
دانلود رایگان مقاله تعریف، دسترسی و توسعه موفق یادگیری الکترونیکی
چکیده
این پژوهش به پیشرفت درک چگونگی تعریف، ارزیابی، و توسعه موفق یادگیری الکترونیکی از دیدگاه سیستم های اطلاعاتی می پردازد. در معرفی موفق یادگیری الکترونیکی ، فرض بر این است که موفقیت کلی طرح ابتکاری وابسته به دستیابی موفق در هر یک از سه مرحله توسعه سیستم های یادگیری الکترونیکی : طراحی سیستم، سیستم ارائه و نتیجه گیری سیستم است. برای مطالعه این مدل، نسخه ای آنلاین از روش های کمی وابسته به دوره لیسانس برای تجارت دانشجویان با استفاده از استراتژی نمونه سازی توسعه داده شده است. چهار سیکل توسعه ترسیم شده، هر کدام از، طراحی، پیاده سازی، آزمایش و ارتقاء تشکیل شده اند. یافته های حاصل از این مطالعه با استفاده از مدل موفق پیشنهادی برای ارزیابی موفق یادگیری الکترونیکی مورد تایید قرار گرفته است. علاوه بر این، روش عمل پژوهش نیز انگیزه زیادی برای توسعه موفق یادگیری الکترونیکی از طریق فرآیند تکرار شونده تشخیص، برنامه ریزی عملیاتی، اقدام، ارزیابی، و یادگیری از خود نشان می دهد.
مقدمه
اگر چه پیشرفت های قابل توجه ای انجام شده است، اما مربیان هنوز تازه شروع به بهره برداری در قدرت تبدیل اینترنت کرده اند. این پژوهش گامی بسوی تحقق کامل تر پتانسیل اینترنت برای حمایت از یادگیری می باشد. هدف اصلی این تحقیق، بررسی عامل های موفقیت برای طراحی، توسعه، و ارائه طرح های یادگیری الکترونیکی است. این امر منجر به معرفی مدل موفق یادگیری الکترونیکی به عنوان راهنمایی برای ارزیابی و پالایش طرح ها می شود. برنامه کاربردی شامل دستوالعمل روش های کمی آنلاین برای نشان دادن کاربرد مدل مورد استفاده می باشد. اصطلاح یادگیری الکترونیکی اغلب بجای آموزش از راه دور یا یادگیری از راه دور مورد استفاده قرار می گیرد. که توسط شورای فناوری آموزش (ITC, 1998)، و همچنین مرکز ملی آمار آموزش و پرورش (Waits & Lewis, 2003)، به عنوان فرآیند گسترش یادگیری یا ارائه اصولی یادگیری به مکان های دور از طریق اینترنت، اینترنت/ اکسترانت، صدا، تصویر، پخش ماهواره ای، تلویزیون کابلی، و CD تعریف شده است.
با توجه به وزارت مرکز ملی آموزش و پرورش ایالات متحده برای آموزش آماری، 90 درصد مردم 2 سال و 89 درصد مردم 4 سال در دوره های آموزش از راه دور در سال 2001-2000 ثبت نام کرده اند که به ترتیب 1472000 و 945000 نفر، از مجموع 3077000 نفری که ثبت نام کرده اند، می باشند. از این مدارس، 90 درصد دوره های اینترنتی با استفاده از آموزش مبتنی بر کامپیوتر بطور ناهمزمان بوده است، 80 درصد از برنامه ای برای شروع و یا از اینترنت به عنوان حالت اولیه ارائه آموزشی (Waits & Lewis, 2003) استفاده کرده اند. این آمار از ایده ای آموزش از راه دور مبتنی بر اینترنت که شایع ترین فن آوری یادگیری الکترونیکی است، پشتیبانی می کند و اینکه اینترنت تغییرات چشمگیری برای آموزش و پرورش در آموزش عمومی و بطور خاص آموزش از راه دور به ارمغان آورده است.
