
دانلود رایگان مقاله بررسی اثرات معادلات ساختاری بر رفتار ارتعاشی تیرهای تک سلولی کامپوزیتی
بررسی رفتار ارتعاش آزاد تیرهای کامپوزیتی جدار نازک با مقطع قوطی با در نظر گرفتن فرضیه های مختلف در معادلات ساختاری، انجام شده است. در مدل پیش رو، برخی از اثرات غیر کلاسیک، مانند انحراف مهار شده (محدود) و برش عرضی، دخیل شده اند. نتایج ارتعاش آزاد بر اساس نتایج تجربی و عددی ارزیابی شده اند که در بررسی پژوهش های انجام شده، موجود هستند. فرکانس های طبیعی به دست آمده بر اساس فرضیات مختلف معادلات ساختاری مقایسه شده و نشان داده شده است که این فرض ها نقش مهمی را در کنترل مناسب رفتار ارتعاش آزاد تیرهای کامپوزیتی کوپل پیچشی-خمشی بازی می کنند. نتایج به دست آمده بر اساس معادلات ساختاری پیشنهاد شده نشان می دهد که هم خوانی خوبی با نتایج روش اجزا محدود تا آنجا که فرکانس های طبیعی پایین تر تیرها مهم هستند، وجود دارد.
1. مقدمه
گسترش تئوری تیرهای جدار نازک کامپوزیتی، به طور چشمگیری توجه بسیاری از محققان را در دو دهه گذشته به خود جلب کرده است. معلوم شده که برای دستیابی به درک درست رفتار تیرهای کامپوزیتی جدار نازک، تعدادی از اثرات غیر کلاسیک مانند انحراف محدود، برش عرضی و همچنین مکانیسم های کوپلینگ ساختاری باید با دقت مورد توجه قرار گیرند.
سانگ و لیبرسکو [1] یک مدل که در آن اثرات انحراف محدود و برش عرضی بر رفتار ارتعاشات تیرهای کامپوزیتی مورد بررسی قرار گرفته است پیشنهاد کرده اند. با وارد کردن این اثرات، مقادیر پیش بینی شده فرکانس های طبیعی کمتر از مقادیر به بدست آمده ناشی از صرف نظر کردن از اثرات انحرافی محدود شده میشود. در یک مدل توسعه یافته توسط چاندرا و چوپرا [2] پیشنهاد شده است که تغییر سختی برشی در امتداد خطوط یک مقطع، تأثیر قابل ملاحظه ای بر خصوصیات پیچش و انحراف یک تیر کامپوزیتی دارد. ولووی و هادگس ]3[از یک نظریه خطی مجانبی صحیح برای تیرهای جدار نازک کامپوزیتی استفاده کرده اند. آن ها نشان داده اند که محاسبه گشتاور خمشی گردان و خمش پوسته برای پیش بینی درست سفتی پیچشی تعدادی از تیرهای کامپوزیت جدار نازک مهم هستند. یافته های اخیرتوسط جانگ و همکاران [4] به منظور پیشنهاد روشی که آن را ترکیبی می خوانند، که مخلوطی از رویکردهای نیرو و جابجایی در یک شکل متحد است، مورد استفاده قرار گرفت. آنها سپس به نتایج مشابهی با ولووی و هادگس[3] دست پیدا کردند. چین و لیبرسکو [5] مدلی را که پیشتر سانگ و لیبرسکو[1] توسعه داده بودند، در برابر داده های تجربی تأیید کردند. آنها نشان داده اند که رفتارهای استاتیکی و دینامیکی پیش بینی شده توسط این مدل تصحیح شده با داده های تجربی و سایر مدل های تحلیلی هم خوانی خوبی دارند. سورش و ناگارج [6]، در مقایسه ای جامع بین نتایج تجربی و تحلیلی، نشان داده اند که مدل پیشنهادی خود، که در آن تابع انحراف اصلاح شده و نظریه تغییر شکل برشی بزرگتر در نظر گرفته می شود، می تواند رفتار استاتیکی و دینامیکی تیرهای کامپوزیتی جدارنازک را به شکل کارامدی پیش بینی کند. آنها پیشنهاد کردند، روشی که انحراف مدل شده است، نقش اساسی در درک صحیح تیرهای کامپوزیت جدارنازک دارد.
مدل مورد استفاده در مطالعه حاضر عمدتا بر اساس آثار سانگ و لیبرسکو [1] و چین و لیبرسکو [5] با برخی اصلاحات در معادلات ساختاری است. نشان داده خواهد شد، که این تغییرات می تواند به طور قابل توجهی بر رفتار ارتعاش آزاد تک تیرهای کامپوزیت جدار نازک تک سلولی تاثیرگذار باشند.
