
دانلود رایگان مقاله یک راهکار برای تغییرات در استاندارد های حسابداری
چکیده
حسابداری به منزله زبان تجاری، یک ارتباط تاریخی با توسعه یک اقتصاد پویا داشته و بالطبع اصول و قواعد و فرایندهای به موازات نوسانات بازرگانی نیز تغییر میکند. این نوشته یک دیدگاه اجمالی را از توسعه استانداردهای حسابداری و همچنین لزوم داشتن یک اصول یکسان و واحد حسابرسی در سراسر جهان را خورد کنکاش قرار میدهد. مرور مکتوبات قدیمی حسابداری کاملا با مفاهیم نظری سروکار دارد که برای اخذ یک بینش و بصیرتی در تاجران و متصدیانی که کشورشان به سمت تطابق با ifrs حرکت میکنند، را در فهم استاندارد ها تسهیل بخشیده و منظری از پیشرفت تجارت تاریخی عرضه میکند تا به سمت یک استاندارد بین المللی همگرایی و تقارب کنند.
1. معرفی
تصمیمات مالی ( اعم از سرمایه گذاری و امور مالی ) وابسته و متکی بر کیفیتی داده های مالی همبسته با آن هستند کیفیت داده ها نیز به ترتیب وابسته اند به کیفیتی از استاندارد های حسابداری در اندازه گیری تشخیص ( شناسایی ) عرضه ( ارایه ) ، افشا ( آشکارگی ) داده ها. مطابق unctad isar, 2008 ضرورت تدوین جهانی در بالاترین کیفیت از گزارشات حسابداری در اوایل سال ۱۹۷۰ نمایان شد وقتی که تلاش و کوشش ها جهت ارایه یک شاخص جهانی معتبر و یکسان متمرکز شدند با ارایه مجوز برای معاملات اقتصادی که بنحو مشابه و همسانی در سراسر جهان، بعنوان ماهیتی از حسابداری ، اجرا و عرضه و گزارش شود.
شماری از موسسات ، مولفان، دانشگاهیان و محققان حرفه ای، حسابداری را از زوایای مختلفی تعریف نموده اند؛ برای مثال بنابر ALCPA حسابداری ، هنر ثبت، طبقه بندی و تخلیص به روشی معنادار بوده و نیز دوره های مالی مبادلات بازرگانی و روابطی که بخشی از پارامترهای مالی و تفسیر نتایج مربوطه هستند. investopedia حسابداری ثبت سیستماتیک و جامع از معاملات بازرگانی در یک تجارت تعریف کرده: فرایند تلخیص، پردازش و گزارش دهی این معاملات و همچنین ارایه صورت های مالی که صدها و هزاران معاملات مالی در آن مندرج گشته باشد. دایره المعارف همچنین حسابداری را بعنوان زبان تجاری، در معنای اصلی در حفظ سوابق اقتصادی از فعالیتهای تجاری و مالی تعریف کرده که به سازماندهی در ثبت، گزارش و رویدادهای اقتصادی و معاملات بازرگانی در یک موسسه یا شرکت تجاری کمک پیوند تا برای کاربران یک سیستم عملی و نظری حسابرسی سازماندهی گشته و تخلیص شده و گزارش صورت مالی ارایه دهند. مطابق دایره المعارف ، سیستم حسابداری ، یک سیستم اطلاعاتی مدیریتی ست در جهت جمع آوری و پردازش آمار و ارقام لازم برای تصمیم بگیران تا طرحها و فعالیتهای سازمان تجاری و چرخه پردازشی داده ها از یک سیستم حسابداری جامع و کامل کنترل نمایند. ساختار کلی شامل ۵ فعالیت همبسته با جستجوی داده های مالی عبارتند از: گردآوری یا ثبت داده ها، طبقه بندی داده ها با پردازش (شامل محاسبه و تلخیص ) نگهداری یا ذخیره نتایج و گزارش نتایج.