چگونه باید موفقیت یادگیری الکترونیکی را ارزیابی کرد؟ تلاش برای رسیدگی به این سوال مهم منجر به حجم زیادی از مطالعات حکایتی برای ارزیابی تاثیر برنامه های یادگیری الکترونیکی در معیارهای مختلف مانند معیار یادگیری (Pittinsky & Chase, 2000)، فرصت های یادگیری (Jewett, 1998)، سبک های یادگیری (Byrne,2003)، محیط یادگیری (Jung و همکاران, 2002؛ Wang & Bagaka، 2003)، نتایج یادگیری (McClelland, 2001؛ Motiwallo و Tello، 2000؛ Teh، 1999)، شیوه های تدریس (Owston & Wideman, 1998؛ Savenye, Olina & Niemczyk، 2001)، و هزینه – سود (Lawhead و همکاران، 1997؛ Smith، 2001) شده است.
این دیدگاه به ظاهر متنوع از آنچه که موفقیت در یادگیری الکترونیکی تشکیل می دهد با توجه به اینکه تحقیقات در این زمینه در مرحله شکل گیری است با تشخیص نسبتا جدید وعده های یادگیری الکترونیکی، دیدگاهی تعجب آور نیست. برای ارزیابی و بررسی طرح های یادگیری الکترونیکی نیاز به یکپارچه سازی و تنظیم مدلی جامع و کلی است. یکی دیگر از ضعف های این مطالعه، این است که معیار موفقیت تنها از ارزیابی نتایج حاصل از تلاش توسعه بدست آمده است. همچنین نیاز به گسترش دیدگاه برنامه موفق با توجه به نتیجه فرآیند یا دیدگاه کیفی کل است. این پژوهش این به این نیازها رسیدگی می کند.
بر اساس نظریه های الگوی توسعه سیستم های اطلاعاتی کاربر محور، این مقاله به توسعه و مطالعه مدل برای راهنمایی طراحی، توسعه و ارائه طرح موفق یادگیری الکترونیکی می پردازد. اعتبارسنجی نظریه توسعه برنامه یادگیری الکترونیکی از دیدگاه سیستم های اطلاعاتی توسط تشخیص پیشتیبانی می شود که هر دوی این تلاش ها برای هدف مشترک کنترل فن آوری های جدید به منظور پاسخگویی بهتر نیازهای کاربران انجام می شود. علاوه بر این، کارهایی توسط محققین سیستم های اطلاعاتی برای تشخیص عواملی که به موفقیت سیستم های اطلاعاتی کمک می کند انجام شده است. ما به این نتیجه رسیدیم که نظریه ها و دانش های متراکم از اوایل 1980 در موضوع موفقیت سیستم های اطلاعاتی می تواند در دنبال کردن موفقیت در یادگیری الکترونیکی مفید باشد. در نتیجه، ما مدل موفق سیستم های اطلاعاتی را برای یادگیری الکترونیکی تطبیق داده ایم. در نتیجه مدل موفق یادگیری الکترونیکی نه تنها به عنوان معیاری برای تضمین کیفیت در تلاش های یادگیری بکار می رود، بلکه به عنوان یک استراتژی برای حصول اطمینان از موفقیت در آینده برای توسعه و ارزیابی چنین طرح هایی نیز بکار می رود.
ما با معرفی مدل موفق یادگیری الکترونیکی شروع کردیم و چگونگی کاربرد آن را در زمینه عملیاتی خاص نشان دادیم: که دوره آنلاین در روش های کمی برای عملیات تجاری می باشد. مدل مورد نظر سپس از طریق چهار سیکل تحقیق در این زمینه تایید شده است. نتایج حاصل از تحقیق ارائه شده و مورد بحث قرار گرفته است. ما با توصیف بخش های اصلی این تحقیق با توجه به مقالات پیشین در یادگیری الکترونیکی، دستورالعمل های را برای تحقیقات بعدی در نظر گرفته ایم .
