاضا هستند. به منظور ایجاد روش جامع ارزیابی ریسک، مرور ادبیات گسترده ای برای شناسایی عوامل خطر که ممکن است انجام شود بر پذیرش رایانش ابری تأثیر می گذارد. در این زمینه عوامل خطر مختلفی شناسایی شدند. پس از انتخاب ویژگی و شناسایی عوامل خطر، مورد استفاده برای انتخاب موثرترین ویژگی ها با استفاده از الگوریتم های رگرسیون خطی. سپس از تکنیکهای AI-ML مانند درخت تصمیم (DTC)، طبقهبندیکننده فیلتر تصادفی، ستاره k با روش RMSE استفاده میشود. تجزیه و تحلیل تهدیدات در محیط CC نتایج تجربی تقسیم مجموعه داده را به (95٪ -5٪) نشان داد. بهترین نتیجه را از هر پارتیشن بندی باقی مانده ارائه می دهد و علاوه بر این الگوریتم DTC ارائه شده را ارائه می دهد بهترین نتایج از کل مجموعه داده های مورد استفاده در تنظیمات آزمایشی می باشد.
1. مقدمه
ابر [1] یکی از پرکاربردترین و پویاترین اختراعات است که تمرکز فناوران را در صحنه جهانی جلب کرد. اگرچه رایانش ابری با پاداش های بزرگی مانند خدمات اندازه گیری شده، کشش سریع، مقیاسپذیری و مهمترین آن هزینه کم برای شرکتها است با نسبت خوبی از خطرات امنیتی تعبیه شده است که توسط هیچ شرکت دیگری وجود ندارد که بتوان آن را نادیده گرفت. خطر امنیتی که از طیف وسیعی از آسیب پذیری های ذاتی هر یک سرچشمه می گیرد نوع سیستم رایانش ابری و در غیاب امنیت قابل اعتماد دستورالعمل ها، بی میلی ظاهری از سوی سازمان ها وجود دارد برای اتخاذ یک محیط قدرتمند به نام رایانش ابری می باشد [2].
بدون زحمت در مورد تعمیرات فیزیکی و فنی یا چالش های مدیریت منابع اصلی، رایانش ابری کاربرانی که قادر به کنترل و دسترسی به منابع خود به صورت آنلاین با کمک اینترنت در هر زمان بدون توجه به مکان هستند [3]. علاوه بر این، منابع آن مقیاس پذیر و پویا نیز می باشد. این یک پلتفرم محاسباتی مستقل است که کاملاً با محاسبات ابزار و شبکه متفاوت است. بهترین مثال رایانش ابری را می توان در Google Apps مشاهده کرد که در دسترسی به خدمات از طریق مرورگر کمک می کند و می تواند به راحتی بر روی تعداد زیادی از رایانه ها از طریق پیوندهای اینترنتی نصب شود [4]. با استفاده از اینترنت، منابع به راحتی از محیط ابری از هر مکان و در هر زمان در سراسر جهان قابل دسترسی هستند. در مقایسه با سایر مدل های محاسباتی، از نظر هزینه کمتر است. به عنوان ارائه دهنده خدمات پاسخگو برای دسترسی و در دسترس بودن خدمات مختلف، هزینه نگهداری آن ناچیز است و مشتریان با مدیریت آزاد می مانند و مسائل نگهداری منابع در انتهاست. به خاطر این ویژگیها، رایانش ابری بر اساس تقاضا یا محاسبات ابزار نامیده میشود. یکی از ویژگی های مهم رایانش ابری مقیاس پذیری آن است و از طریق مجازی سازی سرورهای آنها به دست می آید [5،6]. به نرم افزار، محاسبات، خدمات ذخیره سازی و دسترسی به داده ها می دهد که نیازی به دانش کاربر نهایی پیکربندی سیستم ندارد و خدمات یا موقعیت فیزیکی را ارائه می دهد.