2. تاریخچه موسسات حسابداری تجاری و استاندارهایش:
حسابداری از مراحل متنوعی در مناطق مختلف جهان، گسترش و توسعه یافته و در دوره های زمانی متعددی با اقتصاد جوامع ، همبسته و وابسته ست. افزایش تدریجی در تولید و معاملات اقتصادی از هر زمان دیگری وابسته به تسهیلات و تجهیزات تکنولوژیکی گشته تا همه دشواری های اقتصادی را مدیریت و اداره کند. مردم ناچار از ثبت و ضبط بودند. بنابر نظر alexander 2002 برای اولین بار مردم بین النهرین شروع به ثبت معاملات بازرگانی بروی خاک گل و سفال کرده و سپس روی برگه های پاپیروس در مصر پیشروی کردند. الکساندر تاریخچه رشد حسابداری را مختصرا چنین شرح میدهد:
تاریخچه حسابداری یک تجارت بشری ست که کارکردی فراتر از نوشتن و اعداد و شمارش دارد. ۵ هزار سال قبل از پیدایش سیستم ثبت دوطرفه، تمدنهای سامری و آشوری، بابلی _ کلدانی در بین النهرین ، برخی از روش های ثبتی بازرگانی قدیمی را ابداع کردند. حسابداری حکومتی در مصر باستان در اسلوبی مشابه بین النهرین تدوام یافته و نمودارهای زیادی برای انبارگردانی های سلطنتی ترسیم می شد تا مالیاتهای پرداختی و خدمات شهری را در سطح ماهرانه ای توزیع و مدیریت میکردند تا زمان سلسله چینی chao ۱۱۲۲_۲۵۶ تغییرات قابل توجهی مشهود نبود تااینکه در قرن ۱۹ نطفه سیستم ثبت دوطرفه فرایند سازی گشت. در قرن پنجم قبل از میلاد یونانیان از حسابداری عمومی استفاده کردند تا به شهروندان برای کنترل منابع رسمی شان، اختیارات قانونی تفویض نمایند. شاید آنان سهم بسزایی در حسابرسی بخاطر تمهید مقدمات سکه زنی مالی حدودا ۶۰۰ سال قبل از میلاد دارند. حسابداران بانکی و رسمی در روم باستان ثبت های سنتی بوسیله سران قبیله و طایفه صورت می گرفت در اثنای اینکه ثبت روزانه دخل و خرج خانوار در دفترهای روزانه و ماهانه و نقدی بعنوان نسخه هزینه ها شناخته می شد: codex accepti et expensi ..... شاید حسابها بطور منظم بوسیله اعضای ارشد و افسر خزانه داری در مجلس سنای بمحض ترک اداره ارزیابی و تفحص میگشت.نوآوری رنسانس استرالیایی ( قرن ۱۴ تا ۱۵ ) بعنوان پدر حسابداری مدرن شناخته میشود. luca paci oli یک مرد واقعی رنسانسی با دانشی از ادبیات ، هنر، ریاضیات تجارت و علوم بود و در عصری که فقط اندکی سواد داشتند او سیستم ثبت دوطرفه را اختراع کرده و در سال ۱۴۹۴ درکتابی انتشار داد: summa de arithmetrica, geometria, proportion et proportion ali taim .
در تاریخ انجمن حسابداران حرفه ای ، اولین حسابرسی ملی ، انجمن آمریکایی حسابداری عمومی در سال ۱۸۸۷ عرضه شد که بعدا در سال ۱۹۷۵ بنام موسسه آمریکایی حسابداران مستقل AICPA نامگذاری گشت. در سال ۱۹۴۰ حسابداری حرفه ای صورتحساب سرمای ها بنحو فزاینده ای بکار گرفته شد برای اندازهگیری مقدار سرمایه جهت اینکه موعد برگه ترازنامه را متعادل کند. صورتحساب مالی بطور فزاینده ای یک مرکز بازرگانی گشته و در سال ۱۹۷۱ موسسه حسابداران آمریکایی در لزوم تضمین در کلاسهای سالانه سهامداران شرکت ها شروع شد. ( الکساندر ۲۰۰۲ ).
بنابر نظر stephan zeff در مجله cpa بطور عمومی اصطلاح اصول معقول حسابداری GAAP مورد استفاده واقع گشته و برای اولین بار موسسه حسابداران آمریکایی بعنوان ALCPA شناخته شدند که ظهرنویسی ایالتی را نیز در قانون بررسی اوراق بهادار سال ۱۹۳۳ را آغاز کردند و بوسیله قوانین u.s تصویب شد. کمیسیون بورس اوراق بهادار SEC با تمرکز بر شرکتهای عمومی در سال ۱۹۷۳ هیات تدوین استانداردهای حسابداری بهای تمام شده FASB را انتخاب کرد تا در بخش خصوصی استانداردهای کنترلی رسمی را در صورتهای مالی موسسات غیرانتفاعی تدوین و وضع کنند. در سال ۱۹۸۴ هیات حسابرسی رسمی GASB تحت حفاظ موسسه مالی حسابرسی FAF تشکیل شد برای صدور اصول و سایر ارتباطاتی که اطلاعات سودمندی در اختیار کاربران گزارشهای مالی رسمی میگذارد.
