
دانلود رایگان مقاله کاربردهای فناوری اطلاعات در هتلداری و گردشگری
چکیده
صنایع گردشگری و هتلداری, فناوری اطلاعات را به طور گسترده ای پذیرفته اند تا هزینه ها را کاهش دهند، بهره وری عملیاتی را افزایش دهند و مهمتر از همه کیفیت خدمات و تجربه مشتری را بهبود بخشند. این مقاله, یک بازنگری جامع از مقالات منتشر شده در 57 مجله تحقیقات گردشگری و هتلداری از سال 2005 تا 2007 را ارائه می کند. با گروه بندی یافته ها به رده های مصرف کنندگان، فن آوری ها و تامین کنندگان، این مقاله در مورد تکامل کاربردهای فناوری اطلاعات در صنعت گردشگری و هتلداری صحبت می کند. این مقاله نشان می دهد که فناوری اطلاعات به طور فزاینده ای برای فعالیت های رقابتی سازمان های گردشگری و هتلداری و همچنین مدیریت توزیع و بازاریابی سازمان ها در مقیاس جهانی بسیار مهم است.
مقدمه
رقابت شدید در محیط کسب و کار امروز بدان معنی است که کسب و کارهای گردشگری و هتلداری باید به سختی کار کنند تا بتوانند رقابت کنند. موفقیت یک کسب و کار تا حدی به توانایی آن در دستیابی و استفاده از اطلاعات به روز شده برای کمک به فرایندهای مدیریت و بازاریابی بستگی دارد. از این رو، فناوری اطلاعات (IT) به سازمان کمک می کند تا اطلاعات را به صورت پویا مدیریت کند و از طریق کمک به تصمیم گیرندگان برای سرمایه گذاری و تصمیم گیری مناسب، بر رقابت تجاری تاثیر می گذارد. فناوری اطلاعات به مشتریان کمک می کند تا خواسته های مربوط به اطلاعات به موقع و دقیق را برآورده سازند و انتشار فناوری اطلاعات در صنایع گردشگری و هتلداری اخیراً با نرخ بی سابقه ای افزایش یافته است (Connolly و Lee، 2006؛ Singh و Kasavana، 2005). این امر از حضور گسترده سیستم های فناوری اطلاعات که برای کمک به مدیران در ارائه خدمات با کیفیت به مشتریان خود و افزایش بهره وری عملیاتی و کنترل هزینه های همکاری می کنند, مشهود است. محققان اظهار داشته اند که فناوری اطلاعات، با عمل کردن به عنوان محافظ و ارتقادهنده، مستقیماً بر تجارب و رفتار گردشگران تاثیر می گذارد (Kim و Ham، 2007؛ Singh، Kim و Huh، 2006؛ Winata و Mia، 2005).
از نظر استراتژیک, IT به تدریج موجب تغییر شکل ساختار اساسی صنعت و جامعه (Buhalis، 1998، 2003) می شود. IT می تواند دانش را در مرکز یک رقابت تجاری قرار دهد (Chathoth، 2007؛ Ham، Kim و Jeong، 2005). علاوه بر این Law و جوهراتنام (2005) پیشنهاد دادند که فناوری اطلاعات می تواند ماهیت محصولات و فرآیندهای گردشگری و هتلداری، فرآیندها، کسب و کارها و رقابت را تغییر دهد و برای سازمان های گردشگری و هتلداری که موفق به ساخت سیستم های IT مناسب نشده اند، هدایت و مدیریت کسب و کار اطلاعات-محور آنها که به رقابت آنها آسیب می رساند, مشکل است.
گردشگری و هتلداری, پدیده های اجتماعی هستند و صنایع مرتبط با آنها عمدتاً کاربردی هستند. محققان در این زمینه تحقیقاتی را انجام داده اند و در حال انجام آنها هستند که دانش نوآورانه ای را تولید می کند که به نفع این صنایع و در نهایت جامعه خواهد بود. همان طور که سرمایه گذاری و اتخاذ فناوری اطلاعات در حال حاضر یکی از اجزای ضروری کسب و کار گردشگری و هتلداری است، فناوری اطلاعات نیز یک ابزار برای ایجاد و خلق تغییر است. به همین ترتیب، فناوری اطلاعات اخیراً توجه محققان گردشگری و هتلداری در سراسر جهان را جلب کرده است که یافته های آنها در مجلات تحقیقاتی منتشر شده است. Niininen، Buhalis و مارس (2007) نشان دادند که فناوری اطلاعات از محوریت مشتریان پشتیبانی می کند، در حالیکه مصرف کنندگان قادر به استفاده از تکنولوژی برای انتخاب و سفارشی کردن محصولات خود و همچنین تجربه شخصی خود هستند.
