
دانلود رایگان مقاله اثر محافظت کننده ویتامین D بر پولیپ بینی انسان
خلاصه
زمینه: پولیپ بینی یک برآمدگی خوش خیم مخاط به داخل حفره ی بینی است که دارای منشاء چندفاکتوری می باشد. نشان داده شده است که ویتامین D دارای پتانسیل تحریک سیستم ایمنی است و می تواند به عنوان بازدارنده ی تکثیر سریع سلول عمل کند.
هدف مطالعه: تعیین خاصیت ایمنی زایی و اثر احتمالی ویتامین D در جلوگیری از تکثیر سریع پولیپ بینی انسان.
مواد و روش: 30 نفر بیمار انتخاب شده و در سه گروه مساوی تقسیم شدند.گروه اول (نمونه های سالم). گروه دوم بمدت 4 هفته مقادیر پایینی از ویتامین D (1000IU) را به صورت خوراکی دریافت کردند.گروه سوم مقادیر بالایی(4000IU) از ویتامین D را به صورت خوراکی در طول 4 هفته دریافت کردند. هر کدام از گروه های 2 و 3 خود به دو زیر گروه تقسیم شدند، زیرگروه B بیماران قبل از دریافت ویتامین D و زیرگروهA بیماران پس از دریافت ویتامین D.از همه ی افراد گروه بیوپسی(نمونه برداری از بافت زنده) برای تست های هیستولوژیکی و تعیین ایمونوهیستولوژیکی و تعیین بیان گیرندهای TOLL مانند انجام شد.
نتایج: بیماران قبل از دریافت ویتامینD ( گروههای 2b , 3b) با علایم ظاهری مانند (درد چهره ای ، سردرد، سیاه شدگی بینی، تخلیه ی بینی، ترشح پشت بینی و اخلال در بویایی) و شواهد اندوسکوپیک لوند و مک کی مانند(پولیپ، ادم و تخلیه) ، تخریب اپیتلیوم تنفسی، تجمع مقدار زیادی از فیبرهای کلاژن در لامیناپروپیا و بیان بالای TLR-9 حاضر شدند. گروه دریافت کننده ی دوز بالای ویتامین D اپیتلیوم تنفسی تقریبا سالمی داشته و کاهش چشمگیری در علایم ظاهری و اندوسکوپیک نشان دادند. درصد تجمع کلاژن و بیان گیرنده یtlr-9 نیز به میزان چشمگیری کاهش یافت ولی این کاهش در مقدار کلاژن و بیان TLR-9 در دوز پایین ویتامین D چشمگیر نبود.
نتیجه گیری: نقش ویتامینD در محافظت در برابر پولیپ بینی چشمگیر است بخصوص زمانیکه در دوزهای بالاتر استفاده می شود که باعث کاهش اندازه ی پولیپ بینی و بهبود علایم و نشانه های پولیپ می شود.
مقدمه
رینوسینوزیت مزمن(CRS) یک بیماری مزمن است که با التهاب مخاط های سینوسی شناخته میشود.علایم CRS شامل آبریزش جلویی/عقبی بینی، گرفتگی بینی، کاهش حس بویایی و فشار در بینی است که اغلب دو مورد از این علایم علی رغم مراقبت های پزشکی تا 12 هفته تداوم دارند. عوامل ایجاد بیماری CRS هنوز به صورت کامل شناخته نشده است اما به نظر می رسد حساسیت، عفونت های باکتریایی و ویروسی و مشکلات ساختاری در ایجاد آن نقش داشته باشند.CRS اغلب بر اساس تست های هیستولوژیکی و فیزیکی به دو گروه تقسیم می شود: رینوسینوزیت مزمن همراه با پولیپ بینی و رینوسینوزیت مزمن بدون پولیپ بینی.
مطالعات اخیر نشان میدهد که رینوسینوزیت مزمن همراه با پولیپ بینی با سطوح افزایش یافته ی IL-5, IL-13 ، EOTAXIN و پروتیین کاتیونی ائوزینوفیلی (ECP) شناخته می شود.