فناوری رایانش ابری بر روی سه SPI (نرم افزار) مختلف کار می کند زیرساخت پلت فرم) مدل ها و چهار استقرار (عمومی، خصوصی، مدلهای ترکیبی و جامعه [7]. بر اساس استفاده یا نیاز مصرف کننده می تواند از سرویس(های) ابر استفاده کرده و ابر را مستقر کند. در حال حاضر، دارای سه نوع مدل خدمات است که SPI (نرم افزار) نیز نامیده می شود زیرساخت پلت فرم) مدل هایی که در زیر آورده شده است [8]:
Ø SaaS (نرم افزار به عنوان یک سرویس) [9]:-
این یک طرح توزیع و استقرار نرم افزار است که در آن برنامه ها در قالب خدمات به مشتریان تحویل داده می شوند. برای دسترسی و با استفاده از سرویس یا اپلیکیشنی که در فضای ابری تعبیه شده است، مشتریان به راحتی این امکانات را دریافت می کنند. چنین برنامه ای می تواند اجرا شود وب سرورهای ارائه دهنده خدمات یا ماشین های محاسباتی مشتری. SaaS خدماتی را برای مدیریت پچ به طور کارآمد ارائه می دهد و همکاری را نیز ارتقا می دهد.
کمترین توسعه پذیری و بیشترین میزان مسئولیت ایمن سازی توسط ارائه دهنده ابر گرفته شده است. اساساً از برنامه های ارائه دهنده از طریق شبکه استفاده می کند که "Salesforce.com" یک مثال است، در صورت لزوم اطلاعات برای تعامل بین مصرف کننده و خدمات میزبانی به عنوان بخشی از سرویس در فضای ابری و ارائه خدمات پایه کسب و کار و برنامه ها که شامل پردازش کلمه و ایمیل توسط Google است ارائه میشود [11]
Ø PaaS (پلتفرم خدمات) [11]:-
مشتری با توانمندسازی آنها در سازماندهی برنامه و نرم افزار و برنامه های کاربردی خود در حوزه ابری، به پلتفرم دسترسی پیدا می کند. فناوری اطلاعات در جایی در وسط قرار دارد، با قابلیت توسعه و امنیت ویژگی هایی که باید توسط مشتری استفاده شود. مسئولیت اصلی PaaS در حال استقرار برنامه های مرتبط با مشتری در یک ابر است.
Ø IaaS (زیرساخت به عنوان یک سرویس) [12]:-
این مدل ذخیره سازی، پردازش و دیگر منابع مهم محاسباتی برای مشتری است. این کلاینتها چارچوب اصلی ابر را مدیریت یا کنترل نمیکنند، اما دارای قابلیتهای دسترسی در ذخیرهسازی اولیه، سیستم عامل، مهارتهای محاسباتی هستند. خدمات استاندارد در شبکه داده شده و برنامه های کاربردی مستقر شده است. آی تی به توسعه پذیری بیشتر و کمترین مسئولیت امنیتی که توسط ارائه دهنده ابر بر عهده می گیرد، نیاز دارد. ظرفیت شبکه (سرورها، سوئیچ ها، روترها و سایر سیستم ها) ذخیره سازی، پردازش و سایر منابع محاسباتی اساسی تحت این مدل قرار می گیرند.
رایانش ابری از نظر ویژگی ها بسیار غنی است اما آینده های اصلی Cloud محاسبات به شرح زیر است [13]:
Ø استفاده از خدمات مبتنی بر اینترنت برای پشتیبانی از فرآیند کسب و کار: -
پلتفرم رایانش ابری به شبکههای خاصی محدود نمیشود، اما میتوان از طریق شبکه عظیمی از آنها که اینترنت است، به آن دسترسی داشت. [13].
Ø خدمات IT اجاره ای مبتنی بر ابزار: -
رایانش ابری شامل اجاره منابع محاسباتی مانند پهنای باند شبکه، نرمافزار و سختافزار، بر اساس تقاضا یا بر اساس نیاز، مانند محاسبات ابزاری که پیشروی رایانش ابری بود. بدون نگرانی در مورد هزینه نصب و نگهداری رایانش ابری [13].
این ترکیبی از فنآوریها و روشهای رایج است که در پارادایم زیرساختی جدید تعبیه شده است که انعطافپذیری، مقیاسپذیری، زمان راهاندازی سریعتر، کاهش هزینههای مدیریت، در دسترس بودن به موقع منابع و چابکی کسبوکار را فراهم میکند.
Abstract
Major backbone of today’s competitive and upcoming market is definitely becoming Cloud computing & hence corporate utilize capabilities of cloud computing services. To improve security initiatives by cloud computing service or CRPs, novel types of tools and protocols finds themselves always in demand. In order to build comprehensive risk assessment methodology, extensive literature review was conducted to identify risk factors that may affect cloud computing adoption. In this context various risk factors were identified. After feature selection and identification of risk factors, utilized to select most effective features using linear regression algorithms. Then AI-ML techniques like Decision Tree (DTC), Randomizable Filter Classifier, k-star with RMSE method is used to analyse threats within CC environment. Experimental outcomes depicted that division of dataset to (95%-5%) provided best result out of every remaining partitioning and moreover put forth that DTC algorithm provided best outcomes out of entire data set used in experimental setups.