2. بسط های تئوری
2.1 سینماتیک
برای تکمیل، مدل پیشین توسط سانگولیبرسکو و چین و لیبرسکو، که تحقیق حاضر بیشتربر پایه آن بنا نهاده شده، در زیر ارائه گشته است.
پیکربندی هندسی و سیستم مختصات انتخاب شده در شکل 1 و 2 نشان داده شده اند.
به منظور مدلسازی تیر جدار نازک با مقطع تک سلولی تقویت شده توسط فیبر، فرضیه های زیر مورد استفاده قرار گرفته اند:
1) مقطع های عرضی در صفحات خود تغییر شکل ندارند.
2) اثرات برش عرضی در نظر گرفته شده است. علاوه بر این، تصریح شده که کرنش های برش عرضی،γ_xzو γ_yz، بر روی مقطع عرضی یکنواخت هستند.
3) علاوه بر جابجایی انحرافی در امتداد خطوط میانی (که به عنوان انحراف اولیه خوانده می شود)، انحراف کانتور میانی (به عنوان انحراف ثانویه) نیزگنجانده شده است.
4) فرض شده است که در طول مقطع، σ_nnو N_snدر هنگام اعمال قانون ساختاری تنش کرنش ناچیز هستند.
5) تغییر شکل ها کوچک هستند و تئوری الاستیسیته خطی استفاده شده است.
3. نتایج و بحث ها
در ابتدا، برای اعتبار سنجی بسط های تئوری به منظور حصول اطمینان از اجرای مناسب روش شناسی و فرضیه های متناظر در معادلات ساختاری تلاش شده است. این مهم با بدست آوردن نتایج برای یک تیر با مقطع قوطی کامپوزیتی بر اساس مجموعه سوم فرضیه های داده شده در بالا، و مقایسه نتایج با آنهایی که در حال حاضر در پژوهش های پیشین موجود است و توسط یک آزمایش تجربی به دست آمده اند [20] یا سایر مطالعات تئوری [ 5، 21، 22] حاصل شده است. دو مورد با تنظیمات لایه چینیCAS، که توسط CAS1و CAS2 مشخص میشوند (جدول 1)، در نظر گرفته می شوند. جدول 2 ابعاد هندسی و خواص مواد مورد استفاده درتیرهای با مقطع قوطی مشابه را نشان می دهد.
به منظور مطالعه اثرات سه مجموعه مختلف از معادلات ساختاری در رفتار ارتعاش آزاد تیرهای جدارنازک کامپوزیتی با سطح مقطع قوطی، دو مورد از پیکربندی های لایه چینی که به عنوان CAS3 و CAS4 نامیده میشوند با زوایای مختلف مختلف در نظر گرفته شده اند. این لایه چینی ها ابتدا توسط ولووی و هادگز معرفی شده اند [3]. توالی انباشتگی این لایه ها در جدول 3 آمده است و خواص مواد و ابعاد هندسی مورد استفاده در تحلیل در جدول 2 آورده شده است.
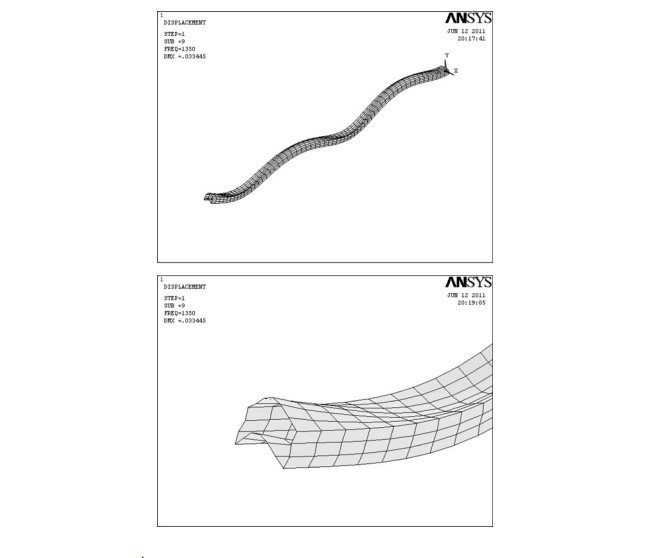
نتایج پیش بینی شده توسط مجموعه های مختلف فرضیه ها با نتایج حاصل از روش اجزا محدود (FEM) که با اجرای یک کد ANSYS با استفاده از نوع المانShell99 بدست می آید، مقایسه شده است.