مدل موفق یادگیری الکترونیکی
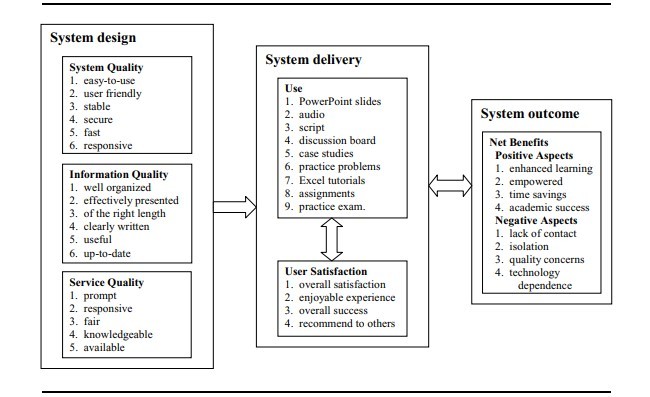
مدل موفق یادگیری الکترونیکی که در اینجا معرفی شده از مدل موفق سیستم های اطلاعاتی بروز شده DeLone و McLean (2003) اقتباس شده است که، به نوبه خود، با توجه به مدل اصلی (DeLone و McLean، 1992) تعمیم یافته است. با توجه به مقالات پیشین در موفقیت سیستم های اطلاعاتی ، DeLone و McLean ، شش مورد از عوامل موفقیت را شناسایی کرده اند که : کیفیت سیستم، کیفیت اطلاعات، استفاده، رضایت کاربر، تاثیر فردی، و تاثیر سازمانی است. که در مدل اصلی موفقیت آنها ترکیب شده همانطور که در شکل 1 نشان داده شده است.
نه تنها مدل اصلی DeLone و McLean در تجهیز موفق سیستم های اطلاعاتی، موثر بوده بلکه به روش فرآیند موفق سیستم های اطلاعاتی نیز کمک کرده است. به مدل اصلی 285 بار در مقالات ژورنال و عملیاتی اشاره شده است، که حاکی از تحقیقات انجام شده، اعتبار، چالش ها و نقدهای آن می باشد. از این مقالات، DeLone و McLean (2003)، 16 مطالعه تجربی را برای حمایت از انجمن ها با توجه به شش مورد نام برده شده شناسایی کرده اند:
Seddon and Kiew (1994)
Goodhue and Thompson (1995)
ABSTRACT
This research advances the understanding of how to define, evaluate, and promote e-learning success from an information systems perspective. It introduces the E-Learning Success Model, which posits that the overall success of an e-learning initiative depends on the attainment of success at each of the three stages of e-learning systems development: system design, system delivery, and system outcome. To study this model, an online version of an undergraduate quantitative methods core course for business students is developed using a prototyping strategy. Four cycles of development are traced, each comprised analysis, design, implementation, testing, and enhancement. Findings from the study confirm the validity of using the proposed success model for e-learning success assessment. In addition, an action research methodology is also found to be a valuable impetus for promoting e-learning success through an iterative process of diagnosing, action planning, action taking, evaluating, and learning.
INTRODUCTION
Although considerable progress has been made, educators still have just begun tapping into the transforming power of the Internet. This research is a step toward more fully realizing the potential of the Internet for supporting learning. Its primary focus is an investigation of the success factors for designing, developing, and delivering e-learning initiatives. This leads to the introduction of the E-Learning Success Model as a guide for evaluation and refinement of these initiatives. An application involving online quantitative methods instruction is used to illustrate the usage of the model.
The term e-learning is often used interchangeably with distance education or distance learning. It is defined by the Instructional Technology Council (ITC,1998), as well as the National Center for Education Statistics (Waits & Lewis, 2003), as the process of extending learning or delivering instructional materials to remote sites via the Internet, intranet/extranet, audio, video, satellite broadcast, interactive TV, and CD-ROM.