1. Introduction
Cloud [1] being one of most versatile and dynamic inventions has brought focus of technologists on the global stage. Although Cloud Computing comes with huge rewards like measured services, rapid elasticity, scalability, and major significant being low cost to companies, more over it is embedded with good proportion of security risks that is not comprised by any other enterprise that can be ignored. The security danger that emanate from the wide range of the vulnerabilities inherent in any type of Cloud computing system and in the absence of reliable security directives, there is an apparent reluctance on the part of organizations to adopt an otherwise a powerful environment called cloud computing [2].
Without bothering regarding physical and technical maintenance or management challenges of original resources, Cloud Computing makes users capable of controlling and reaching their resources online with help from internet at any time irrespective of their locations [3]. Moreover, its resources are scalable and dynamic. It is an autonomous computing platform that is entirely different than utility and grid computing. Cloud Computing best example can be seen as Google Apps; it helps in accessing services through browser and can be easily installed on extensive number of computers over Internet links [4]. Using internet, Resources are easily approachable from cloud environment from any place and at any time across globally. Comparatively to other computing models it is less as far as cost is concern. As service provider is accountable for accessibility and availability of various services, cost of maintenance entangled with it is negligible and clients remain free from management and maintenance issues of resources at provider’s end. Because of these characteristics, Cloud Computing came to be called as simply IT on demand or utility computing. A main significant feature of Cloud Computing is its Scalability and is attained via virtualization of their servers [5,6]. It gives software, computation, storage services and data access that doesn’t need any end-user knowledge of system configuration that delivers services or physical location.
Cloud Computing Technology works on three different SPI (Software Platform Infrastructure) models and four deployments (public, private, hybrid, and community) models [7]. As per the usage or requirement consumer can use the service(s) of the cloud and deploy the cloud. Presently, it has three types of service models also called SPI (Software Platform Infrastructure) models which are given below [8]:
Ø SaaS (Software as a Service) [9]:-
It is a Software distribution and deployment schemes where applications are delivered to clients in form of services. For accessing and utilization of service or an application which is embedded in cloud, costumers receive this facility with ease. Such application can execute on service provider’s Web servers or client’s computing machines. SaaS delivers services for patch management efficiently and also promotes collaboration.
Least extensibility and greatest amount of securing responsibility taken on by the cloud provider. Basically, it uses provider’s applications over a network. “Salesforce.com” is an example, where necessary information for the interaction between the consumer and the service is hosted as part of the service in the cloud and deliverance of basic business services that comprises of word processing and email by Google Apps [10].
Ø PaaS (Service Platform) [11]:-
Client gains accessibility to platform by empowering them in organizing their own application and software and applications in cloud domain. IT lies in the middle at somewhere, with extensibility and security features that must be leveraged by the customer. Main responsibility of PaaS is deploying customer related application to a cloud.
Ø IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service) [12]:-
This model is utilized in delivering storage, lease processing, and various other important resources of computing for their client. These clients doesn’t manage or control basic cloud framework but has accessing capabilities on basic storage, operating system, computing skills as standardized services on given network and deployed applications. It requires greater extensibility and least amount of security responsibility taken on by cloud provider. Network capacity (Servers, Switches, Routers, and other Systems) Storage, Rent processing & other fundamental computing resources comes under this model.
Cloud Computing is quite rich in features but main futures of Cloud Computing are as follows [13]: Ø Use of internet-based services to support business process: -
Platform of Cloud Computing is not constrained to particular networks but can be access via huge network of them all that is Internet [13].
Ø Utility-like based Renting IT-services: -
Cloud Computing comprises in renting of computing resources like network bandwidth, software and hardware, on demand basis or asrequired, like utility computing which was a precursor to Cloud Computing; without worrying about installation and maintenance cost of Cloud Computing [13].
It is a combination of prevailing technologies and methods, embedded in a new infrastructure paradigm which provides improved elasticity, scalability, faster start up time, reduced management costs, just-intime availability of resources and business agility.
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. کارهای مرتبط
3. روش
4. نتیجه و بحث
5. نتیجه گیری
منابع
ABSTRACT
1. Introduction
2. Related work
3. Method
4. Result & discussion
5. Conclusion
References
