
دانلود رایگان مقاله نحوه ایجاد ارزش برای توکن های غیرقابل تعویض
چکیده
توکنهای غیرقابل تعویض (NFT) در سال گذشته رشد فوقالعادهای را به ثبت رساندهاند و انتظار میرود اهمیت آنها با توسعه Web3 افزایش یابد. از دیدگاه برند، NFT ها را می توان به عنوان بازنمایی اجزای برند مانند محصول، لوگو یا تصویر دید. من استدلال می کنم که NFT ها پتانسیل بسیار زیادی برای تبدیل شدن به دارایی های برند مستقل دارند. من نشان میدهم که چگونه میتوان با مرتبط کردن استراتژیهای NFT برند با مراحل قیف بازاریابی به این امر دست یافت. برندها می توانند محصولات فیزیکی خود مانند کفش، پیراهن یا هنر خود را به یک NFT تبدیل کنند تا آگاهی برند را به خود جلب کنند، فرصت های فروش متقابل ایجاد کنند و مالکیت درک قوی تری از عناصر خاص برند ایجاد کنند. نکته مهم این است که NFTها به برندها اجازه می دهند تا یک جامعه برند بسیار جذاب را تشکیل دهند که می تواند از برند حمایت کند، مالکیت محصول آنلاین و آفلاین را ترکیب کند و به طور بالقوه پیوندی بین برند و مصرف کنندگان ایجاد کند. این احتمالات هیجان انگیز یک برنامه تحقیقاتی غنی را ایجاد می کند که در این مقاله ارائه می کنم.
1. مقدمه
توکنهای غیرقابل تعویض (NFT) در سال 2021 هفده میلیارد دلار فروش داشتهاند و در راه شکستن این ارقام در سال 2022 هستند (EY، 2022؛ McKinsey، 2022). سرمقاله Peres, Schreier, Schweidel و Sorescu (2022) NFT ها را به عنوان "دارایی های رمزنگاری شده در یک بلاک چین با کدهای شناسایی منحصر به فرد و ابرداده هایی که آنها را از یکدیگر متمایز می کند" تعریف می کند. از منظر برند، NFT ها را می توان به عنوان بازنمایی اجزای برند، مانند طراحی محصول، لوگو یا تصویر مشاهده کرد. به عنوان مثال، یک NFT برند میتواند دوقلوی دیجیتالی یک محصول فیزیکی، نمایش گرافیکی لوگوی یک برند در محیط دیجیتال یا بلیط یک کنسرت باشد (AdAge، 2022). با این حال، من استدلال می کنم که NFT ها پتانسیل بسیار بیشتری دارند زیرا می توانند به دارایی های برند مستقل تبدیل شوند و بنابراین تا حد زیادی به ارزش ویژه برند کمک می کنند. من پیشنهاد میکنم که این امر میتواند با تأثیرگذاری بر مصرفکنندگان در مراحل پیشخرید، خرید و پس از خرید قیف بازاریابی به دو صورت محقق شود.
اول، NFT ها می توانند به اجزای برند مستقل تبدیل شوند (به عنوان مثال، محصولات جدید) که می توانند نقش مهمی در کل قیف بازاریابی ایفا کنند. راهاندازی یک NFT با نام تجاری میتواند آگاهی از برند را افزایش دهد و مخاطبانی را که قبلاً غیرقابل دسترس بودند (مثلاً نسل زد) جذب کند. به عنوان مثال، Anheuser-Busch چندین مجموعه NFT را با موفقیت همراه با رویدادها (موسیقی، کنسرت) و هدایایی از شرکت های فناوری راه اندازی کرده است (AdAge، 2022). مشتریان همچنین می توانند توسط NFT ها متقاعد شوند که محصولات فیزیکی برند را بخرند، بنابراین فرصت های فروش متقابل ایجاد می شود. نمونه بارز آن برندهای مد دیجیتال مانند نایک و آدیداس است که بسیاری از کفش های فیزیکی را به عنوان NFT فروخته اند و بالعکس (مک کینزی، 2022). در نهایت، برندها می توانند با ایجاد مالکیت درک قوی تر از عناصر خاص برند، مانند لوگو یا طرح برند، وفاداری ایجاد کنند.