3. استاندارد های حسابداری
استانداردهای حسابداری سندی یا اعلامیه کتبی مدت داری که توسط موسسات حسابداری حرفه ای یا مشمولین در آن صادر میشود ( lal 2009. Rawat 2013 ) . DAS و pramanik 2009 اصول حسابداری را بعنوان بیانیه صورتحساب آمرانه تعریف کردند که ناشی از ماهرانه ترین محاسبات مرتبط با جنبه های مختلف اندازه گیری ها، روشها و عرضه محاسبات معاملات و همبسته با مصوبه اصول مطلوب حسابرسی عمومی ست ( GAAP ) همه اینها مطابق با Das و pramanik 2009 ارایه شده اند تا با ملاکها و مقیاس هایی برای تکنیک ها و سیاستهای مالی حسابرسی سروکار داشته و بعنوان روشی راهبردی با محاسبه و عرضه در حسابهای سالانه، برای هدایت آیتم هایی که صورتحساب مالی را میسازند. روشهایی که با مولفه های جامع قراردادی در پیام موسسات و سایر شرکا از جمله وام دهندگان، سهامداران، مدیران فروشندگان و مشتریان مطابقت دارد.
Abstract
Accounting, as a language of business, has a historical connection with the dynamic economic growth and development and its principles, rules and procedures change over time in parallel with the changes in business activities accordingly. This paper deliberates an overview of the historical development of accounting standards and the necessity for having a single accounting standard across the globe through reviewing previous literatures and it totally deals with the theoretical concepts of Accounting Standards to provide an insight to professionals and practitioners in countries that is moving toward adapting or adopting IFRS for the first timeto enhance their understanding of accounting standards and give an overview of their historical launch along with the progress made toward converging into a single international accounting Standard - IFRS.
1. Introduction
Financial decision (both investment and financing), inter alia, depends on the quality of the financial information it relies on. The quality of financial information also in turn depends on the quality of accounting standards used in measuring, recognizing, presenting and disclosing this information. In cognizant of this fact, according to UNCTAD ISAR (2008), the need for a global set of highquality financial reporting standards goes back to the early 1970s when efforts were made to have a single global benchmark that enables direct comparison of corporate financial reports between jurisdictions as such high-quality standards enhance investor’s confidence by allowing economic transactions of a similar nature to be treated, presented and reported in the same manner around the globe which is an essence of accounting.
Large numbers of accounting professional organizations, authors, academics and researchers have defined the term “accounting” from different perspectives. For instance, according to AICPA “Accounting is the art of recording, classifying, and summarizing in a significant manner and in terms of money, transactions and events which are, in part at least of financial character, and interpreting the results thereof”. Investopedia defines Accounting as the systematic and comprehensive recording of financial transactions pertaining to a business; the process of summarizing, analyzing and reporting these transactions; and producing financial statements that summarize a large company's operations, financial position and cash flows over a particular period which are a concise summary of hundreds of thousands of financial transactions it may have entered into over this period (http://www.investopedia.com).Encyclopedia, likewise, defines Accounting as the language of business as it is the basic means of keeping economic histories of a business's activity in monetary terms and that helps an organization to record, report, and evaluate economic events and transactions that affect the business entity (http://www.inc.com/encyclopedia/. To capture each and every economic event and transactions of a business entity which is going to be organized, summarized and reported to the users, an accounting system is designed and implemented. According to encyclopedia, accounting system is “a management information system responsible for the collection and processing of data useful to decision-makers in planning and controlling the activities of a business organization and the data processing cycle of an accounting system encompasses the total structure of five activities associated with tracking financial information: collection or recording of data; classification of data; processing (including calculating and summarizing) of data; maintenance or storage of results; and reporting of results” (http://www.inc.com/encyclopedia).