An investigation of the free vibration behavior of thin-walled composite box-beams is carried out by considering different assumptions in the constitutive equations. Within the present model some non-classical effects, such as restrained warping and transverse shear, are incorporated. Free vibration results are validated against experimental and numerical results, which are available in the literature. The natural frequencies obtained based on the different assumptions of constitutive equations are compared, and it is revealed that these assumptions play an important role in the proper treatment of the free vibration behavior of torsion-bending coupled composite beams. The results obtained based on the proposed constitutive equations are demonstrated to have a good agreement with the finite element results as far as the lower natural frequencies of the beams are concerned.
1. Introduction
The enhancement of the theory of thin-walled composite beams has notably drawn the attention of many researchers in the past two decades. It has been revealed that in order to properly treat the behavior of thin-walled composite beams, a number of nonclassical effects, such as restrained warping, transverse shear, and also the mechanisms of structural couplings, have to be carefully considered.
Song and Librescu [1] have proposed a model in which the effects of restrained warping and transverse shear on the vibration behavior of composite beams are studied. By including these effects, the predicted values of the natural frequencies have become lower than the corresponding values obtained by neglecting restrained warping effects. In a model developed by Chandra and Chopra [2], it is suggested that the variation of shear stiffness along the contour of a crosssection has a significant influence on the warping and twist characteristic of a composite beam. Volovoi and Hodges [3] have used an asymptotically correct linear theory for com posite thin-walled beams. They have revealed that the inclusion of hoop bending moment and shell bending is important for a proper prediction of torsional stiffness of a number of thin-walled composite beams. The latter finding is used by Jung et al. [4] in order to subsequently suggest a so-called mixed method, which combines the force and displacement approaches in a unified form. They have then achieved similar results to those of Volovoi and Hodges [3]. Qin and Librescu [5] have validated the model developed earlier in Song and Librescu [1] against experimental data. They have shown that the static and dynamic behaviors predicted by this refined model are in good agreement with experimental data and other analytical models. Suresh and Nagaraj [6], in a comprehensive comparison between experimental and analytical results, have revealed that their proposed model, in which the refined warping function and higher shear deformation theory are considered, can predict the static and dynamic behavior of thin-walled composite beams efficiently. They suggested that the way the warping is modeled has a significant role in a correct treatment of thin-walled composite beams.
The model that is used in the current study is mainly based on the works by Song and Librescu [1] and Qin and Librescu [5] with some modifications in the constitutive equations. It will be shown that these modifications can significantly influence the free vibration behavior of single-celled thin-walled composite beams.
2. Theoretical Developments
2.1. Kinematics
For completeness, the previous model by Song and Librescu [1] and Qin and Librescu [5], on which the current study is mainly based, is presented below.
The geometric configuration and the chosen coordinate system are depicted in Figures 1 and 2.
In order to model a single-celled cross-section fiberreinforced thin-walled beam, the following assumptions are adopted [5]:
(1) The cross-sections do not deform in their own planes.
(2) Transverse shear effects are incorporated. In addition, it is stipulated that the transverse shear strains, xz and yz, are uniform over the cross-sections.
(3) In addition to the warping displacement along the midline contour (referred to as primary warping), the off midline contour warping (referred to as the secondary warping) is also incorporated.
(4) It is assumed that over the cross-section, nn and Nsn are negligibly small when deriving the stress–strain constitutive law.
(5) The deformations are small and linear elasticity theory is used.
3. Results and Discussions
Initially, the validation of the theoretical developments is attempted to ensure the proper implementation of the methodology and the corresponding assumptions in the constitutive equations. This is achieved by obtaining the results for a composite box-beam based on the third set of assumptions given above, and comparing the results with those already available in the literature, which are obtained by an experimental test [20] or other theoretical studies [5, 21, 22]. Two cases with CAS lay-up configurations, which are denoted by CAS1 and CAS2 (see Table 1), are considered. Table 2 shows the geometric dimensions and material properties used in the corresponding box-beams.
In order to study the effects of three different sets of constitutive equations on the free vibration behavior of thin-walled composite box-beams, two cases of lay-up configurations referred to as CAS3 and CAS4 with varying ply angles are considered. These lay-ups have initially been introduced by Volovoi and Hodges [3]. The stacking sequences of these layups are given in Table 3 and the material properties and geometric dimensions used in the analysis are listed in Table 2.
The predicted results by different sets of assumptions are compared with finite element method (FEM) results that are obtained by implementing an ANSYS code using Shell99 element type.
1. مقدمه
2. بسط های تئوری
2.1 سینماتیک
2.2. معادلات ساختاری
2.3. معادلات حرکت
3. نتایج و بحث ها
4. نتیجه گیری
منابع
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Developments
2.1. Kinematics
2.2. Constitutive Equations
2.3. Equations of Motion
3. Results and Discussions
4. Conclusions
References