دوم، NFT ها می توانند جامعه برندی را تشکیل دهند که می تواند از برند حمایت کند. همانطور که صفحات وب تجارت را متحول کردند و رسانه های اجتماعی یک کانال ارتباطی دو طرفه با مصرف کنندگان ایجاد کردند، NFT ها می توانند کاتالیزوری برای موج سوم تجارت از طریق قدرت جوامع برند آنلاین باشند (Schau, Muñiz, &Arnould, 2009). دیسکورد، تلگرام و Reddit پلتفرمهای رسانههای اجتماعی بسیار جذاب، غیرمتمرکز و ناشناس هستند که کاربران زمان زیادی را در آن صرف میکنند (اینفلوئنسر مارکتینگ هاب، 2022). برندها می توانند از پلتفرم ها برای ایجاد تعامل با مشتری در جوامع NFT از طریق پیام های ارگانیک یا محتوای خلاقانه استفاده کنند که می تواند آگاهی از برند را افزایش دهد. به عنوان مثال، مجله تایم از دیسکورد برای مشارکت کاربران با بازی ها و چالش های روزانه استفاده می کند (Ewen, 2021). برندها همچنین میتوانند از جنبههای اجتماعی NFTها برای ترکیب مالکیت NFT با موارد استفاده آفلاین استفاده کنند و قصد خرید برای محصولات برند را افزایش دهند. این کار را می توان با دادن پاداش به دارندگان NFT با دسترسی به کالاهای انحصاری (مانند The Hundredsو Adam Bomb Squad)، خدمات ممتاز (به عنوان مثال اولویت در نشستن در کنسرت ها)، یا حتی مهمانی های خصوصی (مانند Bored Ape Yacht Club) انجام داد. ) (AdAge، 2022؛ Kaczynski & Kominers، 2021). در نهایت، برندها با طراحی داستان های معتبر و خلاقانه پیرامون هویت برند، با مصرف کنندگان پیوند ایجاد می کنند
به طور کلی، این مقاله قصد دارد با پیشنهاد اینکه NFT ها می توانند به دارایی های برند مستقل تبدیل شوند، کمک کند. در این رابطه، من در مورد اینکه چگونه NFTها می توانند با (1) اجزای مستقل برند و (2) تشکیل و استفاده از قدرت جوامع برند NFT برای برندها ارزش ایجاد کنند، بحث می کنم. به طور خاص، من نشان می دهم که چگونه این دو راه می توانند با مراحل قیف بازاریابی مرتبط شوند. در نهایت، من چندین جهت تحقیقاتی هیجان انگیز را برای ایجاد ایده های نوآورانه ایجاد می کنم (به شرایر، پرز، شوایدل و سورسکو، 2021 مراجعه کنید).