به طور کلی برای مدیران گردشگری و هتلداری و به طور خاص برای مدیران بازاریابی, آگاه بودن از تغییرات اخیر در فناوری اطلاعات و ارتباط آنها با خدمات مشتری امری سودمند است. زمانی که توسعه فناوری پیشرفته تر می شود، دست اندکاران صنعتی، مربیان و سیاست گذاران ممکن است در انتخاب، تجزیه و تحلیل، اجرا و پیاده سازی سیستم های جدید فناوری اطلاعات، دچار مشکل می شوند. مجلات تحقیقاتی، به عنوان یک کانال قوی انتشار دانش، می توانند اطلاعات بازنگری شده و بی طرفانه در مورد تجزیه و تحلیل فناوری، ارزیابی و بهترین روش های صنعتی را ارائه دهند. با این حال، علیرغم مقدار زیادی تلاش که محققان گردشگری و هتلداری در مورد تحقیقات فناوری اطلاعات انجام می دهند، تنها چند بررسی از مقالات منتشر شده در زمینه فناوری اطلاعات و یا پیشرفت فناوری اطلاعات در صنعت گردشگری از زمان رشد سریع آن در اوایل دهه 1980 (Frew 2000 ؛ Kirk و Pine 1998؛ Kluge 1996؛ Leung و Law؛ 2005؛ 2007؛ O'Connor و Murphy 2004؛ Buhalis و Law، 2008) وجود دارد. علاوه بر این، مقالات بازبینی محدود هستند، چرا که آنها تنها چند مجله انتخاب شده را بررسی می کنند یا به این دلیل که آنها کارهایی را پوشش می دهند که به لحاظ ماهیت سریع تغییر فناوری اطلاعات و گردشگری، تا حدودی منسوخ شده اند.
با توجه به اهمیت فوق العاده کاربردهای فناوری اطلاعات در صنایع گردشگری و هتلداری, و فقدان مقالات منتشر شده که به بررسی تحولات اخیر در این زمینه می پردازند، در این مقاله تلاش می شود تا محتوای مقاله های فناوری اطلاعات منتشر شده در نشریات تحقیقاتی مهم گردشگری و هتلداری در دوره های 2005 تا 2007 تجزیه و تحلیل شوند. بنابراین این مقاله برای استفاده خوانندگان در درک بهتر کاربردهای اخیر IT در گردشگری و هتلداری از دیدگاه های مختلف مفید می باشد.
روش شناسی
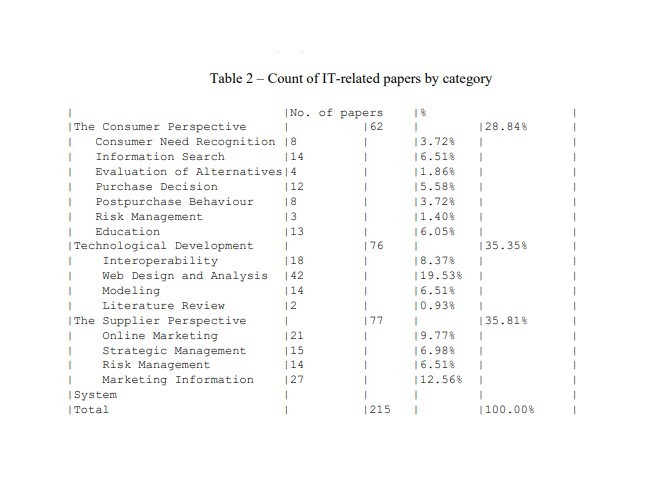
این مطالعه، تحلیل محتوا را برای بررسی مقالاتی که از طریق مجلات مهم گردشگری و هتلداری در سال های 2005 تا 2007 منتشر شده اند، در پیش گرفته است. در حال حاضر هیچ فهرست استاندارد مجلات تحقیقاتی در این زمینه وجود ندارد. فهرست 57 مجله در مقاله آرنت، راویچندران و براون (2007) که به روز ترین و جامع تر است, در جدول 1 ارائه شده است. بنابراین, در این مطالعه برای جمع آوری داده ها استفاده شده است. در دوره 2005 تا 2007، 215 مقاله مربوط به فناوری اطلاعات در مجلات موجود در این فهرست منتشر شده است. در طول فرآیند شناسایی، نویسندگان چکیده ای از هر نشریه را خواندند تا در ابتدا تعیین کنند که آیا مربوط به فناوری اطلاعات است یا خیر. سپس نشریات کامل از این چکیده های شناسایی شده به طور کامل برای تأیید صحت آنها مورد مطالعه قرار گرفتند. این نشریات به سه رده اصلیشدند, یعنی مشتریان، توسعه فناورانه و تامین کنندگان، دسته بندی شدند، که طبق استدلال بوالیز و Law (2008), ذینفعان این صنعت هستند. فقط مقالات پژوهشی داوری شده شمارش شدند، و پیش گفتارهای های سردبیر، ستون های اینترنت و بررسی کنفرانس ها یا کتاب ها حذف شدند. هر کدام از این نشریات، بر اساس نقش آن در فعالیت های عمده بازاریابی در گردشگری، طبقه بندی شدند، همانطور که توسط کوتلر، بوون و مکنس (1999) بیان شده است. سپس نویسندگان به طور مستقل طبقه بندی های اصلی و زیرمجموعه ها را برای تأیید صحت این اصطلاحات بررسی کردند. اگر یک نشریه بیش از یک منطقه را پوشش می داد، تنها محدوده بزرگ تمرکز شمارش می شد. جدول 2, تعداد مقالات در هر رده و زیر رده را خلاصه می کند و سه بخش زیر به تحلیل مقالات منتشر شده در هر رده می پردازند.