پولیب های بینی رایج ترین پولیپ های غیر نئوپلاستیکی در مخاط سینوس بینی هستند. علل ایجاد پولیپ های بینی هنوز نامعلوم است ولی تصور می شود که این بیماری تظاهرات واکنش های پیچیده ی التهابی باشد. رشد این پولیپ ها منجر به مسدود شدند صفحات سینوسی میشود که نیازمند مصرف آنتی بیوتیک برای درمان عفونت و استروئید درمانی برای کاهش بار پولیپ است. تجویز استرویید به صورت خوراکی یا مستقیم اولین مرحله ی درمان پولیپ های بینی است.آنتی هیستامین ها، دکونژستانت ها، و کرومولین سدیم به مقدار کمی مفید هستند. ایمونوتراپی(ایمنی درمانی) میتواند در درمان رینیت های آلرژیک کارآمد باشد اما وقتی به تنهایی استفاده می شود اغلب قادر به حل پولیپ های موجود نیست.در موارد پیشرفته، ممکن است برای برداشتن پولیپ ها و حفظ هوادهی سینوس نیاز به عمل جراحی باشد.
ویتامین D و بسیاری از آنالوگ های آن به جز نقش کلاسیک خود در هوموستازی کلسیم و فسفر ، به عنوان گروه بزرگی از عناصر ضد تکثیر سلول نیز شناخته میشوند. چنین ویژگی هایی نشان میدهد که ویتامین D میتواند برای درمان بیماری های التهابی مزمن استفاده شود.
در مقایسه با سایر ویتامین هایی که برای سلامتی ضروری هستند ویتامینD دارای نقش منحصر بفردی است زیرا از منابع متنوعی قابل دسترسی است. ارگوکلسیفرول(ویتامینD2) از تابش نور فرابنفش بر ارگوسترول به دست می آید که در برخی گیاهان یافت میشود ولی منشاء اصلی آن قارچ ها هستند.کله کلسیفرول (ویتامینD3) از تابش نور UV بر 7- دهیدروکلسترول در پوست جانوران به صورت پرو ویتامین D3 شکل می گیرد که با چند مرحله ایزومریزاسیون به ویتامین D3 تبدیل میشود. بنابراین انسان ها نیازمند دریافت ویتامین D2 و D3 به عنوان بخشی از سبک زندگی خود هستند رژیم های غذایی سرشار از ویتامین D3 (زرده ی تخم مرغ، روغن ماهی) ، غذاهای غنی شده (مانند مارگارین و دانه های خوراکی فرآوری شده که اغلب دارای ویتامین D2 هستند) و مکمل های ویتامینی منابع تامین این ویتامین ها هستند. ویتامین D2 و D3 هر دو به عنوان پیش هورمون عمل می کنند. تبدیل ویتامین D2 و D3 به ترکیبات فعال( فارغ از نوع منشاء) نیازمند یک فرایند هیدروکسیلاسیون آنزیمی دومرحله ای است.
کمبود ویتامین D2 و D3 یک نگرانی بین المللی است که با بیماری هایی مانند راشیتیسم، نرمی استخوان، ضعف عضلانی و بیماری های تنفسی و بیماری های خود ایمنی مانند دیابت نوع یک، ام.اس ، آرتریت روماتویید و بیماری کرون و همچنین سرطان پروستات،سینه و روده ی بزرگ مرتبط است. ویتامین D دارای پتانسیل تحریک ایمنی است و آنالوگ های آن در درمان پسوریازیس موثر هستند. فعال شدن گیرنده های TOLL-مانند منجر به شروع پاسخ های ایمنی سازگارشونده می شود.شناسایی لیگاندهای TLR کد شده توسط پاتوژن یکسری مسیرهای پیام رسانی داخل سلولی را فعال می کند که منجر به القای سریع سایتوکاین ها و کموکاین های پیش التهابی میشود. خصوصا TLR-9 می تواند در پاتوژنسیتی بیماری های خود ایمن مانند SLE نقش مهمی بازی کند.
هدف این مطالعه ارزیابی اثر بازدارندگی احتمالی ویتامین D در تکثیر سلولی و نقش آن در تحریک ایمنی در پولیپ بینی انسان است.
بیماران و روش ها
مطالعه ی حاضر بر روی 30 بیمار (21 مرد و 9 زن ) در دانشکده ی Oto-Rhino-Laryngology در بیمارستان های دانشگاه Benha از سپتامبر 2012 تا می 2013 انجام شد. این مطالعه توسط کمیته ی اخلاق دانشکده ی پزشکی Benha تایید شد.