2. مراحل قیف بازاریابی
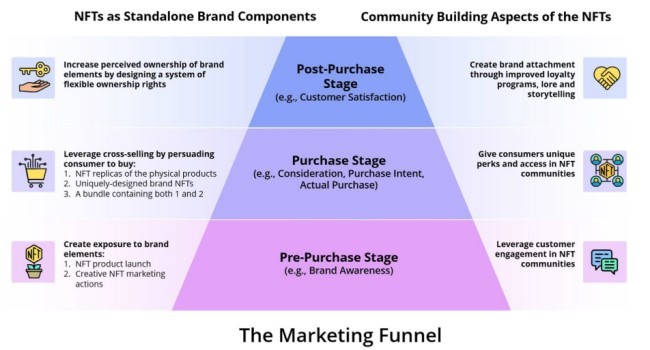
قیف بازاریابی اصطلاحی است که برای توصیف تصمیمگیری متوالی مشتری که در چندین مرحله اتفاق میافتد استفاده میشود (Wiesel, Pauwels, & Arts, 2011). ایده این است که مصرف کنندگان ابتدا باید قبل از توسعه قصد خرید، در مورد یک نام تجاری اطلاعات کسب کنند، سپس تصمیم خرید و مشورت بالقوه پس از خرید را انجام دهند (هوبان و باکلین، 2015). در حالی که قیف بازاریابی گاهی اوقات به عنوان قیف خرید نیز شناخته می شود، بنابراین به طور گسترده تری کل فرآیند تکامل روابط مشتری و برند (و نه تنها قبل از خرید) را نشان می دهد. بنابراین، قیف بازاریابی به طور کلی پذیرفته شده است که از سه مرحله تشکیل شده است: پیش خرید (به عنوان مثال، آگاهی برند)، خرید (به عنوان مثال، قصد خرید، خرید)، و پس از خرید (به عنوان مثال، رضایت مشتری، وفاداری) (دی بروین. و لیلین، 2008؛ راجرز، 1995؛ شوایدل، 2022). سپس برندها استراتژی های بازاریابی متناسب با هر مرحله قیف بازاریابی را طراحی می کنند (ویزل و همکاران، 2011).
3. چگونه برندها می توانند از NFT ها در مراحل قیف بازاریابی استفاده کنند
با تکیه بر این ایده که NFTها میتوانند اجزای برند مستقل باشند و از قدرت جوامع برند استفاده کنند، در ادامه توضیح میدهم که چگونه برندها میتوانند از NFT برای تأثیرگذاری بر مصرفکنندگان در امتداد قیف بازاریابی استفاده کنند (شکل 1 را ببینید).
3.1. مرحله پیش خرید
اساس همه برندها و تلاش های بازاریابی، ایجاد نگرش های پیش از خرید است. در حالت ایده آل، مصرف کنندگان قادر خواهند بود برند را در مرحله خرید تشخیص دهند و به خاطر بسپارند (دی بروین و لیلین، 2008). برای انجام این کار، برندها باید تلاش های NFT خود را بر ایجاد آگاهی از برند از طریق قرار گرفتن در معرض عناصر خود متمرکز کنند.
3.1.1. NFTها به عنوان اجزای برند مستقل در مرحله پیش خرید
برندها می توانند از راه اندازی محصول NFT به عنوان یک کاتالیزور برای ایجاد آگاهی برند به دلایل مختلف استفاده کنند (گلپر، پرز، و الیاشبرگ، 2018). اولا، راه اندازی NFT می تواند نام تجاری را در معرض مخاطبانی قرار دهد که قبلاً غیرقابل دسترس بودند. چرخه تبلیغات NFT توسط علاقه مندان به ارزهای رمزنگاری شده، کاربران نسل زد، دیسکورد و جمعیتی که بیشتر به سمت فناوری می روند، تقویت می شود (Howarth, 2022). به عنوان مثال، یک استراتژی برند موثر میتواند راهاندازی یک NFT در همکاری با مجموعه NFT تاسیس شده باشد که میتواند برند را در معرض مخاطبان جدید قرار دهد. به طور معمول، بازار NFT در مجموعههایی سازماندهی میشود که شامل تعداد مجموعهای از اقلام (مثلاً 10000) تحت یک موضوع یا چتر است (نادینی، 2021). نمونههای برجسته مجموعههای معتبر NFT عبارتند از Bored Ape Yacht Club (BAYC)، با هر NFT انواع مختلفی از یک «میمون خسته» با ویژگیهایی که کمیاب بودن آنها را تعیین میکند. نمونه دیگر World of Women است، مجموعه ای از پرتره های زنانه که هدف آن طرح مسائل مهم پیرامون تنوع و شمول است. این مجموعههای معتبر قیمتهای ورودی دهها هزار دلار در OpenSea (بزرگترین بازار NFT) دارند (NonFungible، 2022). موارد اخیر همکاریهای برند شامل مشارکت بین آدیداس و سندباکس، خرید برند مد دیجیتال RTKFT توسط نایک و توسعه تلویزیون هوشمند سامسونگ سازگار با NFT با همکاری Nifty Gateways است (AdAge، 2022). این همکاریها به هر دو طرف کمک کرده است زیرا برندها مخاطبان جدیدی پیدا کردهاند در حالی که مجموعههای NFT تبلیغات و مشروعیت پیدا کردهاند.