2. Accounting, Professional organizations and Accounting Standards: History
Accounting has evolved through different stage of development at different parts of the world and at different periods of time depending on the economic development of the society. The gradual increase in production and economic transactions from time to time has, depending on technological enhancement, created difficulty to memorize and manage all these economical events and compel people to record. According to Alexander (2002), people started recording economic transactions for the first time on clay in Mesopotamia and then advanced to record on Papyrus in Egypt. Alexander (2002) described the historical development of accounting concisely as under:
“The history of accounting is that of human commerce, and even more fundamentally, of writing and the use of numbers and counting. Five thousand years before the appearance of double entry, the Assyrian, Chaldaean-Babylonian and Sumerian civilizations were flourishing in the Mesopotamian Valley, producing some of the oldest known records of commerce. Governmental accounting in ancient Egypt developed in a fashion similar to the Mesopotamians and extensive records were kept, particularly for the network of royal storehouses within which the "in kind" tax payments were kept. Pre-Christian China also used accounting chiefly as a means of evaluating the efficiency of governmental programs and the civil servants who administered them but a level of sophistication was achieved during the Chao Dynasty (1122 - 256 B.C.) which was not surpassed in China until after the introduction of double entry processes in the 19 century. In the 5th century B.C., Greece used "public accountants" to allow its citizenry to maintain real authority and control over their government's finances. Perhaps the most important Greek contribution to accountancy was its introduction of coined money about 600 B.C. Government and banking accounts in ancient Rome evolved from records traditionally kept by the heads of families, wherein daily entry of household receipts and payments were kept in an adversaria or daybook, and monthly postings were made to a cashbook known as a codex accepti et expensi. […] Public accounts were regularly examined by an audit staff, and quaestors were required to account to their successors and the Roman senate upon leaving office. The innovative Italians of the Renaissance (14th -16th century) are widely acknowledged to be the fathers of modern accounting. Luca Pacioli was a true Renaissance man, with knowledge of literature, art, mathematics, business and the sciences, at a time when few could even read and invented the double-entry system and published in book entitled Summa de arithmetica, geometria, Proportioni et proportionalita in 1494.”
In the history of professional accounting Associations, the first national accounting society, the American Association of Public Accountant was launched in 1887, later named the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA) in 1957. In the 1940s, the accounting profession increasingly used the funds statement to measure the actual flow of monies, rather than simply the sum of working capital changes between balance sheet dates. The funds statement increasingly became a staple for the financial statement and, in 1971, the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants began requiring its inclusion in stockholders' annual reports (Alexander, 2002).
According to Stephen Zeff in The CPA Journal, the term Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) was used for the first time in 1936 by the American Institute of Accountants (known as the AICPA since 1957). Federal endorsement of GAAP began with legislation like the Securities Act of 1933 and the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, laws enforced by the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) that target public companies (http://www.accounting.com/resources/gaap/).In 1973, Financial Accounting Standard Board (FASB) became the designated organization in the private sector for setting standards that govern the preparation of corporate financial reports along with not-for-profit organizations. In 1984, the Government Accounting Standards Board (GASB) was formed under the Financial Accounting Foundation (FAF) umbrella to issue standards and other communications that result in decision-useful information for users of government financial reports.
3. Accounting Standards
Accounting standard is a written statement or document issued from time to time by institutions of the accounting profession or institutions in which it has sufficient involvement (Lal, 2009; Rawat, 2013). Das and Pramanik (2009, p194) also defined Accounting Standards as “the authoritative statements of best accounting practices issued by recognized expert accountancy bodies relating to various aspects of measurements, treatments and disclosures of accounting transactions and events, as related to the codification of Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP).” These are, according to Das and Pramanik (2009), stated to be the norms of accounting policies and practices by way of codes or guidelines to direct as to how the items, which make up the financial statements, should be dealt with in accounts and presented in the annual accounts. Accounting methods thus are an integral component of the contracting between firms and other parties, including lenders, shareholders, managers, suppliers and customers (Ball, 2006, p7).
چکیده
1. معرفی
2. تاریخچه موسسات حسابداری تجاری و استاندارهایش:
3. استاندارد های حسابداری
4. استانداردهای حسابداری خارجی ( برون مرزی )
5. استانداردهای گزارشی صورت مالی:
5.1 مبادلات پیشرفته در سطح بینالمللی IFRS
5.2 فرایند تدوین اصول IASB:
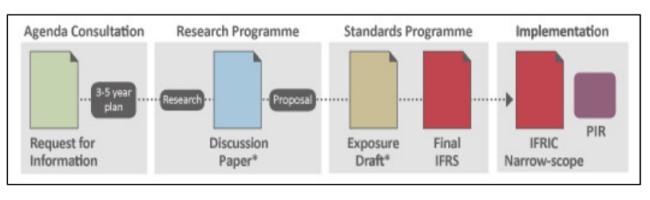
5.3 موعد انتقال ، زمان پذیرش ، وقت گزارش دهی:
6. نتیجه گیری
منابع
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Accounting, Professional organizations and Accounting Standards: History
3. Accounting Standards
4. Objective of Accounting Standards
5. International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS)
5.1. Progress of IFRS Conversion in the International Level
5.2. IASB’s Standard Setting Processes
5.3. IFRS Transition Date, Adoption Date of and Reporting Date
6. Conclusions
References