ویتامین D3 (کله کلسیفرول) از واحد پزشکی شرکت داروسازی گرفته شد. ویتامین به صورت خوراکی و روزانه در دو دوز مصرف شد (دوز پایین 1000IU و دوز بالا 4000IU).
بیماران به سه گروه مساوی تقسیم شدند( 7 نفر مرد و سه نفر زن).
گروه I. (شاهد): بیماران پذیرش شده در دپارتمان ORL برای عمل اتوپلاستی با مخاط بینی عادی.
گروهII. (بیماران مبتلا به پولیپ بینی که دز پایینی از ویتامین D را دریافت کرده اند)
گروهIII.(بیماران مبتلا به پولیپ بینی که دوز بالایی از ویتامین DF را دریافت کرده اند).
ارزیابی ها در ابتدای مطالعه برای همه ی بیماران انجام شد و 4 هفته پس از شروع مصرف ویتامین D بیماران گروه II و III دروباره ارزیابی شدند.
Abstract
Background: Nasal polyps (NPs) are benign pedicled mucosal protrusions into the nasal cavity of multifactorial origin. Vitamin D has been demonstrated as having potential immunomodulatory activity and act as an antiproliferative agents.
Aim of the work: To determine the possible antiproliferative effect and immunomodulatory activity of VD on human nasal polyposis.
Material and methods: Based on thirty patients and divided equally into 3 groups. Group Ι (healthy subjects). Group ΙΙ were received low daily oral dose of VD(1000 IU) for 4 weeks. Group ΙΙΙ were received high daily oral dose of VD(4000 IU) for 4 weeks.Each group ΙΙ and ΙΙΙ divided into 2 subgroups; group b: patients with NP before taking VD and group a: patients with NP after taking. Nasal biopsies were obtained of all groups for histological examination and immunohistochemical detection of Toll-like receptors 9 expression.
Results: patients of nasal polyps before VD taking (groups IIb and IIIb) presented with symptoms of Visual Analogue Scale, VAS score (facial pain, headache, nasal blockage, nasal discharge, post-nasal drip and olfactory disturbance) and endoscopic appearance of Lund and Mackey score (polypi, edema and discharge), damage of respiratory epithelium, extensive accumulation of collagen fibers in lamina propria and highly expressed TLR-9. The high dose VD group (IIIa) showed near normal respiratory epithelium, significant decrease (P<0.05) in all symptoms of VAS score, endoscopic appearance of Lund and Mackey score. The mean area % of submucosal accumulation of collagen fibers and TLR-9 expression were also significant decreased but decrease was insignificant (P<0.05) in the low dose VD group (IIa).
Conclusion: VD participate significantly in protection against human nasal polyposis when used by high therapeutic dose, by reducing the size of nasal polyps, relieving the symptoms and signs of nasal polyposis.
Introduction
Chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS) is a chronic disease characterized by inflammation of the sinonasal mucosa. Symptoms of CRS include anterior and/or posterior rhinorrhea, nasal obstruction, decreased sense of smell, and nasal pressure, at least 2 of which persist for 12 weeks despite medical management. The pathogenesis of CRS is not fully understood at this time; however, allergy, bacterial and fungal infections, and structural anomalies have all been theorized to play a role [1]. CRS is often divided into 2 groups based on histology and physical examination: chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps and chronic rhinosinusitis without nasal polyps [2].
Recent studies suggest that chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps characterized by significantly elevated levels of IL-5, IL-13, eotaxin, and eosinophil cationic protein (ECP) [3].
Nasal polyps (NP) are common chronic non-neoplastic polyps of the nasal or paranasal sinus mucosa. The pathogenesis of NP is still unclear, but the disease is believed to be a manifestation of complex inflammatory reactions [4]. Growth of these polyps leads to obstruction of the sinonasal passages, requiring repeated courses of antibiotics to treat underlying infections and steroid therapy to reduce polyp load [5]. Oral and topical nasal steroid administration is the primary medical therapy for nasal polyposis. Antihistamines, decongestants, and cromolyn sodium provide little benefit. Immunotherapy may be useful to treat allergic rhinitis but, when used alone, does not usually resolve existing polyps [6]. In advanced cases, surgery may be necessary to remove the polyps and restore sinus ventilation [5].
Vitamin D (VD) and its different analogues, besides their classic role as regulators of calcium and phosphor homeostasis, have emerged as a large family of antiproliferative agents. Such properties suggested VD potential as a therapy for chronic inflammatory diseases [7].