دوم، راه اندازی محصولات NFT به برندها این امکان را می دهد که در تلاش های بازاریابی خود خلاقیت بیشتری داشته باشند زیرا آنها تقاضا دارند استراتژی های بازاریابی شخصی تر برای مخاطبان خاص. به عنوان مثال، Anheuser-Busch چندین مجموعه را در برندهای Bud Light، Budweiser و Stella Artois راهاندازی کرده است که رویدادهای واقعی (موسیقی، کنسرت) و هدایایی از شرکتهای فناوری را نشان میدهند (AdAge، 2022). سپس به دارندگان NFT فرصتی داده شد تا در Bud Light NEXT رای دهند کالا و دسترسی به رویدادهای شریک. به طور مشابه، مارکها میتوانند عرضه فیزیکی محصولات را با راهاندازی مجموعه NFT ترکیب کنند تا بخشهای سنتیتر مصرفکننده را به NFTها تسهیل کنند. برندهای مصرف کننده مانند Campbell’s، Gap، پیتزا هات و سامسونگ اخیراً این رویکرد را اجرا کرده اند و باعث ایجاد سر و صدا و هیجان در مصرف کنندگان شده است (AdAge, 2022).
Abstract
Non-fungible tokens (NFTs) have registered tremendous growth in the past year, and their importance is expected to increase with the expected development of Web3. From a brand perspective, NFTs can be seen as representations of the brand components, such as the product, the logo, or the image. I argue that NFTs have immense potential to become standalone brand assets. I illustrate how this can be achieved by relating the brand’s NFT strategies to the marketing funnel stages. Brands can turn into an NFT their physical products such as shoes, shirts, or art to attract brand awareness, generate cross-selling opportunities, and spark stronger perceived ownership of certain brand elements. Importantly, NFTs can allow brands to form a highly engaging brand community that can support the brand, blend online and offline product ownership, and potentially create a bond between the brand and consumers. These exciting possibilities generate a rich research agenda I present in this paper.
1. Introduction
Non-fungible tokens (NFTs) have registered a whopping 17 billion USD in sales in 2021 and are on their way to beating these figures in 2022 (EY, 2022; McKinsey, 2022). Peres, Schreier, Schweidel, and Sorescu (2022) editorial defines NFTs as ‘‘cryptographic assets on a blockchain with unique identification codes and metadata that distinguish them from each other.” From a brand perspective, NFTs can be seen as representations of the brand components, such as the product design, the logo, or the image. For instance, a branded NFT can be a digital twin of a physical product, a graphical representation of a brand’s logo in the digital environment, or a ticket to a concert (AdAge, 2022). However, I argue that NFTs have much more potential as they can become standalone brand assets and thus largely contribute to the overall brand equity. I propose that this can be achieved by affecting consumers in the pre-purchase, purchase, and post-purchase stages of the marketing funnel in two ways.
First, NFTs can become standalone brand components (e.g., new products) that can play an important role along the whole marketing funnel. Launching a branded NFT can raise brand awareness and attract previously unreachable audiences (e.g., Gen-Z). For instance, Anheuser-Busch has successfully launched several NFT collections accompanying the launch with events (music, concerts) and giveaways from tech companies (AdAge, 2022). Consumers can also be persuaded by the NFTs to buy the brand’s physical products, thus creating cross-selling opportunities. A prominent example is digital fashion brands like Nike and Adidas, which have sold many physical shoes as NFTs and vice-versa (McKinsey, 2022). Finally, brands can build loyalty by creating stronger perceived ownership of certain brand elements, such as the brand logo or design.