According to the U.S. Department of Education’s National Center for Education Statistics, 90% of public 2-year and 89% of public 4-year institutions offered distance education courses in 2000–2001 with enrollments of 1,472,000 and 945,000, respectively, out of a total enrollment of 3,077,000. Of these schools, 90% offered Internet courses using asynchronous computer-based instruction, and 88% indicated plans to start or increase use of the Internet as a primary mode of instructional delivery (Waits & Lewis, 2003). These statistics support the idea that Internet-based distance education is the most prevalent e-learning technology and that the Internet has brought dramatic changes to education in general and distance learning in particular. In view of this fact, the scope of e-learning in this article focuses primarily on Internet-based distance education.
How should the success of e-learning be evaluated? Attempts to address this important question have resulted in a large volume of anecdotal studies assessing the impact of e-learning programs on various measures such as learning benchmarks (Pittinsky & Chase, 2000), learning opportunities (Jewett, 1998), learning styles (Byrne, 2002), learning environment (Jung et al., 2002.; Wang & Bagaka, 2003), learning outcomes (McClelland, 2001; Motiwallo & Tello, 2000; Teh, 1999), teaching practices (Owston & Wideman, 1998; Savenye, Olina, & Niemczyk, 2001), and cost-benefits (Lawhead et al., 1997; Smith, 2001).
These seemingly diverse views of what constitutes success in e-learning are not surprising given that research in this area is at a formative stage with the relatively recent recognition of the promises of e-learning. There is a need to integrate and formulate a holistic and comprehensive model for assessing and evaluating e-learning initiatives. Another shortcoming of these studies is that success measures are derived from assessing the results of the development effort only. There is also a need to broaden the viewpoint of program success from a result to a process or total quality perspective. This research addresses these needs.
Based on theories of a user-centered information systems development paradigm, this article develops and studies a model to guide the design, development, and delivery of successful e-learning initiatives. The validity of viewing e-learning program development from an information systems perspective is supported by recognizing that both of these efforts are fueled by a common goal of harnessing new technologies to better meet the needs of their users. In addition, a similar journey has been undertaken by information systems researchers in their attempt to identify factors that contribute to information systems success. We concluded that theories and knowledge accumulated since the early 1980s on the topic of information systems success can be beneficial in pursuing success in e-learning. Consequently, we adapt an information systems success model to e-learning. The resulting E-Learning Success Model serves not only as a measure for quality assurance in e-learning efforts, but also as a strategy for ensuring future success in the development and assessment of such initiatives.
We begin by introducing the E-Learning Success Model and indicate how it can be operationalized in a specific context: an online course in quantitative methods for business operations. The model is then validated through four cycles of action research in this context. Results from this research are then presented and discussed. We conclude by characterizing the main contributions of this research to the literature on e-learning and suggesting directions for follow-up investigations.
E-LEARNING SUCCESS MODEL
The E-Learning Success Model introduced here is adapted from DeLone and McLean’s (2003) updated information systems success model which, in turn, is an extension of their original model (DeLone & McLean, 1992). From past literature on information systems success, DeLone and McLean identified six dimensions of success factors: system quality, information quality, use, user satisfaction, individual impact, and organizational impact. These were incorporated into their original overall success model shown in Figure 1.
Not only did DeLone and McLean’s original model succeed in furnishing an integrated view of information systems success, it also helped instill a process approach to information systems success. In the decade following its advent, the original model was referenced 285 times in refereed papers in journals and proceedings, signifying research that applied, validated, challenged, and critiqued it. From this literature, DeLone and McLean (2003) identified 16 empirical studies that rendered support for the associations among the six dimensions of success factors:
Seddon and Kiew (1994)
Goodhue and Thompson (1995)
چکیده
مقدمه
مدل موفق یادگیری الکترونیکی
روش تحقیق عملکردی
نتایج و بحث
نتیجه گیری
منابع
ABSTRACT
INTRODUCTION
E-LEARNING SUCCESS MODEL
ACTION RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
CONCLUSIONS
REFERENCES