Compared with the other known vitamins essential to health, vitamin D is unique in its role because of the diverse sources available. Ergocalciferol (vitamin D2) is sourced from the UV irradiation of ergosterol, which is a steroid found in some plants but largely in fungi. Cholecalciferol (vitamin D3) is synthesized via the UV irradiation of 7-dehydrocholesterol to previtamin D3 in the skin of animals with a further thermal isomerization step to form vitamin D3 [8]. Therefore, humans have a combination of vitamins D2 and D3 available to them as part of a typical lifestyle from ambient UV exposure (vitamin D3), habitual dietary intakes of vitamin D3–rich foods (egg yolks and oily fish), fortified foods (margarine and breakfast cereals, which generally have vitamin D2 fortification), and vitamin supplements (both vitamins D2 and D3 are available). Vitamins D2 and D3 function as prohormones. The conversion of vitamins D2 and D3 into active compounds (irrespective of source) requires a 2-step enzymatic hydroxylation process to occur [9].
Vitamin D (D2, D3, or both) deficiency is an international health concern that has been associated with rickets, osteomalacia, muscle weakness, osteoporosis, and an increased risk of wheezing diseases, autoimmune diseases (eg, type 1 diabetes, multiple sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis, and Crohns disease), and cancer, such as of the prostate, breast, and colon [10]. Vitamin D has been demonstrated as having potential immunomodulatory activity; vitamin D analogues are effective in the treatment of psoriasis [11]. Activation of Toll-like receptors (TLRs) results in initiation of innate and adaptive immune responses [12] . Recognition of pathogen-encoded TLR ligands activates intracellular signalling pathways that culminate in rapid induction of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines [13]. specifically by TLR9, can play an important role in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases, such as SLE [14].
The aim of this study was to evaluate the possible antiproliferative effect and immunomodulatory activity of VD on human nasal polyposis.
Patients and methods
The present study has been conducted on thirty patients (21 males and 9 females) attended Oto-Rhino-Laryngology (ORL) Department, Benha University Hospitals from September 2012 to May 2013. The study was approved by the Local Ethics Committee of Benha Faculty of Medicine.
Vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol) obtained from Medical Union Pharmaceutical Company (24 Mohamed Hassan El Gamal St. 6th Zone, Nasr City, Cairo, Egypt). VD was given daily orally in 2 doses; the low therapeutic dose was 1000 IU and the high therapeutic dose was 4000 IU [8].
Patients were divided into 3 groups; ten in each (7 males and 3 females).
Group I. (control): patients admitted in ORL department for otoplasty surgery with normal nasal mucosa.
Group II. (Patients with NP received low dose VD): Group IIb: before taking VD. Group IIa: after taking VD.
Group III. (Patients with NP received high dose VD): Group IIIb: before taking VD. Group IIIa: after taking dose of VD.
Assessement was done for all patients at the start of the study and 4 weeks after VD taking for patients of groups II and III and every patient in this study submitted for.
خلاصه
مقدمه
بیماران و روش ها
ارزیابی کلی
ارزیابی دقیق
آنالیز آماری
نتایج
نتایج بالینی
داده های عمومی
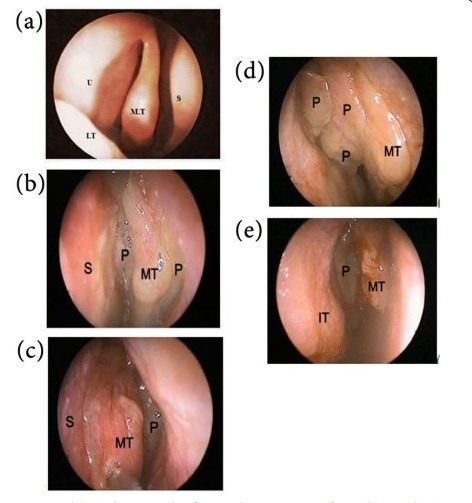
اندوسکوپیک
نتایج هیستولوژیکی
رنگ آمیزی Masson trichrome
ایمنو هیستوشیمی
بحث
نتیجه گیری
منابع
Abstract
Introduction
Patients and methods
Subjective assessment
Objective assessment
Statistical analysis
Results
Clinical results
General data
Endoscopic
Histological results H&E
Masson’s trichrome
Immunohistochemical
Discussion
Conclusion
References