Second, NFTs can form a brand community that can support the brand. As webpages revolutionized commerce and social media have created a two-way communication channel with consumers, NFTs can become the catalyst for the third wave of commerce through the power of online brand communities (Schau, Muñiz, & Arnould, 2009). Discord, Telegram, and Reddit are highly engaging, decentralized, and anonymous social media platforms where users spend an increasing amount of time (Influencer Marketing Hub, 2022). Brands can use platforms to create customer engagement in NFT communities through organic messages or creative content that can increase brand awareness. For example, Time Magazine uses Discord to engage users with daily games and challenges (Ewen, 2021). Brands can also utilize the community aspects of NFTs for blending the NFT ownership with offline use cases, increasing purchase intentions for the brand’s products. This can be done by rewarding NFT holders with access to exclusive merchandise (e.g., The Hundreds’ and Adam Bomb Squad), premium service (e.g., priority in seating in concerts), or even private parties (e.g., Bored Ape Yacht Club yacht party) (AdAge, 2022; Kaczynski & Kominers, 2021). Finally, brands create a bond with consumers by designing authentic and creative storylines around the brand’s identity.
Overall, this article aims to contribute by proposing that NFTs can become standalone brand assets. In this respect, I discuss how NFTs can create value for brands by (1) being standalone brand components and (2) forming and harnessing the power of NFT brand communities. Specifically, I illustrate how these two avenues can be connected with the marketing funnel stages. Finally, I generate several exciting research directions to spark innovative ideas (see Schreier, Peres, Schweidel, & Sorescu, 2021).
2. The marketing funnel stages
The marketing funnel is a term used to describe the sequential customer decision-making that occurs in several stages (Wiesel, Pauwels, & Arts, 2011). The idea is that consumers must first find out about a brand before developing purchase intentions, followed by a purchase decision and potential post-purchase deliberations (Hoban & Bucklin, 2015). While the marketing funnel is also sometimes referred to as the purchase funnel, it thus more broadly represents the entire process of the evolution of customer-brand relationships (and not only before the purchase). Thus, the marketing funnel is generally accepted to be composed of three stages: pre-purchase (e.g., brand awareness), purchase (e.g., purchase intent, purchase), and post-purchase (e.g., customer satisfaction, loyalty) (De Bruyn & Lilien, 2008; Rogers, 1995; Schweidel, 2022). Brands then design tailor-made marketing strategies appropriate for each marketing funnel stage (Wiesel et al., 2011).
3. How can brands leverage NFTs in the stages of the marketing funnel
Building upon the idea that NFTs can be standalone brand components and leverage the power of brand communities, I next illustrate how brands can use NFTs to impact consumers along the marketing funnel (see Fig. 1).
3.1. Pre-purchase stage
The foundation of all brands and marketing efforts is the creation of pre-purchase attitudes. Ideally, consumers will be able to recognize and remember the brand in the purchase stage (De Bruyn & Lilien, 2008). To do so, brands must focus their NFT efforts on creating brand awareness through exposure to their elements.