چشم انداز مصرف کننده
با توجه به Kotler و همکاران. (1999) صرفه نظر از این که یک خرید آنلاین یا آفلاین انجام شود، مصرف کنندگان قبل از هر گونه خرید، از پنج مرحله در فرایند تصمیم گیری خریداران می گذرند. این پنج مرحله شامل شناسایی نیاز، جستجوی اطلاعات، ارزیابی گزینه ها، تصمیم گیری خرید و رفتار پس از خرید می باشد. مطالعات ارائه شده در پنج بخش زیر نشان می دهند که فناوری اطلاعات, نقش مهمی در هر مرحله از فرآیند تصمیم گیری خریداران ایفا می کند.
ABSTRACT
The tourism and hospitality industries have widely adopted information technology [IT] to reduce costs, enhance operational efficiency, and most importantly to improve service quality and customer experience. This paper offers a comprehensive review of articles that were published in 57 tourism and hospitality research journals from 2005 to 2007. Grouping the findings into the categories of consumers, technologies, and suppliers, the paper sheds light on the evolution of IT applications in the tourism and hospitality industries. The paper demonstrates that IT is increasingly becoming critical for the competitive operations of the tourism and hospitality organizations as well as for managing the distribution and marketing of organizations on a global scale.
INTRODUCTION
The intense competition in today’s business environment means that tourism and hospitality businesses have to work hard to maintain and develop their competitiveness. The success of a business, to certain extent, depends on its ability to acquire and utilize updated information to assist its management and marketing processes. Hence, Information Technology (IT) assists organization to manage information dynamically and influences business competitiveness through assisting decision makers to make appropriate investments and decisions. IT helps to meet the demands for timely and accurate information by customers and the IT diffusion in the tourism and hospitality industries has recently increased at an unprecedented rate (Connolly & Lee, 2006; Singh & Kasavana, 2005). This is evident by the ubiquitous presence of IT systems that work cooperatively to assist managers to deliver quality service to their customers and to enhance operational efficiency and control costs. Researchers have stated that IT, by acting as a protector and enhancer, directly influences the experiences and behavior of tourists (Kim & Ham, 2007; Singh, Kim, & Huh, 2006; Winata & Mia, 2005).
More strategically IT is gradually reshaping the fundamental structure of industry and society (Buhalis, 1998, 2003). IT can generate the knowledge at the center of a business’s competitiveness (Chathoth, 2007; Ham, Kim & Jeong, 2005). Law and Jogaratnam (2005) further suggested that IT can transform the nature of tourism and hospitality products, processes, businesses, and competition, and that tourism and hospitality organizations that have failed to master the right IT systems would find difficult to direct and manage their information-intensive business damaging their competitiveness.