3.1.1. NFTs as standalone brand components in the pre-purchase stage
Brands can utilize the NFT product launch as a catalyst to generate brand awareness for several reasons (Gelper, Peres, & Eliashberg, 2018). First, the NFT launch can expose the brand to previously unreachable audiences. The NFT hype cycle is fueled by cryptocurrency enthusiasts, Gen-Z Discord users, and a more technologically oriented crowd (Howarth, 2022). For example, an effective brand strategy can be launching an NFT in collaboration with an established NFT collection which can expose the brand to new audiences. Typically, the NFT market is organized in collections containing a set number of items (e.g., 10.000) under the same theme or umbrella (Nadini, 2021). Prominent cases of reputable NFT collections include the Bored Ape Yacht Club (BAYC), with each NFT presenting different variations of a ‘‘bored ape” with features that determine their rarity. Another example is World of Women, a collection of women portraits that has the aim of raising important issues around diversity and inclusion. These reputable collections have entry prices of tens of thousands of dollars on OpenSea (the largest marketplace for NFTs) (NonFungible, 2022). Recent cases of brand collaborations include the partnership between Adidas and Sandbox, the acquisition of the digital fashion brand RTKFT by Nike, and the development of Samsung’s smart TV compatible with NFT in collaboration with Nifty Gateways (AdAge, 2022). These collaborations have helped both sides as brands have reached new audiences while the NFT collections gained hype and legitimacy.
Second, NFTs product launches enable brands to become more creative in their marketing efforts because they demand more personalized marketing strategies for specific audiences. For instance, Anheuser-Busch has launched several collections across its Bud Light, Budweiser, and Stella Artois brands, which featured real-life events (music, concerts) and giveaways from tech companies (AdAge, 2022). NFT holders were then given a chance to vote on Bud Light NEXT merchandise and gain access to partner events. Similarly, brands can combine physical product launches with an NFT collection launch to ease the more traditional consumer segments into the NFTs. Consumer brands such as Campbell’s, Gap, Pizza Hut, and Samsung have recently executed this approach, generating consumer buzz and excitement (AdAge, 2022).
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. مراحل قیف بازاریابی
3. چگونه برندها می توانند از NFT ها در مراحل قیف بازاریابی استفاده کنند
3.1. مرحله پیش خرید
3.1.1. NFTها به عنوان اجزای برند مستقل در مرحله پیش خرید
3.1.2. جنبه های جامعه سازی NFT ها در مرحله پیش خرید
3.2. مرحله خرید
3.2.1. NFT ها به عنوان اجزای برند مستقل در مرحله خرید
3.2.2. جنبه های جامعه سازی NFT ها در مرحله خرید
3.3. مرحله پس از خرید
3.3.1. NFT ها به عنوان اجزای برند مستقل در مرحله پس از خرید
3.3.2. جنبه های جامعه سازی NFT ها در مرحله پس از خرید
4. چالش ها و جهت گیری های تحقیقاتی آینده
4.1. NFT ها به عنوان اجزای برند مستقل
4.1.1. ساختار ارزش NFT
4.1.2. تناسب بین NFTها، برندها و مصرف کنندگان
4.1.3. NFTها و محصولات فیزیکی برند
4.2. جنبه های جامعه سازی NFT ها
4.2.1. تعامل با مصرف کننده و استراتژی های ارتباطی برند
4.2.2. مزایای جوامع NFT برای مصرف کنندگان و برندها
5. جمع بندی
منابع
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The marketing funnel stages
3. How can brands leverage NFTs in the stages of the marketing funnel
3.1. Pre-purchase stage
3.1.1. NFTs as standalone brand components in the pre-purchase stage
3.1.2. Community building aspects of NFTs in the pre-purchase stage
3.2. Purchase stage
3.2.1. NFTs as standalone brand components in the purchase stage
3.2.2. Community building aspects of NFTs in the purchase stage
3.3. Post-purchase stage
3.3.1. Nfts as standalone brand components in the post-purchase stage
3.3.2. Community building aspects of NFTs in the post-purchase stage
4. Challenges and future research directions
4.1. NFTs as standalone brand components
4.1.1. NFT value structure
4.1.2. The fit between NFTs, brands, and consumers
4.1.3. NFTs and brand’s physical products
4.2. Community building aspects of NFTs
4.2.1. Consumer engagement and brand communication strategies
4.2.2. Benefits of NFT communities for consumers and brands
5. Concluding thoughts
References