Tourism and hospitality are social phenomena, and the industries associated with them are largely application oriented. Researchers in this field have conducted, and will continue to conduct, research that generates innovative knowledge that will benefit these industries and ultimately society. As investment in and the adoption of IT are now an indispensable components of tourism and hospitality business, IT serves as a tool for both enabling and inducing change. As such, IT has recently drawn the attention of tourism and hospitality researchers worldwide, who have disseminated their findings in research journals. Niininen, Buhalis and March (2007) demonstrated that IT support consumer centricity, with consumers being able to use technology to select and customize their products as well as to personalize their experience.
It is advantageous for tourism and hospitality managers in general and marketing managers in particular to be aware of the recent changes in IT and their relationship with customer service. As IT development becomes more sophisticated, industrial practitioners, educators, and policy makers may find increasing difficulty in selecting, analyzing, implementing, and operating new IT systems. Research journals, as a vigorous channel of knowledge dissemination, can offer peer-reviewed and unbiased information on IT analysis, evaluation, and industrial best practice. However, despite the enormous amount of effort spent by tourism and hospitality researchers on investigating IT, there are only a few reviews of the articles published on IT or the progress of IT in the tourism industry since its rapid growth in the early 1980s (Frew 2000; Kirk & Pine 1998; Kluge 1996; Leung & Law, 2005, 2007; O’Connor & Murphy 2004, Buhalis and Law, 2008). Moreover, the review articles that do exist are limited, either because they examine only a few selected journals or because they cover work that is already somewhat outdated given the fast changing nature of IT and tourism.
In view of the paramount importance of IT applications in the tourism and hospitality industries and the absence of published articles that review the recent developments in this area, this paper attempts to analyze the content of IT articles published in the major tourism and hospitality research journals in the period 2005 to 2007. This paper will therefore be of use for readers in better understanding recent IT applications in tourism and hospitality from different perspectives.
METHODOLOGY
This study adopted content analysis to examine articles that were published by major tourism and hospitality journals between 2005 and 2007. At present, there is no standard list of research journals in the field. The list of 57 journals in the paper of Arendt, Ravichandran, and Brown (2007) appears to be the most up-to-date and comprehensive as illustrated in Table 1. This was thus used in this study for data collection. In the period 2005 to 2007, a total of 215 IT-related papers were published in the journals on this list. During the identification process, the authors read the abstract of each publication to initially determine whether it is IT-related. Full-length publications of the identified abstracts were then thoroughly read to confirm their appropriateness. These publications were grouped into the three main categories, namely customers, technological development, and suppliers, which Buhalis and Law (2008) argued represent the industry stakeholders. Only refereed research articles were counted, and editor prefaces, Internet columns, and conference or book reviews were excluded. Each publication was then further categorized based on its role in the major marketing activities in tourism, as stated by Kotler, Bowen, and Makens (1999). The authors then independently reviewed the major categories and sub-categories to confirm the accuracy of these terms. If a publication covered more than one area, then only the major area of focus was counted. Table 2 summarizes the counts of the articles in each category and sub-category, and the following three sections analyze the published articles in each category.
THE CONSUMER PERSPECTIVE
According to Kotler et al. (1999), no matter a purchase is conducted online or offline, consumers will go though the five stages in buyers’ decision making process before any purchase is made. These five stages include need recognition, information search, evaluation of alternatives, purchase decision, and post purchase behavior. The studies presented in the next five sub-sections show IT plays an important role in each of the stages of the buyers’ decision making process.
چکیده
مقدمه
روش شناسی
چشم انداز مصرف کننده
شناخت نیاز مصرف کننده
جستجوی اطلاعات
ارزیابی گزینه ها
تصمیم خرید
رفتار پس از خرید
مدیریت ریسک
آموزش
پیامدهای مدیریتی
توسعه فناورانه
قابلیت همکاری
طراحی و تحلیل وب
مدل سازی
بازنگری نوشته ها
پیامدهای مدیریتی
چشم انداز عرضه کننده
بازاریابی آنلاین
مدیریت راهبردی
مدیریت ریسک
سیستم های اطلاعات بازاریابی
پیامدهای مدیریتی
نتیجه گیری
منابع
ABSTRACT
INTRODUCTION
METHODOLOGY
THE CONSUMER PERSPECTIVE
Consumer Need Recognition
Information Search
Evaluation of Alternatives
Purchase Decision
Post-purchase Behavior
Risk Management
Education
Managerial Implications
TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENT
Interoperability
Web Design and Analysis
Modeling
Literature Review
Managerial Implications
THE SUPPLIER PERSPECTIVE
Online Marketing
Strategic Management
Risk Management
Marketing Information Systems
Managerial Implications
CONCLUSIONS
REFERENCES
